Abstract
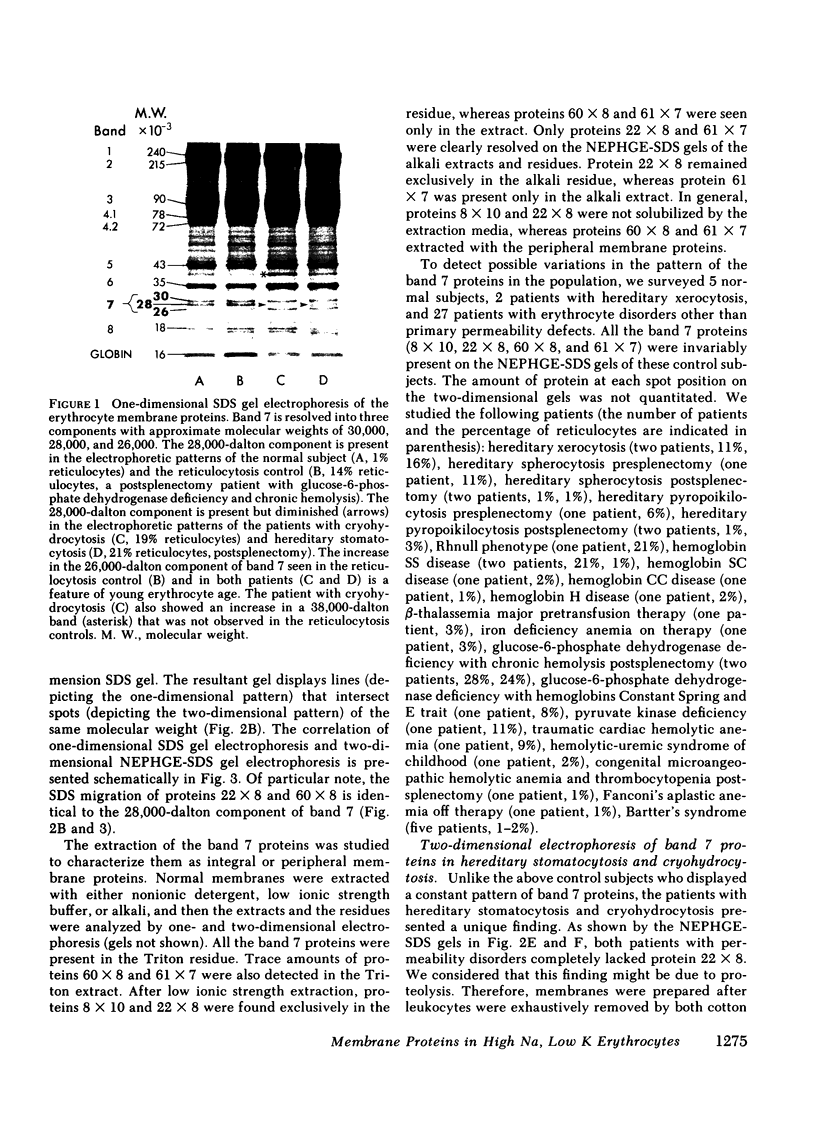
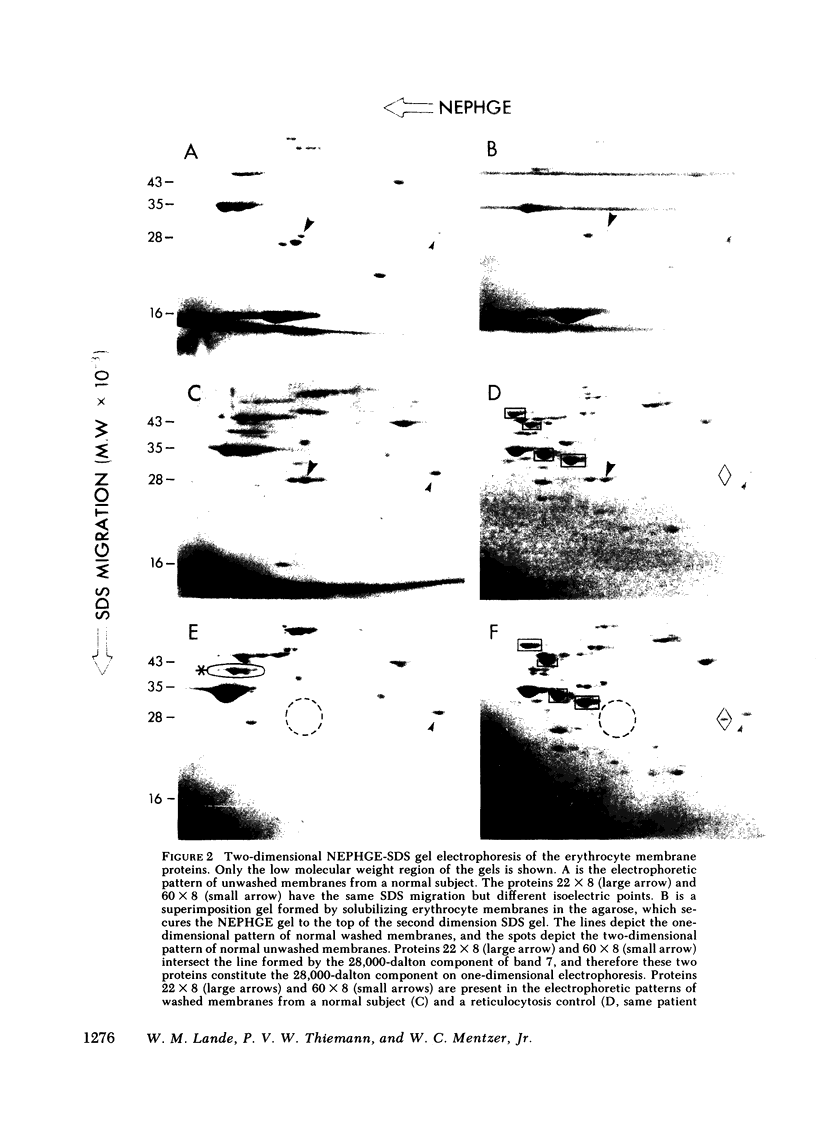
We investigated the erythrocyte membrane proteins of two patients with congenital hemolytic anemia due to increased permeability of the erythrocyte membrane to Na and K (hereditary stomatocytosis and cryohydrocytosis). One-dimensional sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) gel electrophoresis resolved the band 7 erythrocyte membrane proteins into three components with approximate molecular weights of 30,000, 28,000, and 26,000. The 28,000-dalton component was decreased in both patients with permeability disorders. Two-dimensional electrophoresis (nonequilibrium pH gradient electrophoresis in the first dimension combined with SDS gel electrophoresis in the first dimension combined with SDS gel electrophoresis in the second dimension) resolved the 28,000-dalton component from normal erythrocyte membranes into two proteins with different isoelectric points, designated 22 x 8 and 60 x 8. In the patients with hereditary stomatocytosis and cryohydrocytosis, 22 x 8 was completely absent, whereas 60 x 8 was detected as usual. In contrast, all the band 7 proteins (including 22 x 8) were invariably present in a survey of normal subjects and reticulocytosis controls. The unique finding of a missing band 7 protein in the patients with hereditary stomatocytosis and cryohydrocytosis raises the possibility that the absence of this protein is responsible for the increased Na and K permeability in these disorders.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agre P., Orringer E. P., Bennett V. Deficient red-cell spectrin in severe, recessively inherited spherocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 13;306(19):1155–1161. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205133061906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agre P., Orringer E. P., Chui D. H., Bennett V. A molecular defect in two families with hemolytic poikilocytic anemia: reduction of high affinity membrane binding sites for ankyrin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1566–1576. doi: 10.1172/JCI110411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banga J. P., Pinder J. C., Gratzer W. B., Linch D. C., Huehns E. R. An erythrocyte membrane-protein anomaly in march haemoglobinuria. Lancet. 1979 Nov 17;2(8151):1048–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92444-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienzle U., Bhadki S., Knüfermann H., Niethammer D., Kleihauer E. Abnormality of erythrocyte membrane protein in a case of congenital stomatocytosis. Klin Wochenschr. 1977 Jun 15;55(12):569–572. doi: 10.1007/BF01490509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harell D., Morrison M. Two-dimensional separation of erythrocyte membrane proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Mar;193(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R., Naeem I. Further studies on the characterization of cylindrin and torin, two extrinsic proteins of the erythrocyte membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 29;670(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R. Release of a macromolecular protein component from human erythrocyte ghosts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Apr 29;150(3):534–537. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. Chemical modification of membranes. I. Effects of sulfhydryl and amino reactive reagents on anion and cation permeability of the human red blood cell. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Aug;58(2):190–210. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.2.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. Chemical modification of membranes. II. Permeation paths for sulfhydryl agents. J Gen Physiol. 1971 Aug;58(2):211–223. doi: 10.1085/jgp.58.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Palek J., Prchal J., Castleberry R. P. Altered spectrin dimer-dimer association and instability of erythrocyte membrane skeletons in hereditary pyropoikilocytosis. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):597–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI110293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. C., Palek J. Spectrin tetramer-dimer equilibrium and the stability of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):586–588. doi: 10.1038/285586a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER G., TOWNES P. L., MACWHINNEY J. B. A NEW CONGENITAL HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA WITH DEFORMED ERYTHROCYTES ("STOMATOCYTES") AND REMARKABLE SUSCEPTIBILITY OF ERYTHROCYTES TO COLD HEMOLYSIS IN VITRO. I. CLINICAL AND HEMATOLOGIC STUDIES. Pediatrics. 1965 Jun;35:906–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malech H. L., Marchesi V. T. Hollow cylinder protein in the cytoplasm of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 28;670(3):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer W. C., Jr, Smith W. B., Goldstone J., Shohet S. B. Hereditary stomatocytosis: membrane and metabolism studies. Blood. 1975 Nov;46(5):659–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer W. C., Lam G. K., Lubin B. H., Greenquist A., Schrier S. L., Lande W. Membrane effects of imidoesters in hereditary stomatocytosis. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(2):275–288. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer W. C., Lubin B. H., Emmons S. Correction of the permeability defect in hereditary stomatocytosis by dimethyl adipimidate. N Engl J Med. 1976 May 27;294(22):1200–1204. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197605272942202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. R., Rickles F. R., Lichtman M. A., La Celle P. L., Bates J., Weed R. I. A new variant of hereditary hemolytic anemia with stomatocytosis and erythrocyte cation abnormality. Blood. 1971 Aug;38(2):184–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter W., Ungefehr K., Tillmann W. Role of the spleen in congenital stomatocytosis associated with high sodium-low potassium erythrocytes. Klin Wochenschr. 1981 Feb 16;59(4):173–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01477477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. Cross-linking the major proteins of the isolated erythrocyte membrane. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 14;66(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Yu J. Selective solubilization of proteins from red blood cell membranes by protein perturbants. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):220–232. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. M., Rothstein A., Weed R. I. Erythrocyte membrane sulfhydryl groups and cation permeability. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Apr;69(2):185–198. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tchernia G., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Deficiency of skeletal membrane protein band 4.1 in homozygous hereditary elliptocytosis. Implications for erythrocyte membrane stability. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):454–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI110275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Richards F. M. An approach to nearest neighbor analysis of membrane proteins. Application to the human erythrocyte membrane of a method employing cleavable cross-linkages. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8005–8018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. D., Ralston G. B. The 'hollow cylinder' protein of erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 5;554(2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Fischman D. A., Steck T. L. Selective solubilization of proteins and phospholipids from red blood cell membranes by nonionic detergents. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):233–248. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]