Abstract
Tangier disease is a rare familial disorder characterized by enlarged orange tonsils, transient peripheral neuropathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and lymphadenopathy, as well as striking reductions in plasma high density lipoproteins (HDL) and their major protein constituents, apolipoproteins (apo)A-I and A-II. In order to test the hypothesis that Tangier patients have abnormal apoA-I or apoA-II, the in vitro lipoprotein binding and in vivo metabolic characteristics of these proteins isolated from normal and Tangier plasma, were studied in normal subjects and patients with Tangier disease.
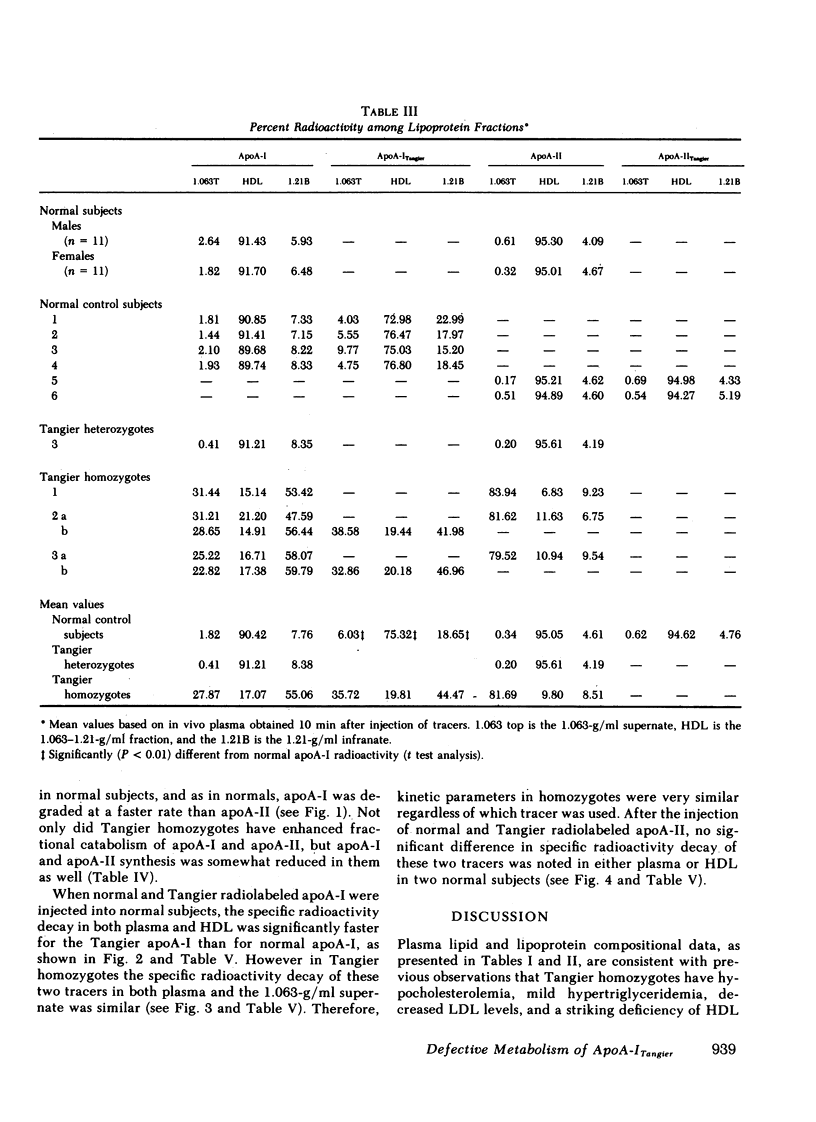
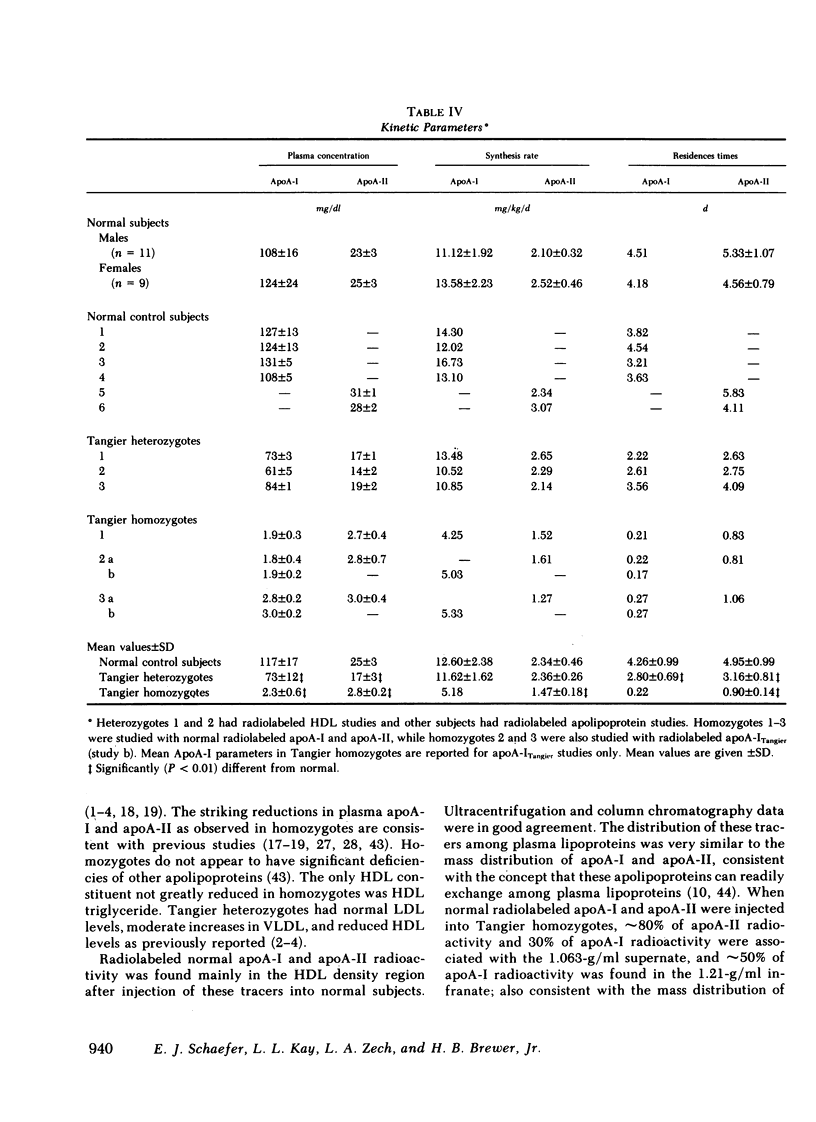
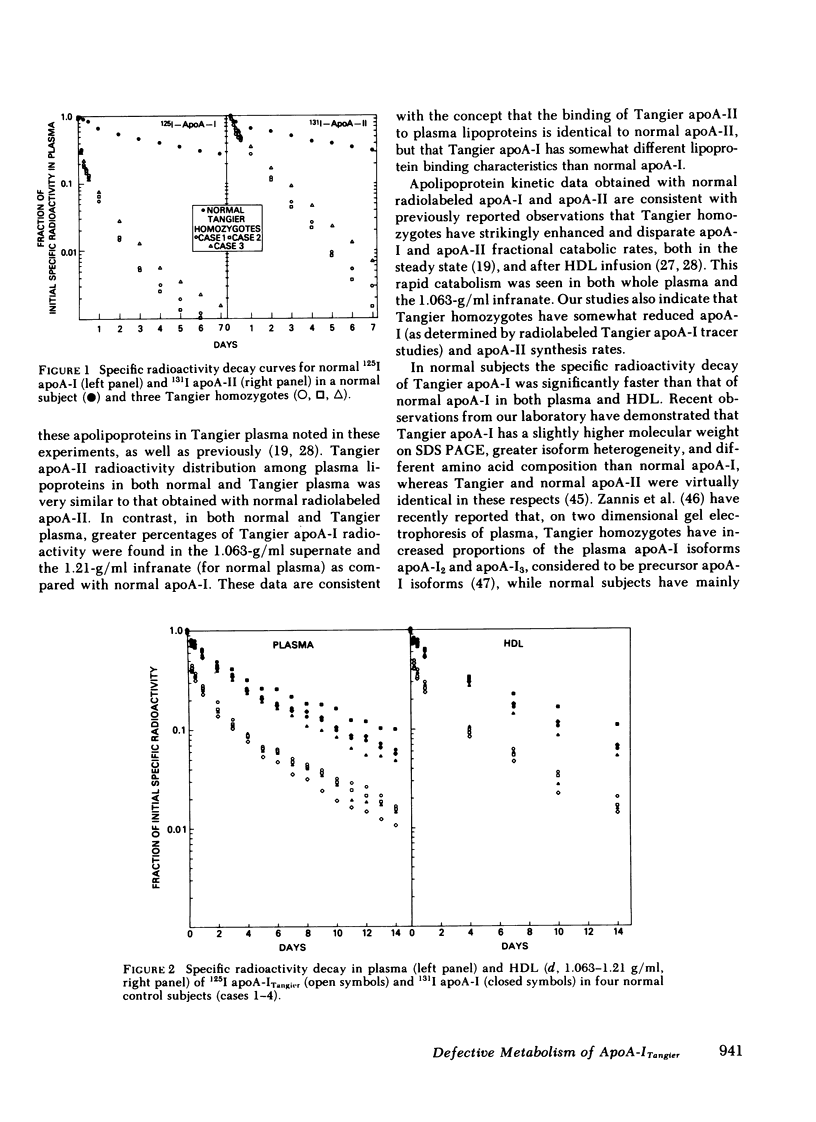
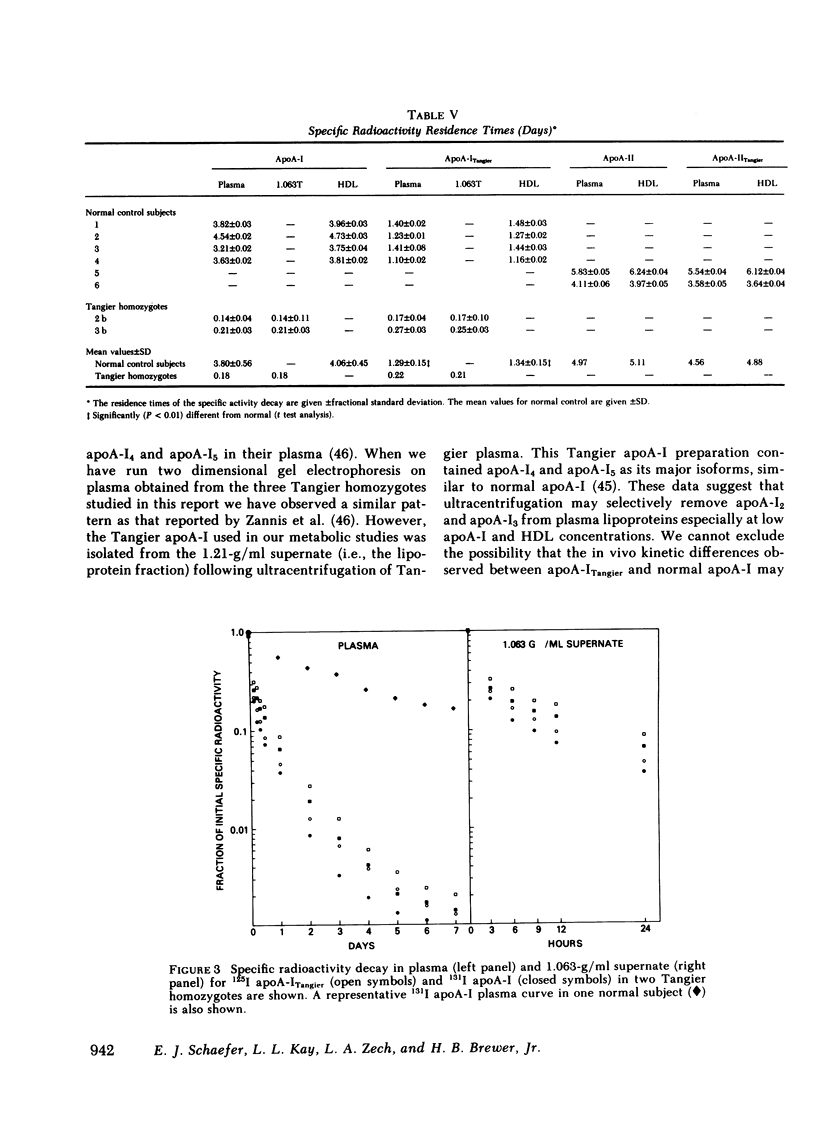
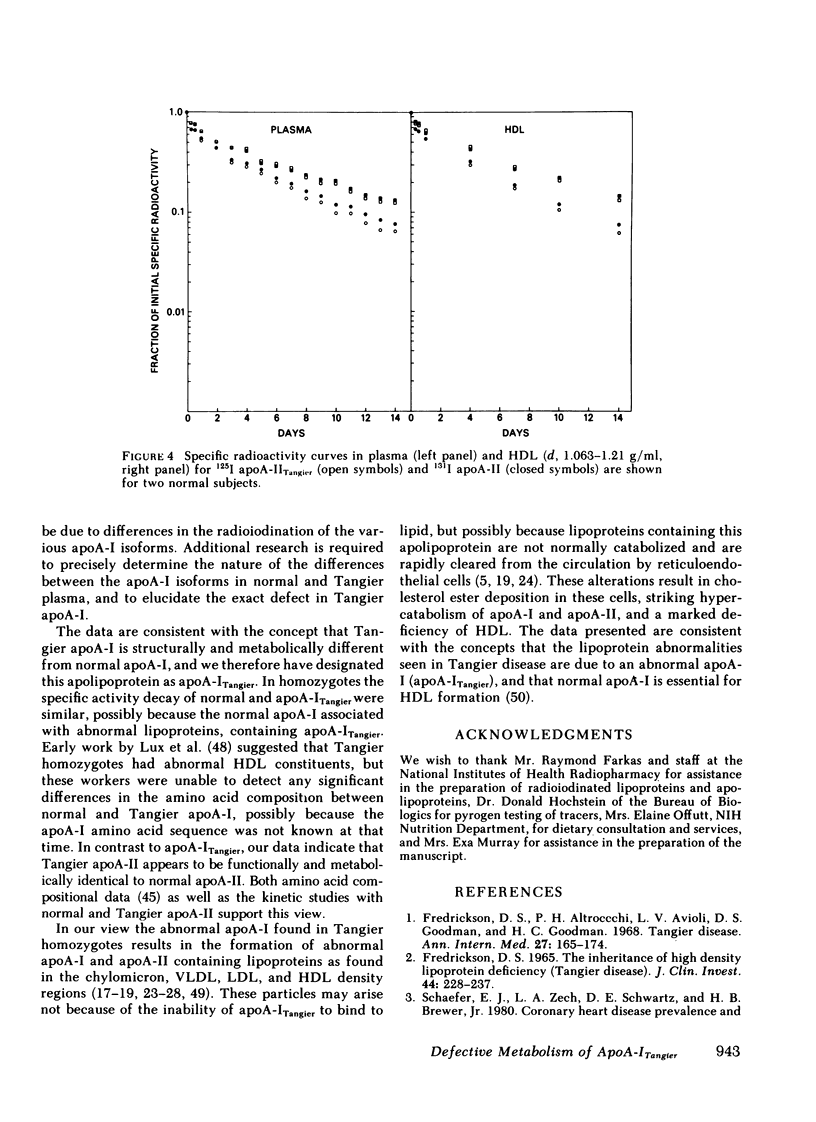
After incubation with normal plasma, significantly greater percentages of radiolabeled Tangier apoA-I were associated with the 1.063-g/ml supernate (6%) and the 1.21 g/ml infranate (19%), and a lower percentage with HDL (75%), than those observed for normal apoA-I (2, 8, and 90%, respectively). In contrast, the lipoprotein binding properties of normal and Tangier apoA-II were very similar. Following the injection of radiolabeled normal and Tangier apoA-I into normal subjects (n = 4), the mean residence times of the specific activity for apoA-ITangier were significantly lower, both in plasma (1.29 d) and in HDL (1.34 d), than those observed for normal apoA-I (3.80 and 4.06 d). In Tangier homozygotes the decay rates of these tracers were very rapid and were similar. No significant differences between the kinetics of normal and Tangier apoA-II were observed in normal subjects (n = 2).
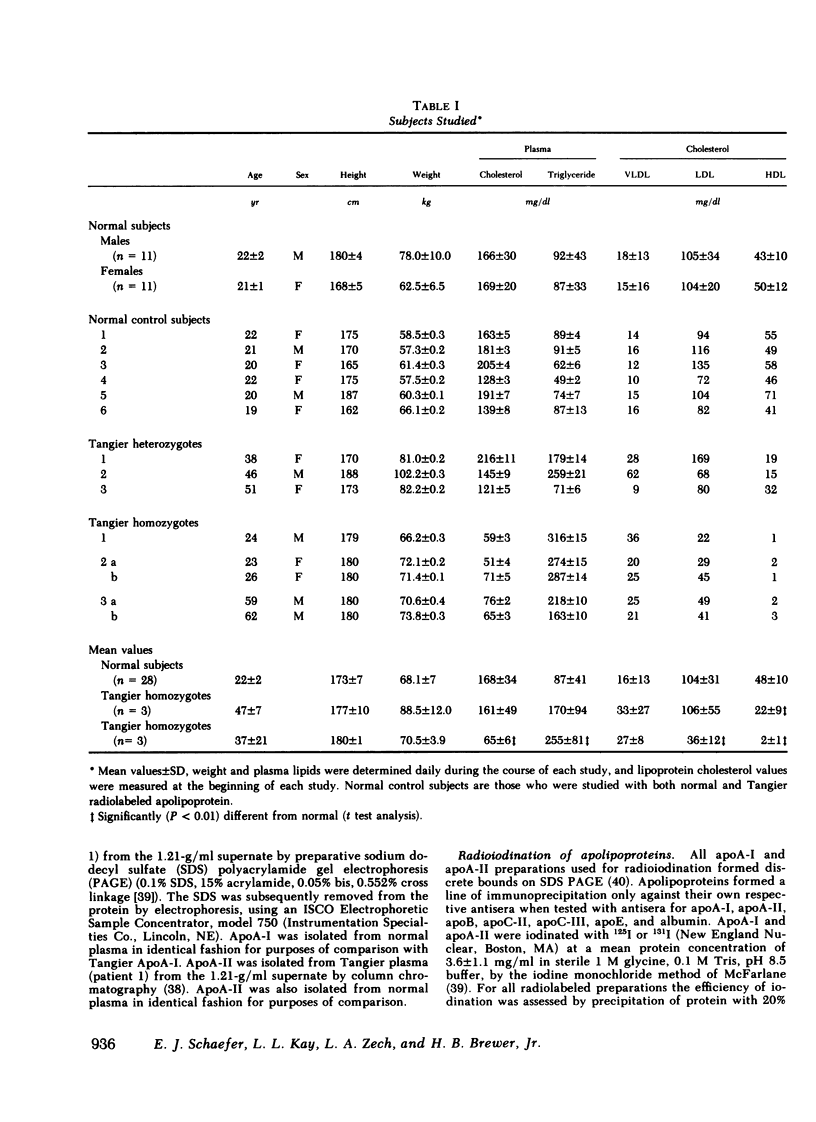
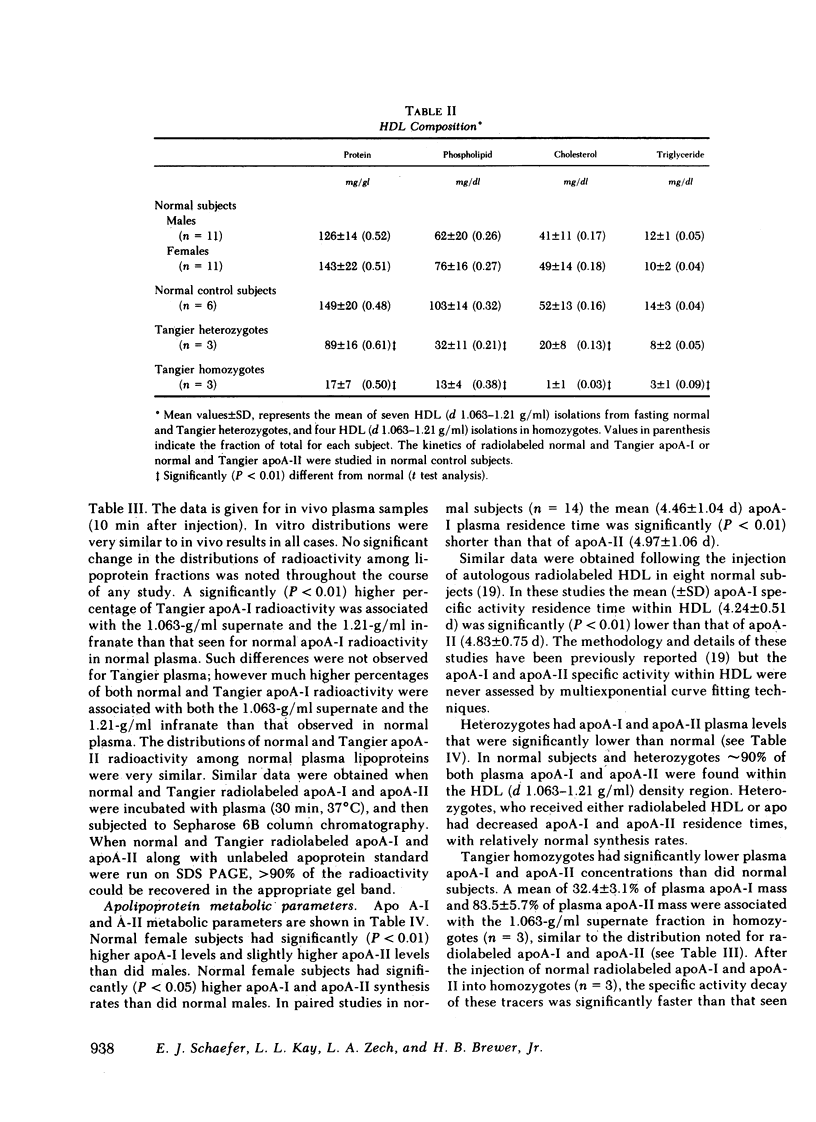
Tangier homozygotes (n = 3) had mean plasma HDL cholesterol, apoA-I, and apoA-II concentrations that were 4, 2, and 11% of normal (n = 24), respectively, whereas for heterozygotes (n = 3) these values were 46, 62, and 68% of normal. In homozygotes, in contrast to normals or heterozygotes, a significant fraction of both apoA-I and apoA-II were found in the 1.063-g/ml supernate instead of in HDL. Homozygotes had apoA-ITangier synthesis rates and residence times that were 41 and 5% of values observed for normal apoA-I in normal subjects, and for apoA-II in homozygotes, these parameters were 63 and 18% of normal. Heterozygotes had apoA-I synthesis rates and residence times that were 92 and 66% of normal, and for apoA-II these values were 101 and 64% of normal.
These data are consistent with the concept that apoA-ITangier is functionally and metabolically distinct from normal apoA-I, and is the cause of the striking hypercatabolism of apoA-I and apoA-II, and the lipoprotein abnormalities observed in Tangier disease.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alaupovic P., Schaefer E. J., McConathy W. J., Fesmire J. D., Brewer H. B., Jr Plasma apolipoprotein concentrations in familial apolipoprotein A-I and A-II deficiency (Tangier disease). Metabolism. 1981 Aug;30(8):805–809. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Capurso A., Smootz E., Wellner U. Apoprotein A metabolism in Tangier disease. Atherosclerosis. 1978 Aug;30(4):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(78)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assmann G., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Forte T. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein in Tangier Diesase. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):242–252. doi: 10.1172/JCI108761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARR D. P., RUSS E. M., EDER H. A. Protein-lipid relationships in human plasma. II. In atherosclerosis and related conditions. Am J Med. 1951 Oct;11(4):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(51)90183-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Fairwell T., LaRue A., Ronan R., Houser A., Bronzert T. J. The amino acid sequence of human APOA-I, an apolipoprotein isolated from high density lipoproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 14;80(3):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer H. B., Jr, Lux S. E., Ronan R., John K. M. Amino acid sequence of human apoLp-Gln-II (apoA-II), an apolipoprotein isolated from the high-density lipoprotein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1304–1308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P., Doyle J. T., Gordon T., Hames C. G., Hjortland M. C., Hulley S. B., Kagan A., Zukel W. J. HDL cholesterol and other lipids in coronary heart disease. The cooperative lipoprotein phenotyping study. Circulation. 1977 May;55(5):767–772. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.55.5.767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalvardjian A., Rudnicki E. Determination of lipid phosphorus in the nanomolar range. Anal Biochem. 1970 Jul;36(1):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90352-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. The measurement of apolipoprotein A-I and A-II levels in men and women by immunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):43–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI108767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. C., Kuwabara T., Cogan D. G., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Ocular manifestations of familial high-density lipoprotein deficiency (Tangier disease). Arch Ophthalmol. 1979 Oct;97(10):1926–1928. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1979.01020020374020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., Alaupovic P., Suenram C. A. Determination of apolipoprotein A and its constitutive A-I and A-II polypeptides by separate electroimmunoassays. Clin Chem. 1976 Mar;22(3):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrans V. J., Fredrickson D. S. The pathology of Tangier disease. A light and electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1975 Jan;78(1):101–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman R. M., Green P. H., Lees R. S., Tall A. Apoprotein A-I synthesis in normal intestinal mucosa and in Tangier disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Dec 28;299(26):1424–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197812282992602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinen R. J., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S. Properties of the plasma very low and low density lipoproteins in Tangier disease. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jan;61(1):120–132. doi: 10.1172/JCI108910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. O., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Heinen R. J., Easterling J. C. Abnormal concentration and anomalous distribution of apolipoprotein A-I in Tangier disease. Metabolism. 1978 Feb;27(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. O., Herbert P. N., Fredrickson D. S., Heinen R. J., Easterling J. C. Abnormal concentration and anomalous distribution of apolipoprotein A-I in Tangier disease. Metabolism. 1978 Feb;27(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(78)90162-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert P. N., Forte T., Heinen R. J., Fredrickson D. S. Tangier disease: one explanation of lipid storage. N Engl J Med. 1978 Sep 7;299(10):519–521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197809072991005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman H. N., Fredrickson D. S. Tangier disease (familial high density lipoprotein deficiency). Clinical and genetic features in two adults. Am J Med. 1965 Oct;39(4):582–593. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90081-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. S., Small D. M., Brook J. G., Lees R. S. The storage lipids in Tangier disease. A physical chemical study. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jun;59(6):1045–1054. doi: 10.1172/JCI108727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay L. L., Ronan R., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Tangier disease: a structural defect in apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I Tangier). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2485–2489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G., Alaupovic P. Studies of the composition and structure of plasma lipoproteins. Separation and quantification of the lipoprotein families occurring in the high density lipoproteins of human plasma. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 29;11(18):3419–3428. doi: 10.1021/bi00768a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E., Levy R. I., Gotto A. M., Fredrickson D. S. Studies on the protein defect in Tangier disease. Isolation and characterization of an abnormal high density lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2505–2519. doi: 10.1172/JCI107066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. J., Miller N. E. Plasma-high-density-lipoprotein concentration and development of ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1975 Jan 4;1(7897):16–19. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92376-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rescigno A., Gurpide E. Estimation of average times of residence, recycle and interconversion of blood-borne compounds using tracer methods. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 Feb;36(2):263–276. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-2-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads G. G., Gulbrandsen C. L., Kagan A. Serum lipoproteins and coronary heart disease in a population study of Hawaii Japanese men. N Engl J Med. 1976 Feb 5;294(6):293–298. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197602052940601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Toth J., Edelstein C., Koga S., Stiller E. Fractionation of human serum high density lipoprotein in urea solutions. Evidence for polypeptide heterogeneity. Biochemistry. 1969 Aug;8(8):3309–3316. doi: 10.1021/bi00836a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Anderson D. W., Zech L. A., Lindgren F. T., Bronzert T. B., Rubalcaba E. A., Brewer H. B., Jr Metabolism of high density lipoprotein subfractions and constituents in Tangier disease following the infusion of high density lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1981 Feb;22(2):217–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Blum C. B., Levy R. I., Jenkins L. L., Alaupovic P., Foster D. M., Brewer H. B., Jr Metabolism of high-density lipoprotein apolipoproteins in Tangier disease. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 26;299(17):905–910. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810262991701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Foster D. M., Jenkins L. L., Lindgren F. T., Berman M., Levy R. I., Brewer H. B., Jr The composition and metabolism of high density lipoprotein subfractions. Lipids. 1979 May;14(5):511–522. doi: 10.1007/BF02533471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Heaton W. H., Wetzel M. G., Brewer H. B., Jr Plasma apolipoprotein A-1 absence associated with a marked reduction of high density lipoproteins and premature coronary artery disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1982 Jan-Feb;2(1):16–26. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.2.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Jenkins L. L., Brewer H. B., Jr Human chylomicron apolipoprotein metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90691-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer E. J., Levy R. I., Anderson D. W., Danner R. N., Brewer H. B., Jr, Blackwelder W. C. Plasma-triglycerides in regulation of H.D.L.-cholesterol levels. Lancet. 1978 Aug 19;2(8086):391–393. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91863-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld G., Pfleger B. The structure of human high density lipoprotein and the levels of apolipoprotein A-I in plasma as determined by radioimmunoassay. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):236–246. doi: 10.1172/JCI107758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd J., Patsch J. R., Packard C. J., Gotto A. M., Jr, Taunton O. D. Dynamic properties of human high density lipoprotein apoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1978 Mar;19(3):383–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore B., Shore V. Isolation and characterization of polypeptides of human serum lipoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Nov;8(11):4510–4516. doi: 10.1021/bi00839a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldorf D. S., Levy R. I., Fredrickson D. S. Cutaneous cholesterol ester deposition in Tangier disease. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Feb;95(2):161–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Kurnit D. M., Breslow J. L. Hepatic apo-A-I and apo-E and intestinal apo-A-I are synthesized in precursor isoprotein forms by organ cultures of human fetal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):536–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Lees A. M., Lees R. S., Breslow J. L. Abnormal apoprotein A-I isoprotein composition in patients with Tangier disease. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4978–4986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



