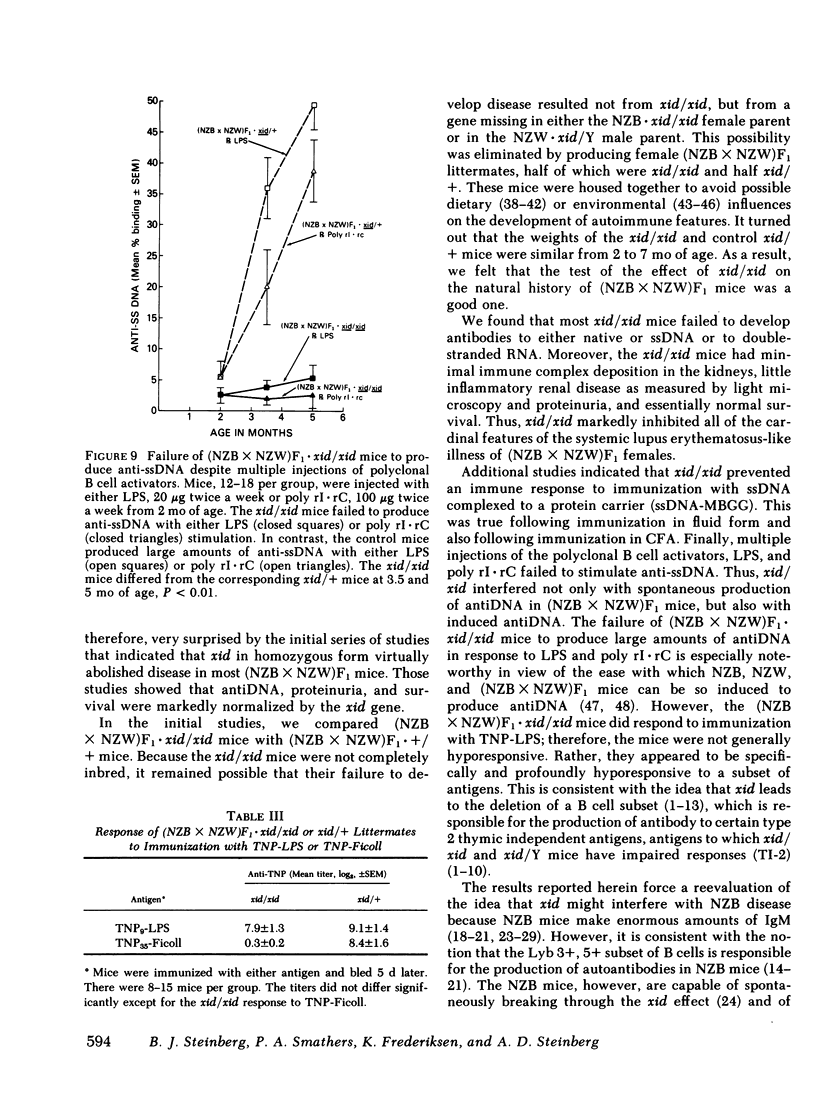
Abstract
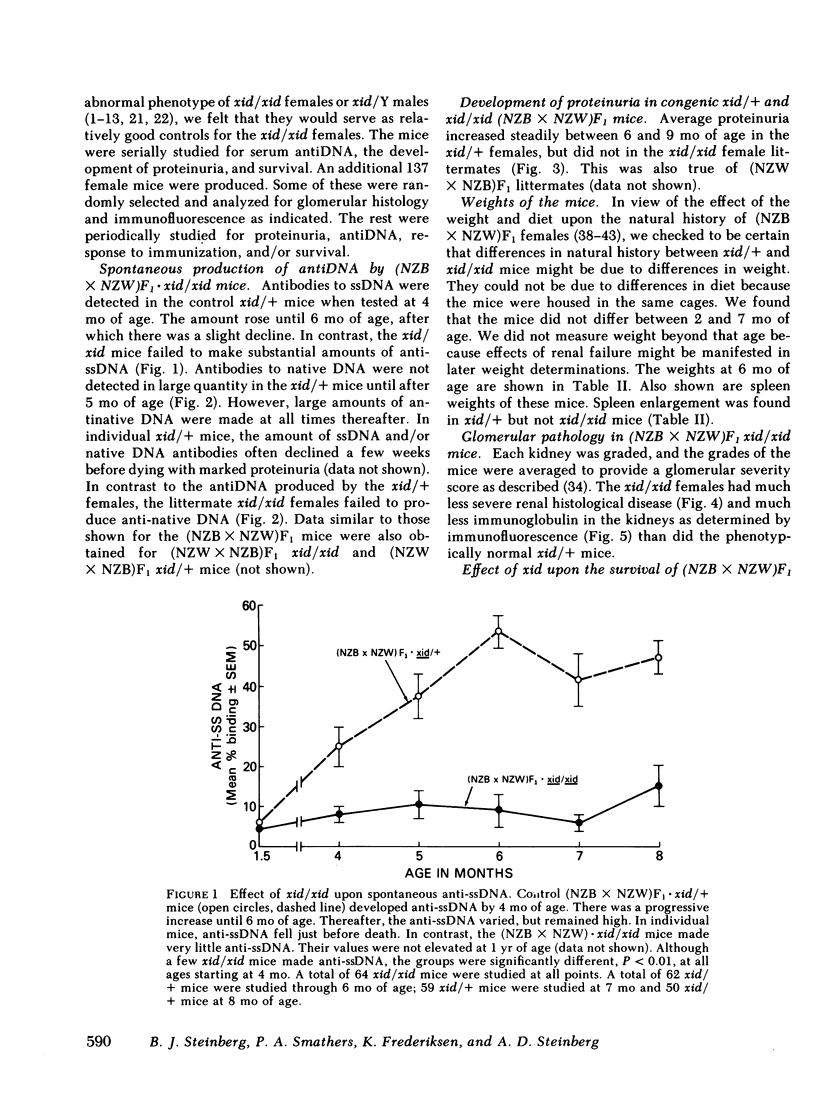
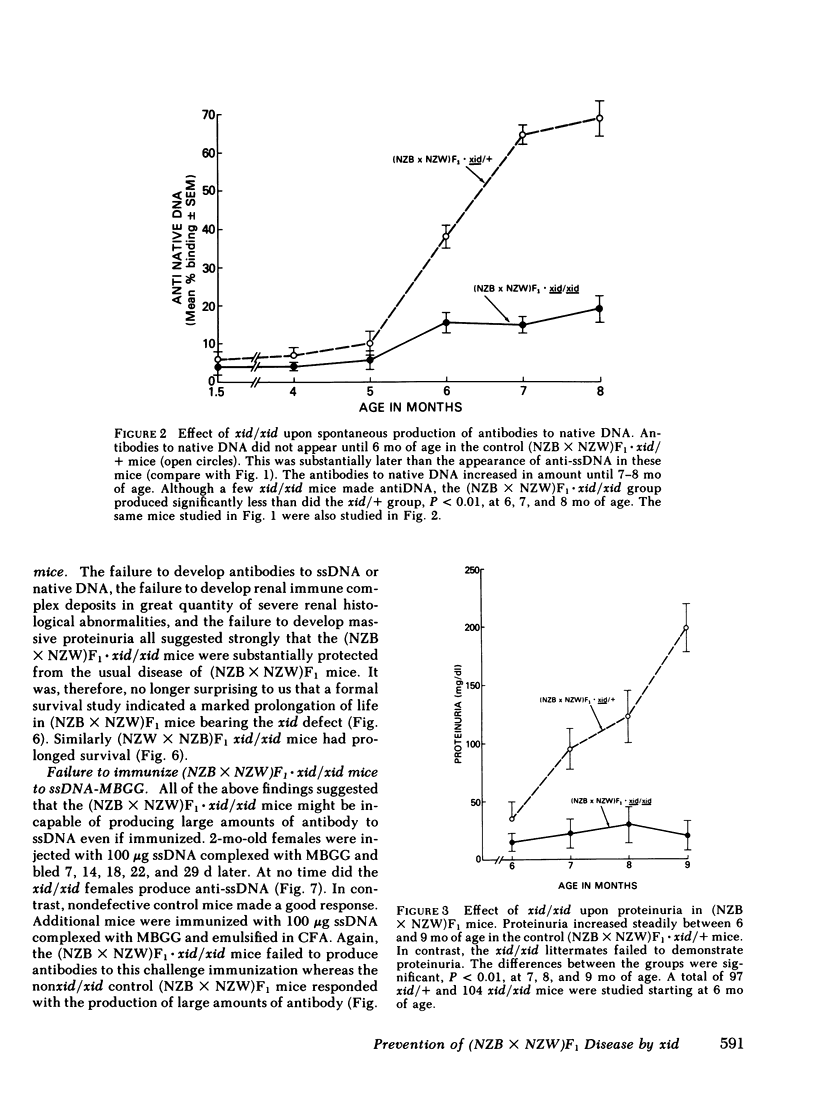
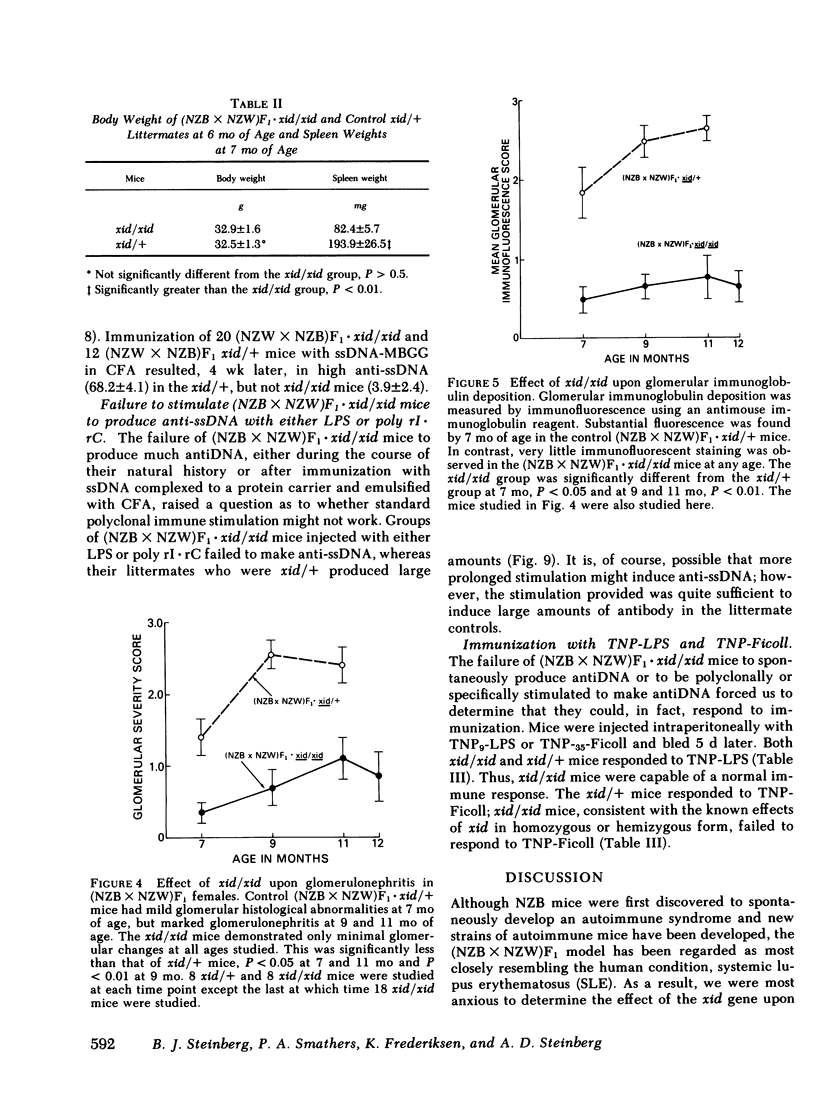
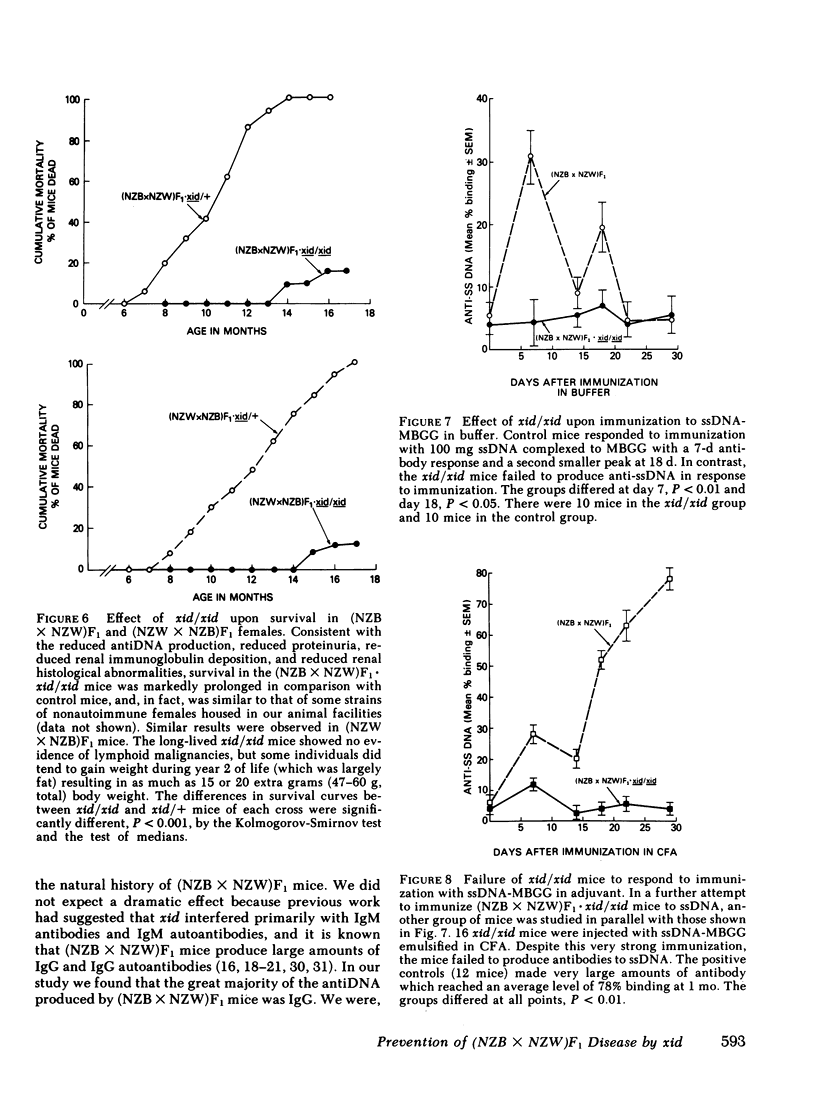
F1 hybrid offspring of New Zealand Black mothers and New Zealand White fathers [(NZB X NZW)F1] female mice develop antibodies to single-stranded (ss) and native DNA, immune complex glomerulonephritis, massive proteinuria, and premature death with renal failure. By a series of matings, congenic (NZB X NZW)F1 . xid/xid mice were prepared. These mice were different from (NZB X NZW)F1 mice in having the X chromosome-linked immune deficiency gene, xid, in homozygous form. Such congenic (NZB X NZW)F1 . xid/xid females failed to develop antibodies to single-stranded or native DNA. They also failed to develop fatal renal disease as measured by proteinuria, glomerular histology, glomerular immunofluorescence, and survival. To control for unknown genetic factors, studies were performed with littermates that were derived by mating NZB . xid/+ females with NZW . xid/Y males such that the resulting offspring were either (NZB X NZW)F1 . xid/xid (and therefore "defective") or (NZB X NZW)F1 . xid/+ [phenotypically like (NZB X NZW)F1]. In these and in additional studies, mice were housed in the same cages and identified by ear tagging so as to avoid possible environmental variations from cage to cage. In these studies, xid/xid mice failed to develop the characteristic signs of autoimmunity, whereas the controls did. Similar results were also obtained with (NZW X NZB)F1 xid/xid mice compared with (NZW X NZB)F1 xid/+ mice. The effect of xid/xid upon (NZB X NZW)F1 mice was further investigated by assessing responses to immunization and polyclonal B cell activation in vivo. The xid/xid mice failed to produce anti-ssDNA following immunization with ssDNA complexed to a protein carrier in fluid form or even emulsified in adjuvant. Finally, the xid/xid mice failed to produce antiDNA in response to multiple injections of the polyclonal activator, bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or the polyclonal activator, polyribose inosinic acid . polyribose cytidylic acid. However, the xid/xid mice were neither generally hyporesponsive nor unable to recognize LPS because they made normal antibody responses following immunization with LPS to which multiple trinitrophenyl groups were chemically attached. We conclude from these studies that xid/xid, which is known to cause the deletion of a B cell subset, has a profound affect upon (NZB X NZW)F1 mice, rendering them insusceptible to the naturally occurring autoimmune disease characteristic of (NZB X NZW)F1 mice, and preventing them from producing antibodies to DNA despite purposeful immunization and polyclonal B cell activation. These results force a reevaluation of previous concepts regarding the mechanisms by which xid/xid might interfere with the development of autoimmunity, and a consideration of therapeutic implications.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed A., Scher I., Sharrow S. O., Smith A. H., Paul W. E., Sachs D. H., Sell K. W. B-lymphocyte heterogeneity: development and characterization of an alloantiserum which distinguishes B-lymphocyte differentiation alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):101–110. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsbaugh D. F., Hansen C. T., Prescott B., Stashak P. W., Asofsky R., Baker P. J. Genetic control of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide in mice. II. Relationship between IgM immunoglobulin levels and the ability to give an IgM antibody response. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1499–1512. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amsbaugh D. F., Hansen C. T., Prescott B., Stashak P. W., Barthold D. R., Baker P. J. Genetic control of the antibody response to type 3 pneumococcal polysaccharide in mice. I. Evidence that an X-linked gene plays a decisive role in determining responsiveness. J Exp Med. 1972 Oct 1;136(4):931–949. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.4.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berning A. K., Eicher E. M., Paul W. E., Scher I. Mapping of the X-linked immune deficiency mutation (xid) of CBA/N mice. J Immunol. 1980 Apr;124(4):1875–1877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell H. S., Ahmed A., Scher I., Singer A. Role of accessory cells in B cell activation. II. The interaction of B cells with accessory cells results in the exclusive activation of an Lyb5+ B cell subpopulation. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1340–1348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell H. S., Sharrow S. O., Singer A. Role of accessory cells in B cell activation. I. Macrophage presentation of TNP-Ficoll: evidence for macrophage-B cell interaction. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):989–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowdery J. S., Jr, Taurog J. D., Steinberg A. D. Effect of CBA/N xid on spontaneous production of antibodies to DNA in MRL/1 and NZB backcross mice. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(6):499–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowdery J. S., Laskin C. A., Steinberg A. D. The specificity of in vivo tolerance to haptens in NZB and normal mice after exposure to hapten-modified syngeneic spleen cells. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1571–1576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon F. J., Oldstone M. B., Tonietti G. Pathogenesis of immune complex glomerulonephritis of New Zealand mice. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):65s–71s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois E. L., Strain L. Effect of diet on survival and nephropathy of NZB-NZW hybrid mice. Biochem Med. 1973 Apr;7(2):336–342. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(73)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes G., Yunis E. J., Good R. A. Influence of diet on survival of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1279–1283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend P. S., Fernandes G., Good R. A., Michael A. F., Yunis E. J. Dietary restrictions early and late: effects on the nephropathy of the NZB X NZW mouse. Lab Invest. 1978 Jun;38(6):629–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Steinberg A. D., Nagle R., Knepshield J. H. Therapeutic studies in NZB-W mice. I. Synergy of azathioprine, cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone in combination. Arthritis Rheum. 1972 May-Jun;15(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/art.1780150304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber B., Gershon R. K., Cantor H. Identification of a B-cell surface structure involved in antigen-dependent triggering: absence of this structure on B cells from CBA/N mutant mice. J Exp Med. 1977 Jan 1;145(1):10–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurd E. R., Johnston J. M., Okita J. R., MacDonald P. C., Ziff M., Gilliam J. W. Prevention of glomerulonephritis and prolonged survival in New Zealand Black/New Zealand White F1 hybrid mice fed an essential fatty acid-deficient diet. J Clin Invest. 1981 Feb;67(2):476–485. doi: 10.1172/JCI110056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman J. K. Thymus-independent antigens: the preparation of covalent, hapten-ficoll conjugates. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 1):704–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izui S., McConahey P. J., Dixon F. J. Increased spontaneous polyclonal activation of B lymphocytes in mice with spontaneous autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2213–2219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. D., Cowdery J. S., Steinberg A. D., Gershon R. K. Genetic control of autoimmune disease: interactions between xid and Ipr. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):388–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley H. B., Kysela S., Steinberg A. D. Nucleic acid antibodies in African trypanosomiasis: studies in Rhesus monkeys and man. J Immunol. 1974 Dec;113(6):1921–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lite H. S., Braley-Mullen H. Induction of IgG memory responses with polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is antigen dose dependent. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):928–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manny N., Datta S. K., Schwartz R. S. Synthesis of IgM by cells of NZB and SWR mice and their crosses. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1220–1227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey P. J., Boswell H. S., Scher I., Singer A. Role of accessory cells in B cell activation. IV. Ia+ accessory cells are required for the in vitro generation of thymic independent type 2 antibody responses to polysaccharide antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1345–1347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Steinberg A. D., Schur P. H., Reed N. D. Spontaneous "autoimmune disease" in nude mice. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):688–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E., Scher I., Paul W. E. In vitro responses of CBA/N mice: spleen cells of mice with an X-linked defect that precludes immune responses to several thymus-independent antigens can respond to TNP-lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol. 1976 Oct;117(4):1363–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutsopoulos H. M., Boehm-Truitt M., Kassan S. S., Chused T. M. Demonstration of activation of B lymphocytes in New Zealand black mice at birth by an immunoradiometric assay for murine IgM. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1639–1644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima P. B., Datta S. K., Schwartz R. S., Huber B. T. Localization of spontaneously hyperactive B cells of NZB mice to a specific B cell subset. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4613–4616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsugi Y., Gershwin M. E., Ahmed A., Skelly R. R., Milich D. R. Studies of congenitally immunologic mutant New Zealand mice. VI. Spontaneous and induced autoantibodies to red cells and DNA occur in New Zealand X-linked immunodeficient (Xid) mice without phenotypic alternations of the Xid gene or generalized polyclonal B cell activation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2220–2227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsugi Y., Gershwin M. E., Ahmed A. Study of congenitally immunologic mutant New Zealand mice. V. B cell function of NZB-Xid mice. J Immunogenet. 1981 Apr;8(2):129–137. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-313x.1981.tb00750.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Inhibition of antibodies to nuclear antigen and to DNA in New Zealand mice infected with lactate dehydrogenase virus. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):784–786. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papoian R., Pillarisetty R., Talal N. Immunological regulation of spontaneous antibodies to DNA and RNA. II. Sequential switch from IgM to IgG in NZB/NZW F1 mice. Immunology. 1977 Jan;32(1):75–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D. C., Fothergill J. J., Wadsworth D. C. B lymphocyte activation by insoluble anti-immunoglobulin: induction of immunoglobulin secretion by a T cell-dependent soluble factor. J Immunol. 1979 Aug;123(2):931–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. E., Steinberg A. D. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice. IV. Independent stimulation of antibodies to DNA and RNA. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Nov;12(3):419–427. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prickett J. D., Robinson D. R., Steinberg A. D. Dietary enrichment with the polyunsaturated fatty acid eicosapentaenoic acid prevents proteinuria and prolongs survival in NZB x NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):556–559. doi: 10.1172/JCI110288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Novotny E. A., Hansen C. T., Tjio J. H., Steinberg A. D. Genetic studies in NZB mice. V. Recombinant inbred lines demonstrate that separate genes control autoimmune phenotype. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1187–1197. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveche E. S., Tjio J. H., Steinberg A. D. Genetic studies in NZB mice. III. Induced anti-nucleic acid antibody production. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1454–1460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raveché E. S., Steinberg A. D., Klassen L. W., Tjio J. H. Genetic studies in NZB mice. I. Spontaneous autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1978 May 1;147(5):1487–1502. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves J. P., Taurog J. D., Steinberg A. D. Polyclonal B-cell activation of autoantibodies (CBA/N x NZB)F1 mice by polyinosinic polycytidylic acid. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1981 May;19(2):170–180. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(81)90060-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romain P. L., Cohen P. L., Fish F., Ziff M., Vitetta E. S. The specific B cell subset lacking in the CBA/N mouse is not required for the production of autoantibody in (CBA/N x NZB)F1 male mice. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):246–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenwasser L. J., Huber B. T. The xid gene controls Ia.W39-associated immune response gene function. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1113–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Ahmed A., Strong D. M., Steinberg A. D., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/HN mice. I. Studies of the function and composition of spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):788–803. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Frantz M. M., Steinberg A. D. The genetics of the immune response to a synthetic double-stranded RNA in a mutant CBA mouse strain. J Immunol. 1973 May;110(5):1396–1401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Sharrow S. O., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte defect in CBA/N mice. III. Abnormal development of B-lymphocyte populations defined by their density of surface immunoglobulin. J Exp Med. 1976 Aug 1;144(2):507–518. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.2.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I., Steinberg A. D., Berning A. K., Paul W. E. X-linked B-lymphocyte immune defect in CBA/N mice. II. Studies of the mechanisms underlying the immune defect. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):637–650. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smathers P. A., Steinberg B. J., Reeves J. P., Steinberg A. D. Effects of polyclonal immune stimulators upon NZB.xid congenic mice. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1414–1419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Baron S., Talal N. The pathogenesis of autoimmunity in New Zealand mice, I. Induction of antinucleic acid antibodies by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Aug;63(4):1102–1107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.4.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Huston D. P., Taurog J. D., Cowdery J. S., Ravecheé E. S. The cellular and genetic basis of murine lupus. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:121–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg A. D., Smathers P. A., Boegel W. B. Effects of sex hormones on autoantibody production by NZB mice and modification by environmental factors. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Dec;17(4):562–572. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Hay F. C. Changes in immunoglobulin class and subclass of anti-DNA antibodies with increasing age in N/ZBW F1 hybrid mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Nov;26(2):363–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Moutsopoulos H. M., Rosenberg Y. J., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D. CBA/N X-linked B-cell defect prevents NZB B-cell hyperactivity in F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):31–43. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Raveche E. S., Smathers P. A., Glimcher L. H., Huston D. P., Hansen C. T., Steinberg A. D. T cell abnormalities in NZB mice occur independently of autoantibody production. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):221–234. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Etiopathogenesis of murine SLE. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:179–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonietti G., Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. The effect of induced chronic viral infections on the immunologic diseases of New Zealand mice. J Exp Med. 1970 Jul 1;132(1):89–109. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



