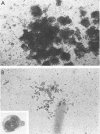
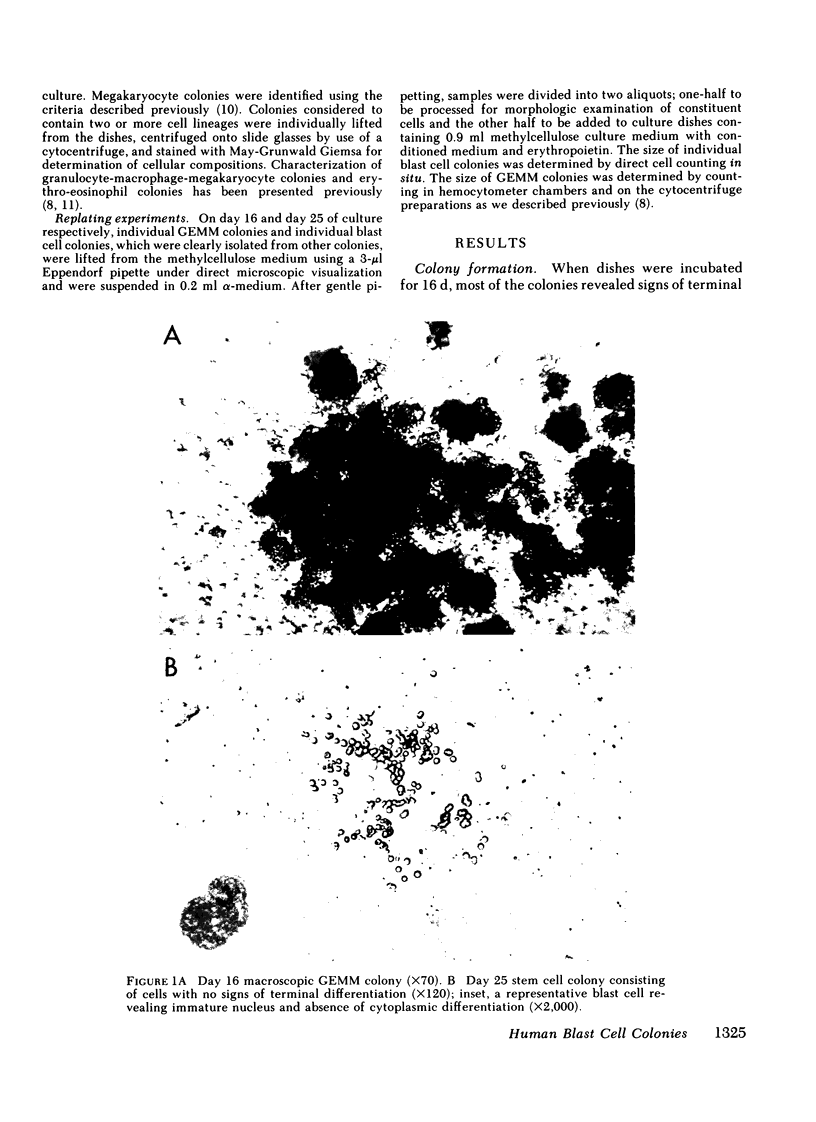
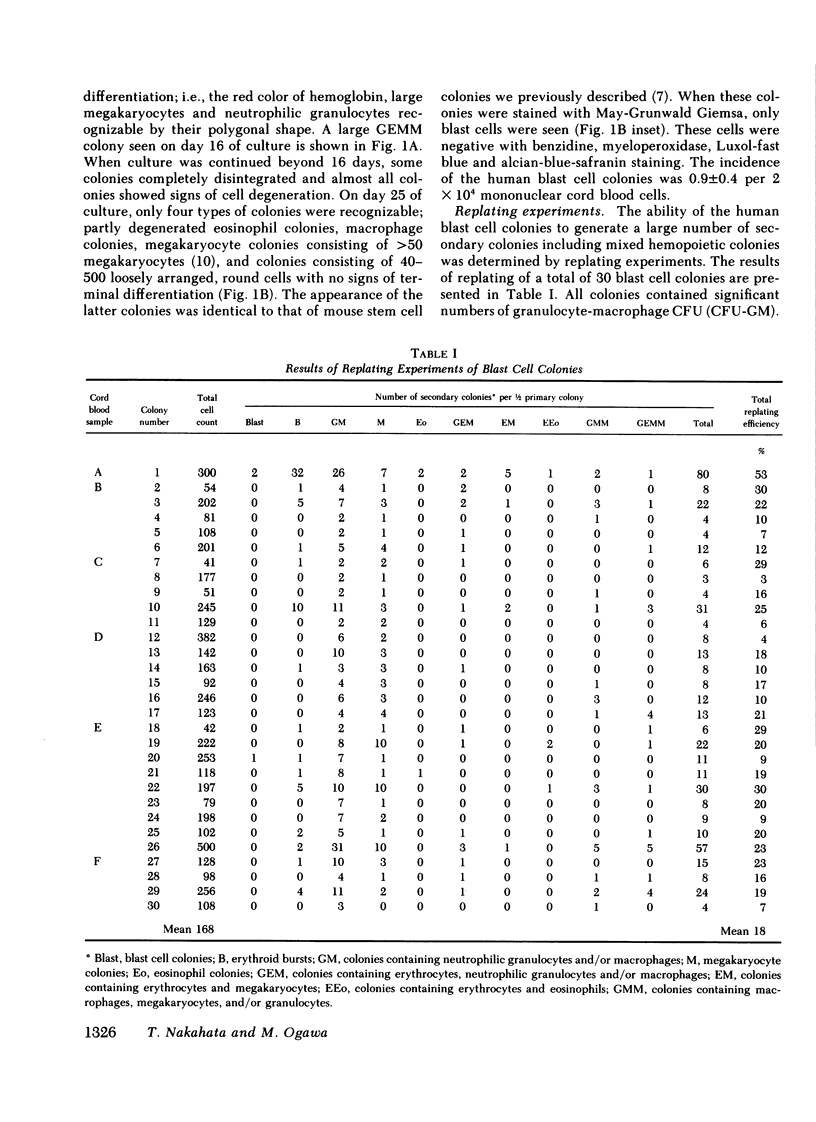
Abstract
We report identification of a unique class of human hemopoietic colony-forming cells with extensive ability to generate progenitors for secondary colonies. Mononuclear cells isolated from human umbilical cord blood formed colonies consisting of 40-500 blast cells after 25 d of incubation in methylcellulose culture in the presence of erythropoietin and medium conditioned by phytohemagglutinin-stimulated leukocytes. Replating of these blast cell colonies revealed that 100% of the primary colonies had the ability to generate secondary colonies, including multipotential colonies. These colonies could be distinguished from other hemopoietic colonies in situ by the complete absence of signs of terminal differentiation. Replating of granulocyte-erythrocyte-macrophage-megakaryocyte (GEMM) colonies, consisting of an average of 2 x 10(4) cells, revealed less capacity for secondary colony formation. This human blast cell colony assay may provide a method for quantitation of more primitive hemopoietic stem cells than progenitors for GEMM colonies (CFU-GEMM) in man.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash R. C., Detrick D. A., Zanjani E. D. Studies of human pluripotential hemopoietic stem cells (CFU-GEMM) in vitro. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauser A. A., Messner H. A. Identification of megakaryocytes, macrophages, and eosinophils in colonies of human bone marrow containing neurtophilic granulocytes and erythroblasts. Blood. 1979 May;53(5):1023–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara H., Ogawa M. Murine hemopoietic colonies in culture containing normoblasts, macrophages, and megakaryocytes. Am J Hematol. 1978;4(1):23–34. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830040105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Eaves A. C., Eaves C. J. Self-renewal of hemopoietic stem cells during mixed colony formation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3629–3633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Sieber F., Winterhalter K. H. Erythroid colony formation in cultures of mouse and human bone marrow: analysis of the requirement for erythropoietin by gel filtration and affinity chromatography on agarose-concanavalin A. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):309–320. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R. Colony formation in agar by adult bone marrow multipotential hemopoietic cells. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Jun;103(3):371–383. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Metcalf D. Pure and mixed erythroid colony formation in vitro stimulated by spleen conditioned medium with no detectable erythropoietin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3879–3882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner H. A., Izaquirre C. A., Jamal N. Identification of T lymphocytes in human mixed hemopoietic colonies. Blood. 1981 Aug;58(2):402–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messner H. A., Jamal N., Izaguirre C. The growth of large megakaryocyte colonies from human bone marrow. J Cell Physiol Suppl. 1982;1:45–51. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041130410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Ogawa M. Clonal origin of murine hemopoietic colonies with apparent restriction to granuclocyte-macrophage-megakaryocyte (GMM) differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Jun;111(3):239–246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041110304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Ogawa M. Identification in culture of a class of hemopoietic colony-forming units with extensive capability to self-renew and generate multipotential hemopoietic colonies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3843–3847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.12.3843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata T., Spicer S. S., Ogawa M. Clonal origin of human erythro-eosinophilic colonies in culture. Blood. 1982 Apr;59(4):857–864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]