Abstract
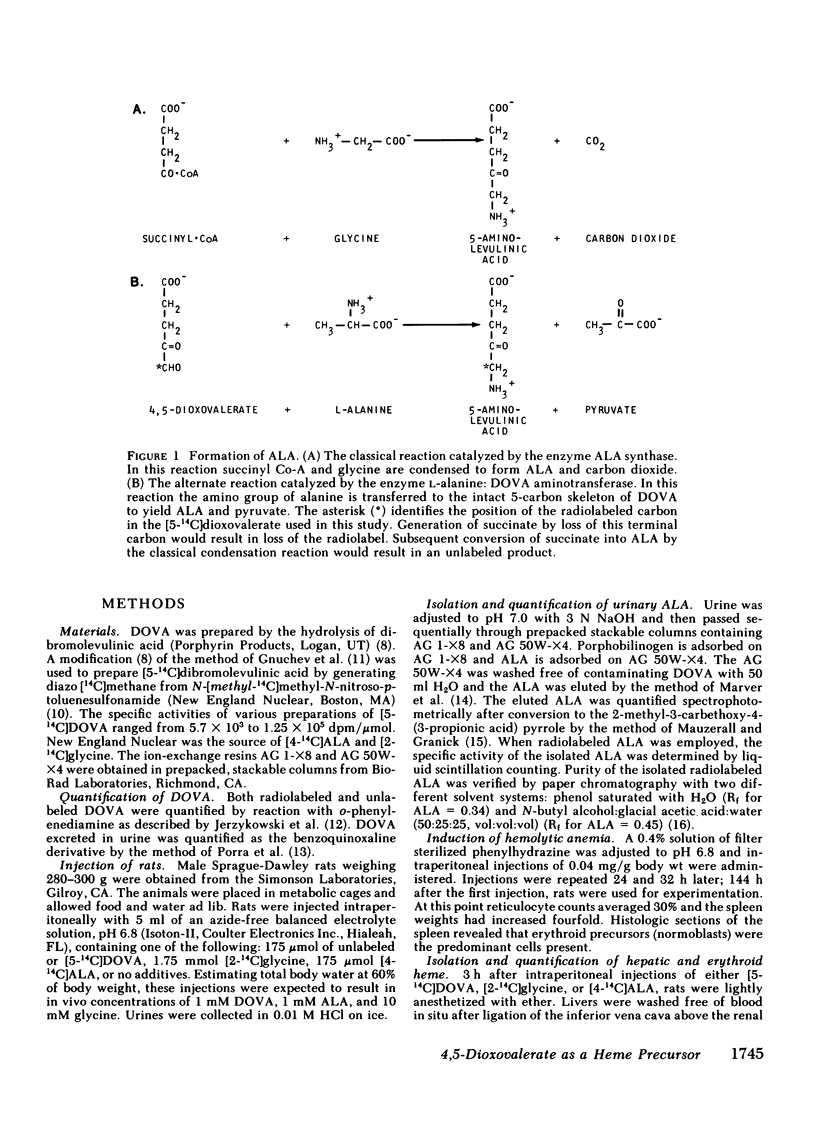
We previously demonstrated an alternate pathway for the biosynthesis of 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) in bovine liver mitochondria and of tetrapyrroles in suspensions of rat hepatocytes (1980. J. Biol. Chem. 255: 3742; 1981. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 78: 5335). This pathway involves a transamination reaction that incorporates the intact 5-carbon skeleton of 4,5-dioxovaleric acid (DOVA) into ALA. We investigated this alternate pathway in vivo by the intraperitoneal injection of DOVA into rats. Incorporation of DOVA and [5-14C]DOVA into urinary ALA and hepatic and erythroid heme was quantified and compared with the incorporation of [4-14C]ALA and [2-14C]glycine into heme. Within 3 h of injection of 175 mumol of DOVA, urinary ALA excretion increased 2.4-fold over controls. After injection of [5-14C]DOVA, 0.11% of the radioactivity was recovered as urinary ALA, which quantitatively accounted for the 2.4-fold increase in ALA excretion. After the injection 175 mumol of [5-14C]DOVA, 0.14% of the radioactivity was recovered after 3 h as hepatic heme. The injection of 1.75 mmol of [2-14C]glycine or 175 mumol of [4-14C]ALA resulted in recovery of 0.2 and 3.4%, respectively, of the radioactivity as hepatic heme after 3 h. These doses of radiolabeled DOVA, glycine, and ALA were injected into rats with phenylhydrazine-induced anemia. Recovery of radioactivity after 3 h as splenic (erythroid) heme was 0.35% for DOVA, 0.072% for glycine, and 0.25% for ALA. These studies establish that the intact 5-carbon skeleton of DOVA can be incorporated into ALA and heme in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERLIN N. I., NEUBERGER A., SCOTT J. J. The metabolism of delta -aminolaevulic acid. 1. Normal pathways, studied with the aid of 15N. Biochem J. 1956 Sep;64(1):80–90. doi: 10.1042/bj0640080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUNSHTEIN A. E., POZNANSKAIA A. A., SPRYSHKOVA R. A., GNUCHEV N. V. O VKLIUCHENII UGLERODNOGO ATOMA C-5 DELTA-AMINOLEVULINOVO I KISLOTY V INOZINOVUIU KISLOTU I GIPOKSANTIN V PECHENI GOLUBIA. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR. 1964 Aug 1;157:982–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajkowski A. S., Friedmann H. C. delta-Aminolevulinic acid formation. Purification and properties of alanine:4,5-dioxovalerate, aminotransferase and isolation of 4,5-dioxovalerate from Clostridium tetanomorphum. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2207–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Castelfranco P. A. 14 C incorporation from exogenous compounds into -aminolevulinic acid by greening cucumber cotyledons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 1;52(1):143–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90966-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale S. I., Gough S. P., Granick S. Biosynthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid from the intact carbon skeleton of glutamic acid in greening barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2719–2723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumm P. J., Thomas G. A., Friedmann H. C. The role of 4,5-dioxovaleric acid in porphyrin and vitamin B12 formation by clostridia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 29;104(2):814–822. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90710-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowdle E., Mustard P., Spong N., Eales L. The metabolism of (5-14C)delta-aminolaevulic acid in normal and porphyric human subjects. Clin Sci. 1968 Apr;34(2):233–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerzykowski T., Winter R., Matuszewski W. gamma,delta-Dioxovalerate as a substrate for the glyoxalase enzyme system. Biochem J. 1973 Dec;135(4):713–719. doi: 10.1042/bj1350713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurgenson J. E., Beale S. I., Troxler R. F. Biosynthesis of delta-aminolevulinic acid in the unicellular rhodophyte, cyanidium caldarium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):149–157. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80285-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissel H. J., Heilmeyer L., Jr Nachweis und Bestimmung von gamma-delta-Dioxovaleriansäure: reversible Umwandlung von gamma-delta-Dioxovaleriansäure und delta-Aminolävulinsäure in Ratten. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 18;177(1):78–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein O., Dörnemann D., Senger H. Two biosynthetic pathways to 5-aminolevulinic acid in algae. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(5-6):725–728. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90152-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M., Schacter B. A., Zipursky A., Israels L. G. The nonerythropoietic component of early bilirubin. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jun;47(6):1281–1294. doi: 10.1172/JCI105820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAUZERALL D., GRANICK S. The occurrence and determination of delta-amino-levulinic acid and porphobilinogen in urine. J Biol Chem. 1956 Mar;219(1):435–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMETH A. M., RUSSELL C. S., SHEMIN D. The succinate-glycine cycle. II. Metabolism of delta-aminolevulinic acid. J Biol Chem. 1957 Nov;229(1):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D. L., Baker-Cohen K. F., Shemin D. Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1224–1230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nandi D. L., Shemin D. Delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. 3. Mechanism of porphobilinogen synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1236–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi T., Mori R. Biosynthesis of porphyrin precursors in mammals. Identity of alanine: gamma, delta-dioxovalerate aminotransferase with alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10335–10339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porra R. J., Klein O., Dörnemann D., Senger H. A fast and convenient assay for 4,5-dioxovaleric acid in biological systems. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(5-6):735–737. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porra R. J., Klein O., Dörnemann D., Senger H. A simple method for the rapid determination of 4,5-dioxovaleric acid in the presence of 2-oxoglutarate and other 2-oxocarboxylic acids. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980;361(2):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H. Formation of bilirubin from erythroid and nonerythroid sources. Semin Hematol. 1972 Jan;9(1):43–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Lester R., Crigler J. F., Jr, Tsong M. Early-labeled peak of bile pigment in man. Studies with glycine-14C and delta-aminolevulinic acid-3H. N Engl J Med. 1967 Dec 21;277(25):1323–1329. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196712212772501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. H., Tsong M., Brown B. W., Schmid R. The sources of bile pigment in the rat: studies of the "early labeled" fraction. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1569–1586. doi: 10.1172/JCI105463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigesada K. Possible occurrence of a succinate-glycine cycle in Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Biochem. 1972 Jun;71(6):961–972. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschudy D. P., Hess R. A., Frykholm B. C. Inhibition of delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydrase by 4,6-dioxoheptanoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9915–9923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Kushner J. P., Burnham B. F. Biosynthesis of porphyrin precursors. Purification and characterization of mammalian L-alanine:gamma,delta-dioxovaleric acid aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3742–3747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Kushner J. P., Burnham B. F. Biosynthesis of porphyrin precursors: kinetic studies on mammalian L-alanine: gamma,delta-dioxovaleric acid aminotransferase. Int J Biochem. 1980;12(5-6):739–744. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(80)90155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F. K., Koch J., Stokstad E. L. Metabolism of 5-hydroxy-4-keto-valeric acid in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 11;40(3):576–582. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90941-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



