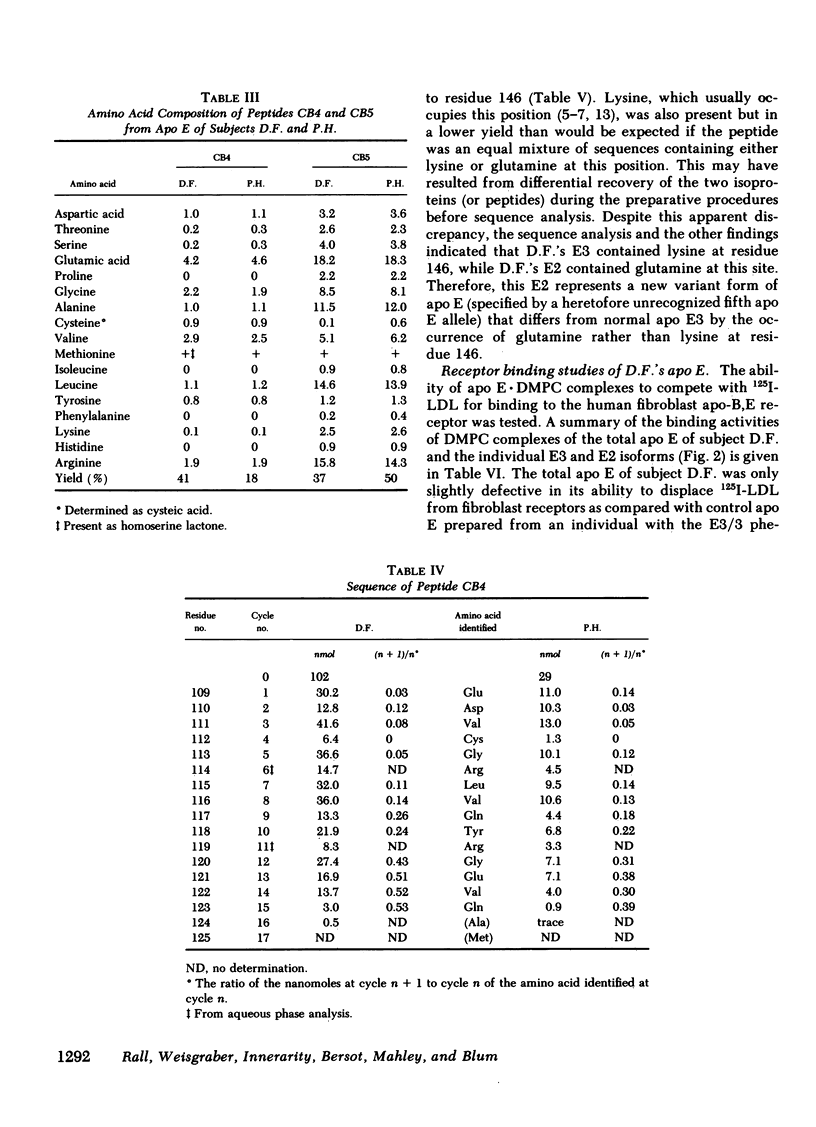
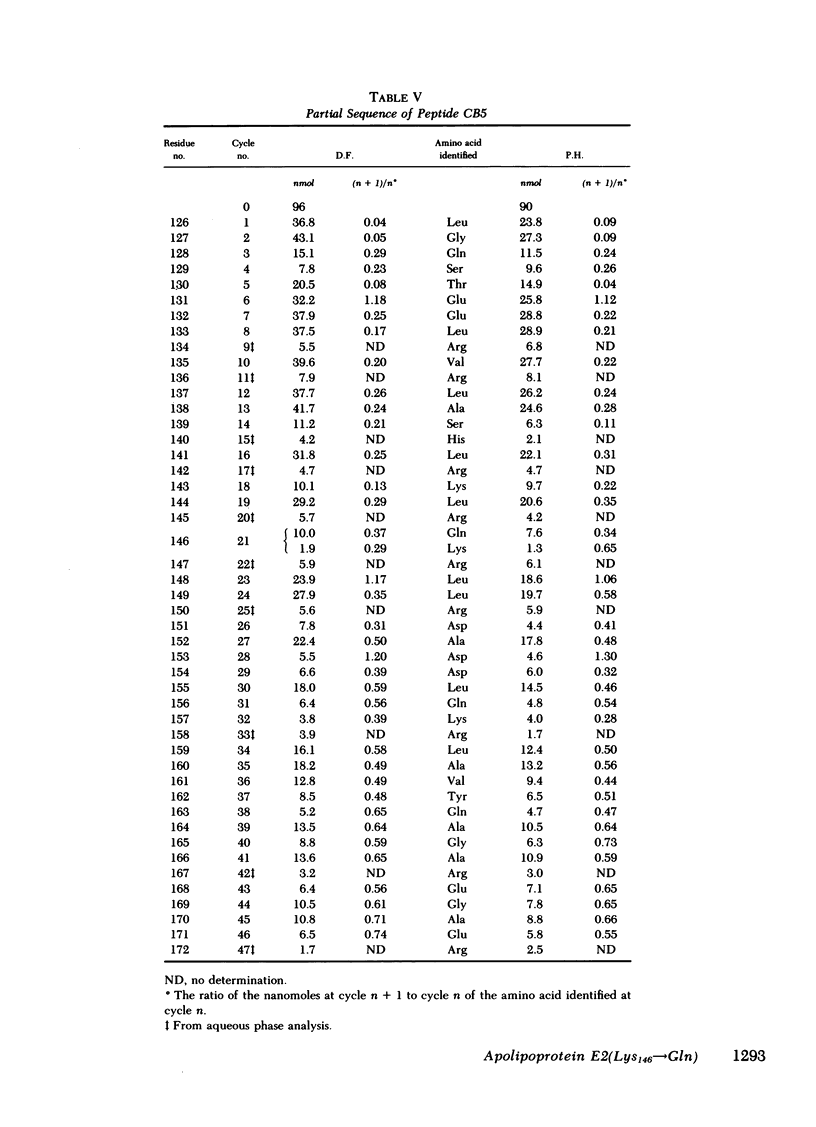
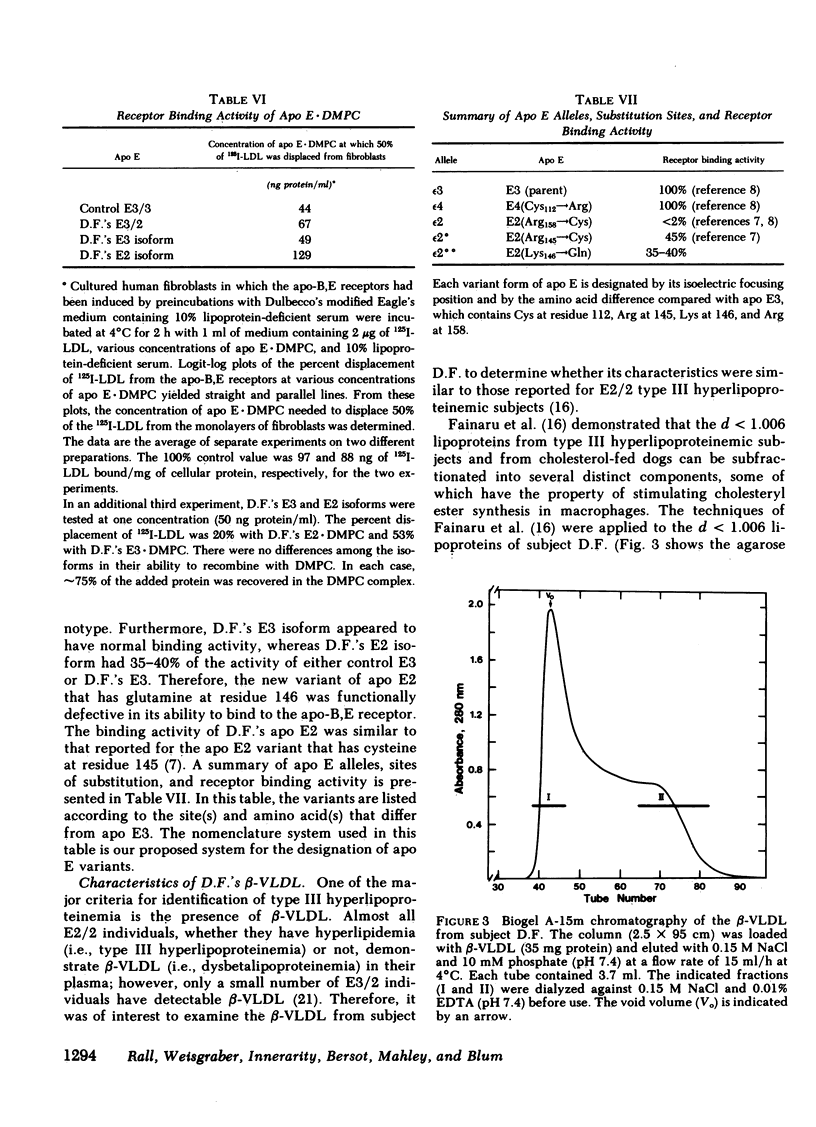
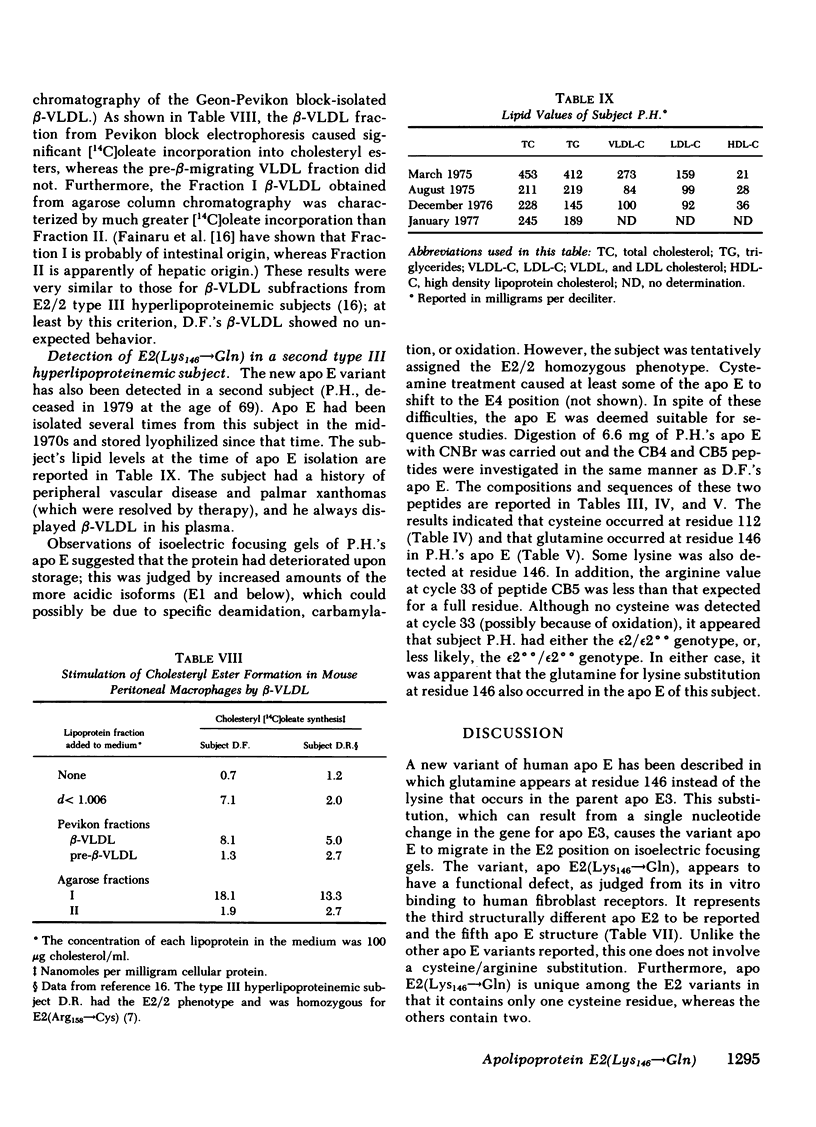
Abstract
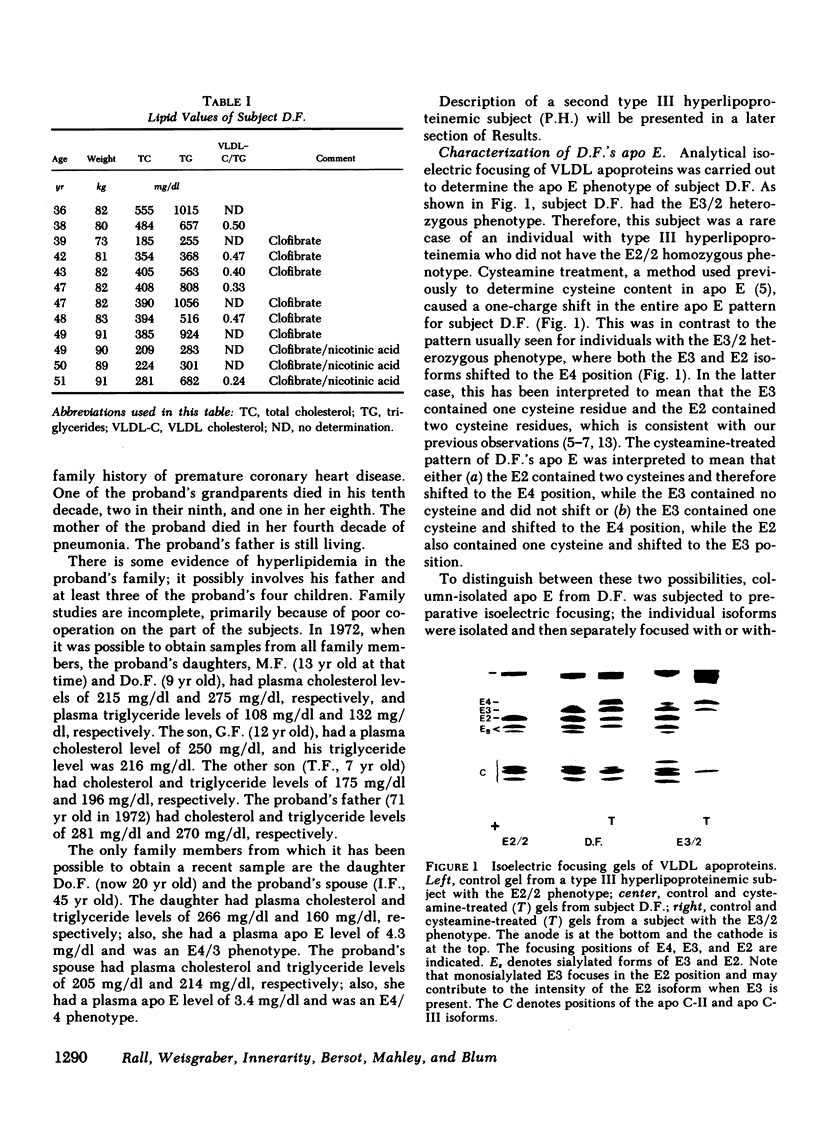
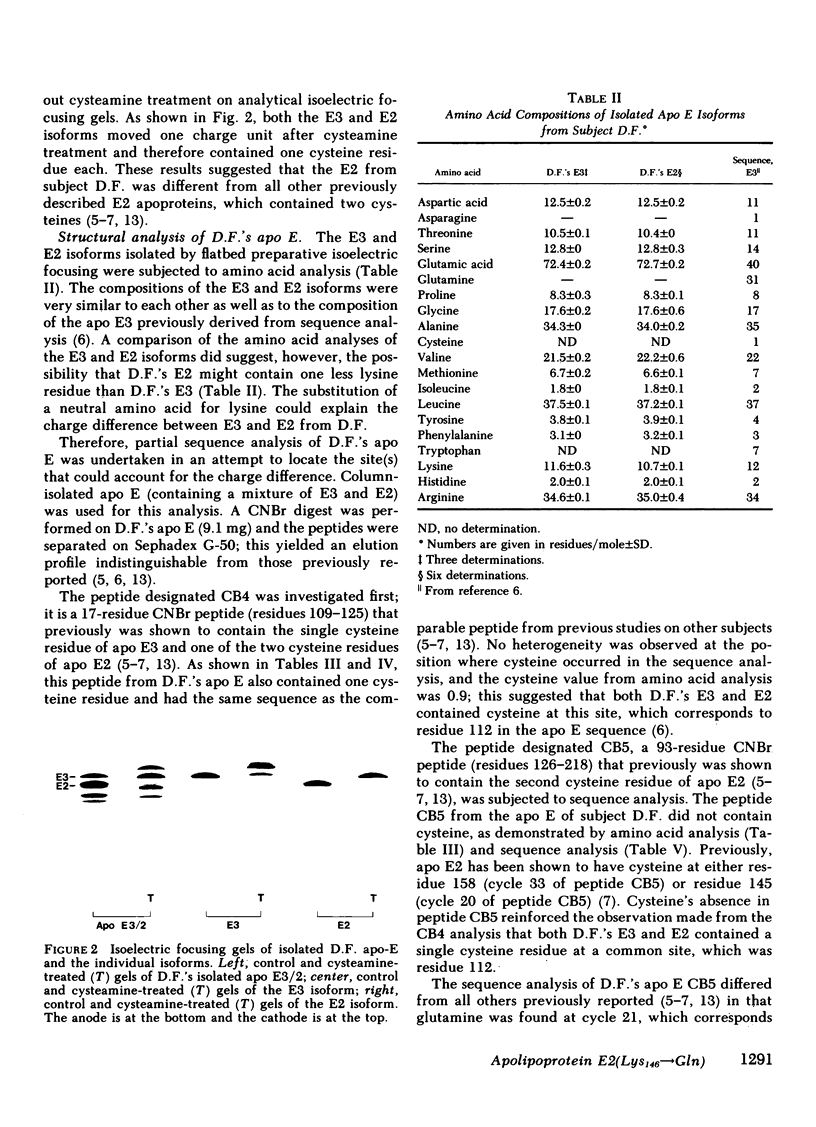
A type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject having the apolipoprotein E (apo E) phenotype E3/2 was identified. From isoelectric focusing experiments in conjunction with cysteamine treatment (a method that measures cysteine content in apo E), the E2 isoform of this subject was determined to have only one cysteine residue, in contrast to all previously studied E2 apoproteins, which had two cysteines. This single cysteine was shown to be at residue 112, the same site at which it occurs in apo E3. From amino acid and sequence analyses, it was determined that this apo E2 differed from apo E3 by the occurrence of glutamine rather than lysine at residue 146. When phospholipid X protein recombinants of the subject's isolated E3 and E2 isoforms were tested for their ability to bind to the human fibroblast apo-B,E receptor, it was found that the E3 bound normally (compared with an apo E3 control) but that the E2 had defective binding (approximately 40% of normal). Although they contained E3 as well as E2, the beta-very low density lipoproteins (beta-VLDL) from this subject were very similar in character to the beta-VLDL from an E2/2 type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject; similar subfractions could be obtained from each subject and were shown to have a similar ability to stimulate cholesteryl ester accumulation in mouse peritoneal macrophages. The new apo E2 variant has also been detected in a second type III hyperlipoproteinemic subject.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTLETT G. R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):466–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum C. B., Aron L., Sciacca R. Radioimmunoassay studies of human apolipoprotein E. J Clin Invest. 1980 Dec;66(6):1240–1250. doi: 10.1172/JCI109975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow J. L., Zannis V. I., SanGiacomo T. R., Third J. L., Tracy T., Glueck C. J. Studies of familial type III hyperlipoproteinemia using as a genetic marker the apoE phenotype E2/2. J Lipid Res. 1982 Nov;23(8):1224–1235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Mahley R. W., Hamilton R. L., Innerarity T. L. Structural and metabolic heterogeneity of beta-very low density lipoproteins from cholesterol-fed dogs and from humans with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):702–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghiselli G., Gregg R. E., Zech L. A., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Phenotype study of apolipoprotein E isoforms in hyperlipoproteinaemic patients. Lancet. 1982 Aug 21;2(8295):405–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90439-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Cholesteryl ester accumulation in macrophages resulting from receptor-mediated uptake and degradation of hypercholesterolemic canine beta-very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1839–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazzard W. R., Warnick G. R., Utermann G., Albers J. J. Genetic transmission of isoapolipoprotein E phenotypes in a large kindred: relationship to dysbetalipoproteinemia and hyperlipidemia. Metabolism. 1981 Jan;30(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Mahley R. W. Binding of arginine-rich (E) apoprotein after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the low density lipoprotein receptors of fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4186–4190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. Canine lipoproteins and atherosclerosis. II. Characterization of the plasma lipoproteins associated with atherogenic and nonatherogenic hyperlipidemia. Circ Res. 1974 Nov;35(5):722–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.5.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagnan A., Havel R. J., Kane J. P., Kotite L. Characterization of human very low density lipoproteins containing two electrophoretic populations: double pre-beta lipoproteinemia and primary dysbetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res. 1977 Sep;18(5):613–622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Identical structural and receptor binding defects in apolipoprotein E2 in hypo-, normo-, and hypercholesterolemic dysbetalipoproteinemia. J Clin Invest. 1983 Apr;71(4):1023–1031. doi: 10.1172/JCI110829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Structural basis for receptor binding heterogeneity of apolipoprotein E from type III hyperlipoproteinemic subjects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4696–4700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall S. C., Jr, Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W. Human apolipoprotein E. The complete amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4171–4178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Kovanen P. T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Utermann G., Weber W., Havel R. J., Kotite L., Kane J. P., Innerarity T. L. Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Apolipoprotein E (role in lipoprotein metabolism and pathophysiology of hyperlipoproteinemia type III). Ric Clin Lab. 1982 Jan-Mar;12(1):23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Hees M., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Jaeschke M., Menzel J. Familial hyperlipoproteinemia type III: deficiency of a specific apolipoprotein (apo E-III) in the very-low-density lipoproteins. FEBS Lett. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):352–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)81125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Langenbeck U., Beisiegel U., Weber W. Genetics of the apolipoprotein E system in man. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):339–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Pruin N., Steinmetz A. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. III. Effect of a single polymorphic gene locus on plasma lipid levels in man. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G., Vogelberg K. H., Steinmetz A., Schoenborn W., Pruin N., Jaeschke M., Hees M., Canzler H. Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E. II. Genetics of hyperlipoproteinemia type III. Clin Genet. 1979 Jan;15(1):37–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Abnormal lipoprotein receptor-binding activity of the human E apoprotein due to cysteine-arginine interchange at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2518–2521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W. Human E apoprotein heterogeneity. Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):9077–9083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Characterization of a unique human apolipoprotein E variant associated with type III hyperlipoproteinemia. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):1759–1762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Breslow J. L. Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zannis V. I., Just P. W., Breslow J. L. Human apolipoprotein E isoprotein subclasses are genetically determined. Am J Hum Genet. 1981 Jan;33(1):11–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]