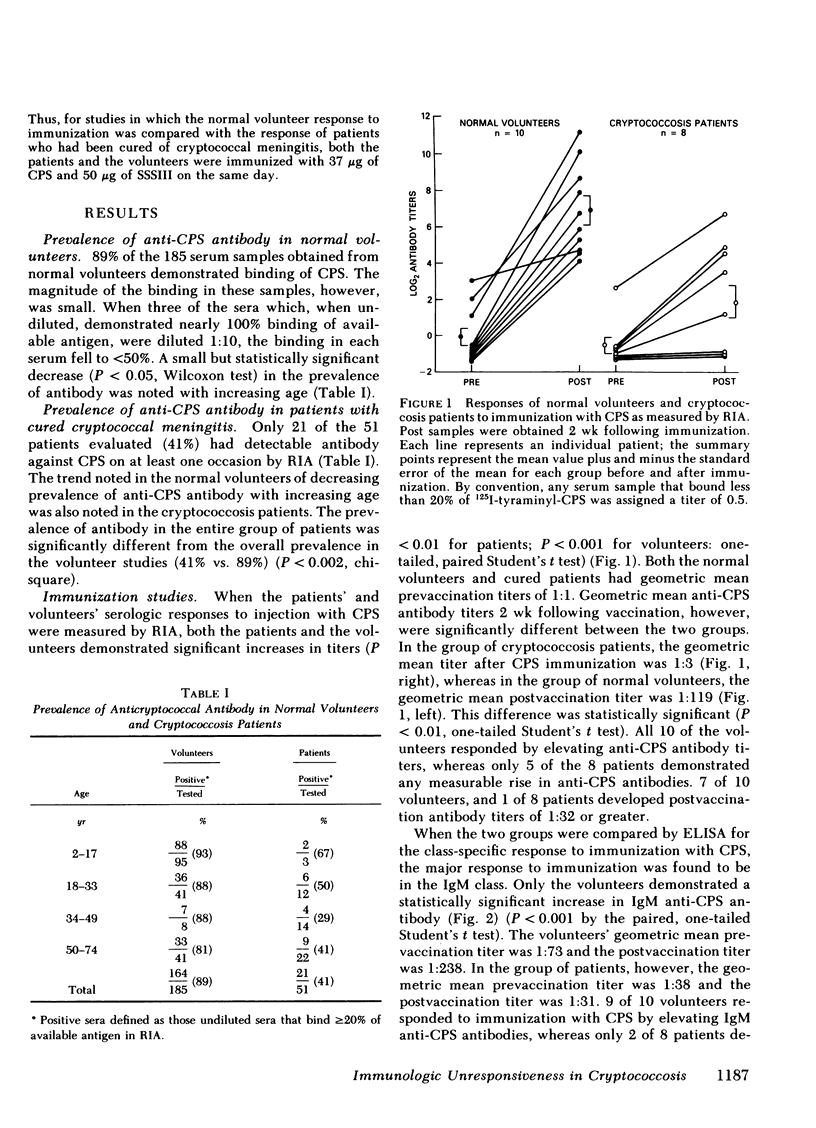
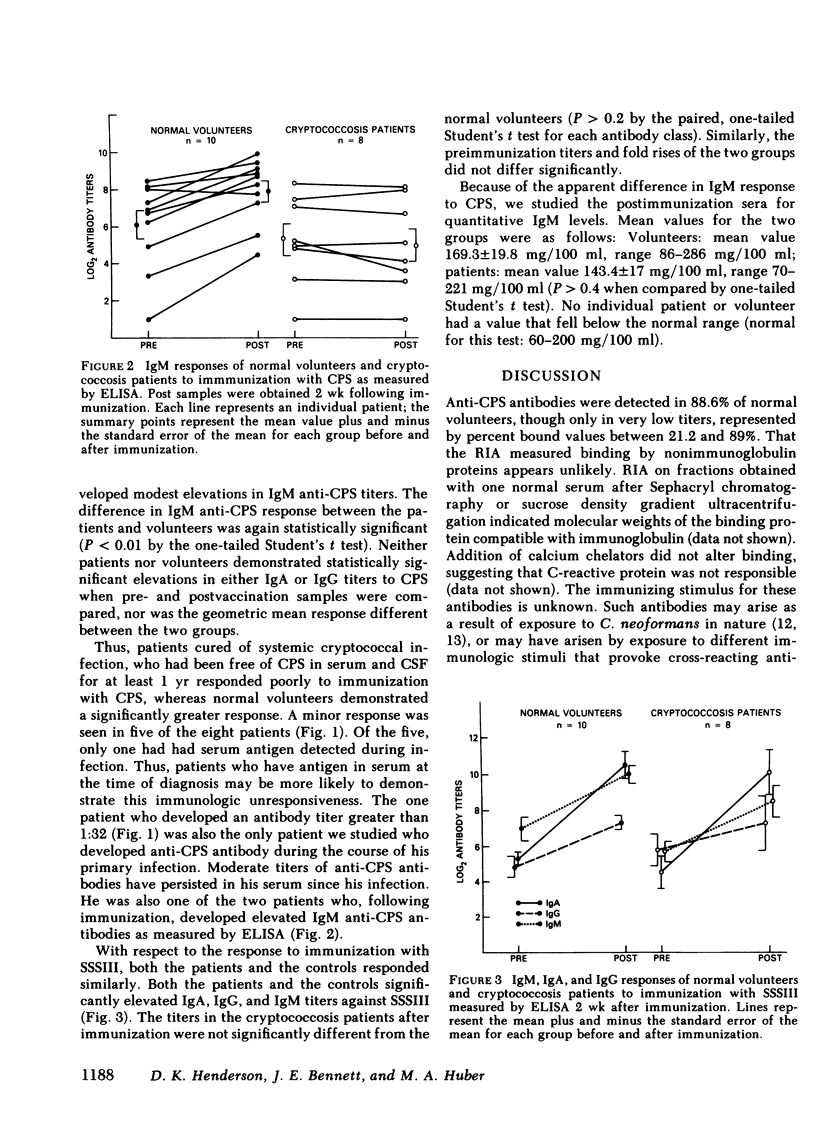
Abstract
A sensitive radioimmunoassay and an antibody class-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were used to determine whether patients cured of cryptococcosis responded normally to immunization with cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide (CPS) and type III pneumococcal polysaccharide. 10 normal volunteers and 8 patients who had been cured of cryptococcal meningitis and who had been cured of cryptococcal meningitis and who had no serious underlying diseases were immunized with both antigens. Geometric mean titers to CPS measured by radioimmunoassay were 1:1 in both groups before vaccination, but were 1:3 in patients and 1:119 in controls following immunization (P less than 0.01, Student's t test). Analysis of the class-specific response to immunization with CPS found little anti-CPS IgG or IgA. Geometric mean postvaccination IgM titers were 1:31 in patients and 1:238 in controls (P less than 0.01). Responses to immunization with type III pneumococcal polysaccharide were similar in patients and controls, with IgA, IgM, and IgG mean titers of 1:1129, 1:369, and 1:158 in patients and 1:1504, 1:1039, and 1:163 in controls (P greater than 0.2 for each antibody class). Cured cryptococcal meningitis is often associated with prolonged specific immunologic unresponsiveness.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ammann A. J., Schiffman G., Austrian R. The antibody responses to pneumococcal capsular polysaccharides in aged individuals. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1980 Jul;164(3):312–316. doi: 10.3181/00379727-164-40868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENNETT J. E., HASENCLEVER H. F. CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS POLYSACCHARIDE: STUDIES OF SEROLOGIC PROPERTIES AND ROLE IN INFECTION. J Immunol. 1965 Jun;94:916–920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOMFIELD N., GORDON M. A., ELMENDORF D. F., Jr DETECTION OF CRYPTOCOCCUS NEOFORMANS ANTIGEN IN BODY FLUIDS BY LATEX PARTICLE AGGLUTINATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1963 Oct;114:64–67. doi: 10.3181/00379727-114-28586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bindschadler D. D., Bennett J. E. Serology of human cryptococcosis. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jul;69(1):45–52. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird G. W., Roy T. C. Human serum antibodies to melibiose and other carbohydrates. Vox Sang. 1980;38(3):169–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1980.tb02346.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C. E., 3rd, Dorsey F. C. Serum immunoglobulin levels throughout the life-span of healthy man. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Nov;75(5):673–682. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-75-5-673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley C. E., 3rd, Dorsey F. C. The effect of aging on human serum immunoglobulin concentrations. J Immunol. 1970 Oct;105(4):964–972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. New color reactions for determination of sugars in polysaccharides. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:313–358. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Bennett J. E. Prognostic factors in cryptococcal meningitis. A study in 111 cases. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):176–181. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS E. E., SORENSEN L. J., WALLS K. W. The antigenic composition of Cryptococcus neoformans. V. A survey of cross-reactions among strains of Cryptococcus and other antigens. J Bacteriol. 1953 Sep;66(3):287–293. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.3.287-293.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon M. A., Vedder D. K. Serologic tests in diagnosis and prognosis of cryptococcosis. JAMA. 1966 Sep 19;197(12):961–967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff G. E., Høiby N. Precipitating antibodies against Neisseria meningitidis in normal sera and their possible origin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Jun;86C(3):123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball H. R., Hasenclever H. F., Wolff S. M. Detection of circulating antibody in human cryptococcosis by means of a bentonite flocculation technique. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Apr;95(4):631–637. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozel T. R., Gulley W. F., Cazin J., Jr Immune response to Cryptococcus neoformans soluble polysaccharide: immunological unresponsiveness. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):701–707. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.701-707.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. L., Rabinovich S. The wide spectrum of cryptococcal infections. Am J Med. 1972 Sep;53(3):315–322. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(72)90174-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., Cozad G. C. Immunological unresponsiveness induced by cryptococcal capsular polysaccharide assayed by the hemolytic plaque technique. Infect Immun. 1972 Jun;5(6):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.6.896-901.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson J. B., Fromtling R. A., Bulmer G. S. Cryptococcus neoformans: size range of infectious particles from aerosolized soil. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):634–638. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.634-638.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden C. W., Michaels R. H., Melish M. Effect of previous infection on antibody response of children to vaccination with capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae Type b. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):69–74. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palosuo T., Milgrom F. Appearance of dextrans and antidextran antibodies in human sera. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1981;65(2):153–161. doi: 10.1159/000232751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey J. P., Fudenberg H. H., Virella G., Kyong C. U., Loadholt C. B., Galbraith R. M., Gotschlich E. C., Parke J. C., Jr Association between immunoglobulin allotypes and immune responses to Haemophilus influenzae and Meningococcus polysaccharides. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):190–192. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90584-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. E., Dahl B. A., Weeks R. J., Tosh F. E. Airborne Cryptococcus neoformans: particles from pigeon excreta compatible with alveolar deposition. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):412–415. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siber G. R., Schur P. H., Aisenberg A. C., Weitzman S. A., Schiffman G. Correlation between serum IgG-2 concentrations and the antibody response to bacterial polysaccharide antigens. N Engl J Med. 1980 Jul 24;303(4):178–182. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198007243030402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Mathews J. D., Schanfield M. S., Matthews J. V., Tait B. D., Morris P. J., Mackay I. R. Interactive effect of Gm allotypes and HLA-B locus antigens on the human antibody response to a bacterial antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):8–15. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



