Abstract
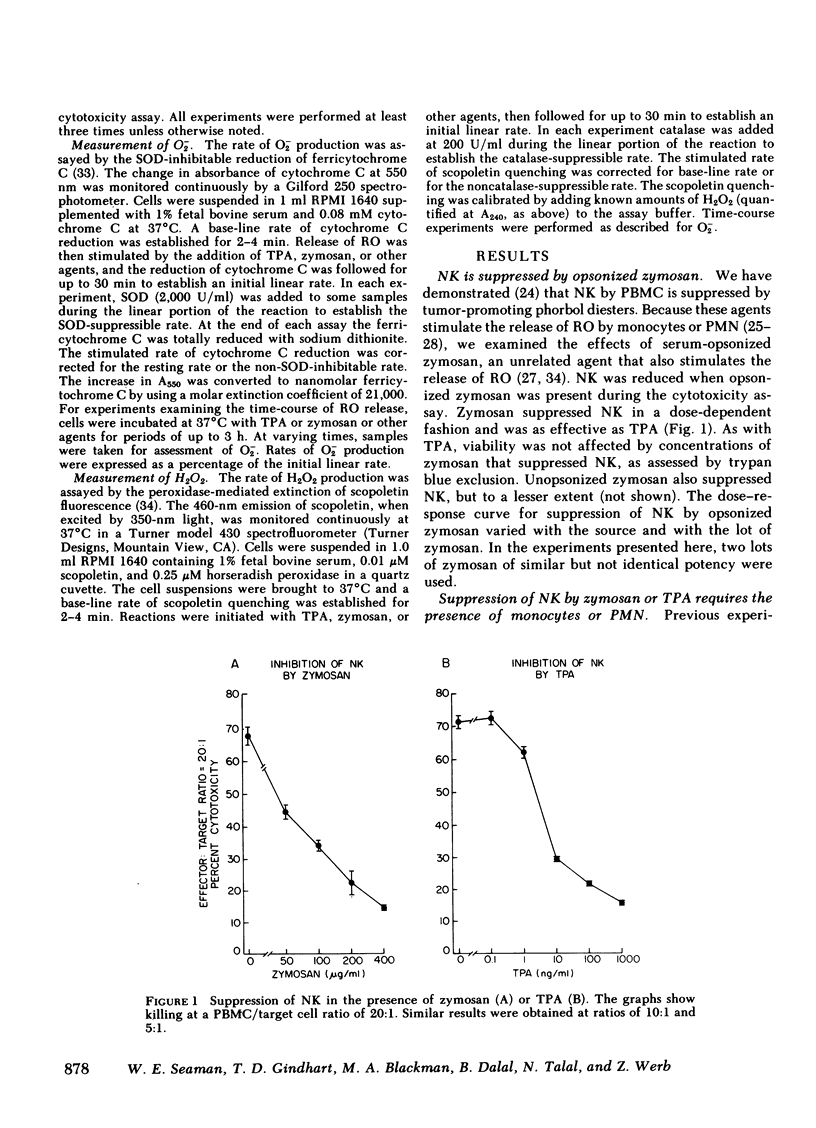
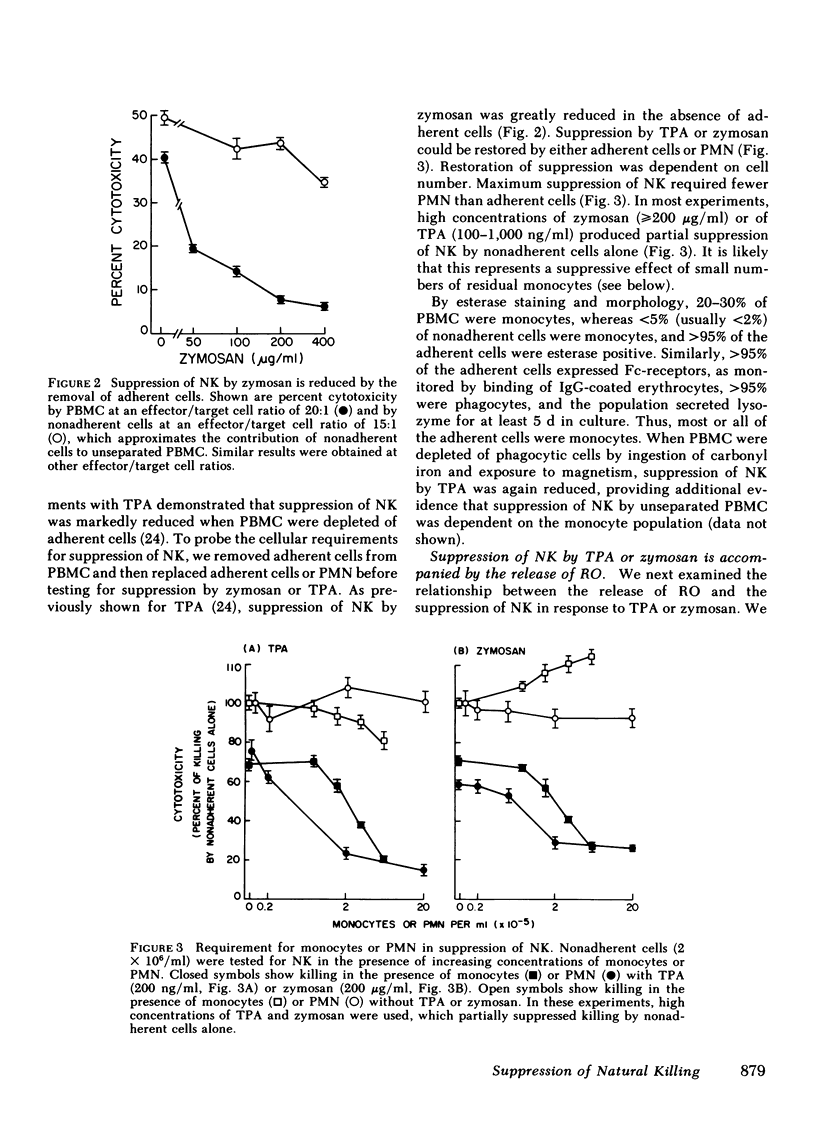
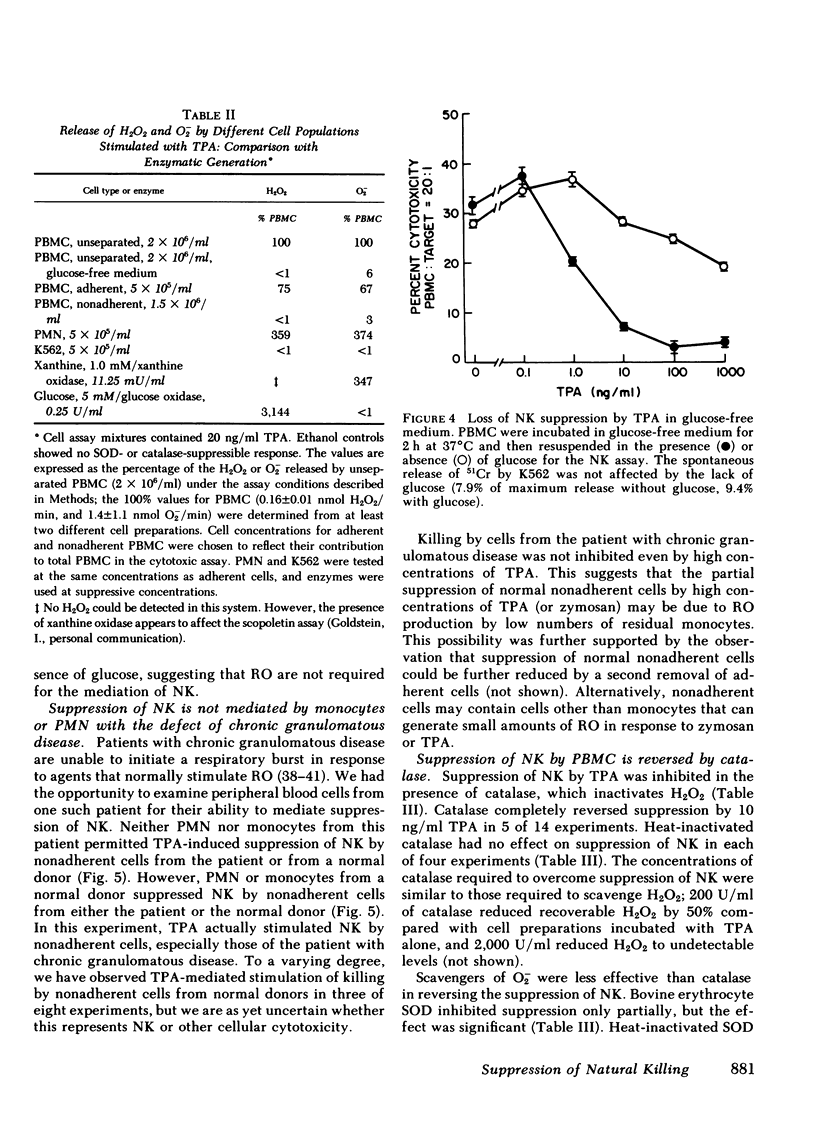
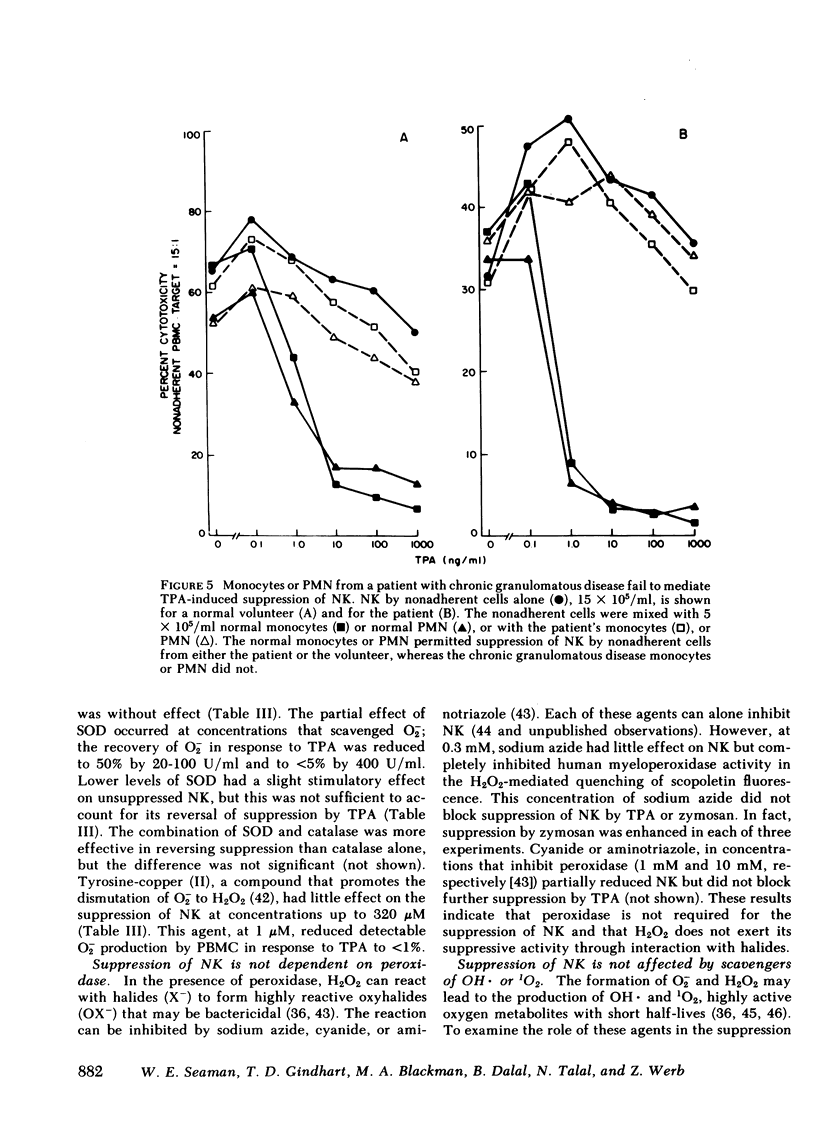
Natural killer cells spontaneously lyse certain tumor cells and may defend against malignancy. We have previously shown that natural killing (NK) by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) is suppressed in vitro by phorbol diester tumor promoters, including 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). We here demonstrate that suppression of NK is mediated by monocytes or polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) and that suppression is dependent on the generation of reactive forms of molecular oxygen (RO), particularly hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). NK was suppressed not only by TPA but also by opsonized zymosan (yeast cell walls), which, like TPA, was not toxic to PBMC. Both TPA and zymosan stimulated the production of superoxide anion (O2-) and H2O2 by PBMC. Production of RO correlated with suppression of NK. When PBMC were depleted of monocytes, the production of RO and the suppression of NK were both markedly reduced. Suppression could be restored by monocytes or PMN, both of which produced RO in response to TPA or zymosan. Suppression of NK was dependent on RO. Monocytes or PMN from a patient with chronic granulomatous disease, whose cells cannot generate RO, did not mediate suppression of NK. Suppression was also reduced in glucose-free medium, which did not support the generation of RO. Suppression of NK by TPA was inhibited by catalase. Bovine superoxide dismutase had a limited effect on suppression, even in high concentration, and tyrosine-copper (II) complex, which also enhances dismutation of O2- to H2O2, had almost no effect on suppression. When H2O2 was directly generated enzymatically from glucose oxidase and glucose, NK was suppressed and suppression was reversed by catalase. NK was also suppressed by the enzymatic generation of O2- from xanthine oxidase and xanthine, but suppression under these conditions was again inhibited by catalase and not by superoxide dismutase, indicating that suppression was due to the secondary formation of H2O2 from O2-. These results indicate that H2O2 is important in suppression of NK. Myeloperoxidase did not appear to play a role in suppression because inhibition of this enzyme by sodium azide, cyanide, or aminotriazole did not prevent suppression of NK. Suppression of NK was reversible; after exposure to zymosan, NK could be partially restored by the addition of catalase and superoxide dismutase or by the removal of zymosan. These studies demonstrate cellular regulation of NK by monocytes or polymorphonuclear leukocytes and indicate a role for RO in immunoregulation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on microexudate-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1372–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault K. A., Springer T. A. Cross-reaction of a rat-anti-mouse phagocyte-specific monoclonal antibody (anti-Mac-1) with human monocytes and natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):359–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 30;298(13):721–725. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803302981305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L. Active oxygen species and the functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Leukocyte oxidase: defective activity in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1967 Feb 17;155(3764):835–836. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3764.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Inhibition of murine natural killer cell activity by prostaglandins. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2682–2687. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Hochman P. S. Do natural killer cells engage in regulated reactions against self to ensure homeostasis? Immunol Rev. 1979;44:13–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Whitten D. M., Babior B. M. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):593–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennert G. Cloned lines of natural killer cells. Nature. 1980 Sep 4;287(5777):47–49. doi: 10.1038/287047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Droller M. J., Perlmann P., Schneider M. U. Enhancement of natural and antibody-dependent lymphocyte cytotoxicity by drugs which inhibit prostaglandin production by tumor target cells. Cell Immunol. 1978 Aug;39(1):154–164. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90090-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb R. H., Herberman R. B. Natural killer cell reactivity: regulatory interactions and among phorbol ester, interferon, cholera toxin, and retinoic acid. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2129–2135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Roos D., Kaplan H. B., Weissmann G. Complement and immunoglobulins stimulate superoxide production by human leukocytes independently of phagocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1155–1163. doi: 10.1172/JCI108191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. G., Weigle W. O. Modulation of lymphocyte activation. I. Inhibition by an oxidation product of arachidonic acid. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):593–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliotis T., Roder J., Klein M., Ortaldo J., Fauci A. S., Herberman R. B. Chédiak-Higashi gene in humans I. Impairment of natural-killer function. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1039–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Wigzell H. Suppression of natural killer cell activity with radioactive strontium: effector cells are marrow dependent. J Immunol. 1977 Apr;118(4):1503–1506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna N., Fidler I. J. Role of natural killer cells in the destruction of circulating tumor emboli. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Oct;65(4):801–809. doi: 10.1093/jnci/65.4.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kärre K., Kiessling R., Roder J., Andersson B., Häyry P. Natural NK-cell targets in the mouse thymus: characteristics of the sensitive cell population. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):765–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E., Graff G., Lands W. E. Accelerative autoactivation of prostaglandin biosynthesis by PGG2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1325–1331. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):230–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochman P. S., Cudkowicz G. Suppression of natural cytotoxicity by spleen cells of hydrocortisone-treated mice. J Immunol. 1979 Sep;123(3):968–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman T. Natural killer funciton in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jan;23(1):30–35. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn D. C., Lehrer R. I. NADPH oxidase deficiency in X-linked chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1975 Apr;55(4):707–713. doi: 10.1172/JCI107980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. L., Levine L. Inhibition of arachidonic acid release from cells as the biochemical action of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Godzik C. A., Cohn Z. A. Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Keele B. B., Jr, Misra H. P., Lehmeyer J. E., Webb L. S., Baehner R. L., RaJagopalan K. V. The role of superoxide anion generation in phagocytic bactericidal activity. Studies with normal and chronic granulomatous disease leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jun;55(6):1357–1372. doi: 10.1172/JCI108055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay H. D., Horwitz D. A. Evidence by reactivity with hybridoma antibodies for a probable myeloid origin of peripheral blood cells active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):847–851. doi: 10.1172/JCI109923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazura J. W., Fanning M. M., Blumer J. L., Mahmoud A. A. Role of cell-generated hydrogen peroxide in granulocyte-mediated killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):93–102. doi: 10.1172/JCI110037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Hochman P. S., Haller O., Shearer G. M., Wigzell H., Cudkowicz G. Evidence for a similar or common mechanism for natural killer cell activity and resistance to hemopoietic grafts. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):655–663. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Pross H., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):117–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa S., Takaku F., Sakamoto S. Serine protease inhibitors inhibit superoxide production by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and monocytes stimulated by various surface active agents. FEBS Lett. 1979 Nov 15;107(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80401-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. C., Shiozawa C., Shaw A., Diener E. Requirement for accessory cells in the antibody response to T cell-independent antigens in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jan;6(1):63–68. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastro A. M., Krupa T. A., Smith P. Interaction of the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate with cells in mixed-lymphocyte culture. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):4078–4082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes M. J., Sharrow S. O., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Identification and separation of Thy-1 positive mouse spleen cells active in natural cytotoxicity and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2851–2860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyasaka N., Sauvezie B., Pierce D. A., Daniels T. E., Talal N. Decreased autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in Sjögren's syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):928–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI109960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Bucalo L. R., Allard J., Wigzell H., Cantor H. Multiple activities of a cloned cell line mediating natural killer cell function. J Exp Med. 1981 Jun 1;153(6):1582–1591. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.6.1582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Brukner L. H., Silverstein S. C., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. I. Pharmacologic triggering of effector cells and the release of hydrogen peroxide. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):84–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Root R. K. Hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages: dependence on sequential activation and triggering. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1648–1662. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Cohn Z. Role of oxygen-dependent mechanisms in antibody-induced lysis of tumor cells by activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1980 Jul 1;152(1):198–208. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohuchi K., Levine L. Tumor promoting phorbol diesters stimulate release of radioactivity from [3H]-arachidonic acid labeled- but not [14C]linoleic acid labeled-cells. Indomethacin inhibits the stimulated release from [3H] arachidonate labeled cells. Prostaglandins Med. 1978 Dec;1(6):421–431. doi: 10.1016/0161-4630(78)90113-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez H. D., Weksler B. B., Goldstein I. M. Generation of a chemotactic lipid from a arachidonic acid by exposure to a superoxide-generating system. Inflammation. 1980 Sep;4(3):313–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00915032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrone W. F., English D. K., Wong K., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: superoxide-dependent activation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack S. B., Tam M. R., Nowinski R. C., Emmons S. L. Presence of T cell-associated surface antigens on murine NK cells. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1818–1821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimtula A., O'Brien P. J. The possible involvement of singlet oxygen in prostaglandin biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):893–899. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90675-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter C., Azzi A., Weser U., Wendel A. Hepatic microsomal dealkylations. Inhibition by a tyrosine-copper (II) complex provided with superoxide dismutase activity. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5061–5066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Kiessling R., Biberfeld P., Andersson B. Target-effector interaction in the natural killer (NK) cell system. II. The isolation of NK cells and studies on the mechanism of killing. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2509–2517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Metcalf J., Oshino N., Chance B. H2O2 release from human granulocytes during phagocytosis. I. Documentation, quantitation, and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):945–955. doi: 10.1172/JCI108024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Blackman M. A., Gindhart T. D., Roubinian J. R., Loeb J. M., Talal N. beta-Estradiol reduces natural killer cells in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2193–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Gindhart T. D., Blackman M. A., Dalal B., Talal N., Werb Z. Natural killing of tumor cells by human peripheral blood cells. Suppression of killing in vitro by tumor-promoting phorbol diesters. J Clin Invest. 1981 May;67(5):1324–1333. doi: 10.1172/JCI110161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Talal N., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A., Ledbetter J. A. Surface antigens on mouse natural killer cells: use of monoclonal antibodies to inhibit or to enrich cytotoxic activity. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):982–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A., Bonavida B., Targan S. Mode of action of interferon-mediated modulation of natural killer cytotoxic activity: recruitment of pre-NK cells and enhanced kinetics of lysis. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):479–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchowitz L., Spilberg I. Chemotactic factor-induced generation of superoxide radicals by human neutrophils: evidence for the role of sodium. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2428–2435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Meyers K. M., Prieur D. J., Starkey J. R. Role of NK cells in tumour growth and metastasis in beige mice. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):622–624. doi: 10.1038/284622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Saksela E. Isolation of human NK cells by density gradient centrifugation. J Immunol Methods. 1980;36(3-4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembala M., Lemmel E. M., Uracz W. Activation of human monocytes for nitroblue tetrazolium reduction and the suppression of lymphocyte response to mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):309–316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



