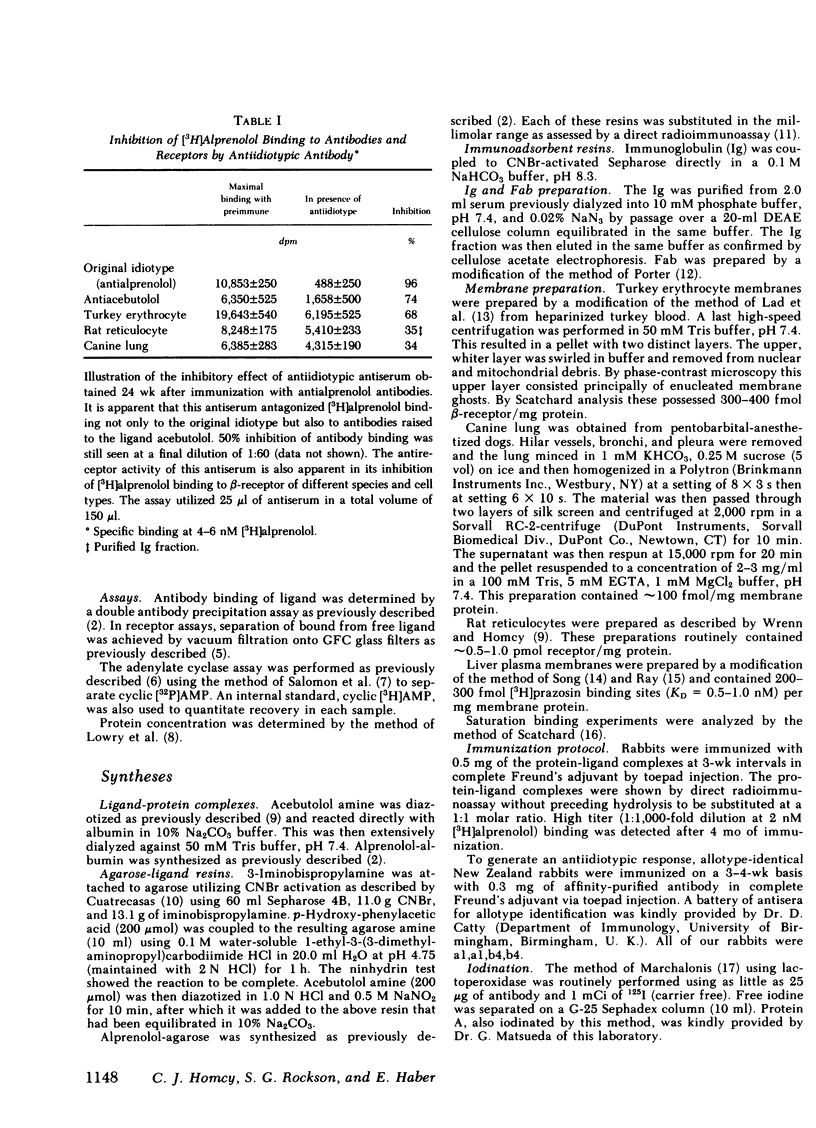
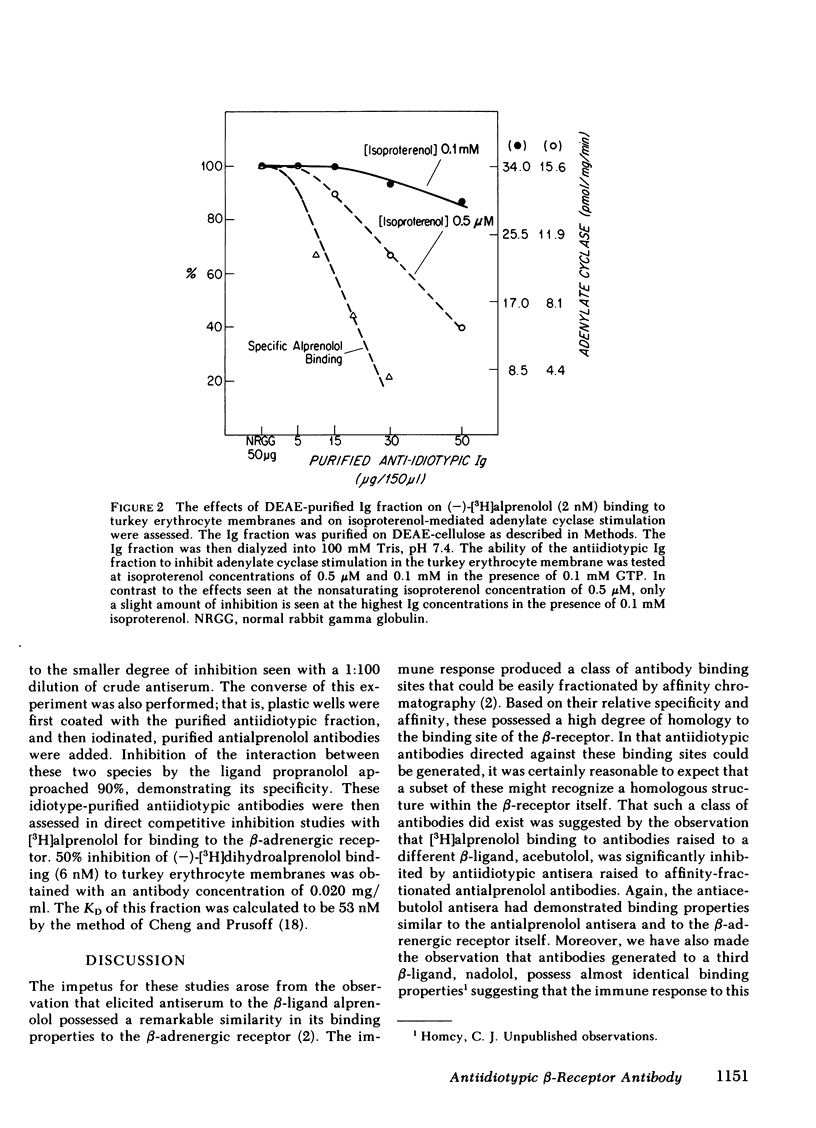
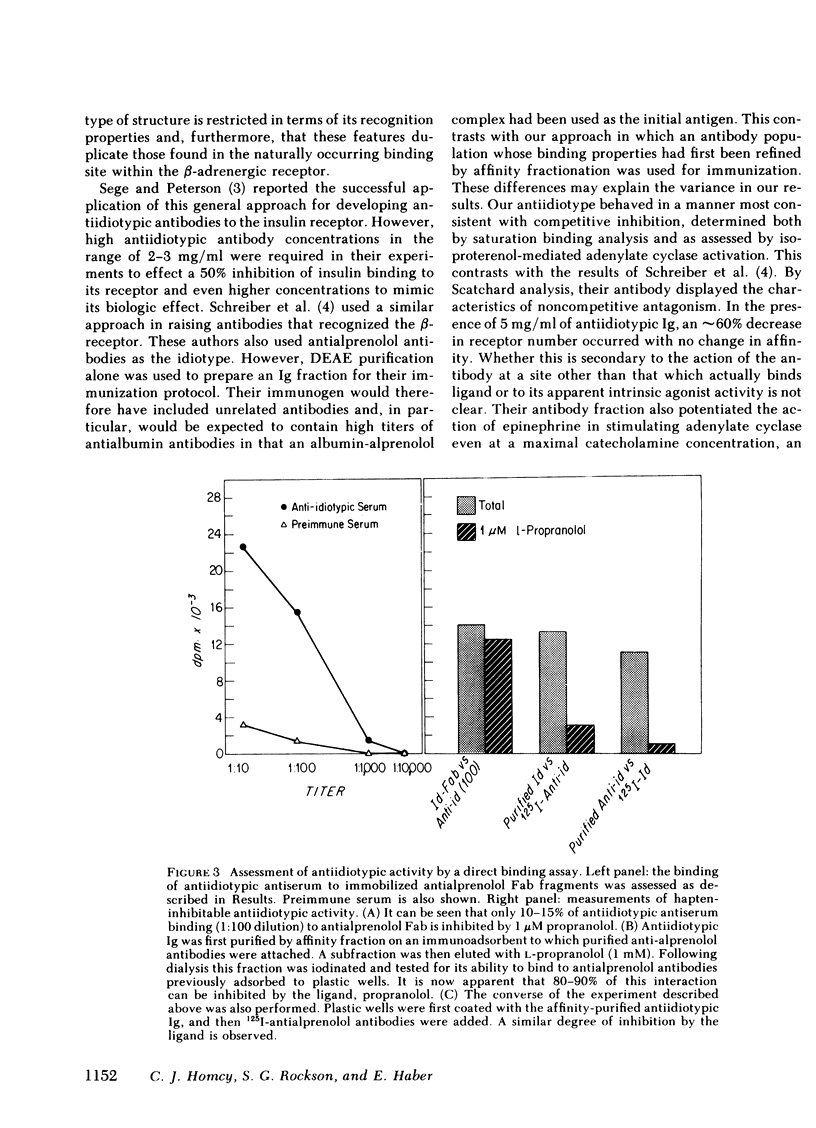
Abstract
Antialprenolol rabbit antibodies were fractionated on an acebutolol affinity resin, followed by L-propranolol elution so as to separate a class of binding sites that mimic the beta-adrenergic receptor. Allotype-identicaL rabbits were immunized with this fraction. After 6 mo, antisera exhibited antiidiotypic activity inhibiting [3H]alprenolol binding to the original antibody and to rabbit antiacebutolol antibodies, which had a spectrum of ligand-binding properties identical to the original idiotype. Those antisera demonstrating the original idiotype. Those antisera demonstrating the most potent antiidiotypic activity also blocked [3H]alprenolol binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor of turkey membrane, canine pulmonary membrane, and rat reticulocyte. An idiotype affinity-purified fraction showed similar activity, inhibiting beta-receptor binding with a calculated dissociation constant (KD) of 53 nM. Isoproterenol-mediated adenylate cyclase activity was also inhibited in a competitive manner. The universality of recognition of these antiidiotypic antisera indicate that the three-dimensional structure of a receptor's binding site can be modeled by a subset of an elicited antibody population.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoebeke J., Vauquelin G., Strosberg A. D. The production and characterization of antibodies against beta-adrenergic antagonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978;27(11):1527–1532. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90480-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Strauss H. W., Kopiwoda S. Beta receptor occupancy. Assessment in the intact animal. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1111–1118. doi: 10.1172/JCI109764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Wrenn S. M., Haber E. Demonstration of the hydrophilic character of adenylate cyclase following hydrophobic resolution on immobilized alkyl residues. Critical role of alkyl chain length. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8957–8964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lad P. M., Nielsen T. B., Preston M. S., Rodbell M. The role of the guanine nucleotide exchange reaction in the regulation of the beta-adrenergic receptor and in the actions of catecholamines and cholera toxin on adenylate cyclase in turkey erythrocyte membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):988–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J. An enzymic method for the trace iodination of immunoglobulins and other proteins. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(2):299–305. doi: 10.1042/bj1130299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshak-Rothstein A., Siekevitz M., Margolies M. N., Mudgett-Hunter M., Gefter M. L. Hybridoma proteins expressing the predominant idiotype of the antiazophenylarsonate response of A/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1120–1124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockson S. G., Homcy C. J., Haber E. Anti-alprenolol antibodies in the rabbit. A new probe for the study of beta-adrenergic receptor interaction. Circ Res. 1980 Jun;46(6):808–813. doi: 10.1161/01.res.46.6.808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rockson S. G., Homcy C. J., Quinn P., Manders W. T., Haber E., Vatner S. F. Cellular mechanisms of impaired adrenergic responsiveness in neonatal dogs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):319–327. doi: 10.1172/JCI110038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Couraud P. O., Andre C., Vray B., Strosberg A. D. Anti-alprenolol anti-idiotypic antibodies bind to beta-adrenergic receptors and modulate catecholamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7385–7389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sege K., Peterson P. A. Use of anti-idiotypic antibodies as cell-surface receptor probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2443–2447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song C. S., Rubin W., Rifkind A. B., Kappas A. Plasma membranes of the rat liver. Isolation and enzymatic characterization of a fraction rich in bile canaliculi. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):124–132. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn S. M., Jr, Homcy C. J. Photoaffinity label for the beta-adrenergic receptor: synthesis and effects on isoproterenol-stimulated adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4449–4453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



