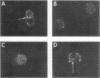
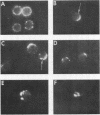
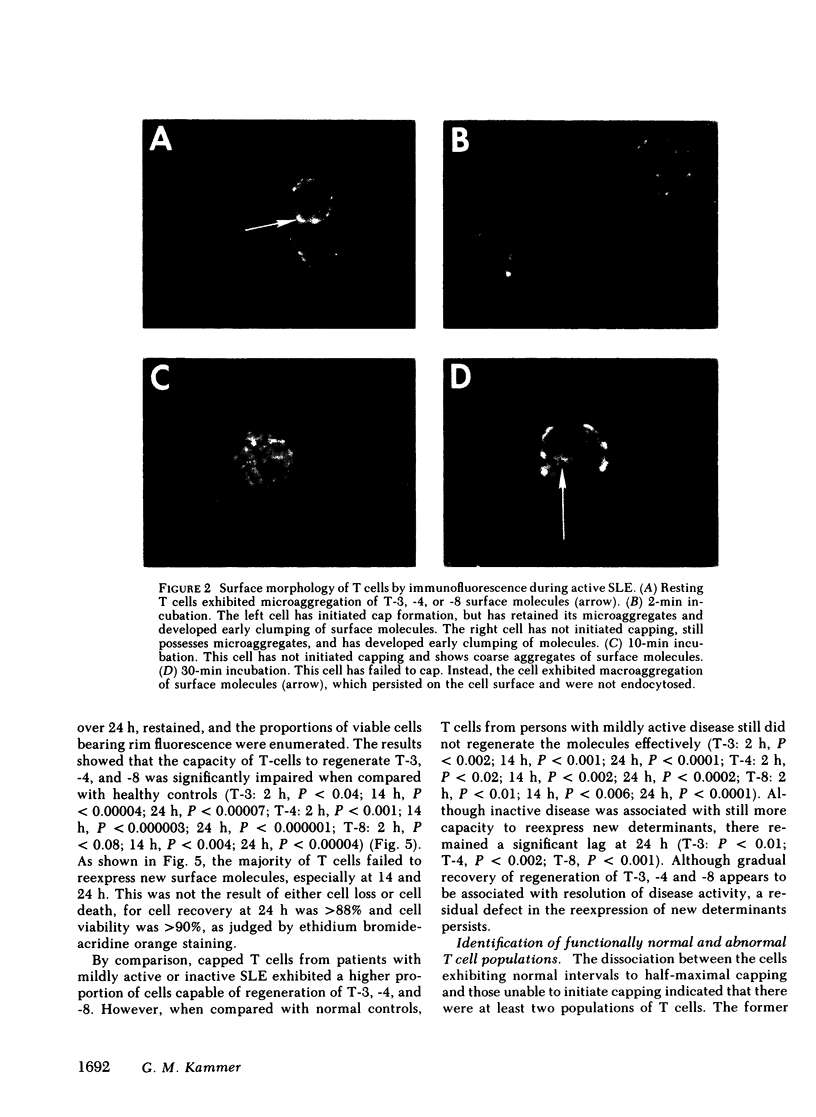
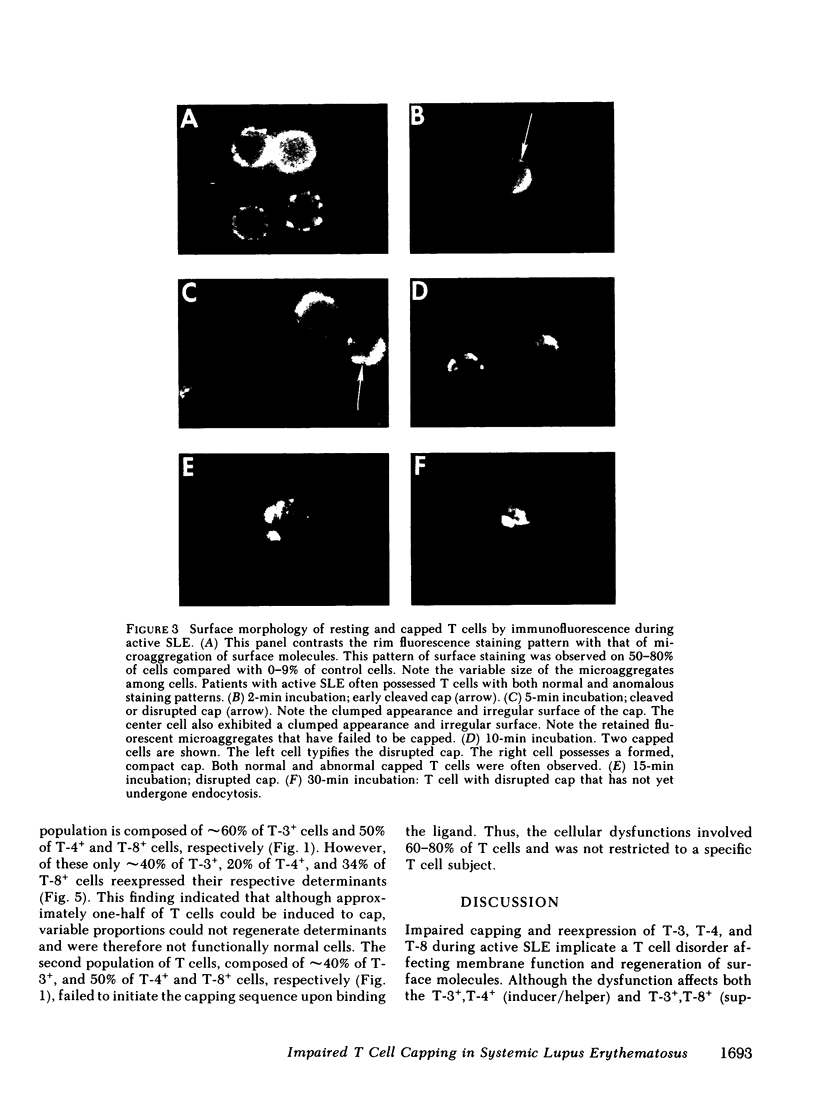
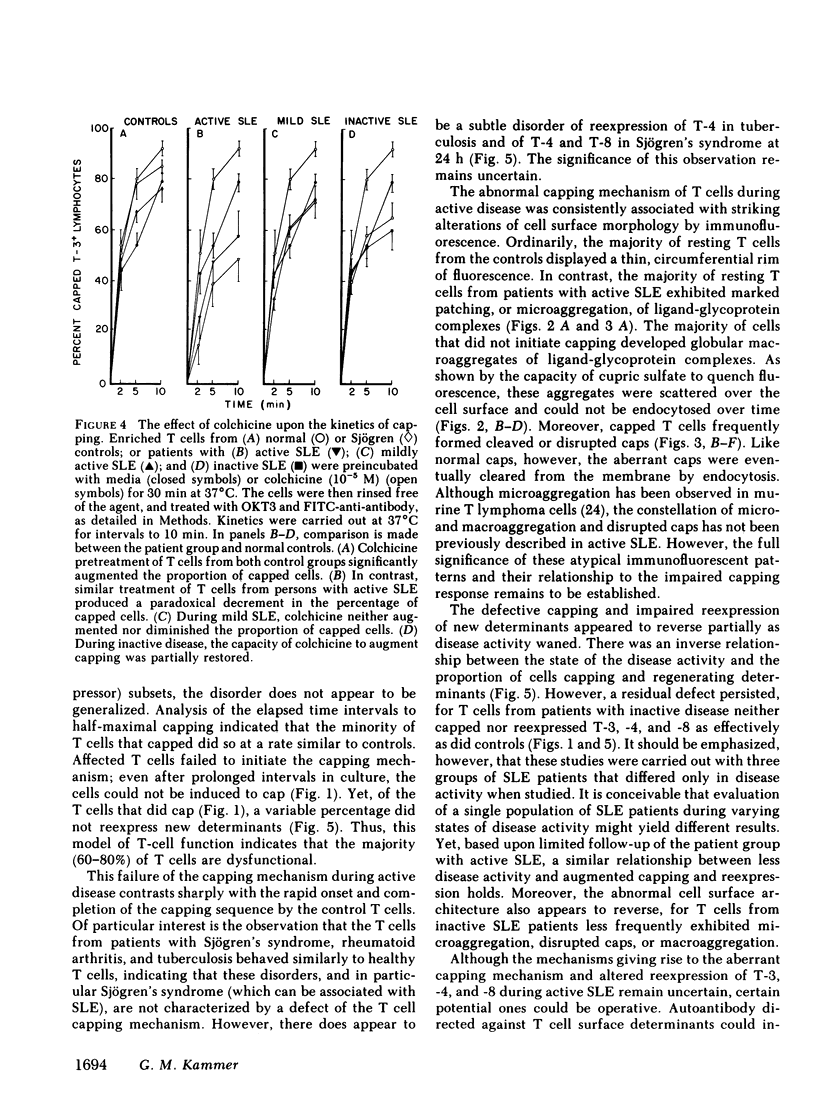
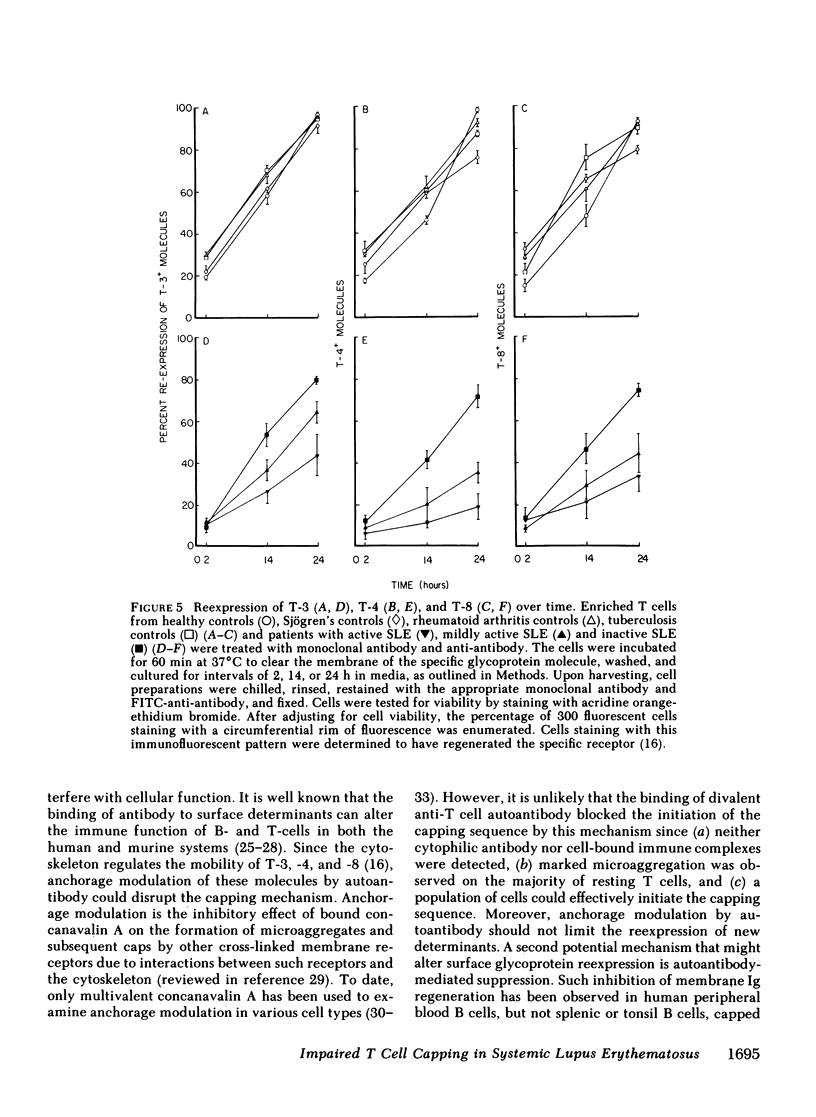
Abstract
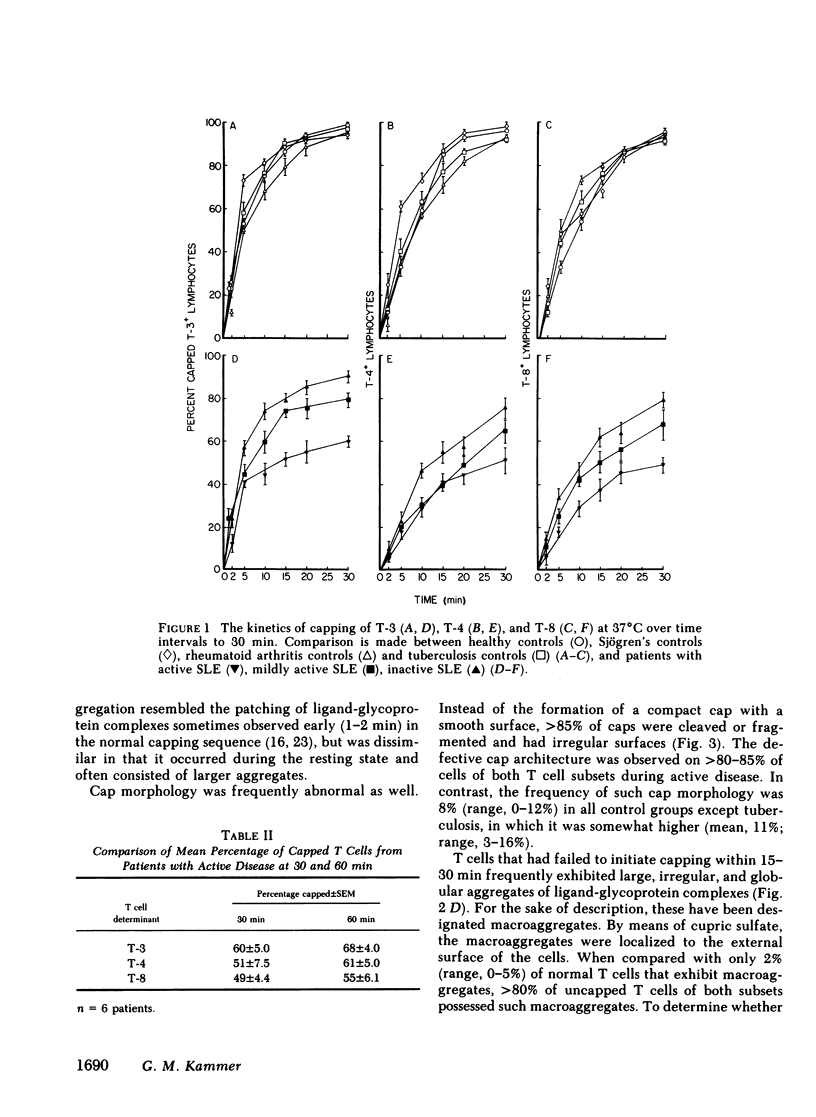
It is currently unclear whether the T cell dysfunctions observed during active systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) reflect a disorder intrinsic to the T cell or defects that result from interaction with anti-T cell autoantibody. To determine whether a disorder intrinsic to the T cell exists in SLE, the T cell capping mechanism was selected as a model of cellular function. The normal T cell capping mechanism is a rapid, energy-dependent and coordinated sequence of membrane events that consists of microaggregation, capping, endocytosis, and regeneration of the surface molecule. The monoclonal antibodies OKT3, OKT4, and OKT8, directed against the T cell-specific membrane glycoproteins T-3, T-4, T-8, served as specific probes of the glycoproteins' mobility within the membrane and membrane glycoprotein regeneration. When compared with greater than 91% T cell capping in normal and control subjects with active Sjögren's syndrome, active rheumatoid arthritis and active tuberculosis, only 49-60% of T cells from active SLE patients completed the capping sequence (SLE vs. healthy controls; T-3, P less than 0.002; T-4, P less than 0.004; T-8, P less than 0.002). Colchicine (10(-5) M), which inhibits microtuble polymerization and augments the rate of normal T cell capping, failed to restore the abnormal capping. However, as judged by the elapsed time intervals to half-maximal capping, the capping kinetics of the T cells able to initiate capping were not significantly different from controls. Fluorescence microscopy demonstrated an abnormal staining pattern characterized by microaggregation of ligand-glycoprotein complexes on resting T cells, coarse aggregation of ligand-glycoprotein complexes over the surfaces of cells that failed to cap, and cleaved or disrupted caps. After clearance of determinants by capping, greater than 94% of T cells from healthy controls regenerated T-3, -4, and -8 within 24 h. In contrast, only 20-40% of capped T cells from active SLE patients reexpressed new determinants. With improving disease activity, the proportion of cells capping and regenerating T-3, -4, and -8 increased, but remained significantly below control levels. In conclusion, this study has identified a disorder of T cell surface glycoprotein mobility and regeneration affecting the majority (60-80%) of both the T-3+, T-4+, (inducer/helper), and T-3+, T-8+ (suppressor) subsets during active SLE. Although the impaired capping and reexpression improve with disease remission, a residual defect persists. The data support the concept of a disorder intrinsic to the T cell in SLE.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcocer-Varela J., Alarcón-Segovia D. Decreased production of and response to interleukin-2 by cultured lymphocytes from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jun;69(6):1388–1392. doi: 10.1172/JCI110579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ault K. A., Unanue E. R. Failure of B lymphocytes in human blood to regenerate surface immunoglobulin after its removal by antibody. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):327–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Pharmacological modification of immunoregulatory T lymphocytes. I. Effect of adenosine, H1 and H2 histamine agonists upon T lymphocyte regulation of B lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):218–230. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch R. E., Rosenthal A. K., Polmar S. H. Pharmacological modification of immunoregulatory T lymphocytes . II. Modulation of T lymphocyte cell surface characteristics. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Apr;48(1):231–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon L. Y., Singer S. J. Transmembrane interactions and the mechanism of capping of surface receptors by their specific ligands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butman B. T., Jacobsen T., Cabatu O. G., Bourguignon L. Y. The involvement of cAMP in lymphocyte capping. Cell Immunol. 1981 Jul 1;61(2):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(81)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. W., Kung P. C., Gingras S. P., Goldstein G. Does OKT3 monoclonal antibody react with an antigen-recognition structure on human T cells? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1805–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier B., Carnaud C., Bach J. F. Selective depression of the xenogeneic cell-mediated lympholysis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1979 Aug;64(2):351–360. doi: 10.1172/JCI109469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. A., Petts V., Luckhurst E., Penny R. The effect of acute and prolonged administration of prednisolone and ACTH on lymphocyte subpopulations. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Jun;28(3):467–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I., Wang J. L. Receptor mobility and receptor-cytoplasmic interactions in lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 May;70(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.5.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S., Steinberg A. D., Haynes B. F., Whalen G. Immunoregulatory aberrations in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1978 Oct;121(4):1473–1479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan J., Koch G. L. Cross-linked surface Ig attaches to actin. Nature. 1978 May 25;273(5660):278–281. doi: 10.1038/273278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gladman D., Keystone E., Urowitz M., Cane D., Poplonski L. Impaired antigen-specific suppressor cell activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Apr;40(1):77–82. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. B., Lahita R. G., Chiorazzi N., Kunkel H. G. Immune function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Impairment of in vitro T-cell proliferation and in vivo antibody response to exogenous antigen. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):885–892. doi: 10.1172/JCI109388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafeman D. G., Smith L. M., Fearon D. T., McConnell H. M. Lipid monolayer-coated solid surfaces do not perturb the lateral motion and distribution of C3b receptors on neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;94(1):224–227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Fauci A. S. The differential effect of in vivo hydrocortisone on the kinetics of subpopulations of human peripheral blood thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):703–707. doi: 10.1172/JCI108982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henis Y. I., Elson E. L. Inhibition of the mobility of mouse lymphocyte surface immunoglobulins by locally bound concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1072–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander N., Pillemer E., Weissman I. L. Effects of Lyt antibodies on T-cell functions: augmentation by anti-Lyt-1 as opposed to inhibition by anti-Lyt-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1148–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H. Impaired immunoregulation in systemic lupus erythematosus: defective adenosine-induced suppressor T lymphocyte generation. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1706–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer G. M., Smith J. A., Mitchell R. Capping of human T cell specific determinants: kinetics of capping and receptor re-expression and regulation by the cytoskeleton. J Immunol. 1983 Jan;130(1):38–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakauer R. S., Clough J. D., Frank S., Sundeen J. T. Suppressor cell function defect in idiopathic systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1979 Nov;14(3):327–333. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(79)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuntz M. M., Innes J. B., Weksler M. E. The cellular basis of the impaired autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):151–153. doi: 10.1172/JCI109270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandler R., Birch R. E., Polmar S. H., Kammer G. M., Rudolph S. A. Abnormal adenosine-induced immunosuppression and cAMP metabolism in T lymphocytes of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7542–7546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. Current concepts in immunology: Regulation of the immune response--inducer and suppressor T-lymphocyte subsets in human beings. N Engl J Med. 1980 Aug 14;303(7):370–373. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198008143030704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi P. J., Hausman P. B., Raff H. V., Stobo J. D. The autologous mixed lymphocyte reaction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Jul;25(7):820–823. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagawa A., Abdou N. I. Suppressor-cell dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Cells involved and in vitro correction. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):789–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI109190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Failure of autologous mixed lymphocyte reactions between T and non-T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. I. Dysfunction of suppressor T-cell activity related to impaired generation of, rather than response to, suppressor cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jul-Aug;21(6):657–664. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakane T., Steinberg A. D., Reeves J. P., Green I. Studies of immune functions of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Complement-dependent immunoglobulin M anti-thymus-derived cell antibodies preferentially inactivate suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 1979 May;63(5):954–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI109396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Control of proliferation and differentiation in B lymphocytes by anti-Ig antibodies and a serum-derived cofactor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2401–2405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strand V., Talal N. Advances in the diagnosis and concept of Sjögren's syndrome (autoimmune exocrinopathy). Bull Rheum Dis. 1979;30(9):1046–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suciu-Foca N., Buda J. A., Thiem T., Reemtsma K. Impaired responsiveness of lymphocytes in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):295–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Modulation of lymphocyte receptor redistribution by concanavalin A, anti-mitotic agents and alterations of pH. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):152–155. doi: 10.1038/246152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahara I., Edelman G. M. Restriction of the mobility of lymphocyte immunoglobulin receptors by concanavalin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):608–612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]