Abstract
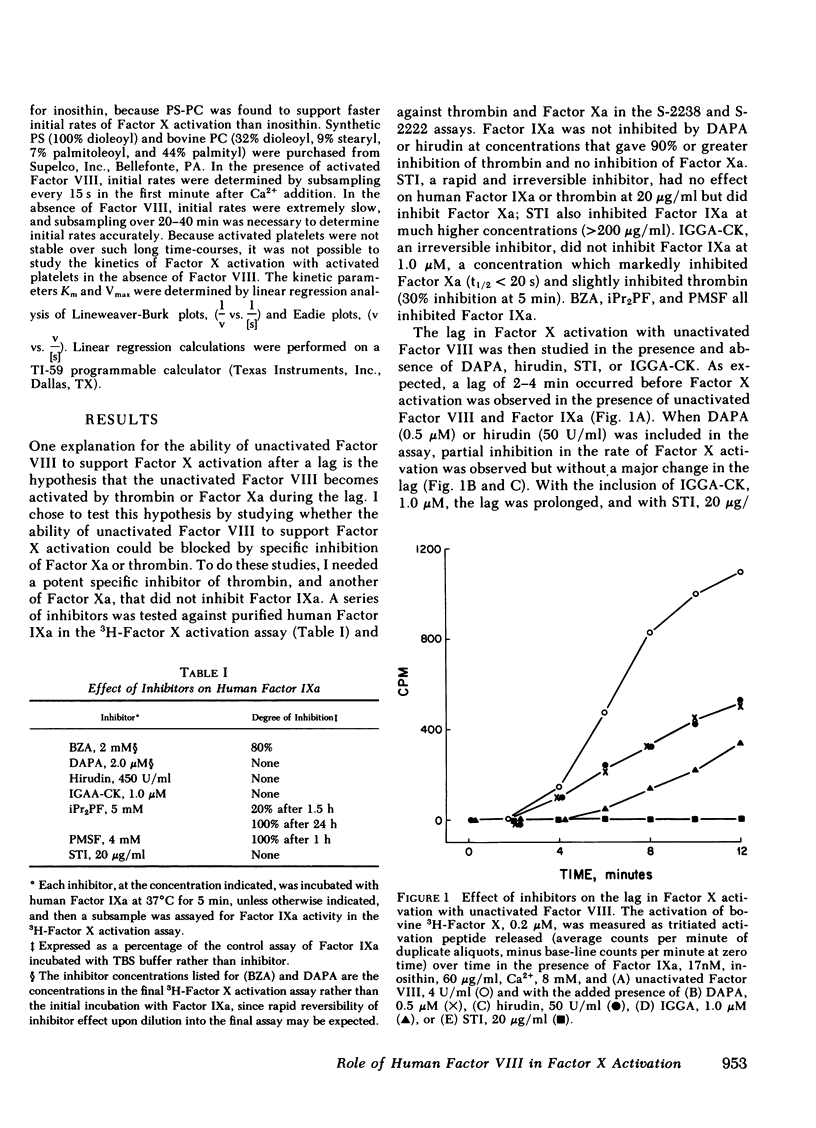
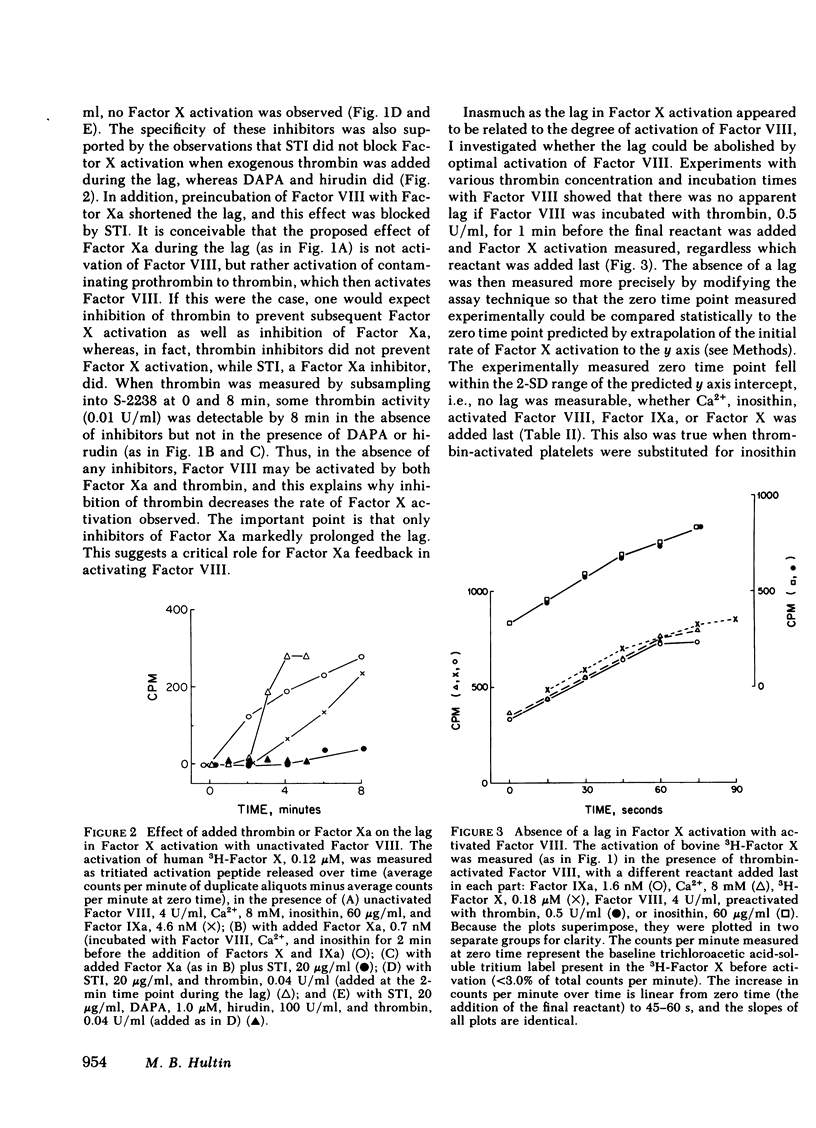
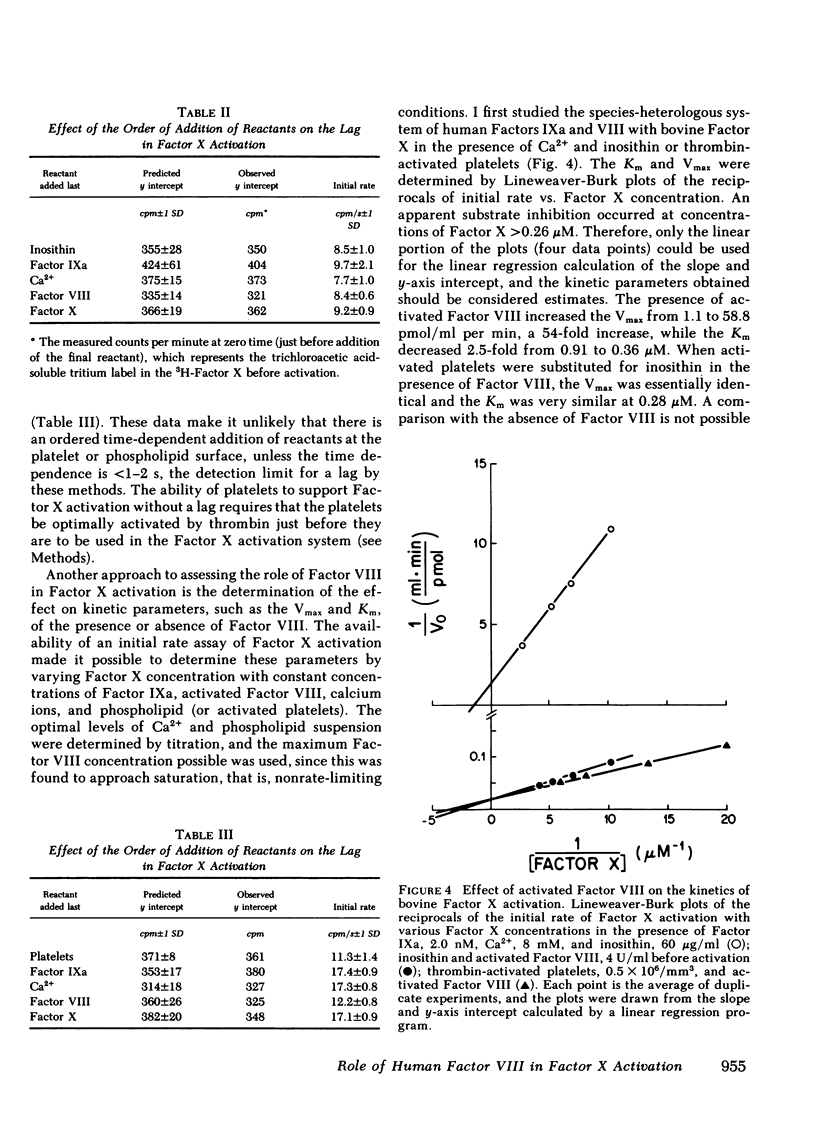
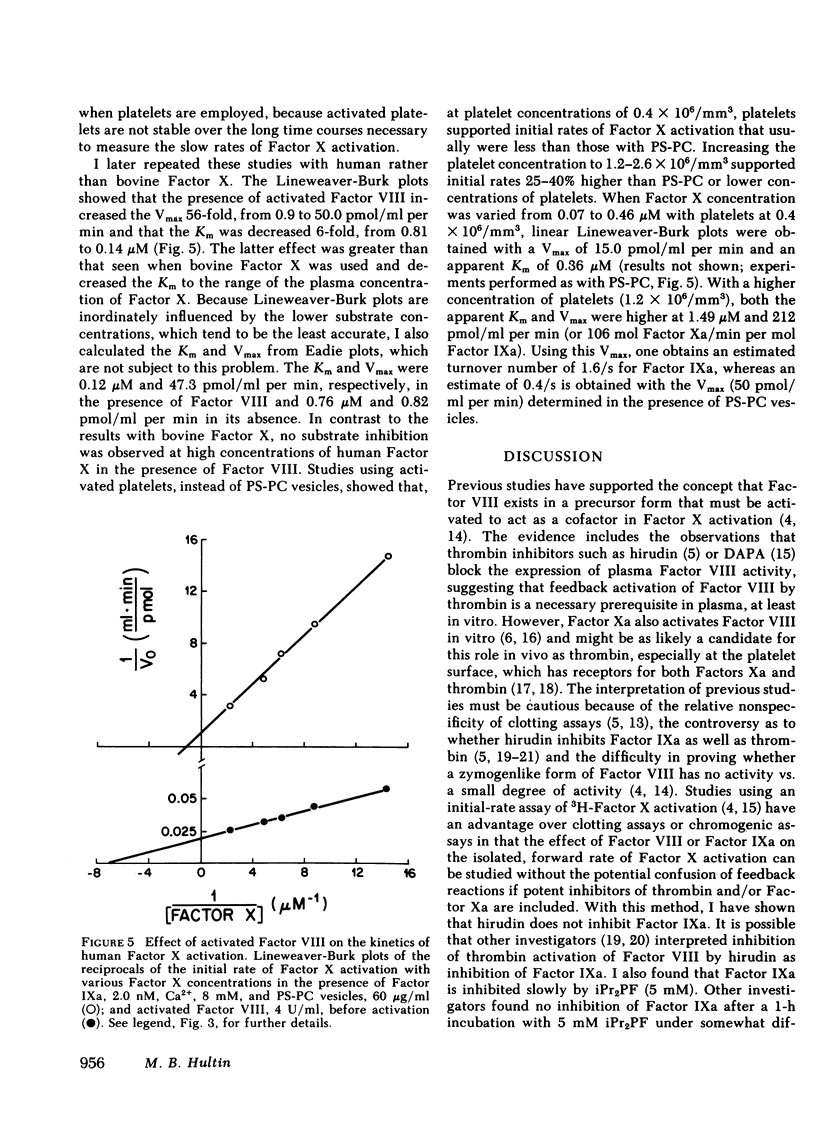
The cofactor function of human Factor VIII in Factor X activation was investigated by an initial-rate assay of 3H-Factor X activation in the presence of human factor IXa, Ca2+, and either phospholipid or fresh washed human platelets. Purified Factor VIII that has not been activated by thrombin or Factor Xa supports Factor X activation after a lag of several minutes. A specific inhibitor of Factor Xa, which had no inhibitory activity against Factor IXa, markedly prolonged this lag, whereas specific thrombin inhibitors did not prolong the lag. These data support the conclusion that unactivated Factor VIII has no ability to support Factor X activation in a purified system until it is activated by Factor Xa feedback during the lag period. When Factor VIII was optimally preactivated by thrombin, the lag was completely abolished, regardless of the order of addition of the other reactants or the phospholipid source. These data indicate that there is no slow, time-dependent ordering of the reactants at the phospholipid or activated platelet surface if Factor VIII has been preactivated. Unactivated platelets did not support Factor X activation by Factors IXa and VIII. The effect of activated Factor VIII on the kinetics of bovine Factor X activation was primarily to increase the Vmax (54-fold), whereas with human Factor X, Factor VIII both increased the Vmax 56-fold and decreased the Km sixfold to 0.14 microM, similar to the plasma concentration of Factor X. Therefore, a change in the plasma factor X concentration would be expected to have a major effect on the rate of Factor X activation in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown J. E., Baugh R. F., Hougie C. Substrate inhibition of the intrinsic generation of activated factor X (Stuart factor). Thromb Res. 1978 Nov;13(5):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(78)90194-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. E., Baugh R. F., Hougie C. The inhibition of the intrinsic generation of activated factor X by heparin and hirudin. Thromb Res. 1980 Jan 1;17(1-2):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Scipio R. G., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. Activation of human factor IX (Christmas factor). J Clin Invest. 1978 Jun;61(6):1528–1538. doi: 10.1172/JCI109073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Coan M. H., Legaz M. E., Davie E. W. The mechanism of activation of bovine factor X (Stuart factor) by intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5290–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B. Activated clotting factors in factor IX concentrates. Blood. 1979 Nov;54(5):1028–1038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Jesty J. The activation and inactivation of human factor VIII by thrombin: effect of inhibitors of thrombin. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultin M. B., Nemerson Y. Activation of factor X by factors IXa and VIII; a specific assay for factor IXa in the presence of thrombin-activated factor VIII. Blood. 1978 Nov;52(5):928–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesty J. Dissociation of complexes and their derivatives formed during inhibition of bovine thrombin and activated factor X by antithrombin III. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1044–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane W. H., Lindhout M. J., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Factor Va-dependent binding of factor Xa to human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):1170–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisiel W., Ericsson L. H., Davie E. W. Proteolytic activation of protein C from bovine plasma. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4893–4900. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosow D. P., Furie B., Forastieri H. Activation of factor X: kinetic properties of the reaction. Thromb Res. 1974 Feb;4(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miletich J. P., Jackson C. M., Majerus P. W. Properties of the factor Xa binding site on human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 10;253(19):6908–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal G. G., Chavin S. I. The role of factors VIII and IX in the activation of bovine blood coagulation factor X. Thromb Res. 1979;16(3-4):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(79)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesheim M. E., Prendergast F. G., Mann K. G. Interactions of a fluorescent active-site-directed inhibitor of thrombin: dansylarginine N-(3-ethyl-1,5-pentanediyl)amide. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 20;18(6):996–1003. doi: 10.1021/bi00573a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I., Schiffman S., Chong M. M. Formation of intrinsic factor-X activator activity, with special reference to the role of thrombin. Br J Haematol. 1971 Dec;21(6):643–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb02727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterud B., Rapaport S. I. Synthesis of intrinsic factor X activator. Inhibition of the function of formed activator by antibodies to factor VIII and to factor IX. Biochemistry. 1970 Apr 14;9(8):1854–1861. doi: 10.1021/bi00810a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitlick F. A., Lundblad R. L., Davie E. W. The role of heparin in intrinsic blood coagulation. J Biomed Mater Res. 1969 Mar;3(1):95–106. doi: 10.1002/jbm.820030109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosing J., Tans G., Govers-Riemslag J. W., Zwaal R. F., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipids and factor Va in the prothrombinase complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):274–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman M. A., Tollefsen D. M., Majerus P. W. The binding of human and bovine thrombin to human platelets. Blood. 1976 Jan;47(1):43–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverberg S. A., Nemerson Y., Zur M. Kinetics of the activation of bovine coagulation factor X by components of the extrinsic pathway. Kinetic behavior of two-chain factor VII in the presence and absence of tissue factor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8481–8488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomela H., Blombäck M., Blombäck B. The activation of factor X evaluated by using synthetic substrates. Thromb Res. 1977 Feb;10(2):267–281. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(77)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer M. E., Pizzo S. V., McKee P. A. Is there a precursive, relatively procoagulant-inactive form of normal antihemophilic factor (factor VIII)? Blood. 1979 Oct;54(4):916–927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdorf-Hansen J. F., Zucker M. B. Effect of temperature and inhibitors on serotonin-14C release from human platelets. Am J Physiol. 1971 Jan;220(1):105–111. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.220.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vehar G. A., Davie E. W. Preparation and properties of bovine factor VIII (antihemophilic factor). Biochemistry. 1980 Feb 5;19(3):401–410. doi: 10.1021/bi00544a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dieijen G., Tans G., Rosing J., Hemker H. C. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3433–3442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



