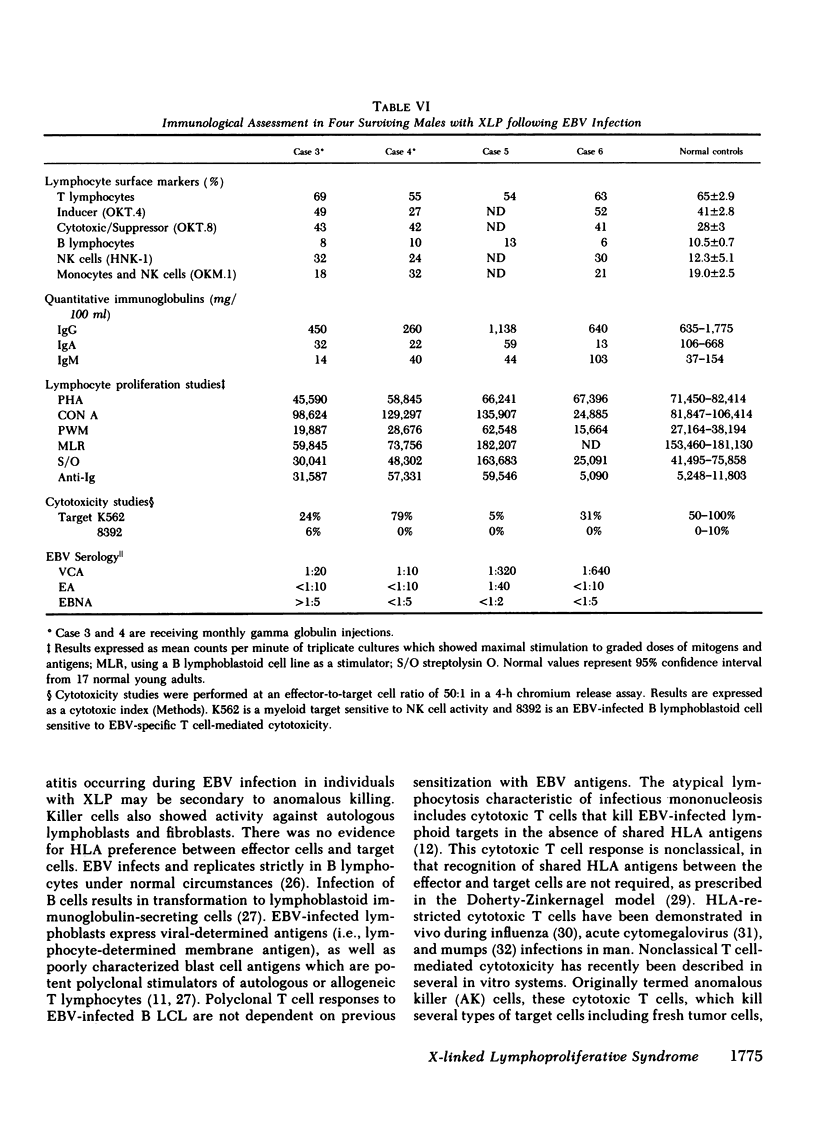
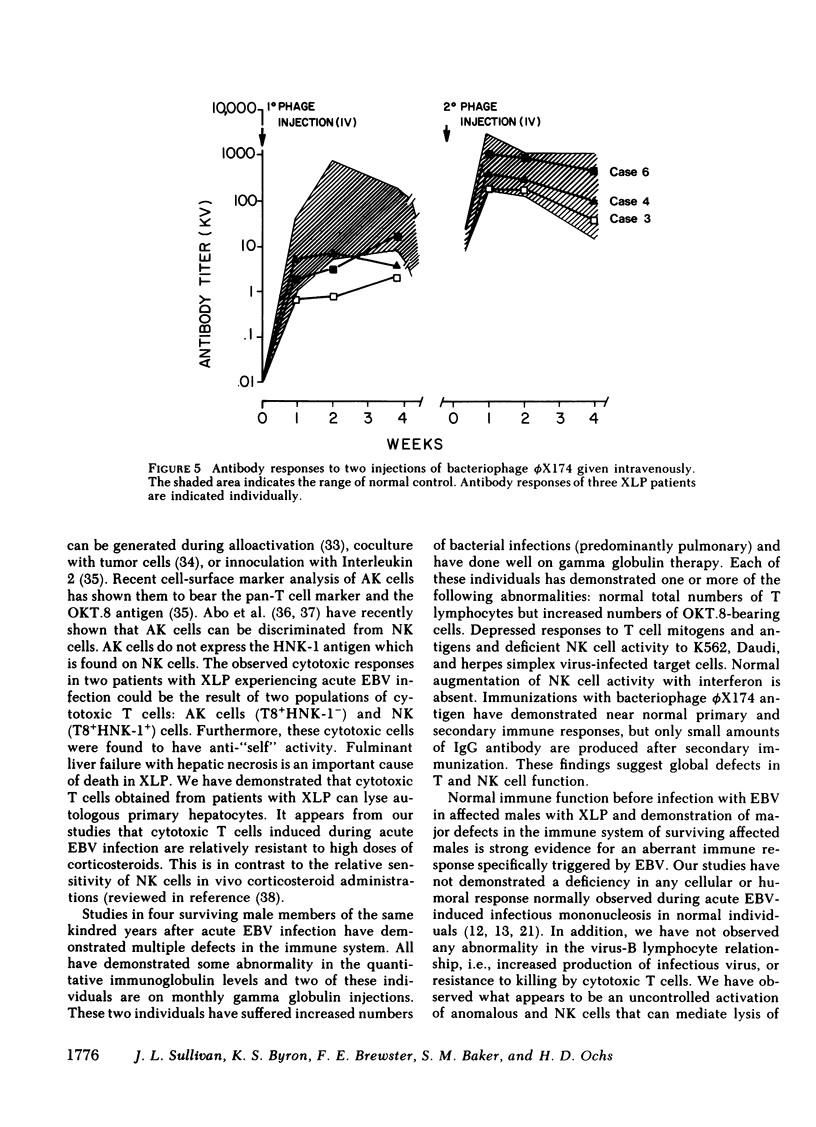
Abstract
The X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome is characterized by immunodeficiency to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) manifested by severe or fatal infectious mononucleosis and acquired immunodeficiency. We studied immune responses in six males of a well-characterized kindred with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Two males were studied before and during acute fatal EBV infection. Both individuals demonstrated normal cellular and humoral immunity before EBV infection. During acute EBV infection, both individuals developed vigorous cytotoxic cellular responses against EBV-infected and -uninfected target cells. Anomalous killer and natural killer T cell activity was demonstrated against a variety of lymphoid cell lines, autologous fibroblasts and autologous hepatocytes. Effector cells responsible for anomalous killing reacted with a pan-T cell monoclonal antibody, and belonged to the OKT.8 T cell subset. Death in each case was caused by liver failure, but one patient developed extensive liver necrosis, whereas the other developed a massive infiltration of the liver with EBV-infected immunoblasts after aggressive immunosuppressive therapy. Immunological studies were performed on four males who had survived EBV infection years previously. They demonstrated global cellular immune defects with deficiencies of lymphocyte proliferative responses to mitogens and antigens, humoral immune deficiencies, abnormalities of regulatory T cell subsets and deficient natural killer cell activity. We propose that an aberrant immune response triggered by acute EBV infection results in unregulated anomalous killer and natural killer cell activity against EBV infected and uninfected cells. These studies suggest that global immune defects appearing in males with X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome who survive EBV infection are epiphenomenon.
Full text
PDF


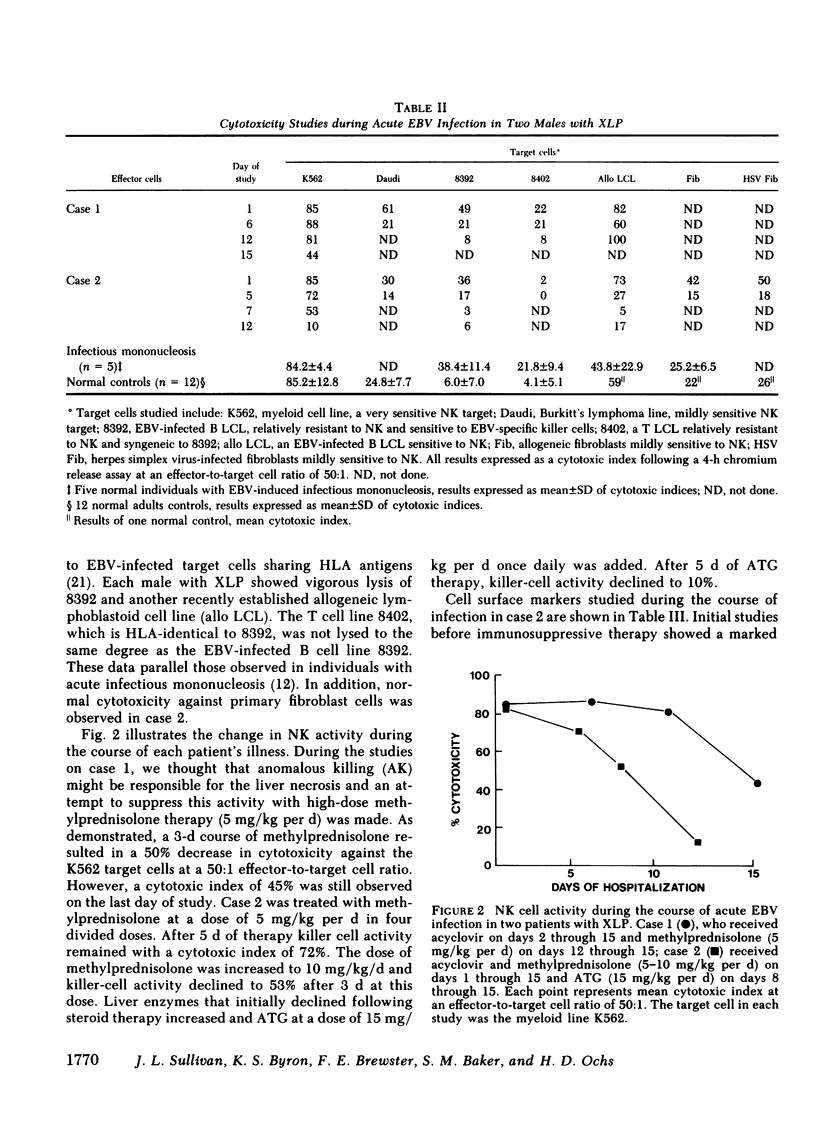
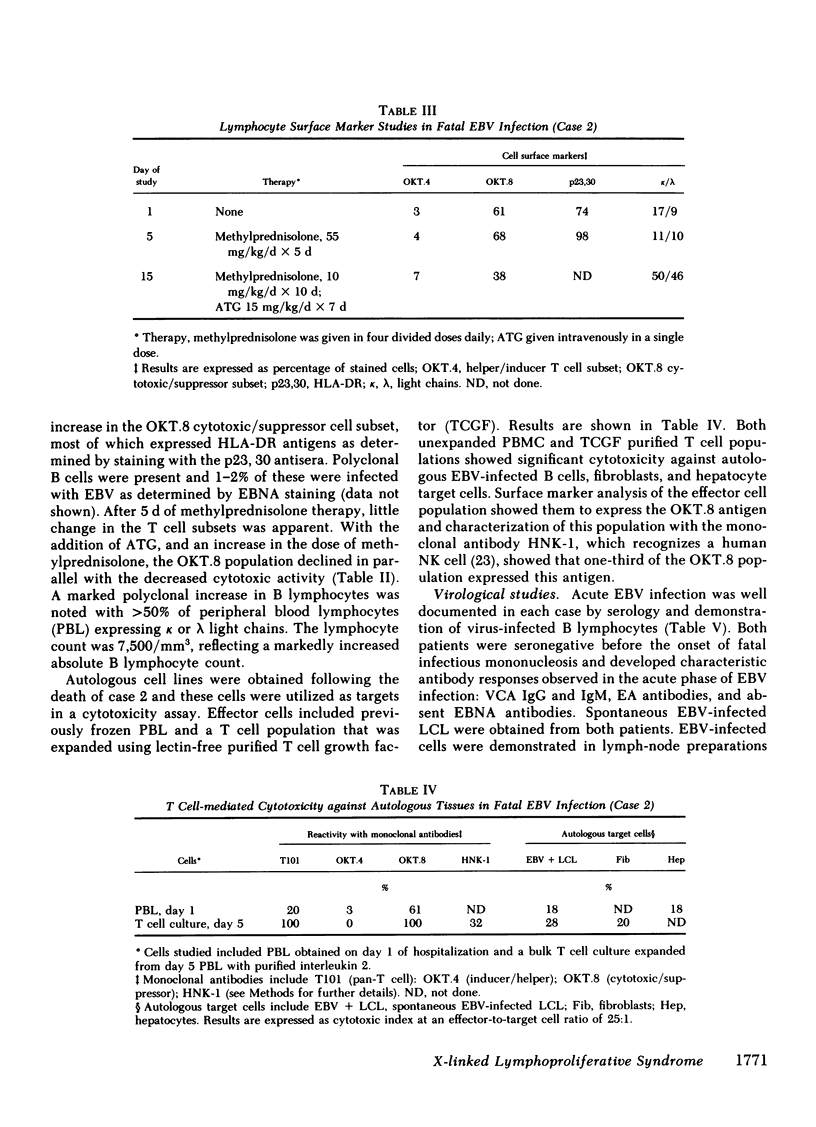
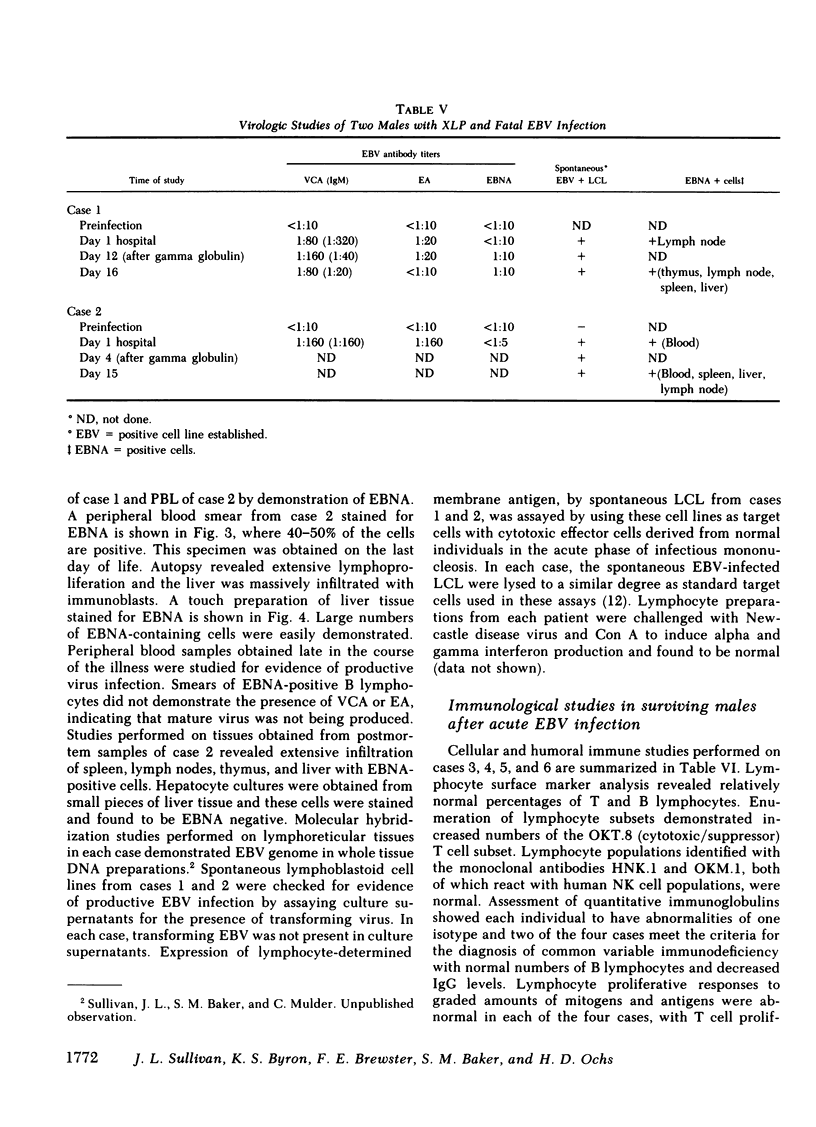

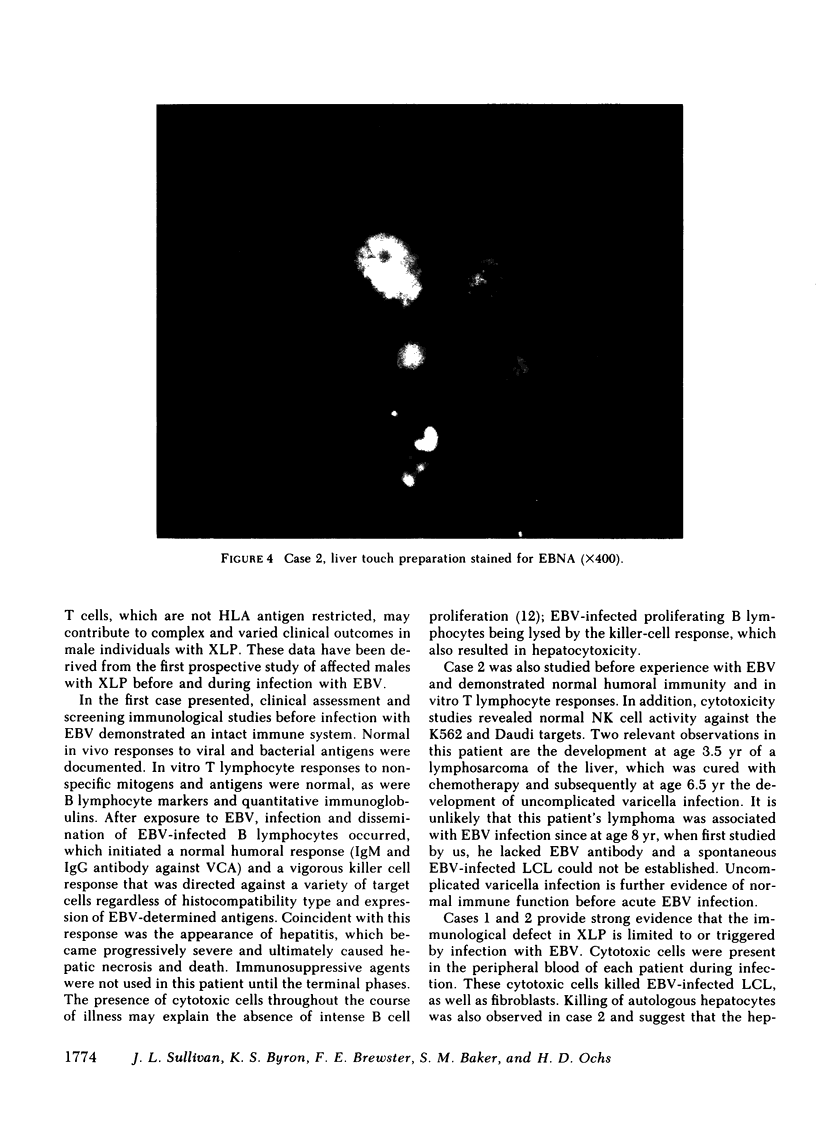


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo T., Balch C. M. A differentiation antigen of human NK and K cells identified by a monoclonal antibody (HNK-1). J Immunol. 1981 Sep;127(3):1024–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. II. Distinguishing phenotypic and functional properties of natural killer cells from activated NK-like cells. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1758–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abo T., Cooper M. D., Balch C. M. Characterization of HNK-1+ (Leu-7) human lymphocytes. I. Two distinct phenotypes of human NK cells with different cytotoxic capability. J Immunol. 1982 Oct;129(4):1752–1757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar R. S., DeLor C. J., Clausen K. P., Hurtubise P., Henle W., Hewetson J. F. Fatal infectious mononucleosis in a family. N Engl J Med. 1974 Feb 14;290(7):363–367. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197402142900704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird A. G., Britton S., Ernberg I., Nilsson K. Characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus activation of human B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):832–839. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching C., Lopez C. Natural killing of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected target cells: normal human responses and influence of antiviral antibody. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):49–56. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.49-56.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby B. M., Shaw J. E., Elion G. B., Pagano J. S. Effect of acyclovir [9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine] on Epstein-Barr virus DNA replication. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):560–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.560-568.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cupps T. R., Fauci A. S. Corticosteroid-mediated immunoregulation in man. Immunol Rev. 1982;65:133–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. T-cell-mediated immunopathology in viral infections. Transplant Rev. 1974;19(0):89–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1974.tb00129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis F. A., Rook A. H., Qi Y. H., Schild G. C., Riley D., Pratt R., Potter C. W. HLA restricted virus-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses to live and inactivated influenza vaccines. Lancet. 1981 Oct 24;2(8252):887–891. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fothergill J. J., Wistar R., Jr, Woody J. N., Parker D. C. A mitogen for human B cells: anti-Ig coupled to polyacrylamide beads activates blood mononuclear cells independently of T cells. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):1945–1949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton J. K., Paquin L. A., Sullivan J. L., Maurer H. S., Cruzi F. G., Provisor A. J., Steuber C. P., Hawkins E., Yawn D., Cornet J. A. X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome registry report. J Pediatr. 1980 Apr;96(4):669–673. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80735-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth H. W., Kress L., Kress H. G., Ott H. F., Eckert G. Demonstration of primary cytotoxic T cells in venous blood and cerebrospinal fluid of children with mumps meningitis. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2411–2415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangi R. J., Niederman J. C., Kelleher J. E., Jr, Dwyer J. M., Evans A. S., Kantor F. S. Depression of cell-mediated immunity during acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1974 Nov 28;291(22):1149–1153. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197411282912202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provisor A. J., Iacuone J. J., Chilcote R. R., Neiburger R. G., Crussi F. G. Acquired agammaglobulinemia after a life-threatening illness with clinical and laboratory features of infectious mononucleosis in three related male children. N Engl J Med. 1975 Jul 10;293(2):62–65. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197507102930202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., Cassel C. K., Yang J. P., Harper R. X-linked recessive progressive combined variable immunodeficiency (Duncan's disease). Lancet. 1975 Apr 26;1(7913):935–940. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purtilo D. T., DeFlorio D., Jr, Hutt L. M., Bhawan J., Yang J. P., Otto R., Edwards W. Variable phenotypic expression of an X-linked recessive lymphoproliferative syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1977 Nov 17;297(20):1077–1080. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197711172972001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Jr, Kirmani N., Rook A. H., Manischewitz J. F., Jackson L., Moreschi G., Santos G. W., Saral R., Burns W. H. Cytotoxic t cells in cytomegalovirus infection: HLA-restricted T-lymphocyte and non-T-lymphocyte cytotoxic responses correlate with recovery from cytomegalovirus infection in bone-marrow-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jul 1;307(1):7–13. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198207013070102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedman B. M., Klein G. Cellular localization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated complement-fixing antigen in producer and non-producer lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1973 May;11(3):499–520. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910110302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J., Smith D., Niederman J. Mitotic EBNA-positive lymphocytes in peripheral blood during infectious mononucleosis. Nature. 1980 Sep 25;287(5780):334–335. doi: 10.1038/287334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Sullivan J. L., Periman P. O., Perlin E. Cell-mediated immunity to Epstein-Barr-virus-transformed lymphoblastoid cells in acute infectious mononucleosis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 4;293(23):1159–1163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512042932301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto K., Freed H. J., Purtilo D. T. Antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus in families with the X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):921–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J. K., Golub S. H. Studies on cytotoxicity generated in human mixed lymphocyte cultures. I. Time course and target spectrum of several distinct concomitant cytotoxic activities. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1415–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J., Sakamoto K., Ip S. H., Hansen P. W., Purtilo D. T. Abnormal lymphocyte subsets of X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2618–2620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeley J., Svedmyr E., Weiland O., Klein G., Moller E., Eriksson E., Andersson K., van der Waal L. Epstein Barr virus selective T cells in infectious mononucleosis are not restricted to HLA-A and B antigens. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):293–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Byron K. S., Brewster F. E., Purtilo D. T. Deficient natural killer cell activity in x-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):543–545. doi: 10.1126/science.6158759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Byron K. S., Brewster F. E., Sakamoto K., Shaw J. E., Pagano J. S. Treatment of life-threatening Epstein-Barr virus infection with acyclovir. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Ochs H. D., Schiffman G., Hammerschlag M. R., Miser J., Vichinsky E., Wedgwood R. J. Immune response after splenectomy. Lancet. 1978 Jan 28;1(8057):178–181. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90612-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan J. L., Ochs H. D., Wedgwood R. J. In vitro responses to a B-lymphoblastoid cell line in immunodeficiency diseases. J Clin Immunol. 1982 Apr;2(2):150–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00916899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vánky F., Gorsky T., Gorsky Y., Masucci M. G., Klein E. Lysis of tumor biopsy cells by autologous T lymphocytes activated in mixed cultures and propagated with T cell growth factor. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):83–95. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedgwood R. J., Ochs H. D., Davis S. D. The recognition and classification of immunodeficiency diseases with bacteriophage phiChi 174. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1975;11(1):331–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]