Abstract
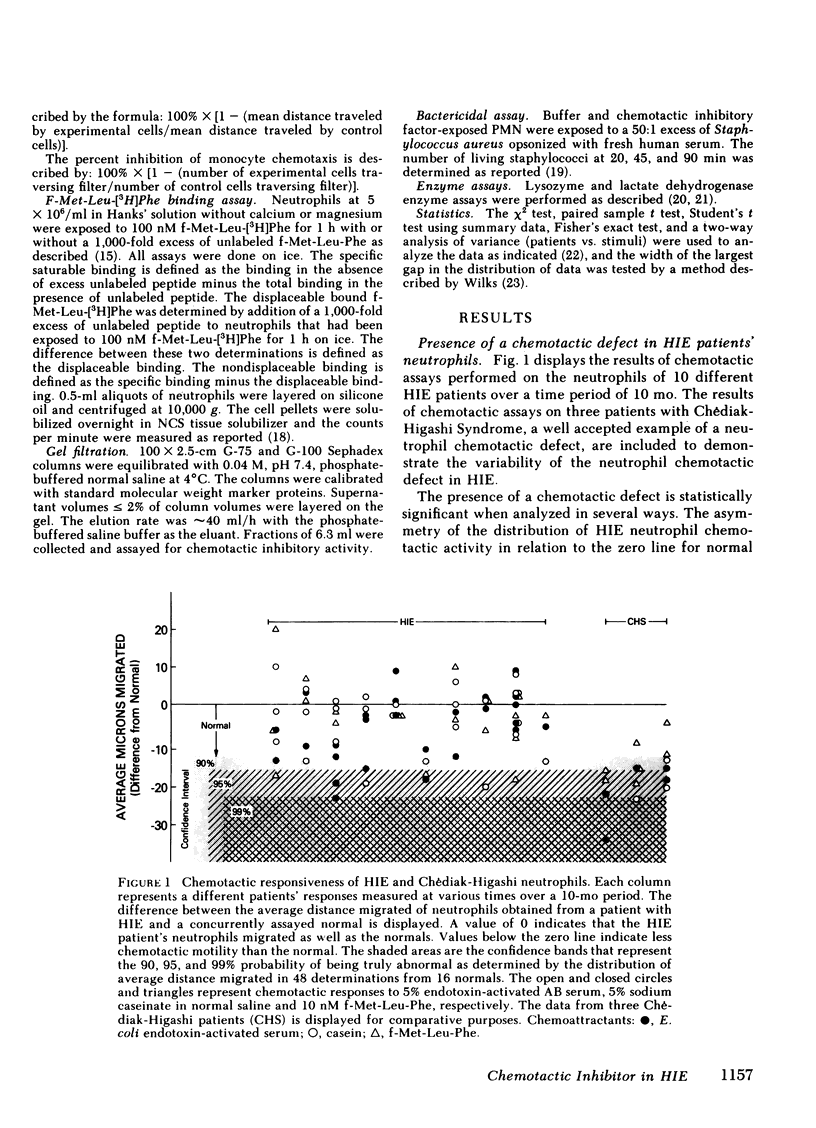
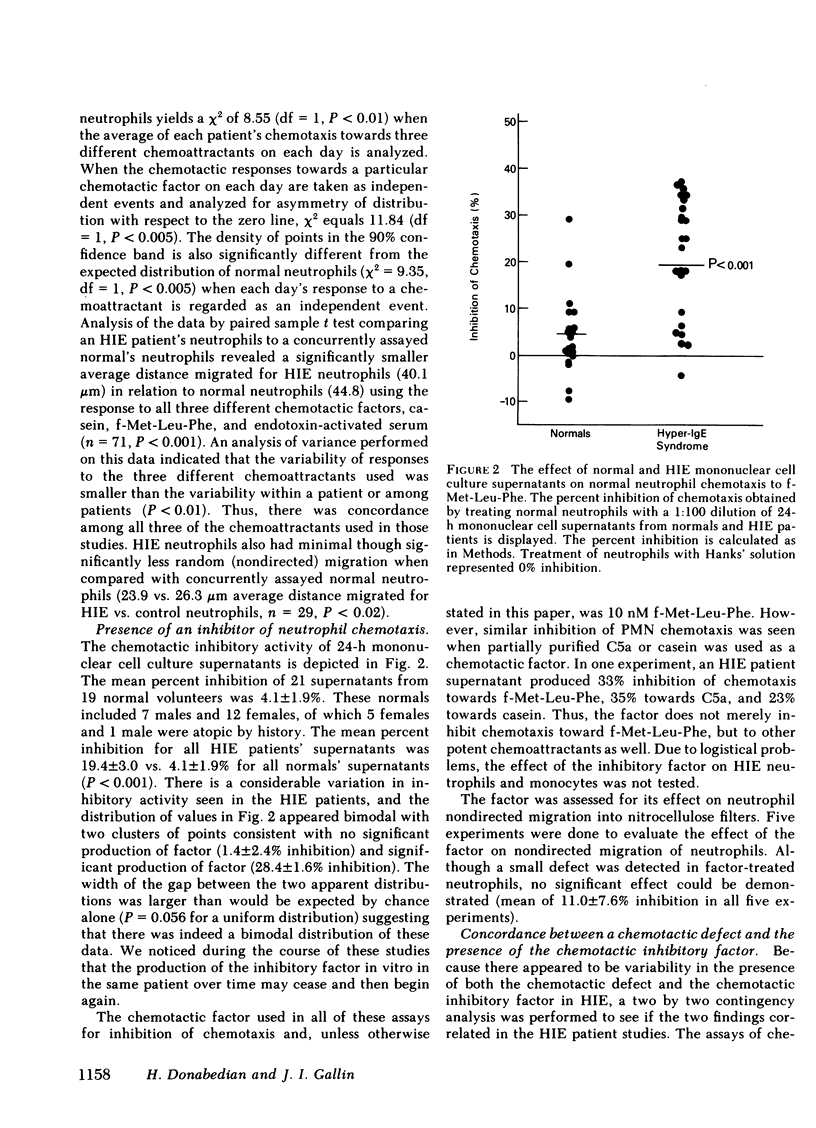
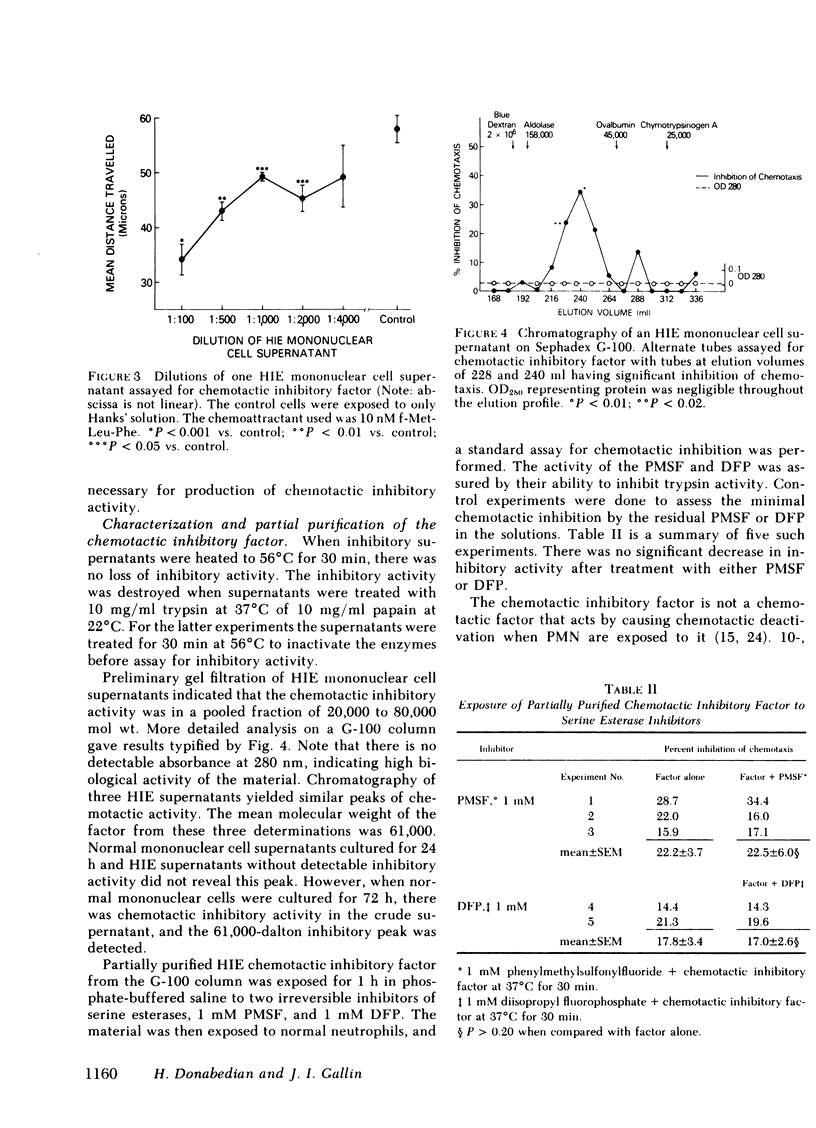
The chemotactic responsiveness of the neutrophils of 10 patients with the hyperimmunoglobulin E-recurrent infection syndrome (HIE) were compared with neutrophils from normal volunteers over a 10-mo period. HIE neutrophils as a group displayed significantly less chemotactic motility than control neutrophils. The data from individual patients were variable, being normal or abnormal on different days. Mononuclear cells from HIE patients, when cultured for 24 h in the absence of serum or a mitogen, produced a factor that inhibited normal neutrophil and monocyte chemotaxis. Mononuclear cells from normal volunteers with and without atopy or from patients with parasites or bacterial infections did not produce such an inhibitory factor. The production of this chemotactic inhibitory factor in vitro was variable over time, but it correlated with the presence of an in vitro neutrophil chemotactic defect. The chemotactic inhibitory factor was partially purified and was found to contain protein, to be stable at 56 degrees C, and to have a molecular weight of approximately 61,000. Irreversible inhibitors of serine esterases do not inactivate the factor. The factor is produced by esterase-negative mononuclear cells and is not toxic to neutrophils. This chemotactic inhibitory factor may be the basis of the variable chemotactic defect in HIE neutrophils.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger M., Kirkpatrick C. H., Goldsmith P. K., Gallin J. I. IgE antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus and Candida albicans in patients with the syndrome of hyperimmunoglobulin E and recurrent infections. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2437–2443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Becker W. G. Abnormalities in the regulation of human IgE synthesis. Immunol Rev. 1978;41:288–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1978.tb01469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Wray B. B., Belmaker E. Z. Extreme hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and undue susceptibility to infection. Pediatrics. 1972 Jan;49(1):59–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Root R. K., Kimball H. R., Kirkpatrick C. H. Defective neutrophil chemotaxis and cellular immunity in a child with recurrent infections. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Apr;78(4):515–519. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-78-4-515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis S. D., Schaller J., Wedgwood R. J. Job's Syndrome. Recurrent, "cold", staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet. 1966 May 7;1(7445):1013–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donabedian H., Gallin J. I. Deactivation of human neutrophil chemotaxis by chemoattractants: effect on receptors for the chemotactic factor f-Met-Leu-Phe. J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):839–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk W., Goodwin R. H., Jr, Leonard E. J. A 48-well micro chemotaxis assembly for rapid and accurate measurement of leukocyte migration. J Immunol Methods. 1980;33(3):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenberg W. R., Marx J. J., Jr, Hansen R. L., Haselby R. C. Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome: response to transfer factor and ascorbic acid therapy. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Feb;12(2):132–142. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Malech H. L., Davis J. M., Klempner M. S., Kirkpatrick C. H. Disorders of phagocyte chemotaxis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Apr;92(4):520–538. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-4-520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Wright D. G., Schiffmann E. Role of secretory events in modulating human neutrophil chemotaxis. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1364–1374. doi: 10.1172/JCI109257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geha R. S., Reinherz E., Leung D., McKee K. T., Jr, Schlossman S., Rosen F. S. Deficiency of suppressor T cells in the hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):783–791. doi: 10.1172/JCI110315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. A neutrophil-immobilizing factor derived from human leukocytes. I. Generation and partial characterization. J Exp Med. 1972 Dec 1;136(6):1564–1580. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.6.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Rocklin R. E. Amplification of the activity of human leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) by the generation of a low molecular weight inhibitor of PMN leukocyte chemotaxis. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):891–896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J. G., STRAUSS B. STUDIES ON HEAT-LABILE OPSONIN IN RABBIT SERUM. J Immunol. 1964 Jan;92:145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Estensen R. D., Hogan N. A., Quie P. G. Severe staphylococcal disease associated with allergic manifestations, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E, and defective neutrophil chemotaxis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Nov;88(5):796–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Ochs H. D., Quie P. G., Clark R. A., Pabst H. F., Klebanoff S. J., Wedgwood R. J. Defect in neutrophil granulocyte chemotaxis in Job's syndrome of recurrent "cold" staphylococcal abscesses. Lancet. 1974 Sep 14;2(7881):617–619. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)91942-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Quie P. G. Raised serum-IgE levels and defective neutrophil chemotaxis in three children with eczema and recurrent bacterial infections. Lancet. 1974 Feb 9;1(7850):183–187. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92493-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katona I. M., Tata G., Scanlon R. T., Bellanti J. A. Hyper IgE syndrome: a disease with suppressor T cell deficiency. Ann Allergy. 1980 Nov;45(5):295–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Gotoh Y., Narukami H., Miyamoto Y., Honda M. Case report: a hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome with serum inhibitor against immune functions. Ann Allergy. 1981 Feb;46(2):86–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawhinney H., Killen M., Fleming W. A., Roy A. D. The hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome--a neutrophil chemotactic defect reversible by histamine H2 receptor blockade? Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Dec;17(4):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90144-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Partial characterization of leukocyte inhibitory factor by concanavalin A-stimulated human lymphocytes (LIF Con A). J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1161–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E. Products of activated lymphocytes: leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) distinct from migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1461–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Rosenthal A. S. Evidence that human leukocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) is an esterase. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer K., Baerlocher K., Price P., Krech U., Quie P. G., Douglas S. D. Staphylococcal IgE antibodies, hyperimmunoglobulinemia E and Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 12;300(15):835–838. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904123001506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Becker E. L. The deactivation of rabbit neutrophils by chemotactic factor and the nature of the activatable esterase. J Exp Med. 1968 Apr 1;127(4):693–709. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.4.693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Kirkpatrick C. H., Gallin J. I. Effects of levamisole on normal and abnormal leukocyte locomotion. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):941–950. doi: 10.1172/JCI108716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



