Abstract
Receptors on erythrocytes and malaria parasites mediate specific attachment and junction formation between these cells that lead to invasion of the erythrocytes. We identified monoclonal antibody A9 and its subclone A9D3 that bound to rhesus erythrocytes and blocked invasion of the erythrocytes by Plasmodium knowlesi merozoites. The monoclonal antibodies did not block attachment, the initial step in invasion, although swelling and crenation of the erythrocyte, which normally occur after attachment, were rarely observed in the presence of antibody. The monoclonal antibody immunoprecipitated rhesus erythrocyte band 3. It bound to erythrocytes of another Old World monkey, the kra monkey, but not to erythrocytes of New World monkeys, chimpanzees, or man. Since the antibody did not bind to human erythrocytes, we could test for nonspecific toxicity to the parasite by studying the effect of the ascites and purified antibody on invasion of human erythrocytes. The antibody caused a minimal reduction in invasion of human erythrocytes, a reduction no greater than that seen with an unrelated monoclonal antibody. Further evidence that the inhibition was specific came from study of Fab fragments of A9D3. Column-purified Fab fragments reduced invasion of rhesus erythrocytes without affecting invasion of human erythrocytes. Fab fragments preabsorbed with rhesus erythrocytes did not inhibit invasion. From the above data, we conclude that band 3 is involved in a stage in the invasion process after initial recognition.
Full text
PDF



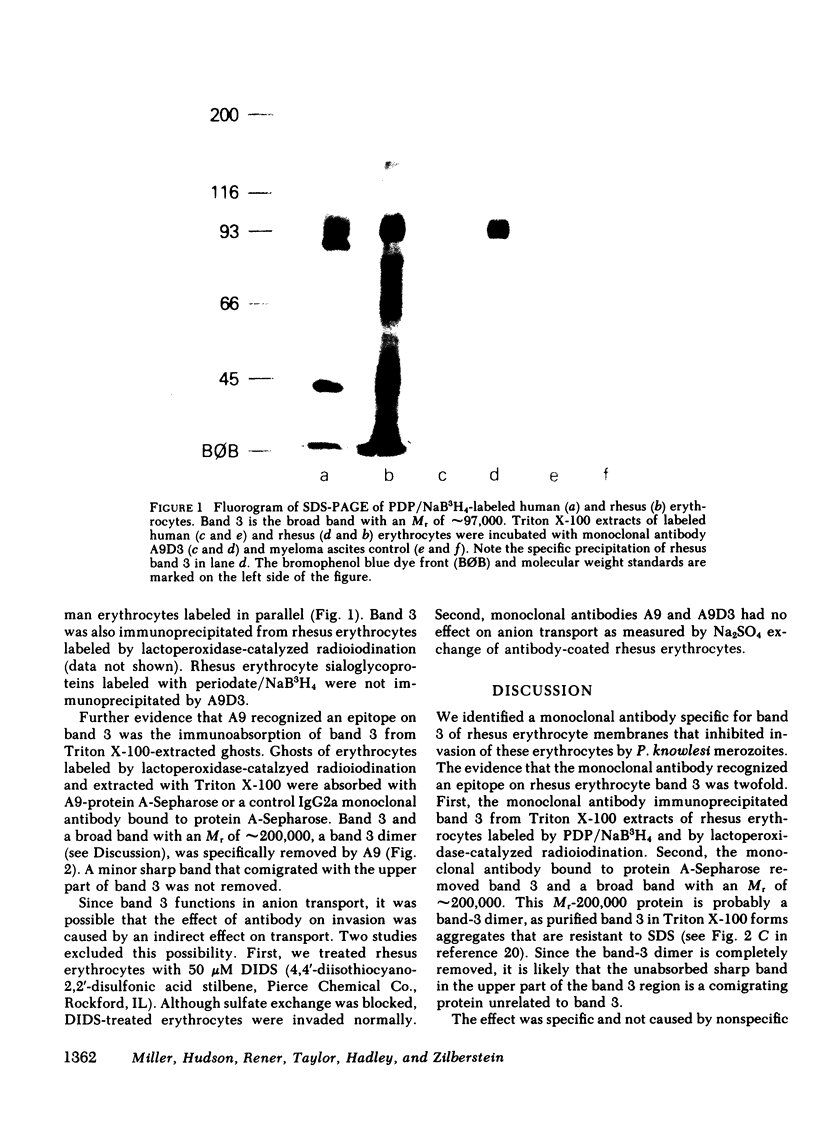
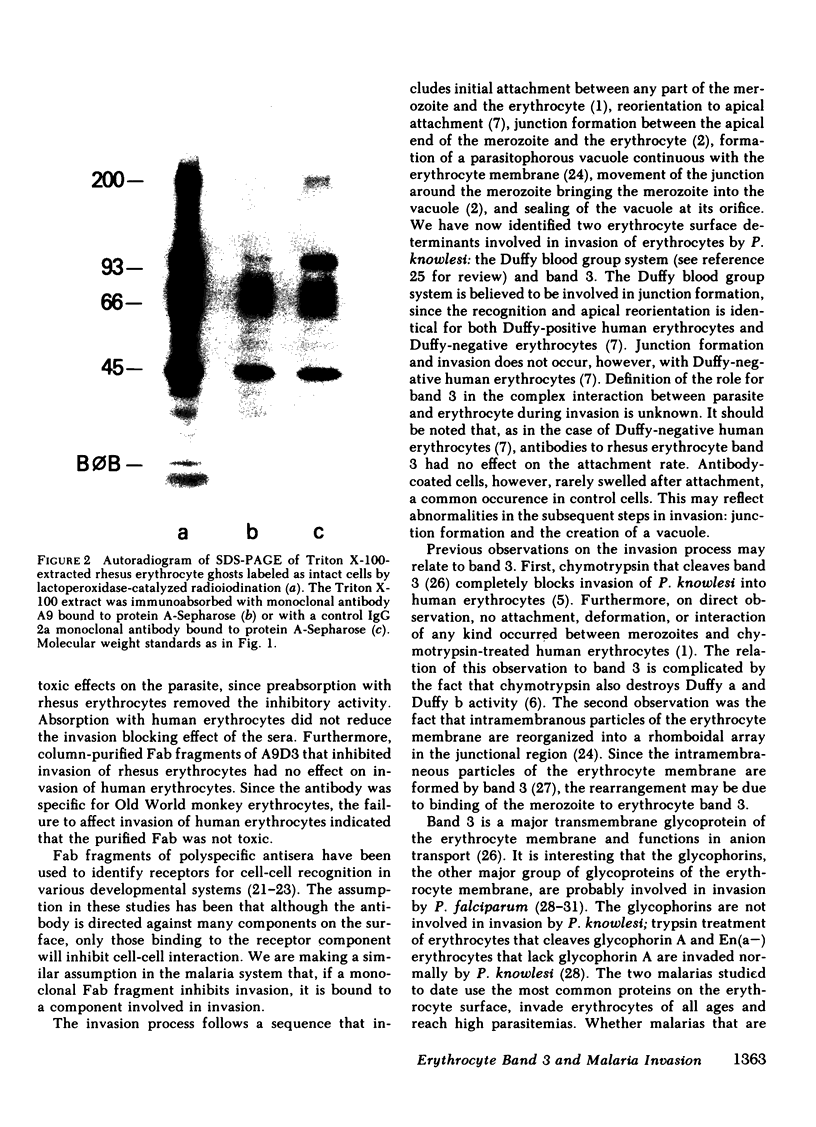

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Johnson J., Rabbege J. Erythrocyte entry by malarial parasites. A moving junction between erythrocyte and parasite. J Cell Biol. 1978 Apr;77(1):72–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikawa M., Miller L. H., Rabbege J. R., Epstein N. Freeze-fracture study on the erythrocyte membrane during malarial parasite invasion. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):55–62. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolotti R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. A cell surface molecule involved in aggregation of embryonic liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4831–4835. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackenbury R., Thiery J. P., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. I. An immunological assay for molecules involved in cell-cell binding. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6835–6840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIN W., CONTACOS P. G., COATNEY G. R., KIMBALL H. R. A NATURALLY ACQUITED QUOTIDIAN-TYPE MALARIA IN MAN TRANSFERABLE TO MONKEYS. Science. 1965 Aug 20;149(3686):865–865. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3686.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik I. Z., Balshin M., Breuer W., Rothstein A. Pyridoxal phosphate. An anionic probe for protein amino groups exposed on the outer and inner surfaces of intact human red blood cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 10;250(13):5130–5136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabantchik Z. I., Knauf P. A., Rothstein A. The anion transport system of the red blood cell. The role of membrane protein evaluated by the use of 'probes'. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 29;515(3):239–302. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(78)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak J. A., Miller L. H., Whitehouse W. C., Shiroishi T. Invasion of erythrocytes by malaria merozoites. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):748–750. doi: 10.1126/science.803712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England B. J., Gunn R. B., Steck T. L. An immunological study of band 3, the anion transport protein of the human red blood cell membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 May 29;623(1):171–182. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein N., Miller L. H., Kaushel D. C., Udeinya I. J., Rener J., Howard R. J., Asofsky R., Aikawa M., Hess R. L. Monoclonal antibodies against a specific surface determinant on malarial (Plasmodium knowlesi) merozoites block erythrocyte invasion. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahmberg C. G., Andersson L. C. Selective radioactive labeling of cell surface sialoglycoproteins by periodate-tritiated borohydride. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5888–5894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfre G., Howe S. C., Milstein C., Butcher G. W., Howard J. C. Antibodies to major histocompatibility antigens produced by hybrid cell lines. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):550–552. doi: 10.1038/266550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyafil F., Babinet C., Jacob F. Cell-cell interactions in early embryogenesis: a molecular approach to the role of calcium. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):447–454. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGHEE R. B. The infection by Plasmodium lophurae of duck erythrocytes in the chicken embryo. J Exp Med. 1953 Jun;97(6):773–782. doi: 10.1084/jem.97.6.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Aikawa M., Johnson J. G., Shiroishi T. Interaction between cytochalasin B-treated malarial parasites and erythrocytes. Attachment and junction formation. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):172–184. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Dvorak J. A., Shiroishi T., Durocher J. R. Influence of erythrocyte membrane components on malaria merozoite invasion. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1597–1601. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Haynes J. D., McAuliffe F. M., Shiroishi T., Durocher J. R., McGinniss M. H. Evidence for differences in erythrocyte surface receptors for the malarial parasites, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium knowlesi. J Exp Med. 1977 Jul 1;146(1):277–281. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.1.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., Mason S. J., Dvorak J. A., McGinniss M. H., Rothman I. K. Erythrocyte receptors for (Plasmodium knowlesi) malaria: Duffy blood group determinants. Science. 1975 Aug 15;189(4202):561–563. doi: 10.1126/science.1145213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. H., McAuliffe F. M., Mason S. J. Erythrocyte receptors for malaria merozoites. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):204–208. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison M. The determination of the exposed proteins on membranes by the use of lactoperoxidase. Methods Enzymol. 1974;32:103–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)32013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER R. R. The hydrolysis of rabbit y-globulin and antibodies with crystalline papain. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:119–126. doi: 10.1042/bj0730119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Jungery M., Weatherall D. J., Parsons S. F., Anstee D. J., Tanner M. J. Glycophorin as a possible receptor for Plasmodium falciparum. Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):947–950. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasvol G., Wainscoat J. S., Weatherall D. J. Erythrocytes deficiency in glycophorin resist invasion by the malarial parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):64–66. doi: 10.1038/297064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins M. Inhibitory effects of erythrocyte membrane proteins on the in vitro invasion of the human malarial parasite (Plasmodium falciparum) into its host cell. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):563–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell K. F., Gerhardt S., Schöppe-Fredenburg A. Kinetic characteristics of the sulfate self-exchange in human red blood cells and red blood cell ghosts. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):319–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01869675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva P. P., Nicolson G. L. Freeze-etch localization of concanavalin A receptors to the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghost membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Sep 23;363(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]