Abstract
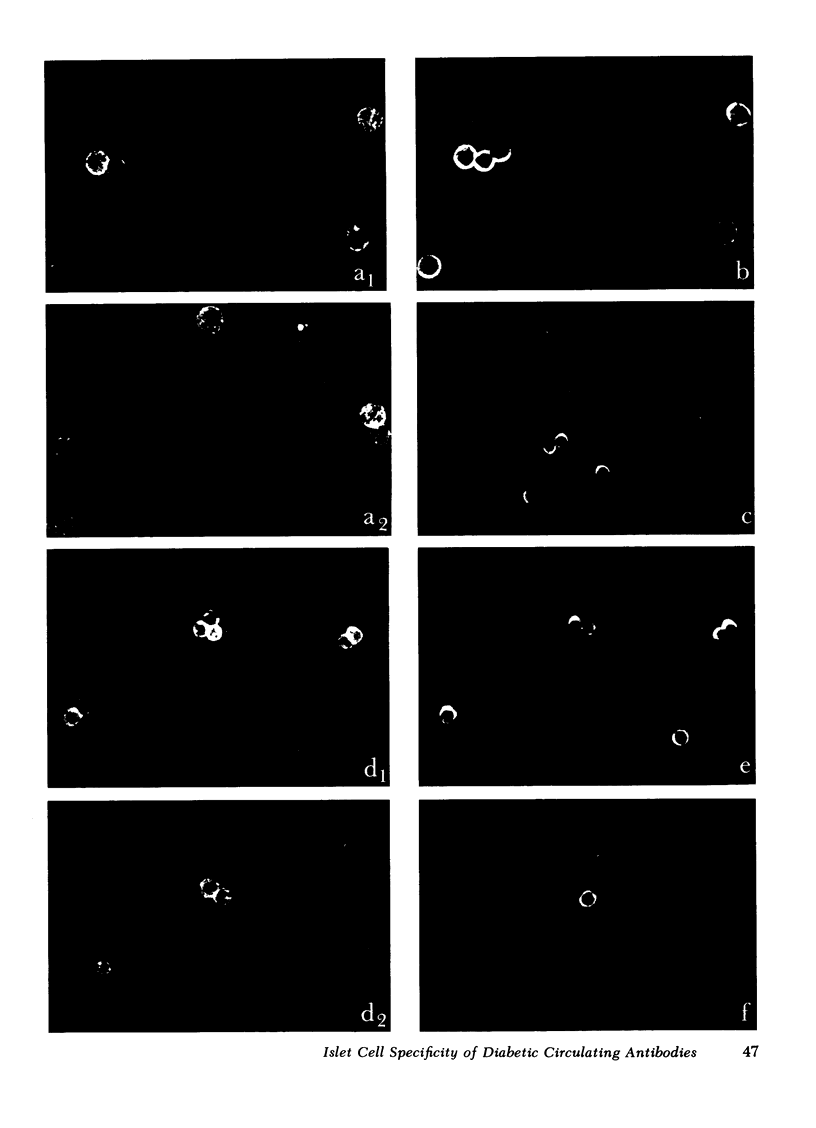
Viable rat islet cells were used to detect islet cell surface antibodies (ICSA) in the sera of diabetic and control patients. ICSA were present in almost all recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetics younger than 30 yr (15/16); their incidence in other diabetics (6/22) was also higher than in normal controls (1/18) or in patients with autoimmune thyroiditis (1/12). The varying specificity of the ICSA for the different islet cell types led to the recognition of class I sera, whose ICSA bind exclusively to B cells, class II sera, binding only to A and pancreatic polypeptide (PP) cells and class III sera, reacting with the three islet cell types but not with D cells. Most recent-onset insulin-dependent diabetics younger than 30 contained class I-ICSA, which is consistent with an autoimmune basis of their disease and with an involvement of surface antibodies in the B cell destruction. The presence of class II ICSA in three older diabetics and in one normal control raises the question whether autoimmune reactions against A and PP cells exist and are associated with a distinct entity in islet disease.
It is concluded that the autoimmune form of diabetes mellitus represents a heterogeneous group, in which ICSA-positive patients can be distinguished on the basis of their ICSA-binding to one or more islet cell types.
Three techniques can be used for the further identification of circulating ICSA, namely binding experiments with purified A or B cells, electron microscopical analysis of ICSA-binding islet cells purified by fluorescence-activated cell sorting, and the immunocytochemical characterization of ICSA-positive cells.
Full text
PDF

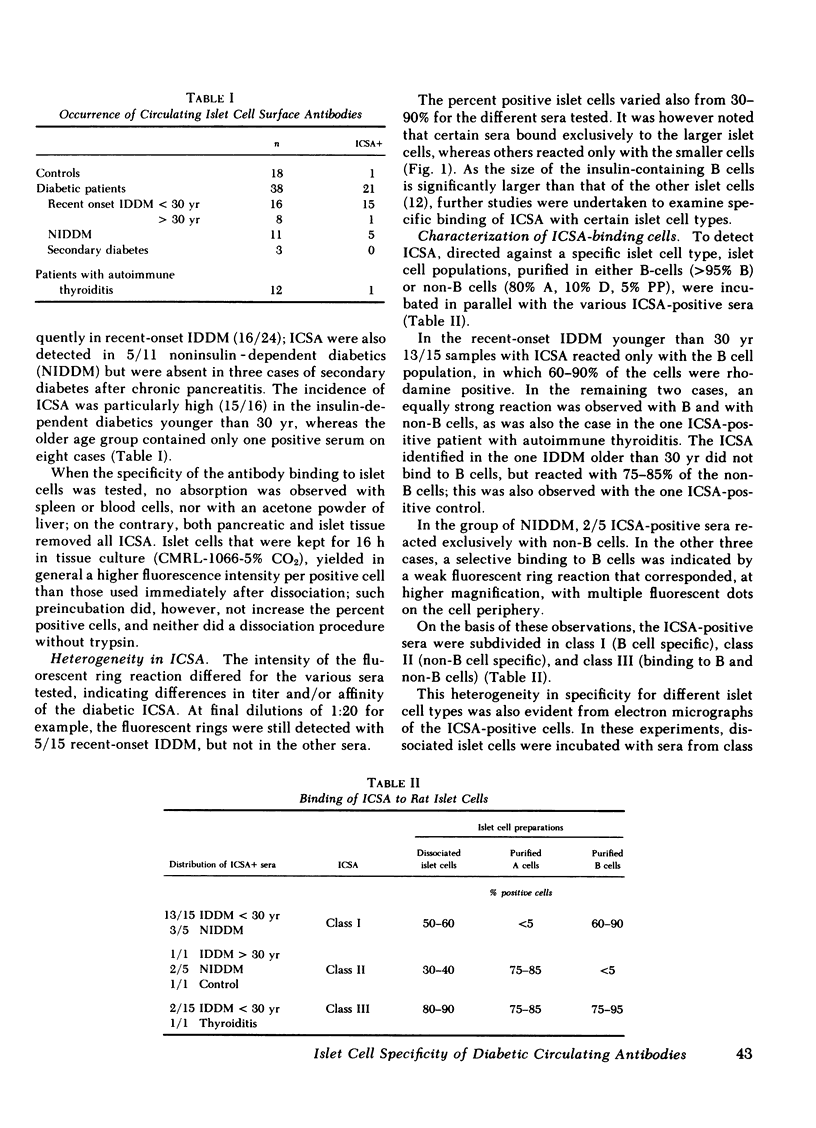

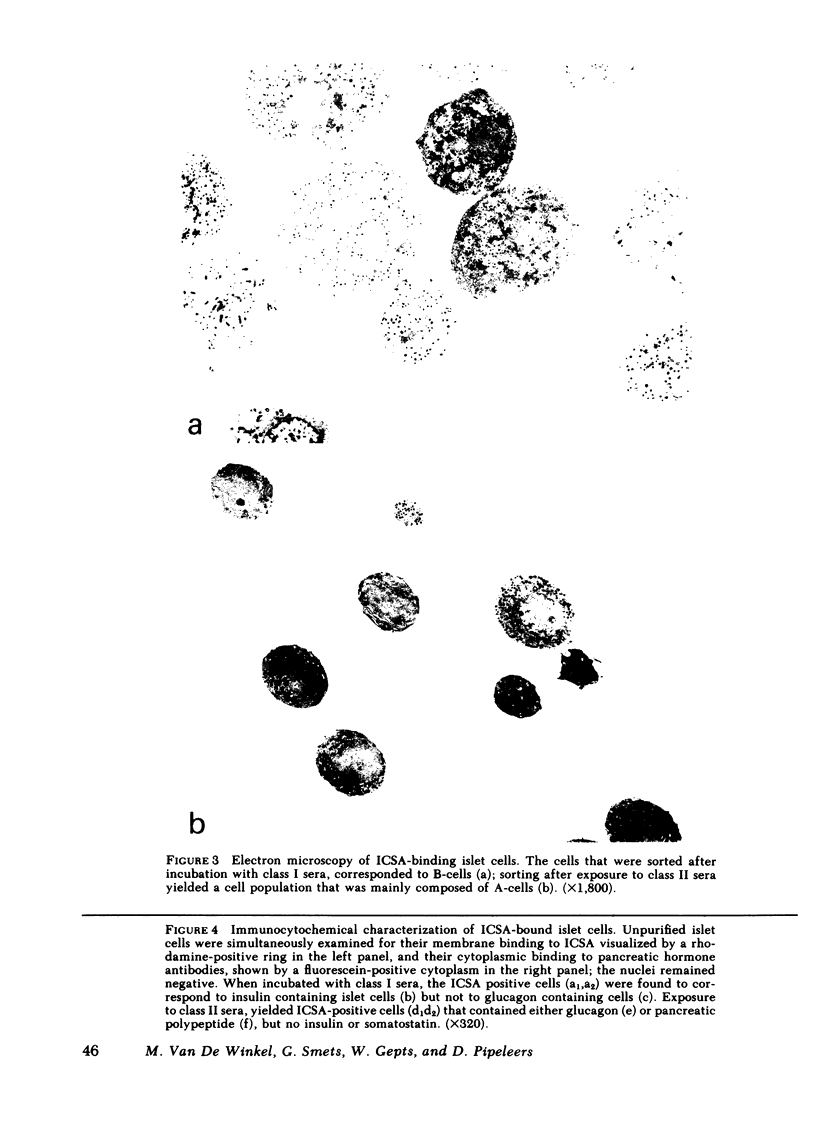


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boitard C., Debray-Sachs M., Pouplard A., Assan R., Hamburger J. Lymphocytes from diabetics suppress insulin release in vitro. Diabetologia. 1981 Jul;21(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF03216222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., Gorsuch A. N., Cudworth A. G., Doniach D. Complement-fixing islet-cell antibodies in type-I diabetes: possible monitors of active beta-cell damage. Lancet. 1980 Mar 29;1(8170):668–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Florin-Christensen A., Doniach D. Islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet. 1974 Nov 30;2(7892):1279–1283. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, McDevitt H. O. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the initial lesion. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 11;304(24):1454–1465. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106113042403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prete G. F., Betterle C., Padovan D., Erle G., Toffolo A., Bersahi G. Incidence and significance of islet-cell autoantibodies in different types of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1977 Oct;26(10):909–915. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.10.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobersen M. J., Scharff J. E., Ginsberg-Fellner F., Notkins A. L. Cytotoxic autoantibodies to beta cells in the serum of patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1980 Dec 25;303(26):1493–1498. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198012253032601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenbarth G. S., Morris M. A., Scearce R. M. Cytotoxic antibodies to cloned rat islet cells in serum of patients with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):403–408. doi: 10.1172/JCI110048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gepts W. Pathologic anatomy of the pancreas in juvenile diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1965 Oct;14(10):619–633. doi: 10.2337/diab.14.10.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Sci Am. 1976 Mar;234(3):108–117. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0376-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine W. J., McCallum C. J., Gray R. S., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Farquhar J. W., Vaughan H., Morris P. J. Pancreatic islet-cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus correlated with the duration and type of diabetes, coexistent autoimmune disease, and HLA type. Diabetes. 1977 Feb;26(2):138–147. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.2.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanatsuna T., Lernmark A., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F. Block in insulin release from column-perifused pancreatic beta-cells induced by islet cell surface antibodies and complement. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):231–234. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Freedman Z. R., Hofmann C., Rubenstein A. H., Steiner D. F., Jackson R. L., Winter R. J., Traisman H. S. Islet-cell-surface antibodies in juvenile diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 24;299(8):375–380. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808242990802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lernmark A., Hägglöf B., Freedman Z., Irvine J., Ludvigsson J., Holmgren G. A prospective analysis of antibodies reacting with pancreatic islet cells in insulin-dependent diabetic children. Diabetologia. 1981 Apr;20(4):471–474. doi: 10.1007/BF00253410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCuish A. C., Jordan J., Campbell C. J., Duncan L. J., Irvine W. J. Cell-mediated immunity to human pancreas in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1974 Aug;23(8):693–697. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.8.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nerup J., Andersen O. O., Bendixen G., Egeberg J., Poulsen J. E. Anti-pancreatic cellular hypersensitivity in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1971 Jun;20(6):424–427. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.6.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A. A method for the purification of single A, B and D cells and for the isolation of coupled cells from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00257436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sensi M., Pozzilli P., Gorsuch A. N., Bottazzo G. F., Cudworth A. G. Increased killer cell activity in insulin dependent (type 1) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1981 Feb;20(2):106–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00262010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]