Abstract
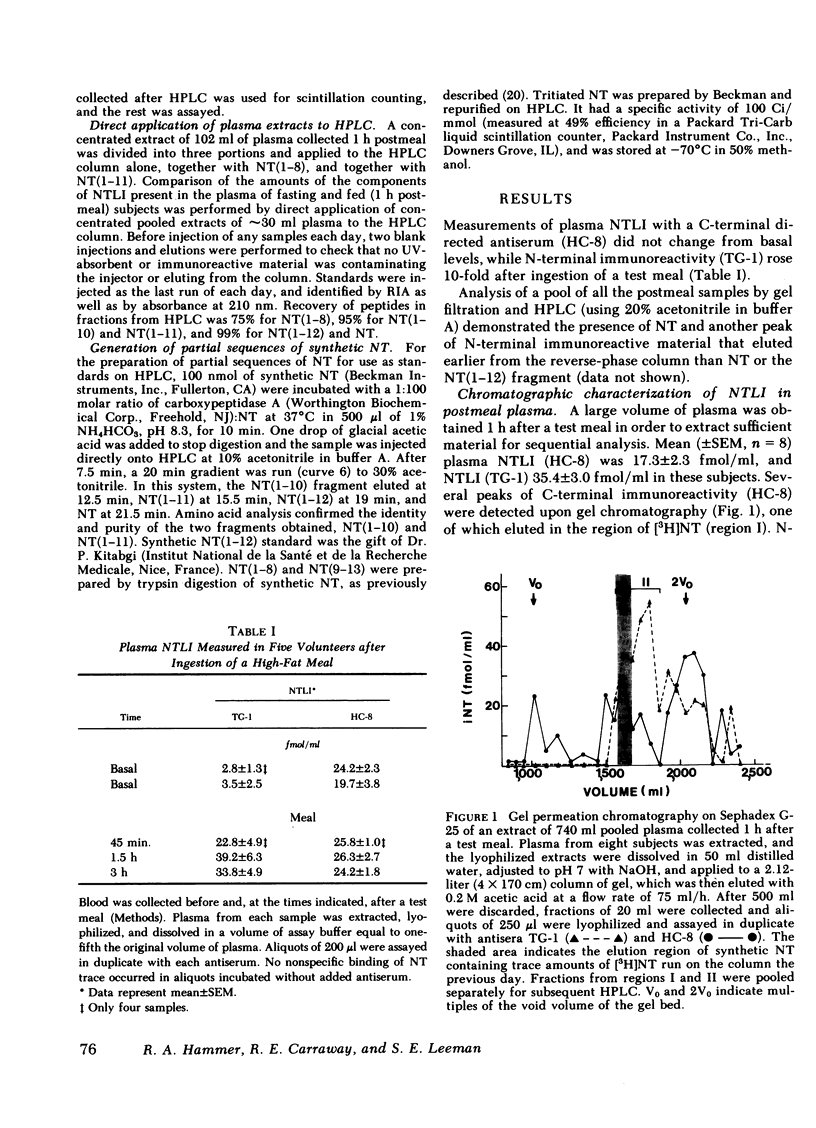
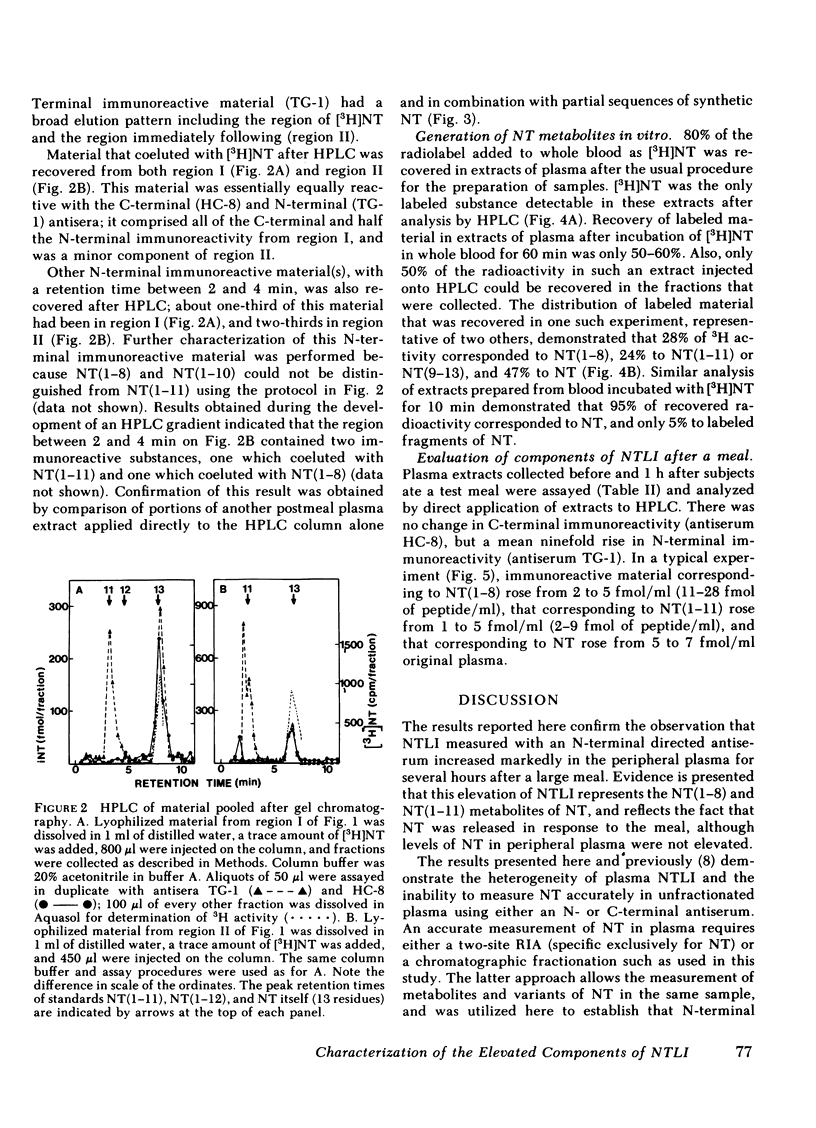
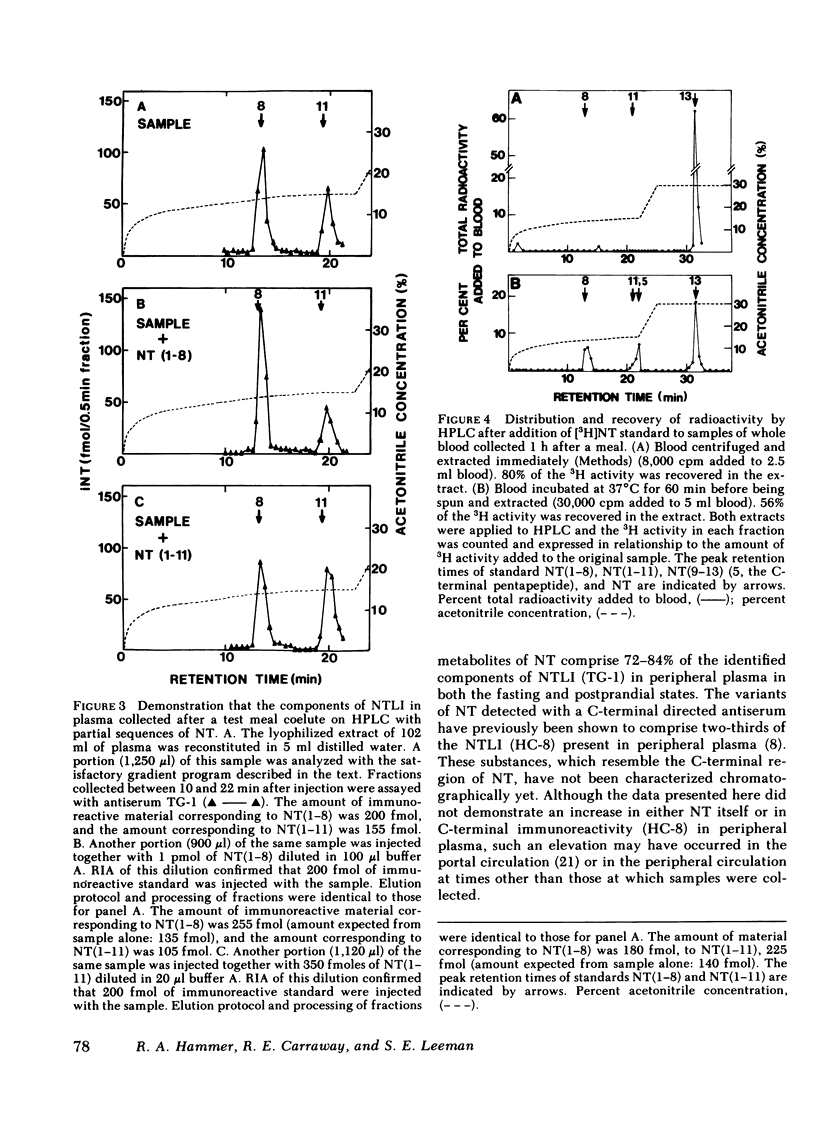
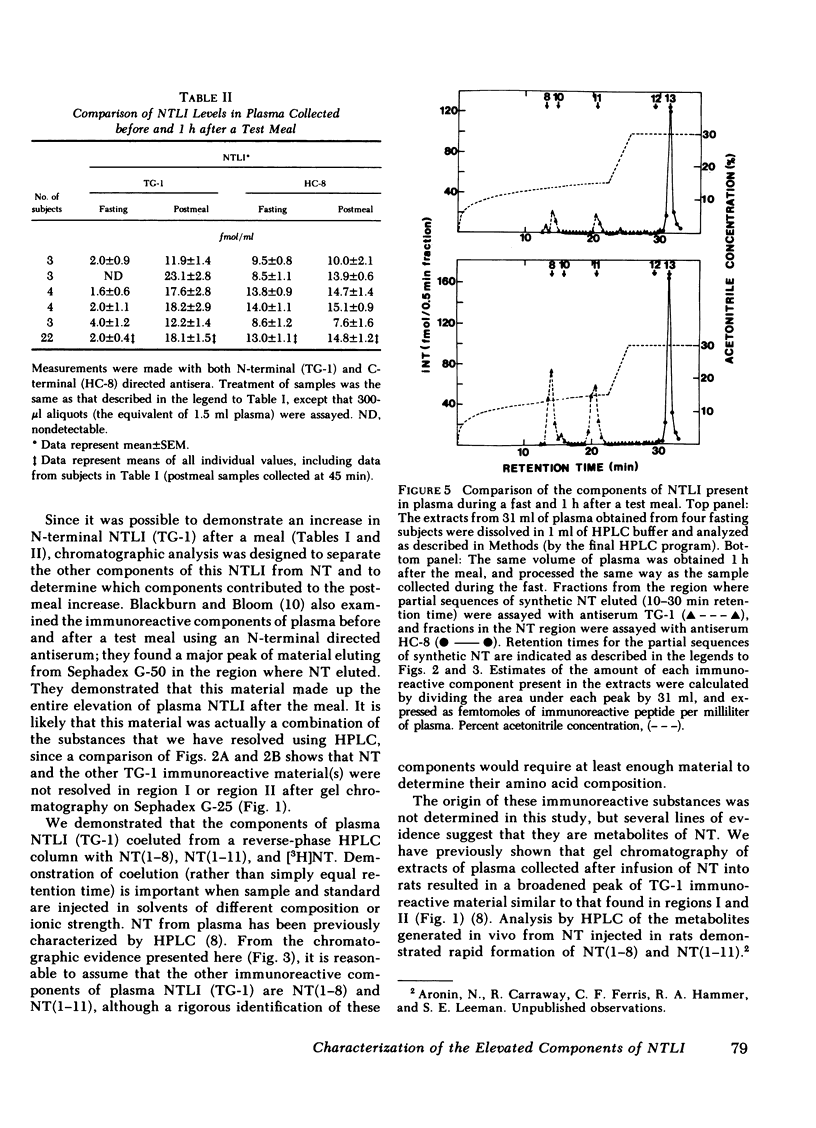
The detection of an elevation in neurotensinlike immunoreactivity in peripheral plasma for several hours after a meal has been confirmed and shown to be primarily due to the presence of aminoterminal fragments of neurotensin (NT) rather than to NT itself. We have developed a procedure to separate and characterize these N-terminal cross-reacting substances, and to estimate the contributions of these constitutents to plasma neurotensinlike immunoreactivity. Gel chromatography of pooled plasma extracts on Sephadex G-25 followed by reverse-phase high pressure liquid chromatography indicated that peptides coeluting with NT and its N-terminal partial sequences NT(1-8) and NT(1-11) were present in plasma. Comparison of plasmas collected before and 1 h after a defined meal, in five experiments, demonstrated no change in C-terminal immunoreactivity and an 8- to 10-fold rise in N-terminal immunoreactivity. Chromatographic analysis of pooled pre- and postmeal plasma in four experiments showed that essentially all of this elevation in neurotensinlike immunoreactivity measured with an N-terminal directed antiserum was due to increases in NT(1-8) and NT(1-11), while NT itself, measured using a C-terminal directed antiserum, did not increase appreciably in peripheral plasma 1 h after the meal. Generation of tritiated substances with the same elution times as NT(1-8) and NT(1-11) did occur after incubation of [3H]NT with whole blood in vitro, providing supporting evidence that these fragments are metabolites of NT. The marked elevation in the circulating levels of these fragments reflects that an increased secretion of NT occurred in response to the test meal. The secreted NT may have acted as a hormone before it was metabolized, or it may only have had a local (paracrine) effect.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn A. M., Bloom S. R. A radioimmunoassay for neurotensin in human plasma. J Endocrinol. 1979 Nov;83(2):175–181. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0830175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E. Neurotensin in plasma: immunochemical and chromatographic character of acid/acetone-soluble material. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):400–406. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Radioimmunoassay for neurotensin, a hypothalamic peptide. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7035–7044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1907–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. F., Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E. Elevation of plasma neurotensin during lipid perfusion of rat small intestine. Peptides. 1981;2 (Suppl 2):263–266. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(81)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R. A., Leeman S. E., Carraway R., Williams R. H. Isolation of human intestinal neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2476–2480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmstaedter V., Taugner C., Feurle G. E., Forssmann W. G. Localization of neurotensin-immunoreactive cells in the small intestine of man and various mammals. Histochemistry. 1977 Jul 18;53(1):35–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00511208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Isolation of a tridecapeptide from bovine intestinal tissue and its partial characterization as neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7053–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Van Rietschoten J., Granier C., Morgat J. L., Menez A., Leeman S., Freychet P. Neurotensin: specific binding to synaptic membranes from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1846–1850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Poustis C., Granier C., Van Rietschoten J., Rivier J., Morgat J. L., Freychet P. Neurotensin binding to extraneural and neural receptors: comparison with biological activity and structure--activity relationships. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Jul;18(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashford M. L., Nilsson G., Rökaeus A., Rosell S. Release of neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) from the gut in anaesthetized dogs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Nov;104(3):375–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06291.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashford M. L., Nilsson G., Rökaeus A., Rosell S. The effect of food ingestion on circulating neurotensin-like immunoreactivity (NTLI) in the human. Acta Physiol Scand. 1978 Oct;104(2):244–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1978.tb06275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens O., Rufener C., Brown M., Vale W., Guillemin R. Evidence for immunoreactive neurotensin in dog intestinal mucosa. Life Sci. 1976 Aug 15;19(4):559–561. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rioux F., Quirion R., Regoli D., Leblanc M. A., St-Pierre S. Pharmacological characterization of neurotensin receptors in the rat isolated portal vein using analogues and fragments of neurotensin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Sep 5;66(4):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler F., Håkanson R., Hammer R. A., Alumets J., Carraway R., Leeman S. E., Zimmerman E. A. Immunohistochemical localization of neurotensin in endocrine cells of the gut. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Mar 16;178(3):313–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00218696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



