Abstract
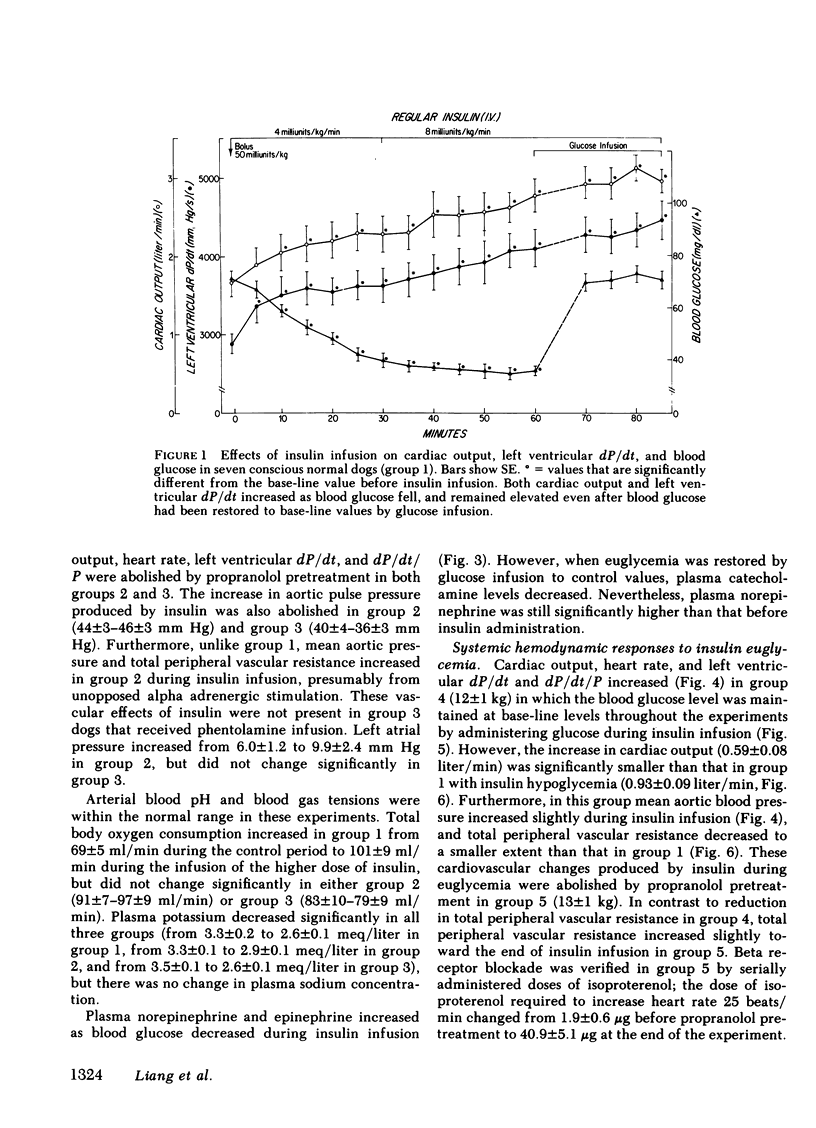
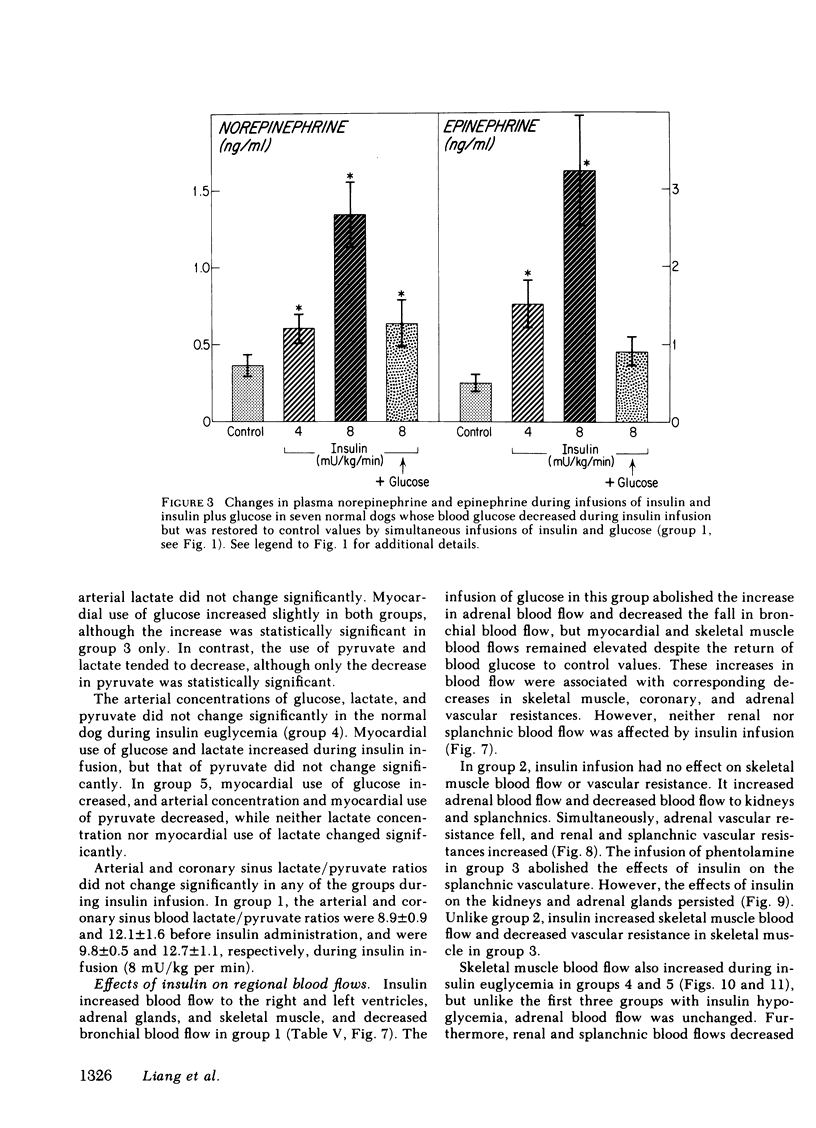
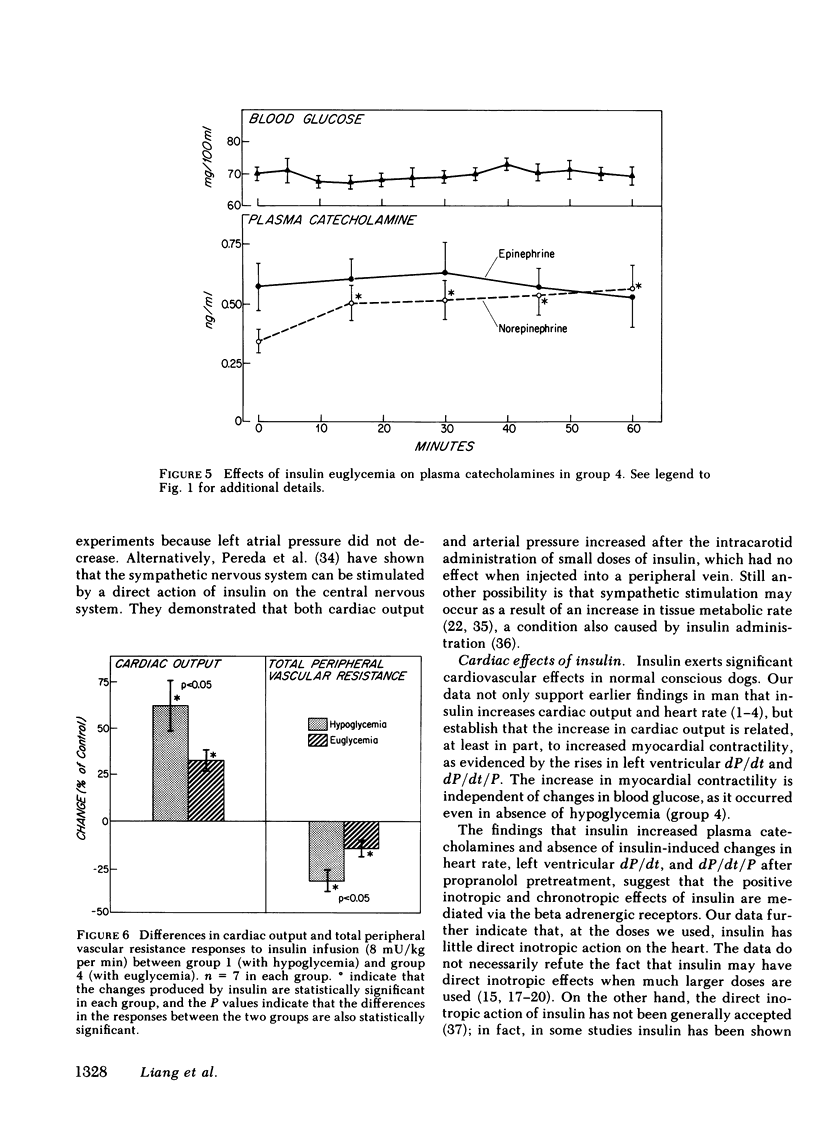
Cardiovascular actions of insulin were studied by intravenous infusions of insulin (4 and 8 mU/kg per min) in normal conscious dogs. This resulted in increases in cardiac output, heart rate, and left ventricular derivative of pressure with respect to time (dP/dt) and dP/dt/P, as blood glucose was reduced. The inotropic and chronotropic effects of insulin were not related to hypoglycemia, as they persisted even when blood glucose was restored to control values or when it was prevented from falling by a simultaneous infusion of glucose. These cardiac effects were accompanied by increases in plasma catecholamines, and were abolished by propranolol pretreatment. Both plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine increased during insulin hypoglycemia, but only norepinephrine increased during insulin infusion when euglycemia was maintained.
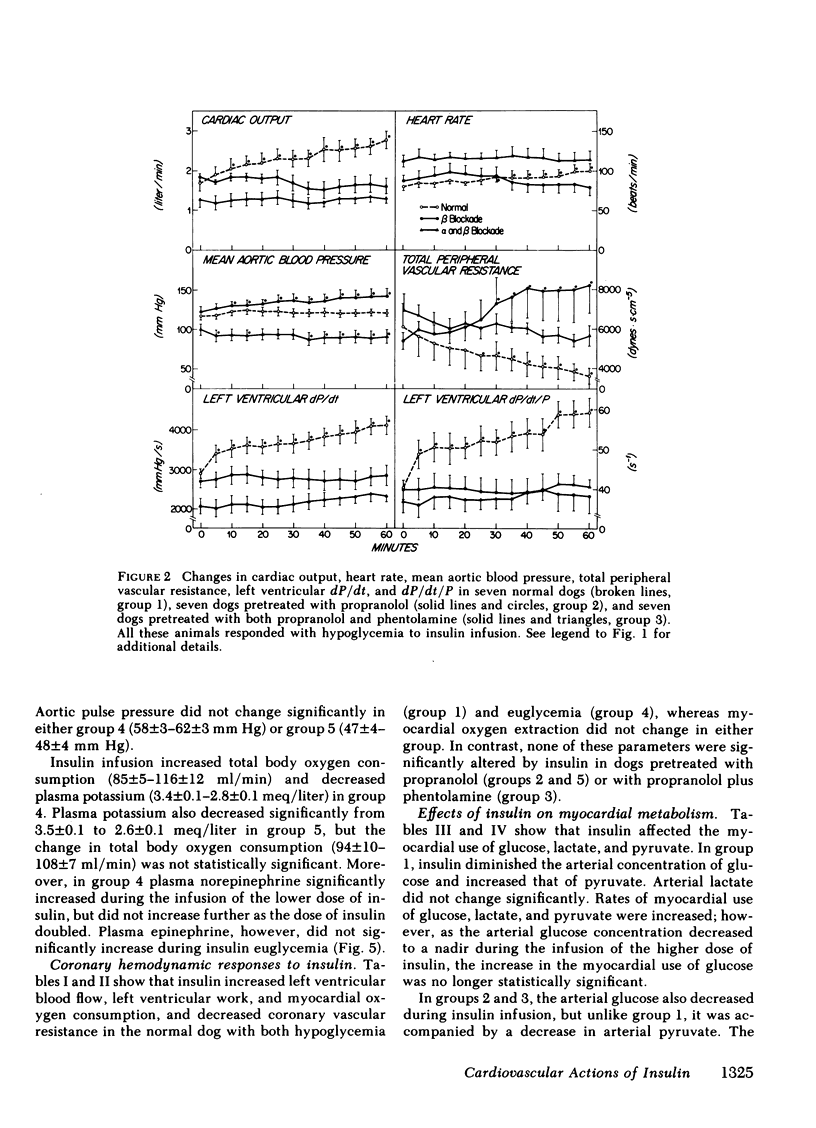
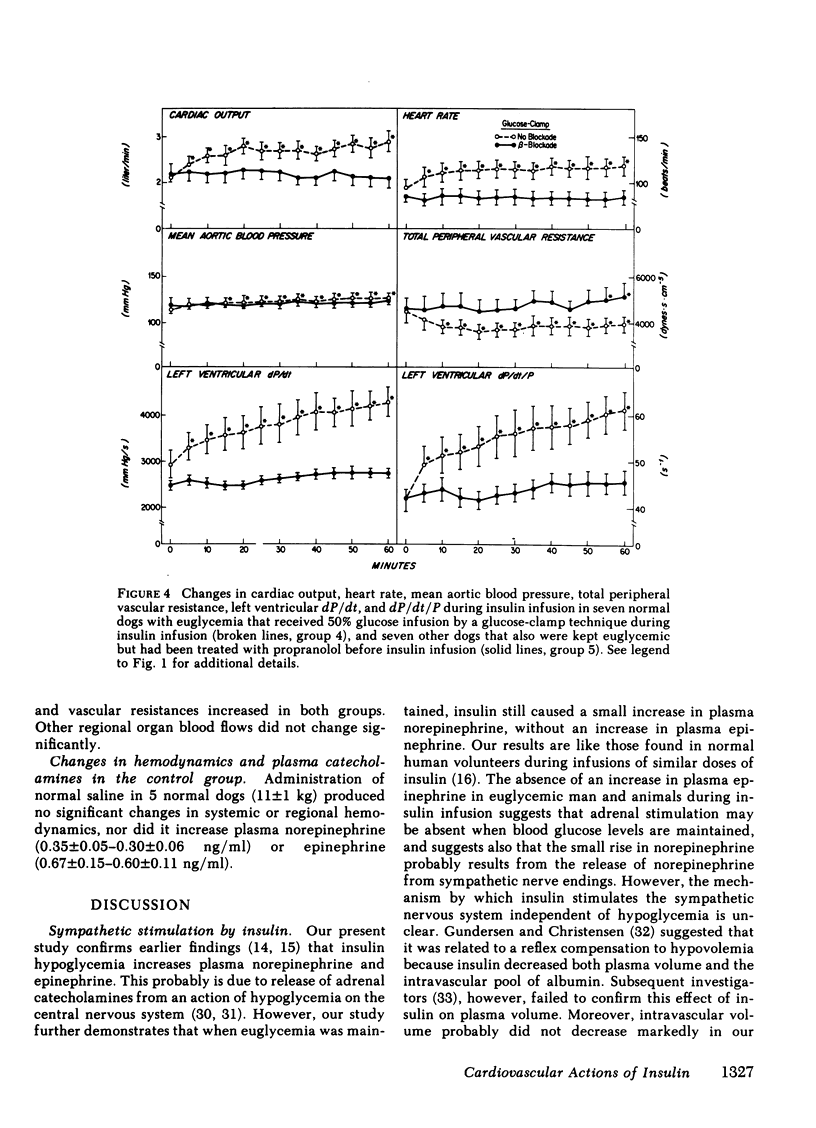
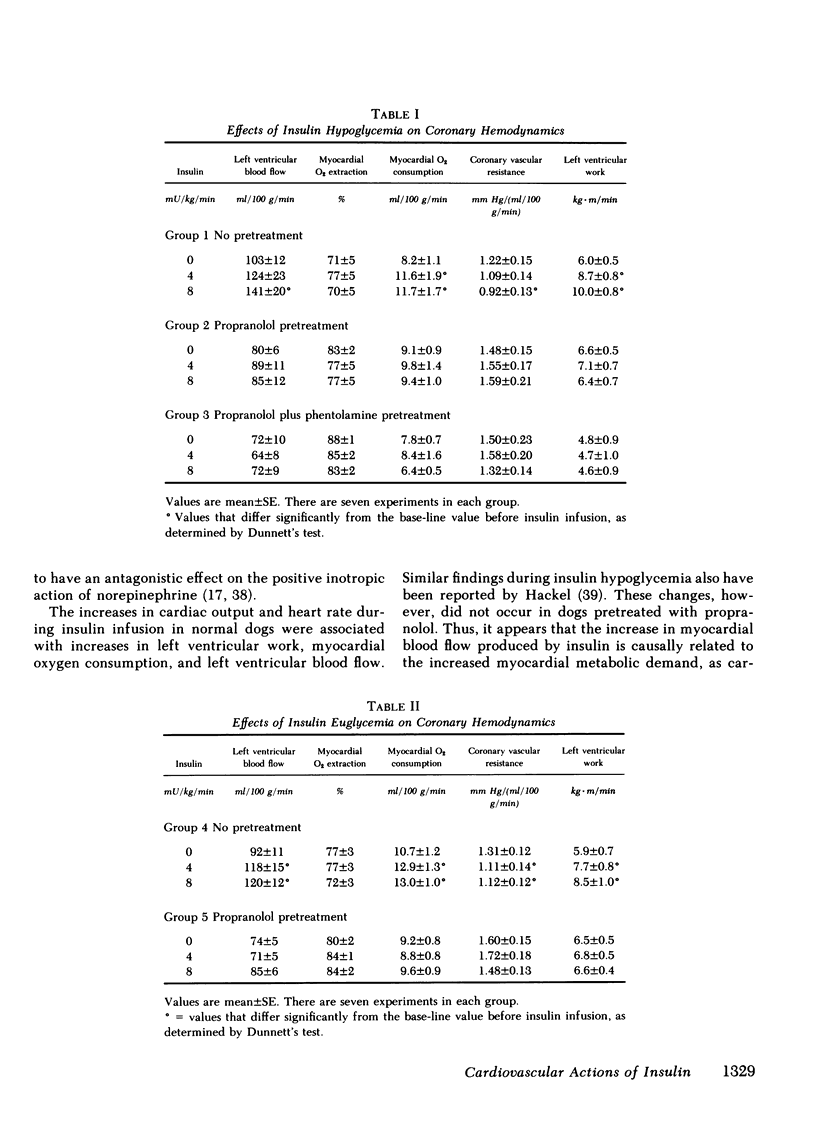
Mean arterial blood pressure did not change significantly during insulin hypoglycemia, but rose if euglycemia was maintained, probably due to the selective increase in norepinephrine in the latter condition. A pressor response also occurred in propranolol-pretreated dogs during insulin hypoglycemia, but was abolished when the animals also had been pretreated with phentolamine, indicating that the vasoconstrictor action of insulin was mediated via alpha adrenergic receptors.
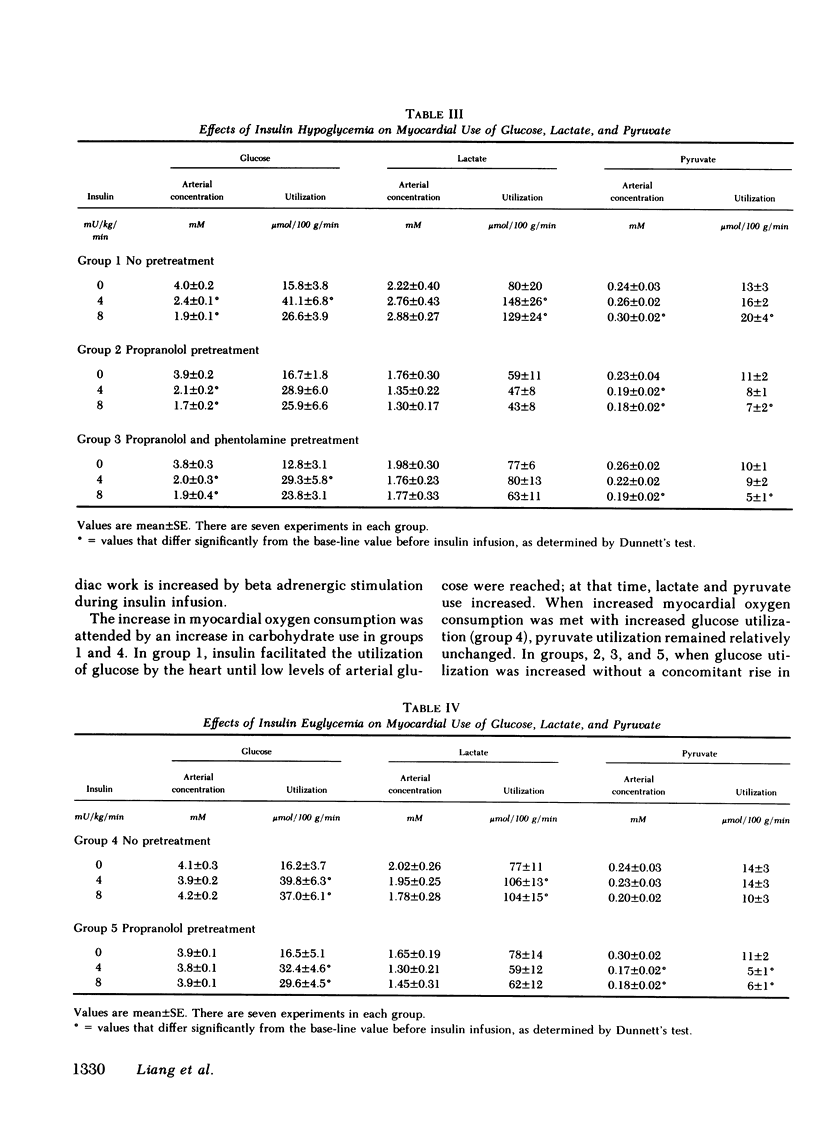
Insulin infusion increased left ventricular work and myocardial blood flow in dogs with and without hypoglycemia. Myocardial blood flow, however, did not change significantly during insulin infusion in dogs pretreated with propranolol. As propranolol also diminished the inotropic response, it appears that the increase in myocardial blood flow caused by insulin in the normal dog is causally related to the increased myocardial metabolic demand.
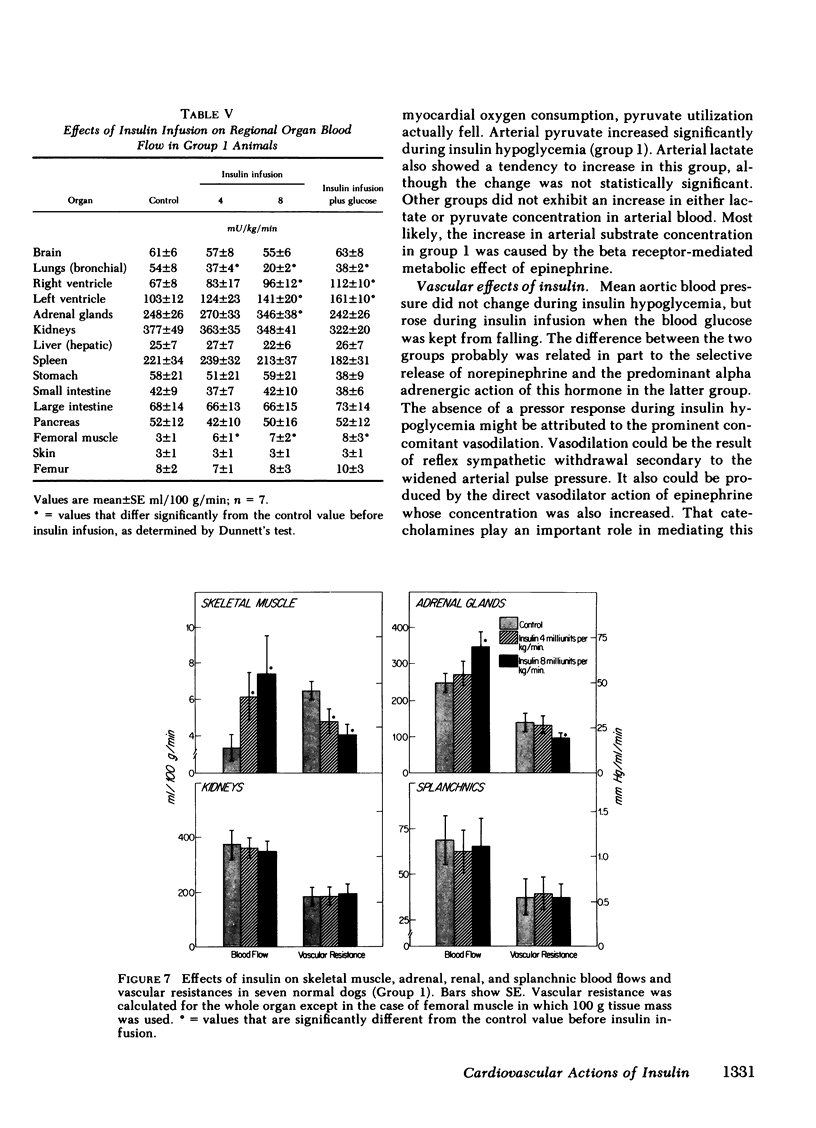
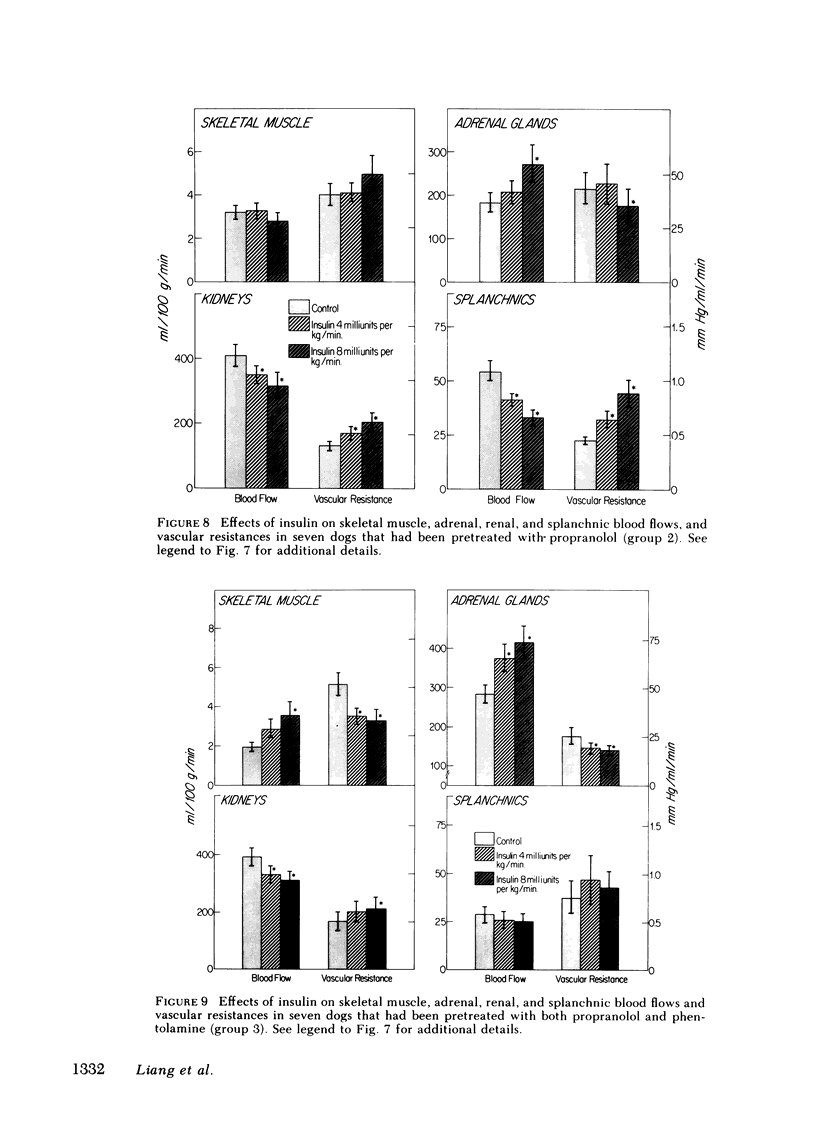
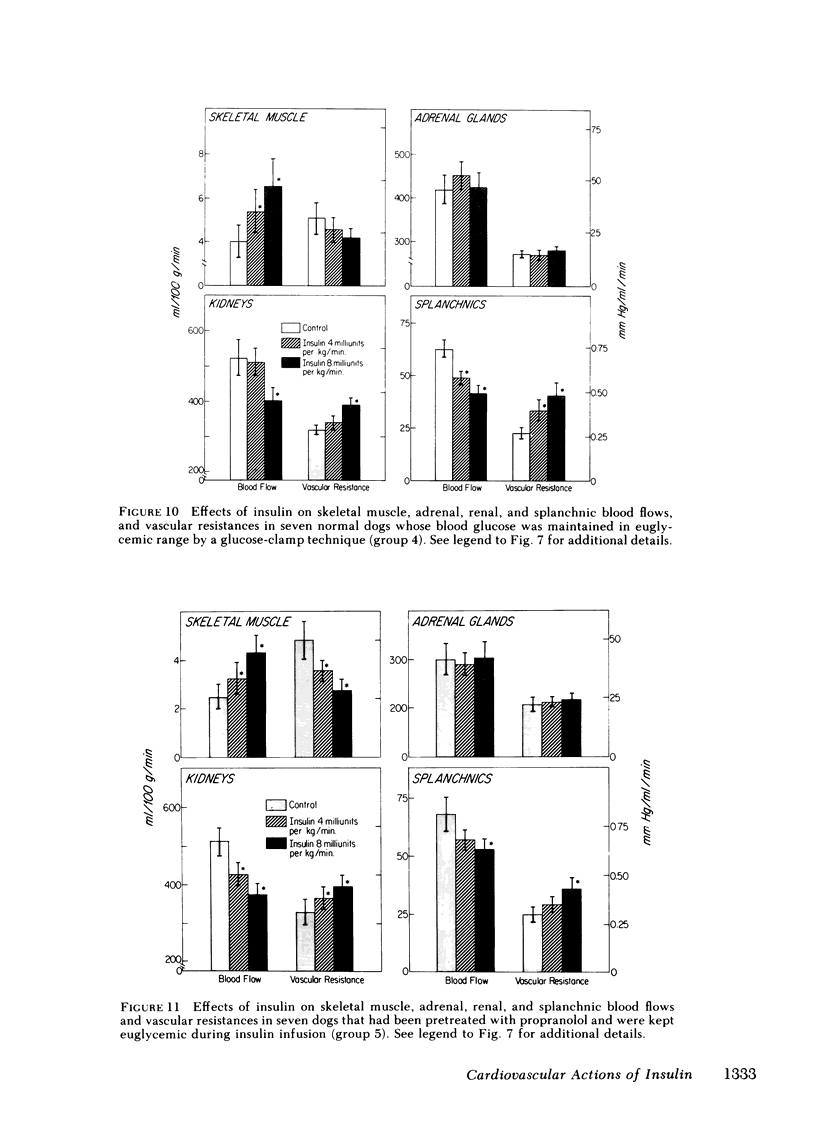
Insulin also produced vasomotor effects on other vascular beds. In skeletal muscle, blood flow was increased under all study conditions, except during insulin hypoglycemia after propranolol-pretreatment when unopposed alpha-mediated vasoconstriction was present. The persistent increase in flow during both alpha and beta adrenergic blockade suggests that insulin has a direct dilator effect on skeletal muscle vasculature. In the adrenal gland, flow was increased except during euglycemia, when no rise in plasma epinephrine was observed, suggesting coupling between adrenal flow and catecholamine release. In the splanchnic bed, flow was decreased during euglycemia, when plasma norepinephrine rose, and during beta adrenergic blockade with propranolol, when unopposed alpha-mediated vasoconstriction also predominated. A similar pattern was found in the kidney, except that renal blood flow also fell after combined alpha and beta adrenergic blockade. The results show that the vasomotor effects on regional flows are mediated both via adrenergic mechanisms, and in the case of skeletal muscle and kidney, via mechanisms unrelated to sympathetic stimulation.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLWOOD M. J., BIRCHALL I., STAFFURTH J. S. Circulatory changes in the forearm during insulin hypoglycaemia studied by regional 24Na clearance and by plethysmography. J Physiol. 1958 Sep 23;143(2):332–342. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLWOOD M. J., GINSBURG J., PATON A. The effect of insulin hypoglycaemia on blood flow in intact and sympathectomized extremities in man. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):97–107. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLWOOD M. J., GINSBURG J. The effect of intra-arterial atropine on blood flow in the hand and forearm during insulin hypoglycaemia. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:486–493. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALLWOOD M. J., HENSEL H., PAPENBERG J. Muscle and skin blood flow in the human forearm during insulin hypoglycaemia. J Physiol. 1959 Sep 2;147:269–273. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARNER B., HEDNER P., KARLEFORS T., WESTLING H. HAEMODYNAMIC CHANGES AND ADRENAL FUNCTION IN MAN DURING INDUCED HYPOGLYCAEMIA. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1963 Nov;44:430–442. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0440430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J., Alberti K. G., Brandsborg O. Plasma catecholamines and blood substrate concentrations: studies in insulin induced hypoglycaemia and after adrenaline infusions. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Sep 12;5(5):415–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Plasma noradrenaline and adrenaline measured by isotope-derivative assay. A review with special reference to diabetes mellitus. Dan Med Bull. 1979 Feb;26(1):17–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISALVO R. J., BLOOM W. L., BRUST A. A., FERGUSON R. W., FERRIS E. B. A comparison of the metabolic and circulatory effects of epinephrine, nor-epinephrine and insulin hypoglycemia with observations on the influence of autonomic blocking agents. J Clin Invest. 1956 May;35(5):568–577. doi: 10.1172/JCI103310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOSEKUN F. O., GRAYSON J., MENDEL D. The measurement of metabolic and vascular responses in liver and muscle with observations on their responses to insulin and glucose. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:581–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOSEKUN F. O. The measurement of metabolic and vascular responses in the human skeletal muscle with observations on its response to insulin and glucose. Clin Sci. 1962 Apr;22:287–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. M., Covell J. W., Malloch C. I., Ross J., Jr Factors influencing indices of left ventricle contractility in the conscious dog. Cardiovasc Res. 1974 May;8(3):299–312. doi: 10.1093/cvr/8.3.299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing S. E., Lee J. C., Rieker R. P. Mechanical and metabolic effects of insulin on newborn lamb myocardium. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1977 Mar 15;127(6):649–656. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(77)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernstene A. C., Altschule M. D. THE EFFECT OF INSULIN HYPOGLYCEMIA ON THE CIRCULATION. J Clin Invest. 1931 Aug;10(3):521–528. doi: 10.1172/JCI100368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRENCH E. B., KILPATRICK R. The role of adrenaline in hypoglycaemic reactions in man. Clin Sci. 1955 Nov;14(4):639–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDLAND I. M., DIETRICH L. S. A rapid enzymic determination of L-lactic acid. Anal Biochem. 1961 Aug;2:390–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(61)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG J., PATON A. Effects of insulin after adrenalectomy. Lancet. 1956 Sep 8;271(6941):491–494. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91973-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFIEN A., MOORE R., ZILELI S., HAVENS L. L., BOLING L., THORN G. W. Plasma epinephrine and norepinephrine levels during insulin-induced hypoglycemia in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1961 Mar;21:296–304. doi: 10.1210/jcem-21-3-296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gundersen H. J., Christensen N. J. Intravenous insulin causing loss of intravascular water and albumin and increased adrenergic nervous activity in diabetics. Diabetes. 1977 Jun;26(6):551–557. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.6.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HACKEL D. B. Effect of insulin on cardiac metabolism of intact normal dogs. Am J Physiol. 1960 Dec;199:1135–1138. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.199.6.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUCKABEE W. E. Control of concentration gradients of pyruvate and lactate across cell membranes in blood. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Sep;9(2):163–170. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himsworth R. L. Hypothalamic control of adrenaline secretion in response to insufficient glucose. J Physiol. 1970 Feb;206(2):411–417. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. C., Downing S. E. Effects of insulin on cardiac muscle contraction and responsiveness to norepinephrine. Am J Physiol. 1976 May;230(5):1360–1365. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.5.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C. S., Hood W. B., Jr Comparison of cardiac output responses to 2,4-dinitrophenol-induced hypermetabolism and muscular work. J Clin Invest. 1973 Sep;52(9):2283–2292. doi: 10.1172/JCI107416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang C. S., Lowenstein J. M. Metabolic control of the circulation. Effects of acetate and pyruvate. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1029–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI109207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi B. R., Medina M., Kniffen F. J. The positive inotropic action of insulin in the canine heart. Eur J Pharmacol. 1972 Apr;18(1):107–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(72)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles D. W., Hayter C. J. The effect of intravenous insulin on the circulatory responses to tilting in normal and diabetic subjects with special reference to baroceptor reflex block and atypical hypoglycaemic reactions. Clin Sci. 1968 Jun;34(3):419–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E., Christensen N. J., Gundersen H. J. The acute effect of insulin on renal haemodynamics and protein excretion in diabetics. Diabetologia. 1978 Sep;15(3):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00421231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niijima A. The effect of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and D-glucose on the efferent discharge rate of sympathetic nerves. J Physiol. 1975 Sep;251(1):231–243. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel D. B., Lee J. C., Downing S. E. Reciprocal inhibition of cardiac responses to norepinephrine and insulin. Am J Physiol. 1977 Dec;233(6):H665–H669. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1977.233.6.H665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka K., Assaykeen T. A., Goldfien A., Ganong W. F. Effect of hypoglycemia on plasma renin activity in dogs. Endocrinology. 1970 Dec;87(6):1306–1317. doi: 10.1210/endo-87-6-1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENHOS J. C., KRAHL M. E. Insulin stimulus of leucine incorporation in rat liver protein. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:249–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. M., Smith R. B., Watkins P. J. Cardiovascular effects of insulin. Br Med J. 1976 Feb 21;1(6007):430–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6007.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. M., Watkins P. J. Provocation of postural hypotension by insulin in diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes. 1976 Feb;25(2):90–95. doi: 10.2337/diab.25.2.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parving H. H., Noer I., Deckert T., Lassen N. A. Intravenous insulin has no effect on transcapillary escape rate of albumin and on plasma volume in short-term juvenile diabetics. Diabetes. 1979 Apr;28(4):282–286. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.4.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peuler J. D., Johnson G. A. Simultaneous single isotope radioenzymatic assay of plasma norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):625–636. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90070-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieker R. P., Lee J. C., Downing S. E. Positive inotropic action of insulin on piglet heart. Yale J Biol Med. 1975 Nov;48(5):353–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Young J. B., Minaker K. L., Stevens A. L., Pallotta J., Landsberg L. Effect of insulin and glucose infusions on sympathetic nervous system activity in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):219–225. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph A. M., Heymann M. A. The circulation of the fetus in utero. Methods for studying distribution of blood flow, cardiac output and organ blood flow. Circ Res. 1967 Aug;21(2):163–184. doi: 10.1161/01.res.21.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Therminarias A., Chirpaz M. F., Lucas A., Tanche M. Calorigenic effect of insulin in hypothermic dogs. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Aug;47(2):342–346. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.47.2.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALLACE J. M., HARLAN W. R. SIGNIFICANCE OF EPINEPHRINE IN INSULIN HYPOGLYCEMIA IN MAN. Am J Med. 1965 Apr;38:531–539. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



