Abstract
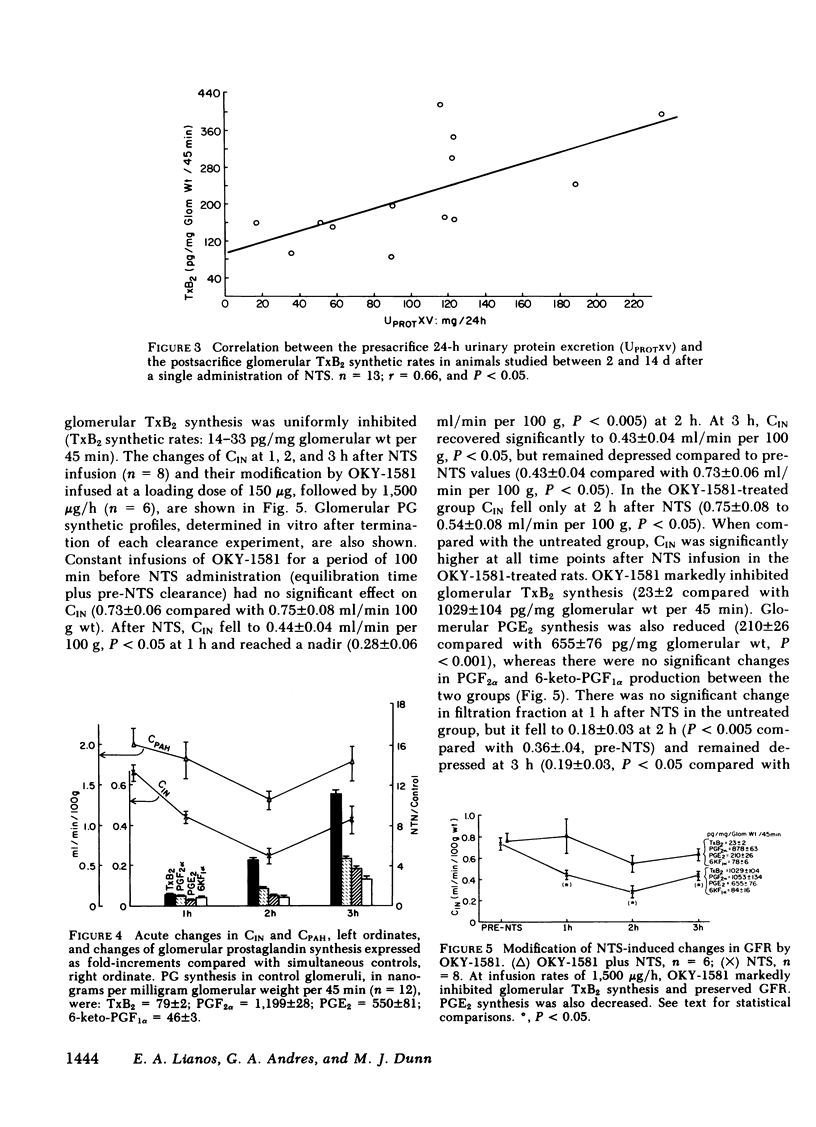
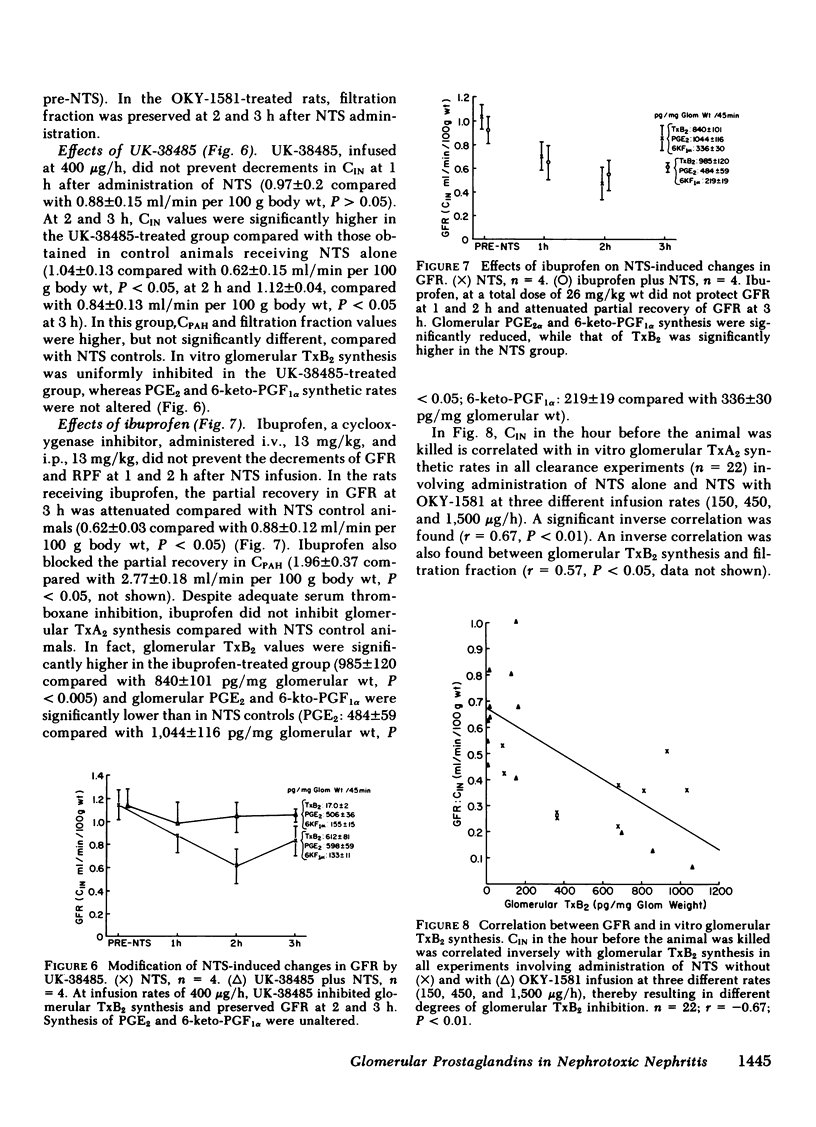
Glomerular arachidonate cyclooxygenation by isolated rat glomeruli was assessed in vitro in antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) antibody-induced glomerulonephritis by radioimmunoassay for prostaglandins (PG) and thromboxane. After a single intravenous injection of rabbit anti-rat GBM serum, we observed enhancement of glomerular thromboxane B2 (TxB2) synthesis as early as 2 to 3 h with smaller increments in PGF2 alpha, PGE2 and 6-keto-PGF1 alpha synthetic rates. On day 2 of the disease, the glomerular synthesis of TxB2 and, to a lesser extent, PGF2 alpha and PGE2 remained enhanced, whereas on days 8, 11, and 14, TxB2 was the only prostanoid synthesized at increased rates. Glomerular TxB2 synthesis correlated with the presacrifice 24-h protein excretion. 60 min after intravenous infusion of anti-GMB serum, glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreased (0.66 +/- 0.04 to 0.44 +/- 0.03 ml/min per 100 g, P less than 0.05), without a significant change in renal plasma flow (RPF): 1.97 +/- 0.23 to 1.80 +/- 0.23 ml/min per 100 g) and without a change in glomerular PG synthetic rates. At 2 h, GFR and RPF reached a nadir (0.25 +/- 0.04 and 1.3 +/- 0.1 ml/min per 100 g, respectively) coinciding with a fivefold increment in glomerular TxB2. By 3 h GFR and RPF partially recovered to 0.43 +/- 0.07 and 1.77 +/- 0.20 ml/min per 100 g, respectively, P less than 0.05, despite further increments in TxB2 synthesis. This recovery of GFR and RPF coincided with increments in vasodilatory PG, (PGE2 and PGI2). The thromboxane synthetase inhibitor OKY-1581 markedly inhibited platelet and glomerular TxB2 synthesis and preserved GFR at 1, 2, and 3 h. Another thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, UK-38485, also completely inhibited platelet and glomerular TxB2 synthesis and prevented decrements of GFR at 2 and 3 h. A cyclooxygenase inhibitor, ibuprofen, inhibited platelet TxB2 and PGE2 synthesis and significantly reduced glomerular PGE2 but not TxB2 synthesis. In the ibuprofen-treated rats, the partial recoveries of GFR and RPF at 3 h were attenuated. The in vitro glomerular TxB2 synthesis correlated inversely with the presacrifice GFR and filtration fraction. These observations indicate that in anti-GBM nephritis there is enhanced synthesis of TxA2 and PG in the glomerulus that mediate changes in renal hemodynamics.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. E., Wilson C. B., Gottschalk C. W. Pathophysiology of experimental glomerulonephritis in rats. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1402–1423. doi: 10.1172/JCI107689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arisz L., Donker A. J., Brentjens J. R., van der Hem G. K. The effect of indomethacin on proteinuria and kidney function in the nephrotic syndrome. Acta Med Scand. 1976;199(1-2):121–125. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1976.tb06701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausiello D. A., Kreisberg J. I., Roy C., Karnovsky M. J. Contraction of cultured rat glomerular cells of apparent mesangial origin after stimulation with angiotensin II and arginine vasopressin. J Clin Invest. 1980 Mar;65(3):754–760. doi: 10.1172/JCI109723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck T. R., Hassid A., Dunn M. J. The effect of arginine vasopressin and its analogs on the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 by rat renal medullary interstitial cells in culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Oct;215(1):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Tucker B. J., Gushwa L. C., Peterson O. W., Wilson C. B. Glomerular immune injury in the rat: the influence of angiotensin II and alpha-adrenergic inhibitors. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):452–461. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Tucker B. J., Wilson C. B. The acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody upon glomerular filtration in the rat. The influence of dose and complement depletion. J Clin Invest. 1978 Apr;61(4):910–921. doi: 10.1172/JCI109016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Wilson C. B. Acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody on the process of glomerular filtration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):899–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI108543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brune K., Glatt M., Kälin H., Peskar B. A. Pharmacological control of prostaglandin and thromboxane release from macrophages. Nature. 1978 Jul 20;274(5668):261–263. doi: 10.1038/274261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. A ROLE OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:99–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. L., Deen W. M., Robertson C. R., Bennett C. M., Glassock R. J., Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Ueki I. F., Rasmussen B. Permselectivity of of the glomerular capillary wall. Studies of experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat using neutral dextran. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1272–1286. doi: 10.1172/JCI108395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray F., Charbonnel B., Maclouf J. Radioimmunoassay of prostaglandins Falpha, E1 and E2 in human plasma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):311–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin L. D., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Hormonal modulation of glomerular function. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):F95–104. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.2.F95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. R., Clark W. F., Cameron J. S. The role of platelets in glomerulonephritis. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1975;5:19–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Sun F. F. Generation of unique mono-hydroxy-eicosatetraenoic acids from arachidonic acid by human neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):406–411. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Malmsten C. L., Kindahl H., Kaplan H. B., Rådmark O., Samuelsson B., Weissmann G. Thromboxane generation by human peripheral blood polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):787–792. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassid A., Konieczkowski M., Dunn M. J. Prostaglandin synthesis in isolated rat kidney glomeruli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1155–1159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jim K., Hassid A., Sun F., Dunn M. J. Lipoxygenase activity in rat kidney glomeruli, glomerular epithelial cells, and cortical tubules. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10294–10299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kniker W. T., Cochrane C. G. The localization of circulating immune complexes in experimental serum sickness. The role of vasoactive amines and hydrodynamic forces. J Exp Med. 1968 Jan 1;127(1):119–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Shigematsu H. Cellular aspects of rabbit Masugi nephritis. I. Cell kinetics in recoverable glomerulonephritis. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1972;10(1):40–50. doi: 10.1007/BF02899714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maclouf J., Pradel M., Pradelles P., Dray F. 125I derivatives of prostaglandins. A novel approach in prostaglandin analysis by radioimmunoassay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 22;431(1):139–146. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(76)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddox D. A., Bennett C. M., Deen W. M., Glassock R. J., Knutson D., Daugharty T. M., Brenner B. M. Determinants of glomerular filtration in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1975 Feb;55(2):305–318. doi: 10.1172/JCI107934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P., Penn G. B., Evans D. J., Peters D. K. The effect of defibrination on nephrotoxic serum nephritis in rabbits. Clin Sci. 1972 May;42(5):643–646. doi: 10.1042/cs0420643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Moncada S., Bunting S., Vane J. R., Hamberg M., Samuelsson B. Identification of an enzyme in platelet microsomes which generates thromboxane A2 from prostaglandin endoperoxides. Nature. 1976 Jun 17;261(5561):558–560. doi: 10.1038/261558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrono C., Ciabattoni G., Pinca E., Pugliese F., Castrucci G., De Salvo A., Satta M. A., Peskar B. A. Low dose aspirin and inhibition of thromboxane B2 production in healthy subjects. Thromb Res. 1980 Feb 1;17(3-4):317–327. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrulis A. S., Aikawa M., Dunn M. J. Prostaglandin and thromboxane synthesis by rat glomerular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):469–474. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Cotran R. S., Pardo V., Unanue E. R. A mononuclear cell component in experimental immunological glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):369–384. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata S., Sakaguchi H., Nagasawa T. Exfoliation of endothelial cytoplasms in nephrotoxic serum nephritis. A study using antiserum against water-soluble glycoprotein isolated from the glomerular basement membrane. Lab Invest. 1978 Feb;38(2):201–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W., Finkelstein N., Aliminosa L., Crawford B., Graber M. THE RENAL CLEARANCES OF SUBSTITUTED HIPPURIC ACID DERIVATIVES AND OTHER AROMATIC ACIDS IN DOG AND MAN. J Clin Invest. 1945 May;24(3):388–404. doi: 10.1172/JCI101618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Jubiz W. OKY-1581: a selective inhibitor of thromboxane synthesis in vivo and in vitro. Prostaglandins. 1981 Sep;22(3):353–363. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(81)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler H. M., Saxton C. A., Parry M. J. Administration to man of UK-37,248-01, a selective inhibitor of thromboxane synthetase. Lancet. 1981 Mar 21;1(8221):629–632. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Cochrane C. G., Muller-Eberhard H. J. Further studies on the chemotactic factor of complement and its formation in vivo. Immunology. 1966 Aug;11(2):141–153. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]