Abstract
Primary sarcoidosis of the pancreas is extremely rare. Clinical presentation is often identical to that of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Preoperative diagnosis of primary pancreatic sarcoidosis is always challenging. We present a 52-year-old man who developed weight loss and obstructive jaundice. Abdomino-pelvic CT scan showed a mass in the pancreatic head. After hepatopancreaticobiliary MDT discussion, a Whipple's procedure was attempted but the mass was deemed unresectable due to invasion of the superior mesenteric vein. Upon completion of palliative chemotherapy, repeat imaging showed significant mass shrinkage. A reattempt Whipple's procedure was successfully undertaken. Histology showed changes of chronic pancreatitis and peripancreatic granulomatous inflammation with no evidence of malignancy and a diagnosis of sarcoidosis was made. Owing to the devastating nature of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, any mass in the pancreas must be thoroughly investigated before a definitive diagnosis is made.
Background
Sarcoidosis of the pancreas is an extremely rare disease, with only 25 reported cases in the English literature. The presentation is often identical to that of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, with painless obstructive jaundice, weight loss and abdominal pain being the most common presenting features. Despite radiological advances, it is often difficult to differentiate an inflammatory mass from a malignant pancreatic tumour. We report the case of a patient who presented with features strongly suggestive of pancreatic adenocarcinoma but who was found to have primary sarcoidosis of the pancreas.
Case presentation
A 52-year-old man with no medical history presented with painless jaundice, back pain and unintentional weight loss of one stone over the last 2 months. An abdominal CT scan demonstrated a 2 cm low attenuation lesion in the head of the pancreas with dilation of the bile ducts (figure 1). CT scan of the chest was normal. Serum CA19-9 was elevated at 118 units/mL (normal range 0–37 U/mL). There were no risk factors for chronic pancreatitis such as gallstones or significant alcohol intake. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography with insertion of a stent was undertaken to relieve jaundice and to obtain biliary brushings, cytology of which showed no evidence of malignancy.
Figure 1.
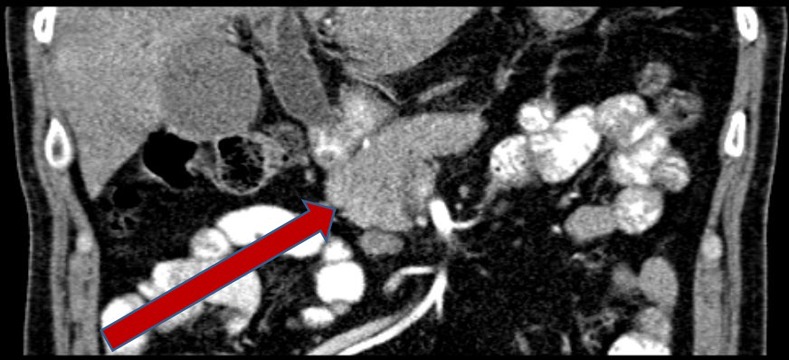
Abdominal CT scan at presentation, demonstrating mass in pancreatic head.
The case was discussed at the regional hepatopancreaticobiliary multidisciplinary meeting (HPB MDM), with a general agreement that the radiological features were consistent with pancreatic tumour and should be resected with Whipple's procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy). At operation, the mass was found to be cicatrised around the superior mesenteric vein (confirmed with intraoperative ultrasound scan) and was deemed unresectable. Palliative biliary bypass and Trucut biopsy of the head of pancreas mass were performed. The pancreatic biopsy had insufficient tissue for histological diagnosis but no malignant cells were found in the sample. Following further discussion, the multidisciplinary team agreed that pancreatic cancer was the most likely diagnosis and palliative chemotherapy was recommended. The patient underwent six cycles of palliative gemcitabine which was tolerated well. Repeat imaging following completion of chemotherapy showed a good reduction in the size of the mass.
The case was further discussed at the HPB MDM and a decision for reattempt at Whipple's resection was made. Peroperatively the pancreas was found to be atrophic with a small hard mass in the head. This time, a plane of dissection was found between the pancreas and superior mesenteric vein and Whipple's procedure was successfully completed. The patient made an uneventful recovery from the procedure.
Histological examination of the resection specimen showed widespread fibrotic and chronic inflammatory changes within the pancreas (figure 2). There was marked atrophy of the pancreatic acini with relative sparing of endocrine islets. Nineteen lymph nodes were recovered from the resected main body of tissue, none of which showed any evidence of malignancy, but many of which contained numerous small, non-caseating epitheliod granulomata without necrosis. Histochemical staining for mycobacteria was negative. It was concluded that, while it was possible the marked fibrosis represented a complete pathological response to chemotherapy, the retention of a normal pancreatic ductocentric lobular architecture made a diagnosis of malignancy unlikely and an inflammatory mass was more likely, with sarcoidosis felt to be the most likely cause.
Figure 2.
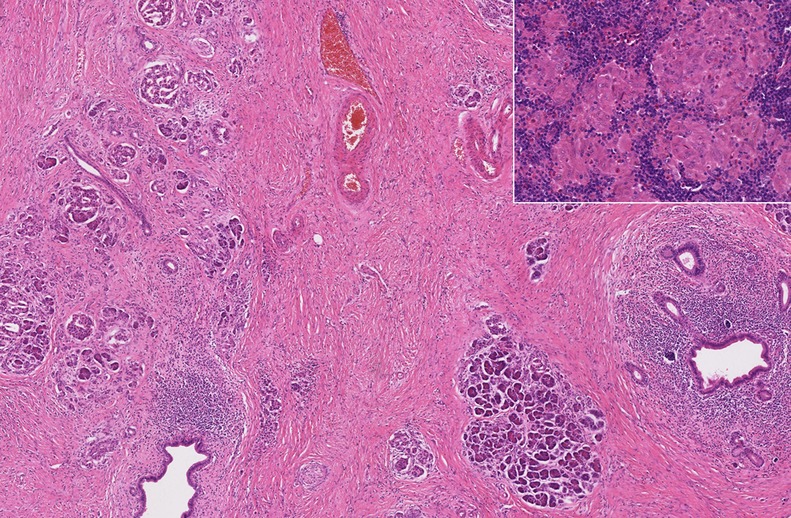
Medium power histological view of pancreatic resection specimen sample showing severe fibrosis, atrophy of pancreatic parenchyma and duct-centred chronic inflammation, with retention of a normal lobular architecture (H&E). Inset: high-power histological view of small epithelioid non-caseating granulomata within peripancreatic lymph nodes, consistent with sarcoidosis (H&E).
ACE levels subsequently proved to be normal and chest imaging revealed no hilar lymphadenopathy or pulmonary fibrosis. On further questioning, the patient's mother was noted to have had sarcoidosis. A final clinical diagnosis of primary pancreatic sarcoidosis was made.
Discussion
Sarcoidosis is a chronic granulomatous multisystem disease characterised by the accumulation of T-lymphocytes, mononuclear phagocytes and non-caseating granulomata. The aetiology of the condition is poorly understood, although the three most commonly suggested possibilities are genetic predisposition, abnormal immunological function and environmental exposure.1 Sarcoidosis predominantly affects the lungs and intrathoracic lymph nodes, but can affect almost any organ. Sarcoidosis involving the pancreas is extremely rare2 and was first described following an autopsy in 1937.3 Pancreatic sarcoidosis often presents in an identical manner to pancreatic adenocarcinoma, with common presenting symptoms including weight loss, anorexia, jaundice and back/abdominal pain.
There are only 25 reported cases in the English literature of histologically proven isolated pancreatic sarcoidosis occurring in patients without prior history of sarcoidosis (table 1).4–27 The diagnosis of sarcoidosis is based upon clinical, radiographic and histological findings. In classic cases with constitutional symptoms, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and erythema nodosum, the diagnosis is relatively straightforward, but isolated organ involvement makes the diagnosis less clearcut. The published literature on isolated pancreatic sarcoidosis has varied diagnostic criteria. Indeed, some of the classic investigative findings of sarcoidosis may be negative in isolated pancreatic sarcoidosis, with only a quarter of reported patients having bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on chest X-ray and ACE levels being normal in 38% of cases.23 Our diagnosis was based upon the patient having histological features of sarcoidosis in conjunction with no other explanatory cause for the pancreatic mass.
Table 1.
Reported cases of primary pancreatic sarcoidosis in the English language literature
| Year | AuthorReference | Patient age | Patient sex | Presenting symptom | Diagnostic/therapeutic procedure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950 | Curran4 | 48 | F | Abdominal pain, fatigue | Open biopsy |
| 1954 | Ryrie5 | 52 | F | Anorexia, jaundice | Open biopsy, cholecystoduodenostomy |
| 1972 | Chaun6 | 52 | M | Abdominal pain, fever, weight loss | Open biopsy |
| 1978 | Caldwell7 | 37 | M | Pruritus | Open biopsy, cholecystoduodenostomy |
| 1981 | Maher8 | 59 | M | Abdominal pain, weight loss, anorexia, nausea | Open biopsy, cholecystoduodenostomy |
| 1988 | Sagalow9 | 25 | F | Abdominal pain | Open biopsy |
| 1993 | Brady10 | 67 | F | Abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia | Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| 1994 | Soyer11 | 51 | F | Abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia | Choledochojejunostomy and gastrojejunostomy |
| 1994 | Toda12 | 66 | M | Back pain, pruritus | Open biopsy |
| 1996 | Rodriguez13 | 41 | F | Abdominal pain | Open biopsy |
| 1997 | Bonhomme14 | 76 | M | Fatigue, weight loss, post-prandial pain | Open biopsy |
| 1999 | Siavelis15 | 61 | M | Weight loss, jaundice | Proximal subtotal Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| 2000 | Bacal16 | 54 | M | Jaundice | Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| 2001 | Frank17 | 76 | M | Abdominal pain | Excision via duodenotomy |
| 2001 | Frank17 | 40 | F | Abdominal pain, jaundice | Pylorus-preserving Whipple's procedure with portal vein reconstruction |
| 2004 | Baroni18 | 42 | F | Abdominal pain, weight loss, fever | Open biopsy |
| 2004 | Peyre19 | 57 | F | Pruritus, jaundice, weight loss | Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy |
| 2004 | Romboli20 | 62 | M | Malaise, abdominal swelling, fever | Endoscopic ultrasound with biopsy |
| 2005 | Wijkstrom21 | 49 | F | Abdominal pain, pruritus, anorexia | Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy |
| 2006 | Okoro22 | 49 | F | Incidental finding on CT | Open biopsy |
| 2006 | Caceres23 | 60 | M | Jaundice, abdominal pain and weight loss | pylorus-preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy and cholecystectomy |
| 2007 | Shukla24 | 54 | M | Lethargy, weight loss, abnormal liver function tests | CT-guided biopsy |
| 2008 | Wellner25 | 68 | F | Abdominal pain, vomiting and dyspnoea | Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| 2011 | Schauer26 | 29 | M | Abdominal pain and jaundice | Subtotal Whipple's procedure |
| 2012 | Kersting27 | 68 | M | Not documented | Not documented |
| 2013 | Our case | 52 | M | Jaundice, back pain, weight loss | Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy |
Despite the tremendous improvements in radiological imaging, rarer tumours or inflammatory masses may still be impossible to distinguish from adenocarcinoma until operative exploration and histological examination of biopsies is undertaken. Even then, not infrequently, biopsies are non-diagnostic. Rare causes of non-malignant masses in the pancreas include focal pancreatitis, pancreatic lipomatosis, congenital abnormalities, such as an accessory spleen and Castleman disease of the pancreas.28
Pancreatic sarcoidosis typically has a hypoechoic appearance on ultrasound and hypoattenuating appearance on contrast-enhanced CT.29 MR features are low signal intensity on T1-weighted images, mild high signal intensity on T2-weighted images and decreased enhancement compared with the normal pancreas after the administration of gadolinium.18 Okoro et al22 performed a positron emission tomography scan which revealed marked hypermetabolic fluorodeoxy-glucose uptake in a pancreatic head mass which was subsequently found to be sarcoidosis. These radiological features would suggest pancreatic sarcoidosis in a patient with known systemic sarcoidosis, but a biopsy-proven diagnosis would be strongly advocated in all cases nonetheless, due to the crucial distinction from pancreatic adenocarcinoma in relation to treatment and prognosis.
This case report highlights an interesting and rare cause of mass in the head of the pancreas. Because pancreatic sarcoidosis often presents in a similar manner to pancreatic adenocarcinoma and is difficult to differentiate on radiological imaging, an adequate tissue biopsy remains the gold standard for making the diagnosis. It is also important to consider other causes of granulomatous inflammation and investigate thoroughly before making a diagnosis of sarcoidosis.
Conclusions
Owing to the devastating nature of pancreatic adenocarcinoma, any mass in the pancreas must be thoroughly investigated before confirming this diagnosis. Despite radiological advances, non-neoplastic causes of pancreatic masses are often difficult to diagnose until operative exploration and histological examination of biopsies. We therefore advocate a comprehensive surgical resection with Whipple's pancreaticoduodenectomy in patients with a distinct head of pancreas mass without another definitive preoperative diagnosis, as a combined diagnostic and therapeutic measure.
Learning points.
It is important to ensure prompt investigation and treatment of all pancreatic masses due to the devastating nature of a diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma.
Despite radiological advances, it is often impossible to diagnose rarer causes of pancreatic masses until histological examination.
Primary pancreatic sarcoidosis is rare and can mimic adenocarcinoma clinically and radiologically.
Classical investigations for sarcoidosis, including chest X-ray and serum ACE levels are often normal in organ-confined sarcoidosis.
Differential diagnosis of pancreatic masses includes pancreatic adenocarcinoma, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours, pancreatic cystic neoplasms, focal pancreatitis, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, tuberculosis, pancreatic lipomatosis, congenital abnormalities such as an accessory spleen and Castleman's disease of the pancreas.
Footnotes
Contributors: AIWM and JA performed the literature review and wrote the case report. ML provided the histology images and edited the manuscript. MT edited the manuscript.
Competing interests: None.
Patient consent: Obtained.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
References
- 1.Baughman RP, Lower EE, du Bois RM. Sarcoidosis. Lancet 2003;2013:1111–18 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garcia C, Kumar V, Sharma OP. Pancreatic sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 1996;2013:28–32 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nickerson DA. Boeck's sarcoid. Report of six cases in which an autopsy was made. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1937;2013:19–29 [Google Scholar]
- 4.Curran JF, Jr, Curran JF., Sr Boeck's sarcoid of the pancreas. Surgery 1950;2013:574–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ryrie DR. Sarcoidosis with obstructive jaundice. Proc R Soc Med 1954;2013:879. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chaun H, King DM, Gofton JP, et al. Sarcoidosis of the pancreas. Am J Dig Dis 1972;2013:725–30 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Caldwelll JH, Evans WE. Granuloma (sarcoid?) of the pancreas. A case report. Am J Gastroenterol 1978;2013:320–2 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Maher L, Choi H, Dodds WJ. Noncaseating granulomas of the pancreas. Probable sarcoidosis. Am J Gastroenterol 1981;2013:222–5 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sagalow BR, Miller CL, Wechsler RJ. Pancreatic sareoidosis mimicking pancreatic cancer. J Clin Ultrasound 1988;2013:131–4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Brady MS, Garfein CF, Klimstra D, et al. Sarcoidosis of the pancreas. J Surg Oncol 1993;2013:132–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Soyer P, Gottlieb L, Bluemke DA, et al. Sarcoidosis of the pancreas mimicking pancreatic cancer: CT features. Eur J Radiol 1994;2013:32–3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Toda K, Souda S, Yoshikawa Y, et al. Narrowing of the distal common bile duct and the portal vein secondary to pancreatic sarcoidosis. Am J Gastroenlerol 1994;2013:1259–61 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rodriguez J, Dyck WP. An unusual case of saroidosis presenting as a pancreatic mass. Am J Gastroenterol 1996;2013:2253–4 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bonhomme A, Dhadamus A, De Bie P, et al. Pancreatic involvement in systemic sarcoidosis: CT findings. J Beige Radiol 1997;2013:116–17 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Siavelis HA, Herrmann ME, Aranha GV, et al. Sarcoidosis and the pancreas. Surgery 1999;2013:456–61 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bacal D, Hoshal VL, Jr, Schaldenbrand JD, et al. Sarcoidosis of the pancreas: case report and review of the literature. Am Surg 2000;2013:675–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Frank JL, Goldman M, Nathanson I, et al. Surgical management of pancreatic sarcoid. Eur J Surg 2001;2013:68–72 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Baroni RH, Pedrosa I, Tavemaraki E, et al. Pancreatic sarcoidosis: MRI features. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004;2013:889–93 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Peyre CG, Wakim M, Mateo R, et al. Unusual cases of jaundice secondary to non-neoplastic bile duct obstruction. Am Surg 2004;2013:620–4 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Romboli E, Campana D, Piscitelli L, et al. Pancreatic involvement in systemic sarcoidosis. A case report. Dig Liver Dis 2004;2013:222–7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wijkstrom M, Bechara RI, Sarmiento JM. A rare nonmalignant mass of the pancreas: case report and review of pancreatic sarcoidosis. Am Surg 2010;2013:79–84 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Okoro N, Moldovanyi C, Wehbi M, et al. Sarcoidosis masquerading as pancreatic cancer. Pract Gastroenterol 2006;2013:83–8 [Google Scholar]
- 23.Caceres M, Sabbaghian MS, Braud R, et al. Pancreatic sarcoidosis: unusual presentation resembling a periampullary malignancy. Curr Surg 2006;2013:179–85 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shukla M, Hassan MF, Toor V, et al. Symptomatic pancreatic sarcoidosis. Case report and review of literature. JOP 2007;2013:770–4 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wellner U, Mattern D, Keck T. Clinical challenges and images in GI. Early peripancreatic and pulmonary sarcoidosis. Gastroenterology 2008;2013:1864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schauer R, Völker U, Kreuzmayr A. An unorthodox pancreatic lesion in a young man presenting with jaundice. Gastroenterology 2011;2013:1563, 1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kersting S, Janot MS, Munding J, et al. Rare solid tumors of the pancreas as differential diagnosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. JOP 2012;2013:268–77 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Low G, Panu A, Millo N, et al. Multimodality imaging of neoplastic and nonneoplastic solid lesions of the pancreas. Radiographics 2011;2013:993–1015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Warshauer DM, Lee JK. Imaging manifestations of abdominal sarcoidosis. Am J Roentgenol 2004;2013:15–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


