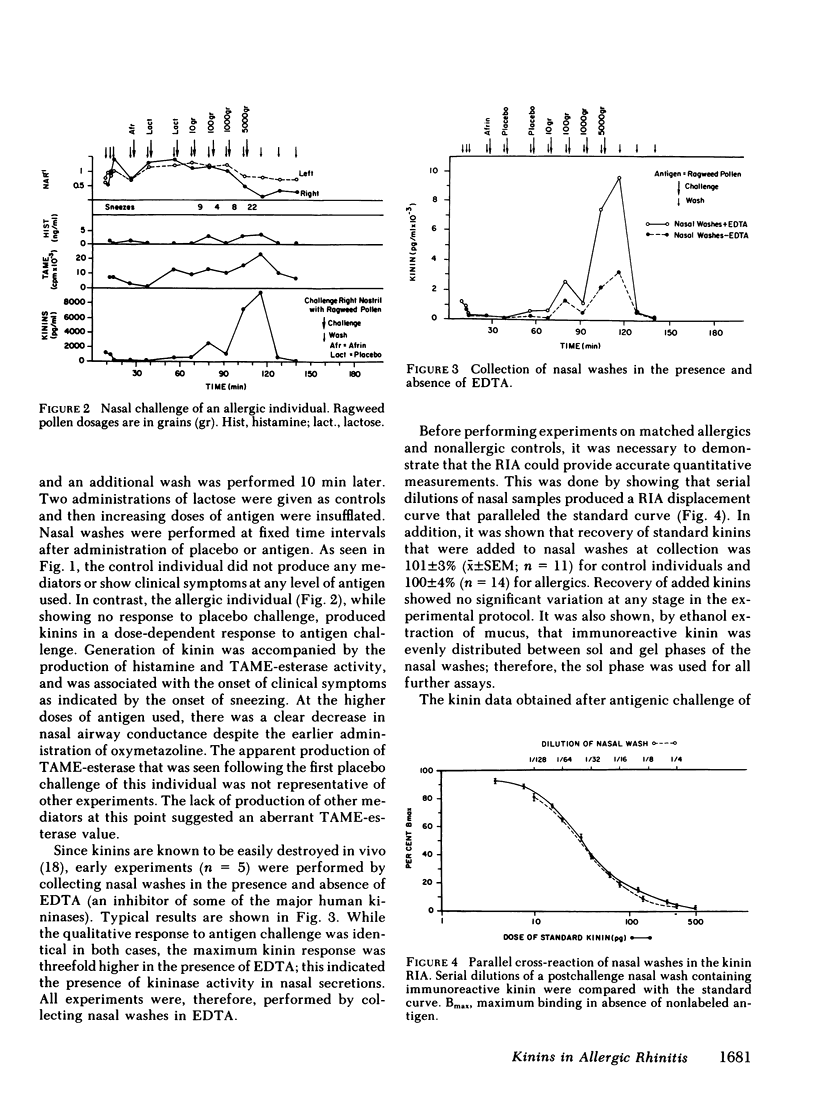
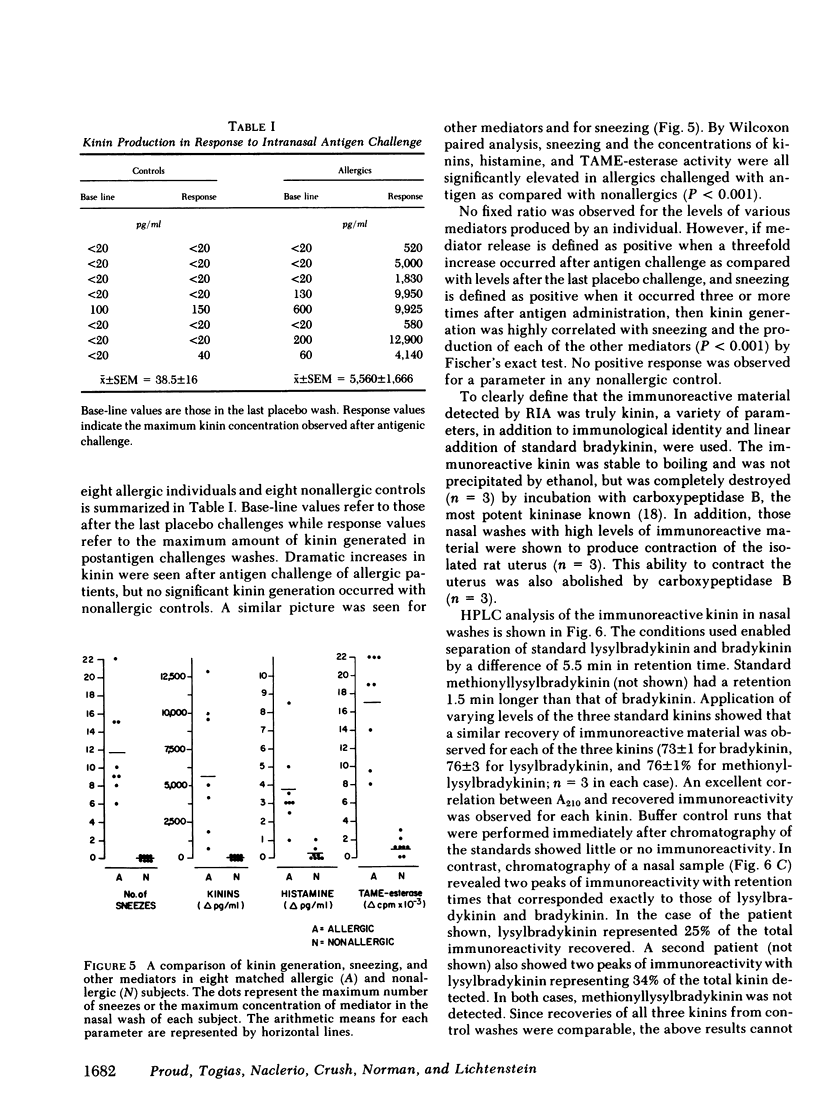
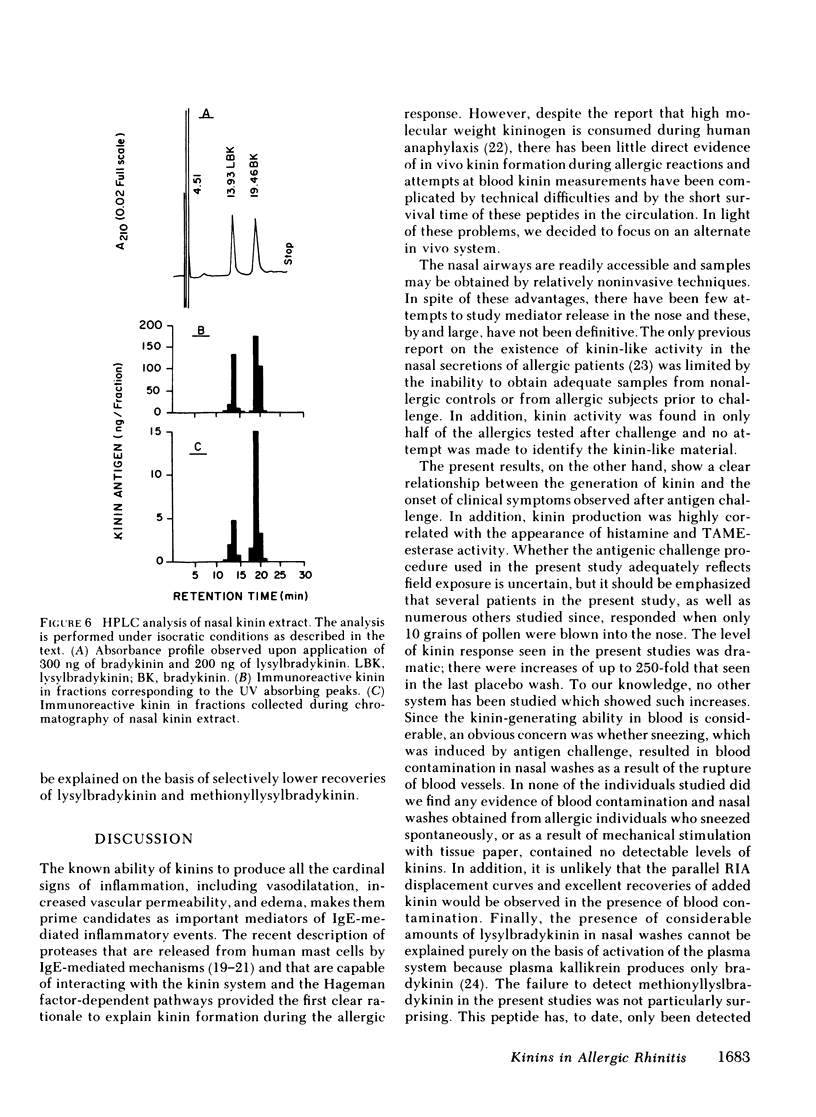
Abstract
Using a recently developed model of nasal challenge, we have obtained data that clearly demonstrate, for the first time, kinin generation during a local allergic reaction in vivo. Allergic individuals (n = 8) and matched nonallergic controls (n = 8) were challenged intranasally with the appropriate antigen and nasal washes were taken before and after challenge. Washes were assayed for kinin, histamine, and [3H]-N-alpha-tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME)-esterase activity. Increased kinin generation was found by radioimmunoassay (RIA) in the nasal washes of all the allergics (5,560 +/- 1,670 pg/ml) but in none of the controls (38 +/- 16 pg/ml). The presence of kinin was highly correlated with that of histamine and TAME-esterase activity and with the onset of clinical symptoms (P less than 0.001). Serial dilutions of nasal washes produced RIA displacement curves that paralleled the standard curve, and recovery of standard kinins that were added to nasal washes was 100 +/- 4% (n = 14). Kinin recovery was identical in both allergics and controls and did not vary significantly with antigen challenge. The immunoreactive kinin in nasal washes was stable to boiling and not precipitated by ethanol, but completely destroyed by carboxypeptidase B. It was evenly distributed between the sol and gel phases of nasal washes. High performance liquid chromatography analysis of the immunoreactive kinin in nasal washes showed it to be a mixture of lysylbradykinin and bradykinin. We conclude that kinins are produced during local allergic reactions in the nose and may contribute to the symptomatology of the allergic response.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe K., Watanabe N., Kumagai N., Mouri T., Seki T., Yoshinaga K. Circulating kinin in patients with bronchial asthma. Experientia. 1967 Aug 15;23(8):626–627. doi: 10.1007/BF02144161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton S., Sanders E. J., Schachter M., Uddin M. Autonomic nerve stimulation, kallikrein content anc acinar cell granules of the cat's submandibular gland. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(2):363–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolovich J., Back N., Arbesman C. E. Kinin-like activity in nasal secretions of allergic patients. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1970;38(4):337–344. doi: 10.1159/000230287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles R., Wilson H. A kallikrein-like substance in cat nasal secretion. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):712–714. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott D. F., Lewis G. P. Methionyl-lysyl-bradykinin, a new kinin from ox blood. Biochem J. 1965 May;95(2):437–447. doi: 10.1042/bj0950437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODFRIEND T. L., LEVINE L., FASMAN G. D. ANTIBODIES TO BRADYKININ AND ANGIOTENSIN: A USE OF CARBODIIMIDES IN IMMUNOLOGY. Science. 1964 Jun 12;144(3624):1344–1346. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3624.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães J. A., Borges D. R., Prado E. S., Prado J. L. Kinin-converting aminopeptidase from human serum. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 15;22(24):3157–3172. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hial V., Keiser H. R., Pisano J. J. Origin and content of methionyl-lysyl-bradykinin, lysyl-bradykinin and bradykinin in human urine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1976 Nov 15;25(22):2499–2503. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(76)90456-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulthén U. L., Borge T. Determination of bradykinin in blood by a sensitive radioimmunoassay. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1976 Dec;36(8):833–839. doi: 10.3109/00365517609081946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maranda B., Rodrigues J. A., Schachter M., Shnitka T. K., Weinberg J. Studies on kallikrein in the duct systems of the salivary glands of the cat. J Physiol. 1978 Mar;276:321–328. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashford M. L., Roberts M. L. Determination of blood kinin levels by radioimmunoassay. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Oct 15;21(20):2727–2735. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newball H. H., Berninger R. W., Talamo R. C., Lichtenstein L. M. Anaphylactic release of a basophil kallikrein-like activity. I. Purification and characterization. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):457–465. doi: 10.1172/JCI109483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newball H. H., Meier H. L., Kaplan A. P., Revak S. D., Cochrane C. G., Lichtenstein L. M. Activation of Hageman factor by proteases released during antigen challenge of human lung. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1981;94:126–133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J. Vasoactive peptides in venoms. Fed Proc. 1968 Jan-Feb;27(1):58–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Perkins M., Pierce J. V., Yates K. N., Highet P. F., Herring P. L., Mangkornkanok/Mark M., Bahu R., Carone F., Pisano J. J. Characterization and localization of human renal kininogen. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10634–10639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud D., Pierce J. V., Pisano J. J. Radioimmunoassay of human high molecular weight kininogen in normal and deficient plasmas. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Apr;95(4):563–574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G. L., Rosenthal R. R., Norman P. S. Inhalation challenge with ragweed pollen in ragweed-sensitive asthmatics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983 Mar;71(3):302–310. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(83)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Tryptase from human pulmonary mast cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11939–11943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scicli A. G., Mindroiu T., Scicli G., Carretero O. A. Blood kinins, their concentration in normal subjects and in patients with congenital deficiency in plasma prekallikrein and kininogen. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Jul;100(1):81–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. L., Kagey-Sobotka A., Bleecker E. R., Traystman R., Kaplan A. P., Gralnick H., Valentine M. D., Permutt S., Lichtenstein L. M. Physiologic manifestations of human anaphylaxis. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1072–1080. doi: 10.1172/JCI109936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBSTER M. E., PIERCE J. V. The nature of the kallidins released from human plasma by kallikreins and other enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Feb 4;104:91–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb17655.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U. Inflammation and mediators. Int J Dermatol. 1980 Oct;19(8):436–442. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1980.tb05894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



