Abstract
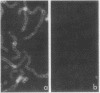
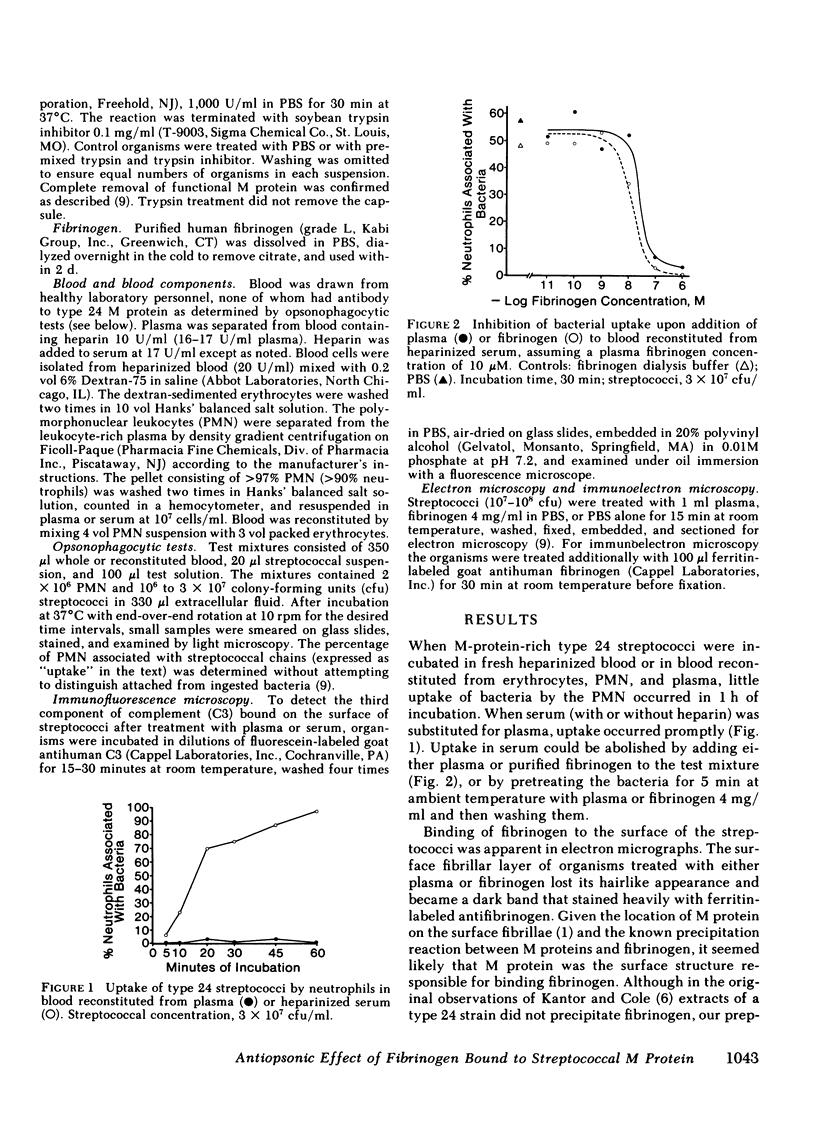
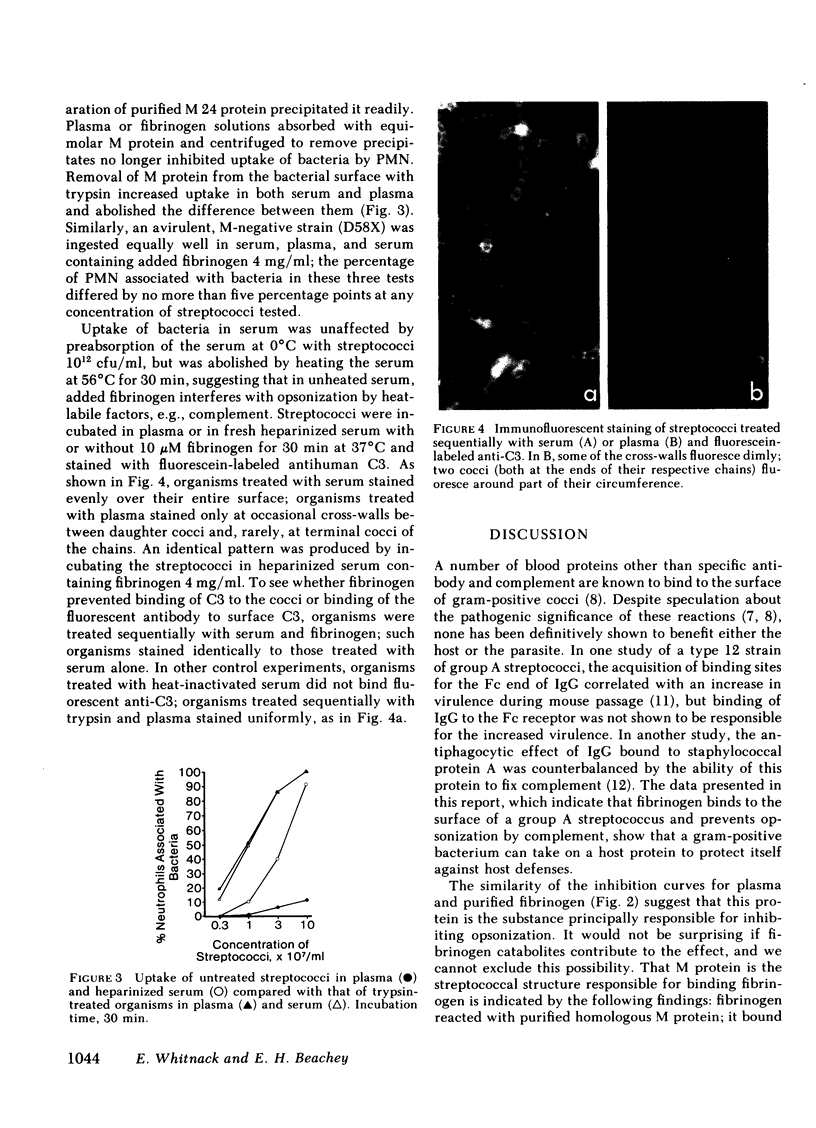
When virulent group A streptococci of M type 24 were incubated in fresh heparinized whole blood or in blood reconstituted from cellular elements and plasma, little uptake by neutrophils occurred as determined by light microscopy. When fresh human serum (with or without added heparin) was substituted for plasma, uptake occurred promptly. Uptake in serum could be prevented by adding either plasma or purified human fibrinogen to the incubation mixtures, or by pretreating the organisms with plasma or fibrinogen. Fibrinogen solutions absorbed with purified homologous M protein and centrifuged to remove precipitates lost their inhibitory activity. Uptake in serum depended on heat-labile factors. Immunofluorescent staining of bacteria using fluorescein-labeled antibody to the third component of complement showed that streptococci incubated in fresh serum bound complement evenly over the entire cell surface, whereas streptococci incubated in fresh plasma or in serum plus fibrinogen fluoresced only at some of the cross-walls between adjacent daughter cocci and at occasional terminal cocci. In electron micrographs, the surface fibrillar layer of streptococci treated with plasma or fibrinogen lost its hairlike appearance and became a dark band that stained heavily with ferritin-labeled antifibrinogen. We conclude that the known antiopsonic effect of M protein derives in part from binding of fibrinogen.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Stollerman G. H., Chiang E. Y., Chiang T. M., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H. Purification and properties of M protein extracted from group A streptococci with pepsin: covalent structure of the amino terminal region of type 24 M antigen. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1469–1483. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisno A. L. Alternate complement pathway activation by group A streptococci: role of M-protein. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1172–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1172-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burova L. A., Christensen P., Grubb R., Jonsson A., Samuelsson G., Schalén C., Svensson M. L. Changes in virulence, M protein and IgG Fc receptor activity in a type 12 group A streptococcal strain during mouse passages. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1980 Aug;88(4):199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1980.tb02629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S., COLE R. M. A fibrinogen precipitating factor (FPF) of group A streptococci. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Oct;102:146–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANTOR F. S. FIBRINOGEN PRECIPITATION BY STREPTOCOCCAL M PROTEIN. I. IDENTITY OF THE REACTANTS, AND STOICHIOMETRY OF THE REACTION. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:849–859. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Schönbeck C., Myhre E. Fibrinogen binding structures in beta-hemolytic streptococci group A, C, and G. Comparisons with receptors for IgG and aggregated beta 2-microglobulin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Oct;87(5):303–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCEFIELD R. C. Current knowledge of type-specific M antigens of group A streptococci. J Immunol. 1962 Sep;89:307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Schmeling D., Cleary P. P., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Quie P. G. Inhibition of alternative complement pathway opsonization by group A streptococcal M protein. J Infect Dis. 1979 May;139(5):575–585. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.5.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Verhoef J., Sabath L. D., Quie P. G. Effect of protein A on staphylococcal opsonization. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):760–764. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.760-764.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Hsu K. C., Gotschlich E. C. Electron microscopic studies on streptococci. I. M antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Nov 1;130(5):1063–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitnack E., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Hyaluronate capsule prevents attachment of group A streptococci to mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):985–991. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.985-991.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]