Abstract
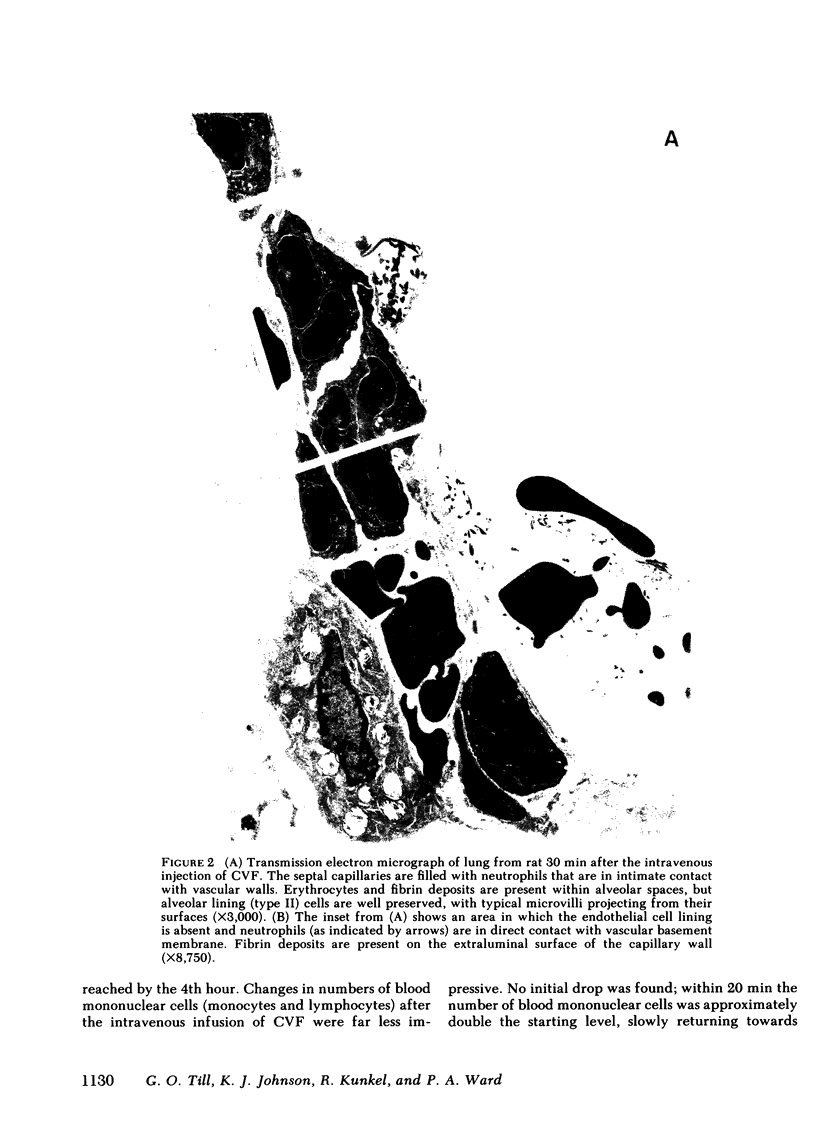
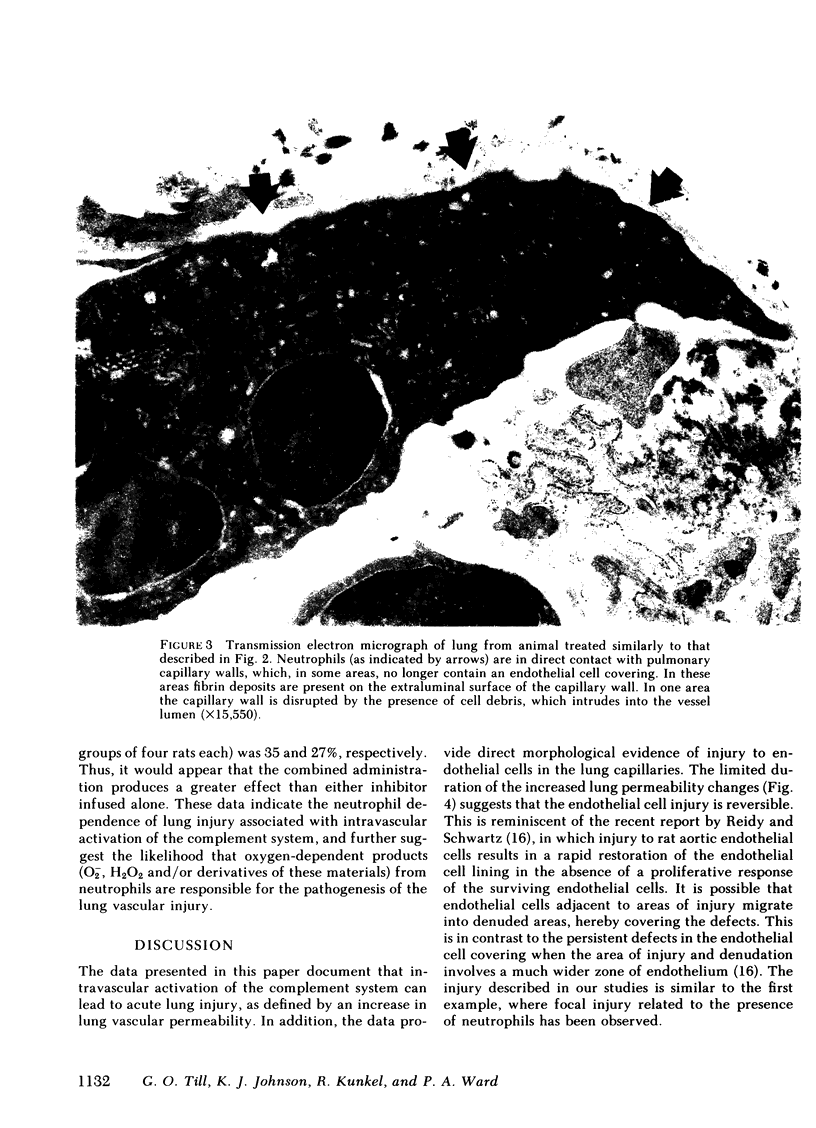
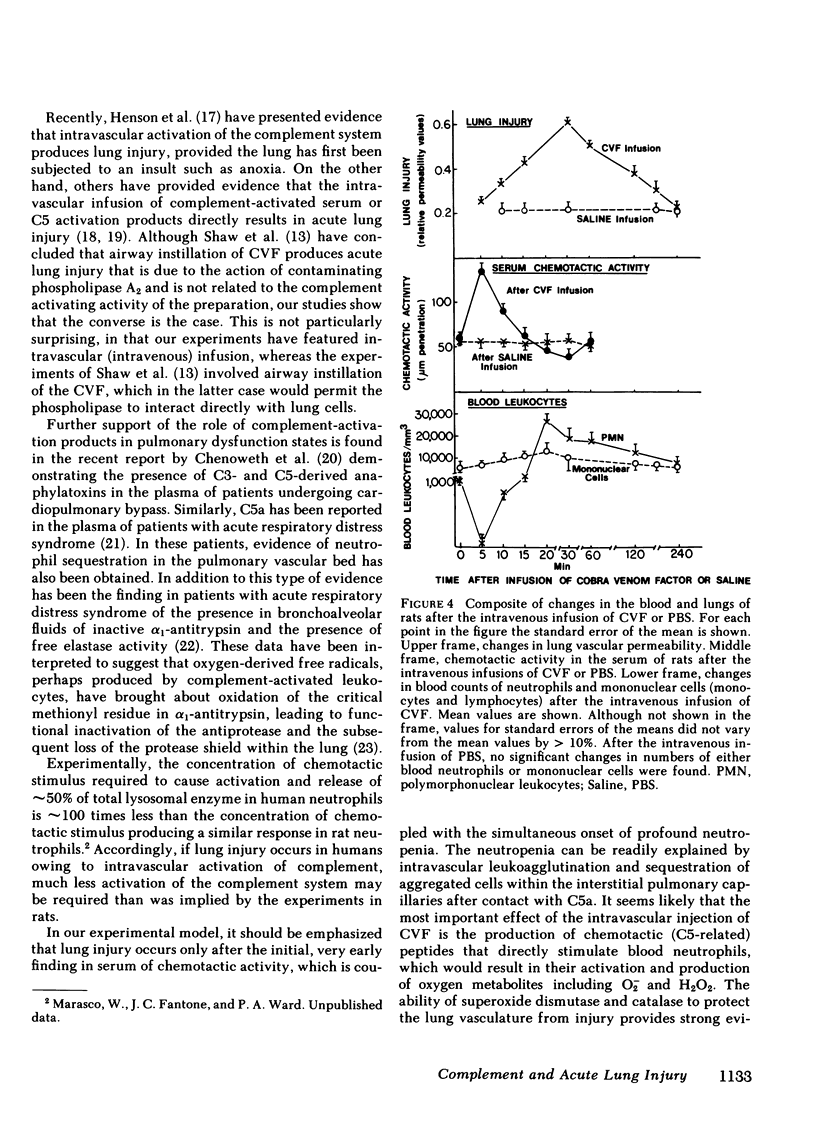
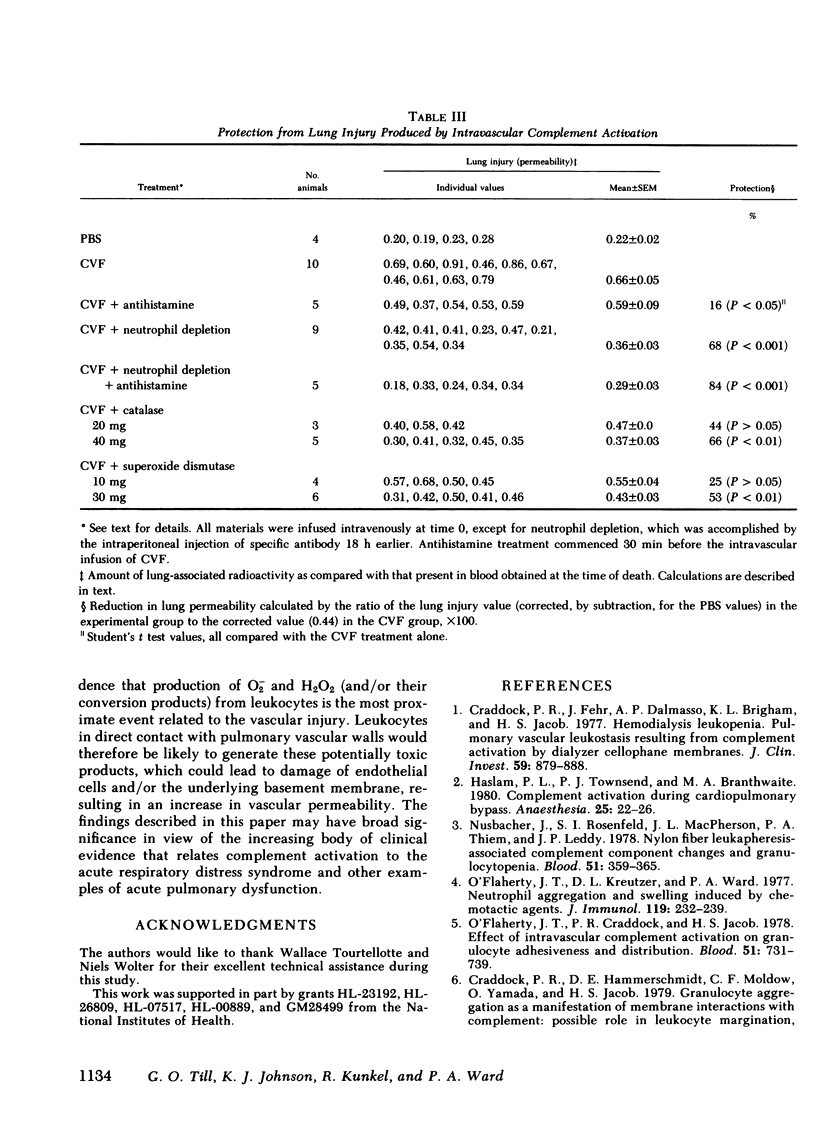
Intravascular activation of the complement system with cobra venom factor results in acute lung injury, which has been quantitated by increases in lung vascular permeability. Cobra venom factor preparations devoid of phospholipase A2 activity retain full lung-damaging capacity. The lung injury is associated with the preceding appearance of chemotactic activity in the serum coincident with the development of a profound neutropenia. The chemotactic activity is immunochemically related to human C5a. Morphologic studies have revealed discontinuities in the endothelial cell lining of lung alveolar capillaries, damage and/or destruction of endothelial cells in these areas, plugging of pulmonary capillaries with neutrophils that are in direct contact with vascular basement membrane, the presence of fibrin in alveolar spaces and in areas adjacent to damaged endothelial cells, and intraalveolar hemorrhage. Lung injury is dramatically attenuated in animals that have been previously neutrophil depleted. Teh intravenous injection of superoxide dismutase or catalase also provides significant protection from the pulmonary damage. Very little protection from the pulmonary damage. Very little protection is afforded by pretreatment of rats with antihistamine. These studies suggest that intravascular activation of the complement system leads to neutrophil aggregation and activation, intrapulmonary capillary sequestration of neutrophils, and vascular injury, which may be related to production of toxic oxygen metabolites by complement-activated neutrophils.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballow M., Cochrane C. G. Two anticomplementary factors in cobra venom: hemolysis of guinea pig erythrocytes by one of them. J Immunol. 1969 Nov;103(5):944–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. In vitro suppression of serum elastase-inhibitory capacity by reactive oxygen species generated by phagocytosing polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):793–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI109364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenoweth D. E., Cooper S. W., Hugli T. E., Stewart R. W., Blackstone E. H., Kirklin J. W. Complement activation during cardiopulmonary bypass: evidence for generation of C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins. N Engl J Med. 1981 Feb 26;304(9):497–503. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198102263040901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D. E., Moldow C. F., Yamada O., Jacob H. S. Granulocyte aggregation as a manifestation of membrane interactions with complement: possible role in leukocyte margination, microvascular occlusion, and endothelial damage. Semin Hematol. 1979 Apr;16(2):140–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., Weaver L. J., Hudson L. D., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Association of complement activation and elevated plasma-C5a with adult respiratory distress syndrome. Pathophysiological relevance and possible prognostic value. Lancet. 1980 May 3;1(8175):947–949. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)91403-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haslam P. L., Townsend P. J., Branthwaite M. A. Complement activation during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anaesthesia. 1980 Jan;35(1):22–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1980.tb03715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn D. C., Meyers A. J., Gherini S. T., Beckmann A., Markison R. E., Churg A. M. Production of acute pulmonary injury by leukocytes and activated complement. Surgery. 1980 Jul;88(1):48–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosea S., Brown E., Hammer C., Frank M. Role of complement activation in a model of adult respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):375–382. doi: 10.1172/JCI109866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Fantone J. C., 3rd, Kaplan J., Ward P. A. In vivo damage of rat lungs by oxygen metabolites. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):983–993. doi: 10.1172/JCI110149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Role of oxygen metabolites in immune complex injury of lung. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2365–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. T., Fein A. M., Lippmann M., Holtzman H., Kimbel P., Weinbaum G. Elastolytic activity in pulmonary lavage fluid from patients with adult respiratory-distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 22;304(4):192–196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101223040402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nusbacher J., Rosenfeld S. I., MacPherson J. L., Thiem P. A., Leddy J. P. Nylon fiber leukapheresis: associated complement component changes and cranulocytopenia. Blood. 1978 Feb;51(2):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Effect of intravascular complement activation on granulocyte adhesiveness and distribution. Blood. 1978 Apr;51(4):731–739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Neutropenia induced by systemic infusion of chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1586–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B. Role of complement in the induction of immunological responses. Transplant Rev. 1976;32:93–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M. Endothelial regeneration. III. Time course of intimal changes after small defined injury to rat aortic endothelium. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. O., Roberts M. F., Ulevitch R. J., Henson P., Dennis E. A. Phospholipase A2 contamination of cobra venom factor preparations. Biologic role in complement-dependent in vivo reactions and inactivation with p-bromophenacyl bromide. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jun;91(3):517–530. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]