Abstract
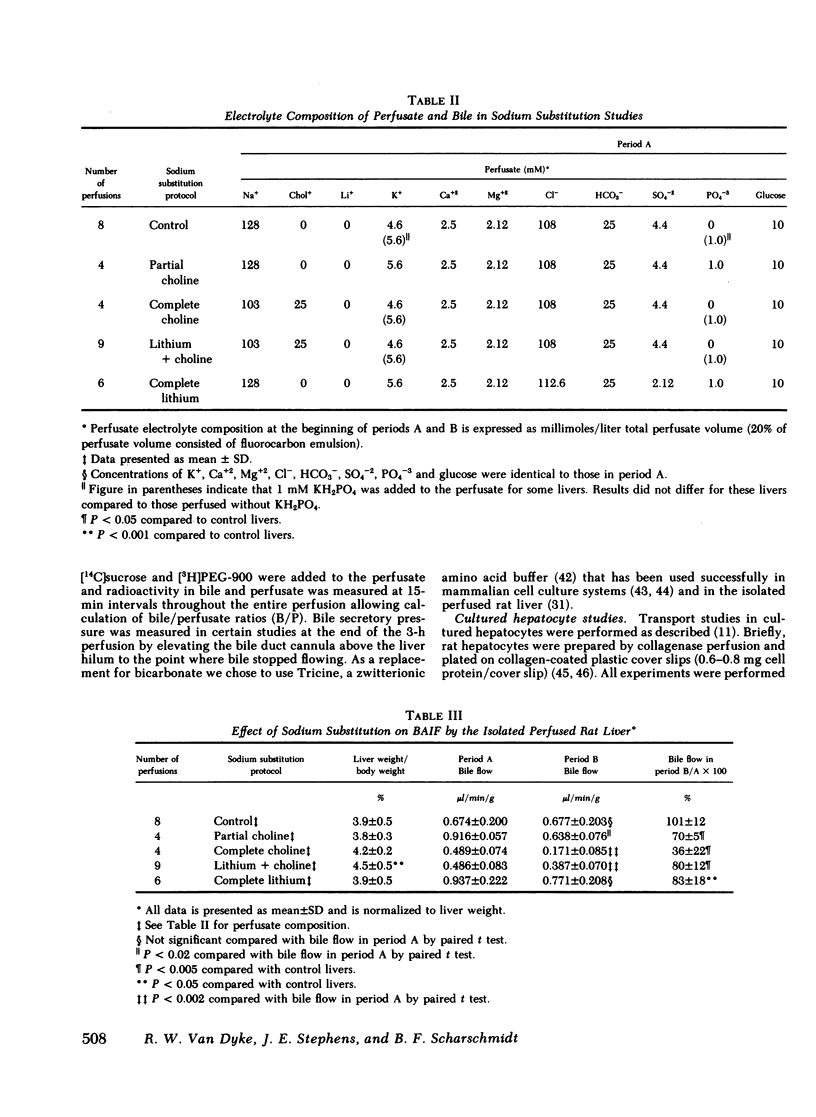
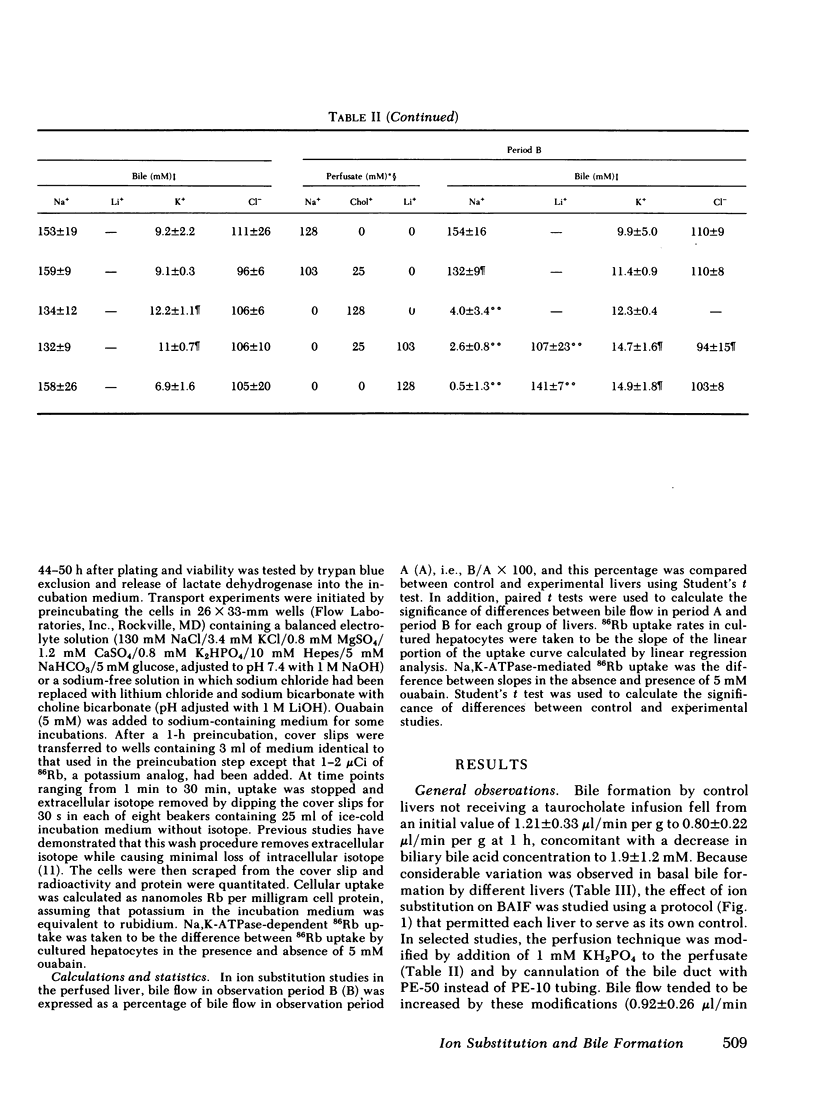
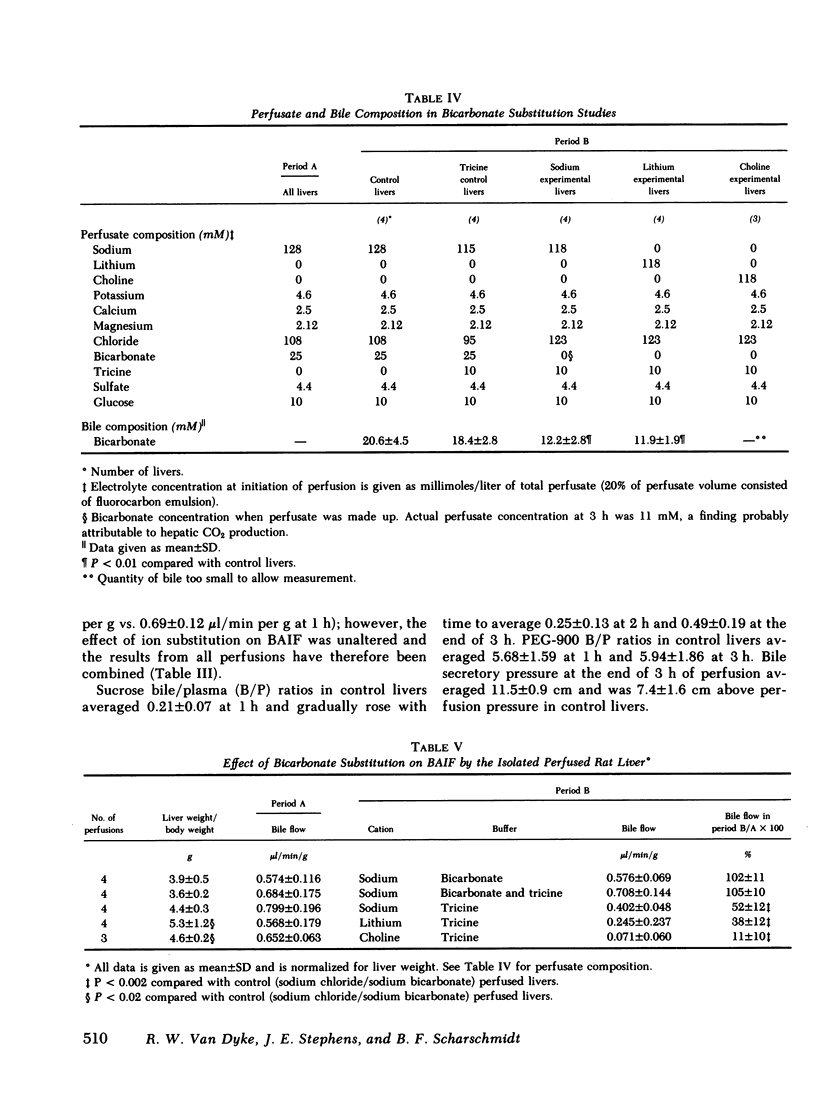
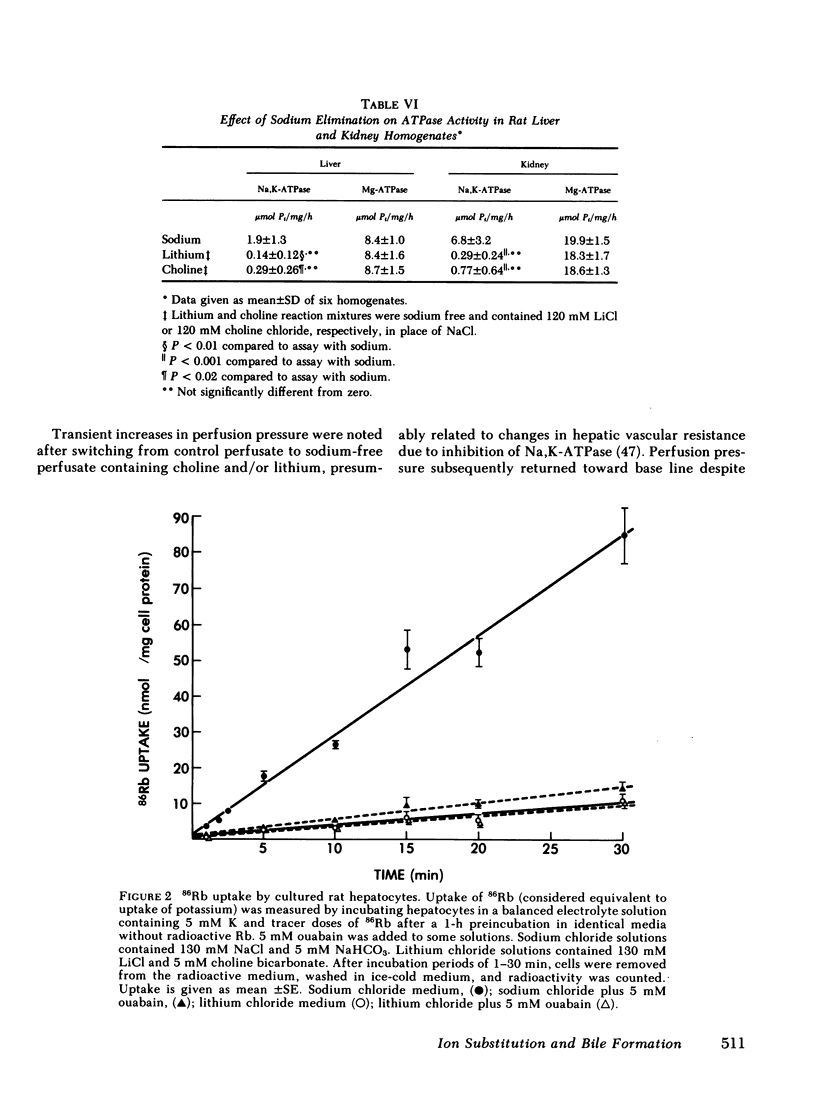
To characterize the transport mechanisms responsible for formation of canalicular bile, we have examined the effects of ion substitution on bile acid-dependent and bile acid-independent bile formation by the isolated perfused rat liver. Complete replacement of perfusate sodium with choline and lithium abolished taurocholate-induced choleresis and reduced biliary taurocholate output by greater than 70%. Partial replacement of perfusate sodium (25 of 128 mM) by choline reduced bile acid-independent bile formation by 30% and replacement of the remaining sodium (103 mM) by choline reduced bile acid-independent bile formation by an additional 64%. In contrast, replacement of the remaining sodium (103 mM) by lithium reduced bile acid-independent bile formation by only an additional 20%, while complete replacement of sodium (128 mM) by lithium reduced bile formation by only 17%, and lithium replaced sodium as the predominant biliary cation. Replacement of perfusate bicarbonate by Tricine, a zwitterionic amino acid buffer, decreased bile acid-independent bile formation by greater than or equal to 50% and decreased biliary bicarbonate output by approximately 60%, regardless of the accompanying cation. In separate experiments, replacement of sodium by lithium essentially abolished Na,K-ATPase activity measured either as ouabain-suppressible ATP hydrolysis in rat liver or kidney homogenates, or as ouabain-suppressible 86Rb uptake by cultured rat hepatocytes. These studies indicate that bile acid(taurocholate)-dependent bile formation by rat liver exhibits a specific requirement for sodium, a finding probably attributable to the role(s) of sodium in hepatic sodium-coupled taurocholate uptake and/or in maintenance of Na,K-ATPase activity. The surprising finding that bile acid-independent bile formation was substantially unaltered by complete replacement of sodium with the permeant cation lithium does not appear to be explained by Na,K-ATPase-mediated lithium transport. Although alternative interpretations exist, this observation is consistent with the hypothesis that much of basal bile acid-independent bile formation is attributable to an ion pump other than Na,K-ATPase, which directly or indirectly mediates bicarbonate transport.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akera T., Yamamoto S., Temma K., Kim D. H., Brody T. M. Is ouabain-sensitive rubidium or potassium uptake a measure of sodium pump activity in isolated cardiac muscle? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 6;640(3):779–790. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwer M. S., Hegner D. Effect of Na on bile acid uptake by isolated rat hepatocytes. Evidence for a heterogeneous system. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 Feb;359(2):181–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson P. S. Identifying secondary active solute transport in epithelia. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jan;240(1):F1–11. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.240.1.F1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner D. L., Lee R. G., Berenson M. M. Protoporphyrin-induced cholestasis in the isolated in situ perfused rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):385–394. doi: 10.1172/JCI110046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUER R. W., LEONG G. F., HOLLOWAY R. J. Mechanics of bile secretion; effect of perfusion pressure and temperature on bile flow and bile secretion pressure. Am J Physiol. 1954 Apr;177(1):103–112. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.177.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUER R. W., PESSOTTI R. L. The effect of choleretic and of hydrocholeretic agents on bile flow and bile solids in the isolated perfused liver. Science. 1952 Feb 8;115(2980):142–143. doi: 10.1126/science.115.2980.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakkeren J. A., Bonting S. L. Studies on (Na+-K+)-activated ATPase. XXI. Changes in (Na+-K+)-activated ATPase activity and ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake rate in regenerating rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):467–472. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balabaud C., Kron K. A., Gumucio J. J. The assessment of the bile salt-nondependent fraction of canalicular bile water in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Feb;89(2):393–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. Activation by lithium ions of the inside sodium sites in (Na+ + K+)-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 8;527(2):472–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90361-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bichara M., Paillard M., Leviel F., Gardin J. P. Hydrogen transport in rabbit kidney proximal tubules--Na:H exchange. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F445–F451. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M., Hammaker L. E., Meyer U. A. Parenchymal cells from adult rat liver in nonproliferating monolayer culture. I. Functional studies. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):722–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissell D. M. Study of hepatocyte function in cell culture. Prog Liver Dis. 1976;5:69–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitzer B. L., Boyer J. L. Cytochemical localization of Na+, K+-ATPase in the rat hepatocyte. J Clin Invest. 1978 Nov;62(5):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI109216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. Canalicular bile formation in the isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1156–1163. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Klatskin G. Canalicular bile flow and bile secretory pressure. Evidence for a non-bile salt dependent fraction in the isolated perfused rat liver. Gastroenterology. 1970 Dec;59(6):853–859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. New concepts of mechanisms of hepatocyte bile formation. Physiol Rev. 1980 Apr;60(2):303–326. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.2.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Reno D. Properties of (Na+ plus K+)-activated ATPase in rat liver plasma membranes enriched with bile canaliculi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L., Scheig R. L., Klatskin G. The effect of sodium taurocholate on the hepatic metabolism of sulfobromophthalein sodium (BSP). The role of bile flow. J Clin Invest. 1970 Feb;49(2):206–215. doi: 10.1172/JCI106229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. E., Herz R. Permselectivity of biliary canalicular membrane in rats: clearance probe analysis. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):E570–E576. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.5.E570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Kern F., Jr, Showalter R., Sutherland E., Sinensky M., Simon F. R. Alterations of hepatic Na+,K+-atpase and bile flow by estrogen: effects on liver surface membrane lipid structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4130–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietmaier A., Gasser R., Graf J., Peterlik M. Investigations on the sodium dependence of bile acid fluxes in the isolated perfused rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Aug 4;443(1):81–91. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon T. E., Al-Awqati Q. Urinary acidification in turtle bladder is due to a reversible proton-translocating ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3135–3138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunham P. B., Senyk O. Lithium efflux through the Na/K pump in human erythrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H. Buffer combinations for mammalian cell culture. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S., Dhumeaux D., Benhamou J. P. Effect on bile formation of inhibitors of sodium transport. Nature. 1969 Sep 20;223(5212):1276–1277. doi: 10.1038/2231276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Hepatocyte bile secretion: current views and controversies. Hepatology. 1981 Jul-Aug;1(4):352–359. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. B., Racker E. Determinants of glycolytic rate in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):749–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L. The effect of estrogen on bile formation in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1969 Apr;48(4):654–663. doi: 10.1172/JCI106023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Fillingame R. H. Energy-transducing H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli. Purification, reconstitution, and subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8230–8236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner R. S. The use of tricine buffer in animal tissue cultures. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):320–321. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. R., Wolk S. W., Rutlen D. L., Powell W. J., Jr Effect of ouabain on total vascular capacity in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jan;69(1):175–184. doi: 10.1172/JCI110429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollan J., Hammaker L., Licko V., Schmid R. Bilirubin kinetics in intact rats and isolated perfused liver. Evidence for hepatic deconjugation of bilirubin glucuronides. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):1003–1015. doi: 10.1172/JCI110111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good N. E., Winget G. D., Winter W., Connolly T. N., Izawa S., Singh R. M. Hydrogen ion buffers for biological research. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):467–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Parrilla R., Toews C. J. Influence of fluorocarbon emulsions on hepatic metabolism in perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1973 Dec;225(6):1384–1388. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1973.225.6.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Peterlik M. Ouabain-mediated sodium uptake and bile formation by isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Apr;230(4):876–885. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.4.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton L. J., Kaplan J. G. Flux of 86Rb in activated human lymphocytes. Can J Biochem. 1977 Jul;55(7):774–778. doi: 10.1139/o77-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Berry M. N., Williams M. C., Severinghaus E. M. A simple and inexpensive membrane "lung" for small organ perfusion. J Lipid Res. 1974 Mar;15(2):182–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks J. B., Meyers W. C., Wellman C. L., Hill R. C., Jones R. S. The effect of cell-free and erythrocyte-containing perfusion in rat livers. J Surg Res. 1980 Aug;29(2):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(80)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison W. G., Wood C. A. Importance of bicarbonate in bile salt independent fraction of bile flow. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E158–E164. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihlenfeldt M. J. Stimulation of Rb+ transport by glucagon in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2213–2218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt N. B. Hepatic bile formation. (Second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1511–1516. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakis G., Yousef I. M. Pathogenesis of lithocholate- and taurolithocholate-induced intrahepatic cholestasis in rats. Gastroenterology. 1978 Oct;75(4):595–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefee E. B., Scharschmidt B. F., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Studies of relationship among bile flow, liver plasma membrane NaK-ATPase, and membrane microviscosity in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1590–1598. doi: 10.1172/JCI109620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinsella J. L., Aronson P. S. Properties of the Na+-H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jun;238(6):F461–F469. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1980.238.6.F461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knodell R. G. Alterations in bile flow and Na+K+ biliary excretion induced by theophylline and ethacrynic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1978 Feb;157(2):306–311. doi: 10.3181/00379727-157-40043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krone W., Huttner W. B., Kampf S. C., Rittich B., Seitz H. J., Tarnowski W. Long-term perfusion of the isolated rat liver: maintenance of its functional state by use of a fluorocarbon emulsion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Nov 4;372(1):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90073-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushlan M. C., Gollan J. L., Ma W. L., Ockner R. K. Sex differences in hepatic uptake of long chain fatty acids in single-pass perfused rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1981 Mar;22(3):431–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVE W. D., BURCH G. E. A comparison of potassium 42, rubidium 86, and cesium 134 as tracers of potassium in the study of cation metabolism of human erythrocytes in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1953 Mar;41(3):351–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latham P. S., Kashgarian M. The ultrastructural localization of transport ATPase in the rat liver at non-bile canalicular plasma membranes. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):988–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Boyer J. L. The effect of thyroid hormone on bile salt-independent bile flow and Na+, K+ -ATPase activity in liver plasma membranes enriched in bile canaliculi. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI108342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Elias E., Boyer J. L. Bile formation in the rat: the role of the paracellular shunt pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1375–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI109258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE E. W., DIETSCHY J. M. NA AND K ACTIVITY COEFFICIENTS IN BILE AND BILE SALTS DETERMINED BY GLASS ELECTRODES. Am J Physiol. 1964 May;206:1111–1117. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.5.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizels M. Effect of sodium content on sodium efflux from human red cells suspended in sodium-free media containing potassium, rubidium, caesium or lithium chloride. J Physiol. 1968 Apr;195(3):657–679. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate absorption by rabbit cortical collecting tubules in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1978 Feb;234(2):F141–F145. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1978.234.2.F141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner P. B., Jr, Sutherland E., Simon F. R. Regulation of hepatic sodium plus potassium-activated adenossine triphosphatase activity by glucocorticoids in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1980 Aug;79(2):212–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel W. Influence of lithium upon the intracellular potential of frog skin epithelium. J Membr Biol. 1977 Dec 15;37(3-4):347–359. doi: 10.1007/BF01940939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recktenwald E., Hess B. Allosteric influence of anions on mitochondrial ATPase of yeast. FEBS Lett. 1977 Apr 1;76(1):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80113-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Relationship between bile flow and Na+, K+-adenosinetriphosphatase in liver plasma membranes enriched in bile canaliculi. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):429–434. doi: 10.1172/JCI108792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Uptake of bile acids by perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):734–742. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodland K. D., Dunham P. B. Kinetics of lithium efflux through the (Na,K)-pump of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 4;602(2):376–388. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros E., Small D. M., Carey M. C. Effects of chlorpromazine hydrochloride on bile salt synthesis, bile formation and biliary lipid secretion in the rhesus monkey: a model for chlorpromazine-induced cholestasis. Eur J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;9(1):29–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1979.tb01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANKER L. S., HOGBEN C. A. Biliary excretion of inulin, sucrose, and mannitol: analysis of bile formation. Am J Physiol. 1961 May;200:1087–1090. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.5.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Keeffe E. B., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Validation of a recording spectrophotometric method for measurement of membrane-associated Mg- and NaK-ATPase activity. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 May;93(5):790–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Keeffe E. B. Isolation of a rat liver plasma membrane fraction of probable canalicular origin. Preparative technique, enzymatic profile, composition, and solute transport. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 7;646(3):369–381. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90305-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharschmidt B. F., Stephens J. E. Transport of sodium, chloride, and taurocholate by cultured rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):986–990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G. Sodium-coupled solute transport of small intestine: a status report. Am J Physiol. 1977 Oct;233(4):E249–E254. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1977.233.4.E249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz L. R., Barth C. A. Taurocholate uptake by adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Aug;360(8):1117–1120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz L. R., Burr R., Schwenk M., Pfaff E., Greim H. Uptake of taurocholic acid into isolated rat-liver cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 15;55(3):617–623. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw H., Caple I., Heath T. Effect of ethacrynic acid on bile formation in sheep, dogs, rats, guinea pigs and rabbits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1972 Jul;182(1):27–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon F. R., Sutherland E., Accatino L. Stimulation of hepatic sodium and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity by phenobarbital. Its possible role in regulation of bile flow. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):849–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavoloni N., Reed J. S., Boyer J. L. Hemodynamic effects on determinants of bile secretion in isolated rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E584–E592. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannagat R. J., Adler R. D., Ockner R. K. Bile acid-induced increase in bile acid-independent flow and plasma membrane NaK-ATPase activity in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):297–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., Ramos O. L. DETERMINANTS OF THE FLOW AND COMPOSITION OF BILE IN THE UNANESTHETIZED DOG DURING CONSTANT INFUSIONS OF SODIUM TAUROCHOLATE. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):161–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI104015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



