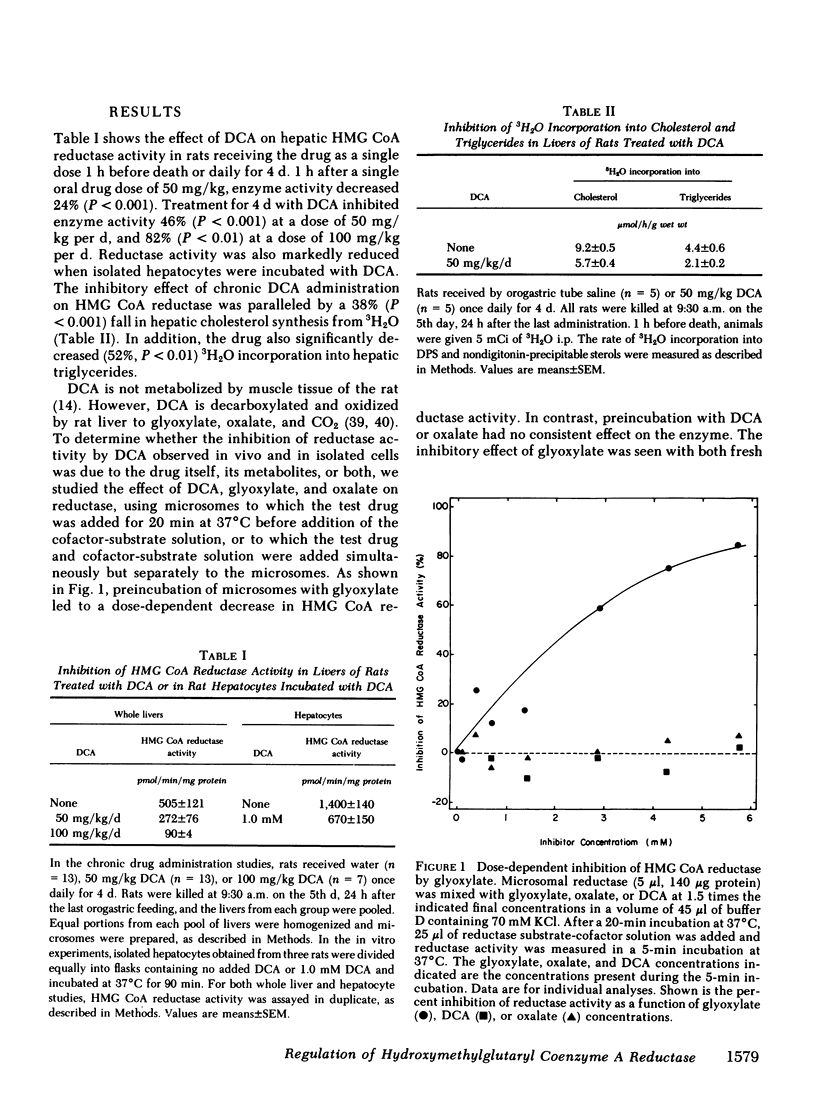
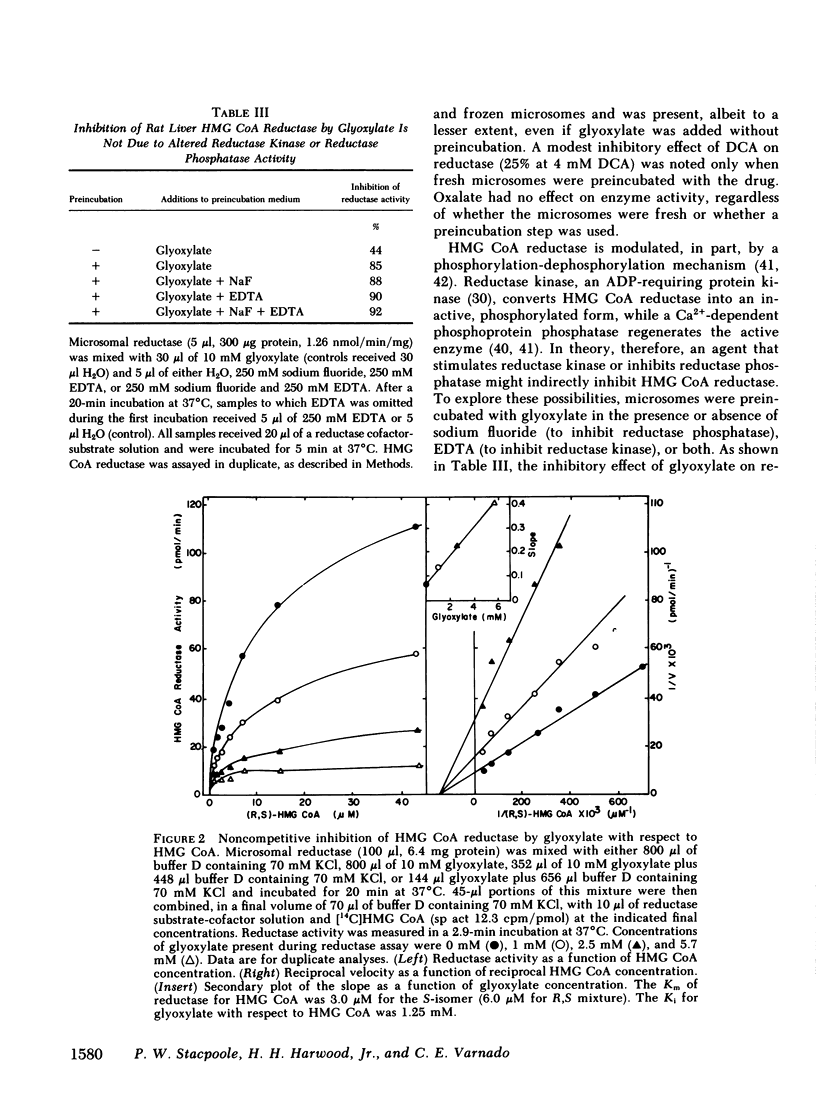
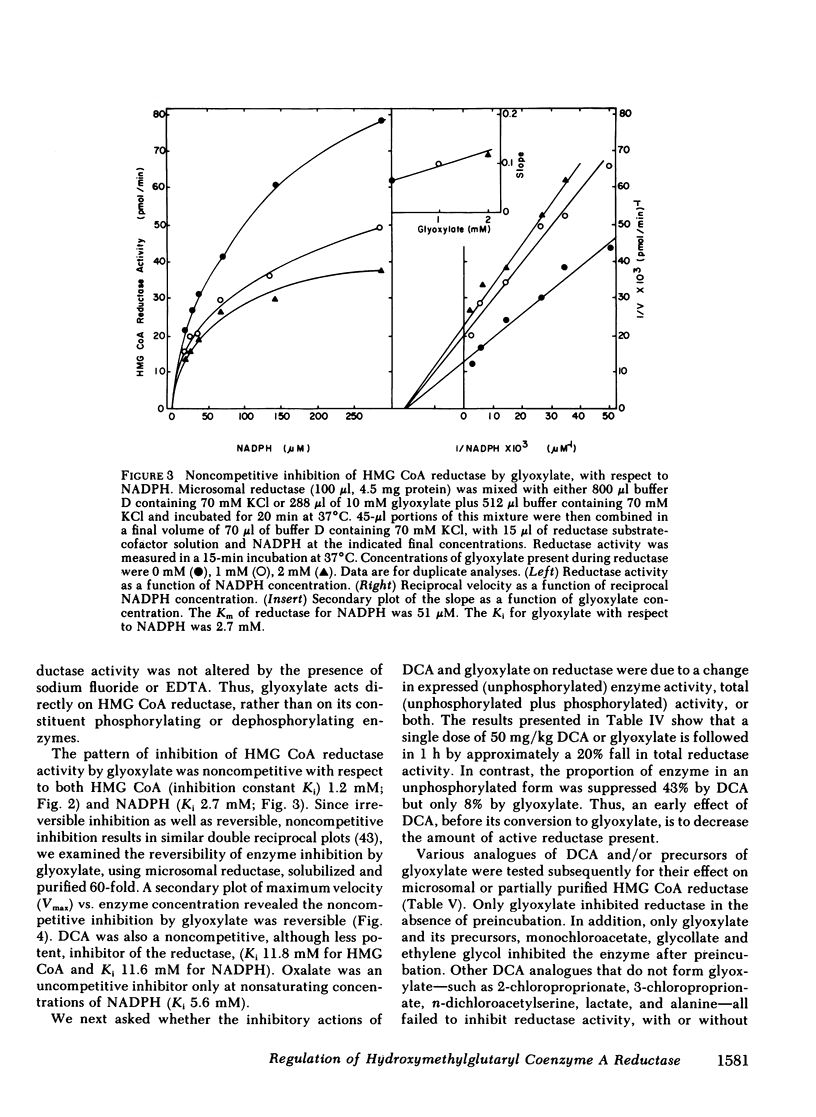
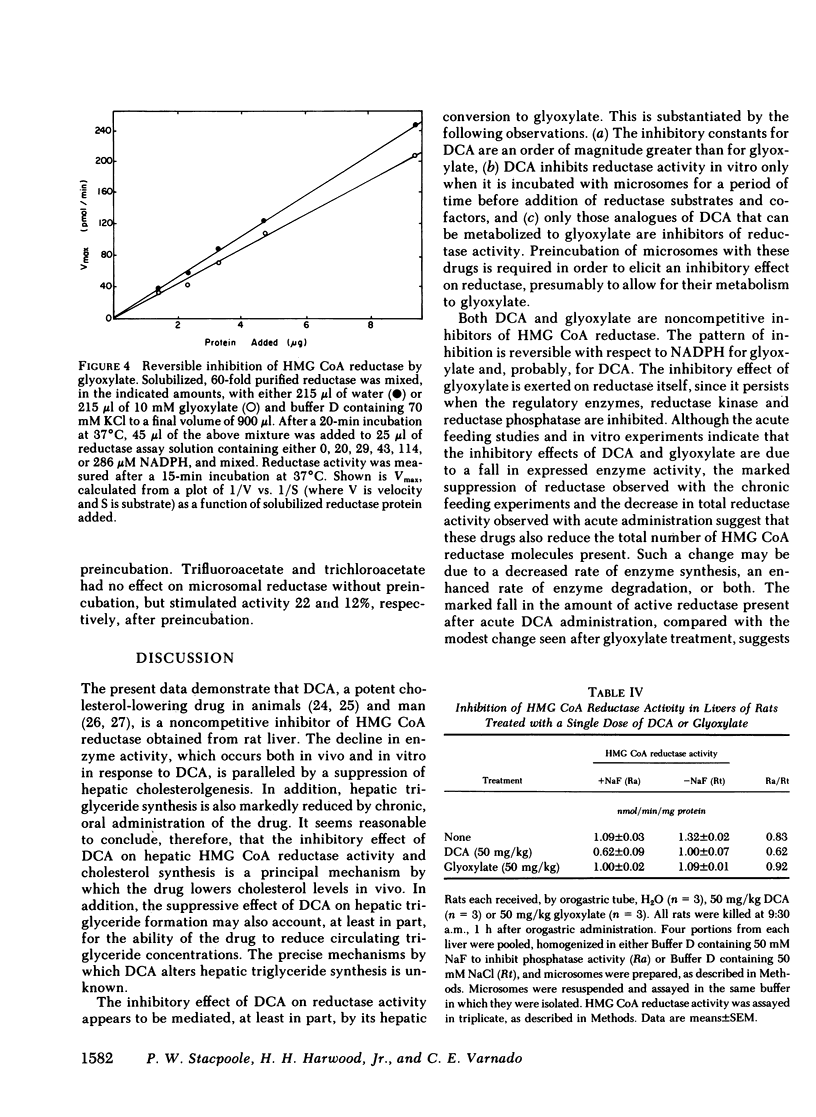
Abstract
Dichloroacetate (DCA) markedly reduces circulating cholesterol levels in animals and in patients with combined hyperlipoproteinemia or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). To investigate the mechanism of its cholesterol-lowering action, we studied the effects of DCA and its hepatic metabolites, glyoxylate and oxalate, on the activity of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG CoA reductase) obtained from livers of healthy, reverse light-cycled rats. Oral administration of DCA for 4 d decreased HMG CoA reductase activity 46% at a dose of 50 mg/kg per d, and 82% at a dose of 100 mg/kg per d. A 24% decrease in reductase activity was observed as early as 1 h after a single dose of 50 mg/kg DCA. The inhibitory effect of the drug was due to a fall in both expressed enzyme activity and the total number of reductase molecules present. DCA also decreased reductase activity when added to suspensions of isolated hepatocytes. With chronic administration, DCA inhibited 3H2O incorporation into cholesterol by 38% and into triglycerides by 52%. When liver microsomes were incubated with DCA, the pattern of inhibition of reductase activity was noncompetitive for both HMG CoA (inhibition constant [Ki] 11.8 mM) and NADPH (Ki 11.6 mM). Inhibition by glyoxylate was also noncompetitive for both HMG CoA (Ki 1.2 mM) and NADPH (Ki 2.7 mM). Oxalate inhibited enzyme activity only at nonsaturating concentrations of NADPH (Ki 5.6 mM). Monochloroacetate, glycollate, and ethylene glycol, all of which can form glyoxylate, also inhibited reductase activity. Using solubilized and 60-fold purified HMG CoA reductase, we found that the inhibitory effect of glyoxylate was reversible. Furthermore, the inhibition by glyoxylate was an effect exerted on the reductase itself, rather than on its regulatory enzymes, reductase kinase and reductase phosphatase. We conclude that the cholesterol-lowering effect of DCA is mediated, at least in part, by inhibition of endogenous cholesterol synthesis. The probable mechanisms are by inhibition of expressed reductase activity by DCA per se and by conversion of DCA to an active metabolite, glyoxylate, which noncompetitively inhibits HMG CoA reductase. These studies thus identify a new class of pharmacological agents that may prove useful in regulating cholesterol synthesis and circulating cholesterol levels in man.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. W., Karounos D., Yoneyama T., Hollingsworth J. W. Dichloroacetate-induced changes in liver of normal and diabetic rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Jul;149(3):814–821. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg Z. H., Stonik J. A., Brewer H. B., Jr 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase: regulation of enzymatic activity by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3678–3682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. N., Friend D. S. High-yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):506–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilbao J. M., Berry H., Marotta J., Ross R. C. Peripheral neuropathy in oxalosis. A case report with electron microscopic observations. Can J Neurol Sci. 1976 Feb;3(1):63–67. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100026020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb D. W., Mapes J. P., Boersma R. W., Harris R. A. Effect of dichloroacetate on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism of isolated hepatocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Apr;173(2):658–665. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90303-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaugre F., Cepanec C., Leroux J. P. Characterization of oxalate as a catabolite of dichloroacetate responsible for the inhibition of gluconeogenesis and pyruvate carboxylation in rat liver cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 14;85(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90666-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaugre F., Leroux J. P., Cartier P. The effects of pyruvate concentration, dichloroacetate and alpha-cyano-4-hydroxycinnamate on gluconeogenesis, ketogenesis and [3-hydroxybutyrate]/[3-oxobutyrate] ratios in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):91–96. doi: 10.1042/bj1720091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. P., Suhrer J. H., Jr, Williams P. E., Lacy W. W., Cherrington A. D. Contribution of the liver and extrasplanchnic tissues to the hypoglycemic action of dichloroacetate in the conscious dog. Diabetes. 1982 Apr;31(4 Pt 1):326–332. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.4.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. P., Williams P. E., Lacy W. W., Cherrington A. D. Effect of dichloroacetate on gluconeogenesis in vivo in the presence of a fixed gluconeogenic substrate supply to the liver. Metabolism. 1981 Sep;30(9):880–885. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo A., Tsujita Y., Kuroda M., Tanzawa K. Inhibition of cholesterol synthesis in vitro and in vivo by ML-236A and ML-236B, competitive inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jul 1;77(1):31–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11637.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundy S. M., Mok H. Y., Zech L., Berman M. Influence of nicotinic acid on metabolism of cholesterol and triglycerides in man. J Lipid Res. 1981 Jan;22(1):24–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris R. A., Crabb D. W. Inhibition of hepatic gluconeogenesis by dichloroacetate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Aug;189(2):364–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90223-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood H. J., Jr, Rodwell V. W. HMG-CoA reductase kinase: measurement of activity by methods that preclude interference by inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase activity or by mevalonate kinase. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jul;23(5):754–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayek A., Woodside W. F. Short-term influences of dichloroacetate on genetically hyperlipemic rats. Metabolism. 1980 Feb;29(2):120–124. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90135-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter C. F., Rodwell V. W. Regulation of vertebrate liver HMG-CoA reductase via reversible modulation of its catalytic activity. J Lipid Res. 1980 May;21(4):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeske D. J., Dietschy J. M. Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J Lipid Res. 1980 Mar;21(3):364–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz R., Tai C. N., Diener R. M., McConnell R. F., Semonick D. E. Dichloroacetate, sodium: 3-month oral toxicity studies in rats and dogs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1981 Feb;57(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(81)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in livers of mice treated with mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1172/JCI109938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmanan M. R., Veech R. L. Measurement of rate of rat liver sterol synthesis in vivo using tritiated water. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 10;252(13):4667–4673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon R. B., Counsell R. E. Determination of the michaelis-menten constant for beta-hydroxy-beta-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Demonstration of a substrate affinity 10-fold greater than previously reported. J Biol Chem. 1976 Sep 25;251(18):5820–5823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabuchi H., Haba T., Tatami R., Miyamoto S., Sakai Y., Wakasugi T., Watanabe A., Koizumi J., Takeda R. Effect of an inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase on serum lipoproteins and ubiquinone-10-levels in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 27;305(9):478–482. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108273050902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister A., Allison S. P., Randle P. J. Effects of dichloroacetate on the metabolism of glucose, pyruvate, acetate, 3-hydroxybutyrate and palmitate in rat diaphragm and heart muscle in vitro and on extraction of glucose, lactate, pyruvate and free fatty acids by dog heart in vivo. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;134(4):1067–1081. doi: 10.1042/bj1341067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbin R. I. Effects of dichloroacetate on lipid metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. Diabetes. 1979 Apr;28(4):265–271. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.4.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. W., Swift L. L., Rabinowitz D., Crofford O. B., Oates J. A., Stacpoole P. W. Reduction of serum cholesterol in two patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia by dichloroacetate. Atherosclerosis. 1979 Jul;33(3):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(79)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. B., Crane C. A., Frantz I. D., Jr Effect of cholestyramine on the fecal excretion of intravenously administered cholesterol-4-14C and its degradation products in a hypercholesterolemic patient. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jul;47(7):1664–1671. doi: 10.1172/JCI105857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moutafis C. D., Myant N. B. The metabolism of cholesterol in two hypercholesterolaemic patients treated with cholestyramine. Clin Sci. 1969 Oct;37(2):443–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom J. L., Rodwell V. W., Mitschelen J. J. Interconversion of active and inactive forms of rat liver hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8924–8934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton R., Harris R. A. Isolation of rabbit liver branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase and regulation by phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14433–14439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribes G., Valette G., Loubatieres-Mariani M. M. Metabolic effects of sodium dichloroacetate in normal and diabetic dogs. Diabetes. 1979 Sep;28(9):852–857. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.9.852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodwell V. W., Nordstrom J. L., Mitschelen J. J. Regulation of HMG-CoA reductase. Adv Lipid Res. 1976;14:1–74. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024914-5.50008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. H., Panini S. R., Rudney H. Rapid, high--yield purification of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jan 1;101(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Nordstrom J. L., Mitschelen J. J., Rodwell V. W., Schimke R. T. Micro assay for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase in rat liver and in L-cell fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 29;370(2):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W. Effect of dichloroacetate on gluconeogenesis in isolated rat hepatocytes. Metabolism. 1977 Feb;26(2):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90046-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W., Felts J. M. Diisopropylammonium dichloroacetate (DIPA) and sodium dichloracetate (DCA): effect on glucose and fat metabolism in normal and diabetic tissue. Metabolism. 1970 Jan;19(1):71–78. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(70)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W., Grundy S. M., Swift L. L., Greene H. L., Slonim A. E., Burr I. M. Elevated cholesterol and bile acid synthesis in an adult patient with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Reduction by a high glucose diet. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1166–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI110361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W., Harman E. M., Curry S. H., Baumgartner T. G., Misbin R. I. Treatment of lactic acidosis with dichloroacetate. N Engl J Med. 1983 Aug 18;309(7):390–396. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198308183090702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W., Moore G. W., Kornhauser D. M. Metabolic effects of dichloroacetate in patients with diabetes mellitus and hyperlipoproteinemia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):526–530. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacpoole P. W., Varnado C. E., Island D. P. Stimulation of rat liver 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase activity by o,p'-DDD. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982 Mar 1;31(5):857–860. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(82)90474-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobert J. A., Hitzenberger G., Kukovetz W. R., Holmes I. B., Jones K. H. Rapid and substantial lowering of human serum cholesterol by mevinolin (MK-803), an inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Atherosclerosis. 1982 Jan;41(1):61–65. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(82)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse S., Cooper R. H., Randle P. J. Mechanism of activation of pyruvate dehydrogenase by dichloroacetate and other halogenated carboxylic acids. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):761–774. doi: 10.1042/bj1410761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Sudo H., Endo A. Therapeutic effects of ML-236B in primary hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 1980 Mar;35(3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(80)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yount E. A., Felten S. Y., O'Connor B. L., Peterson R. G., Powell R. S., Yum M. N., Harris R. A. Comparison of the metabolic and toxic effects of 2-chloropropionate and dichloroacetate. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Aug;222(2):501–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



