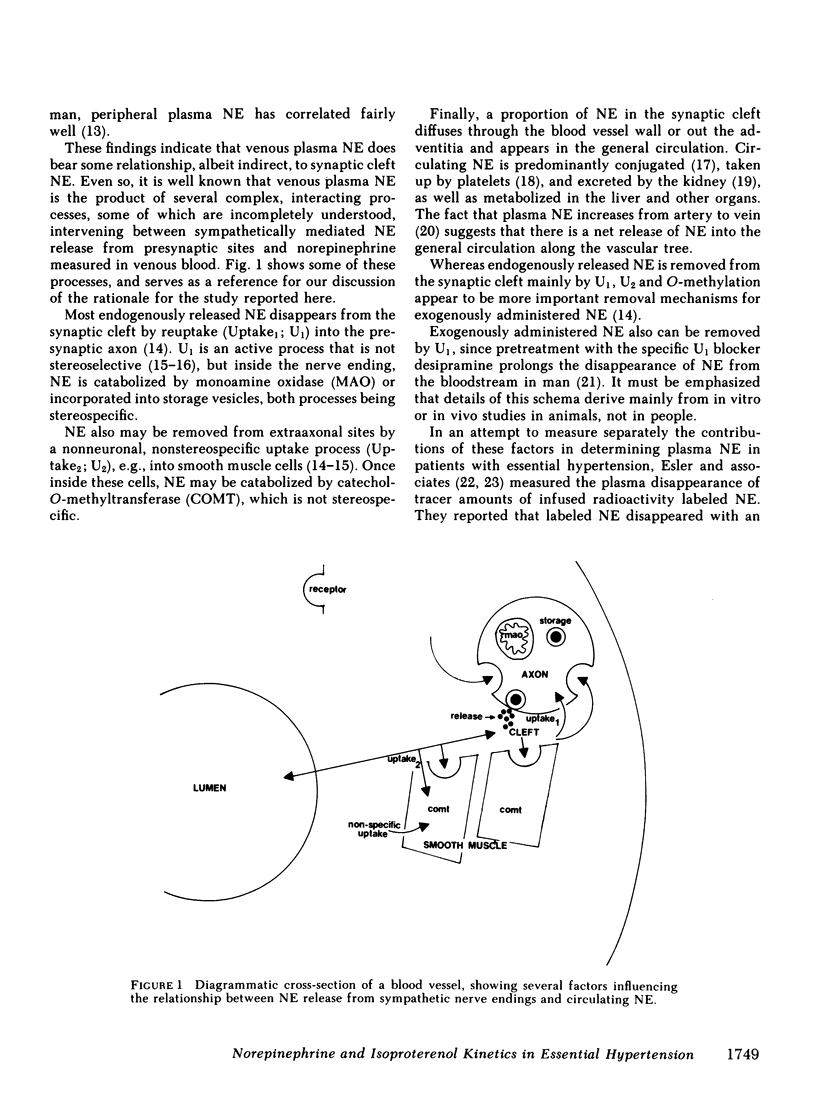
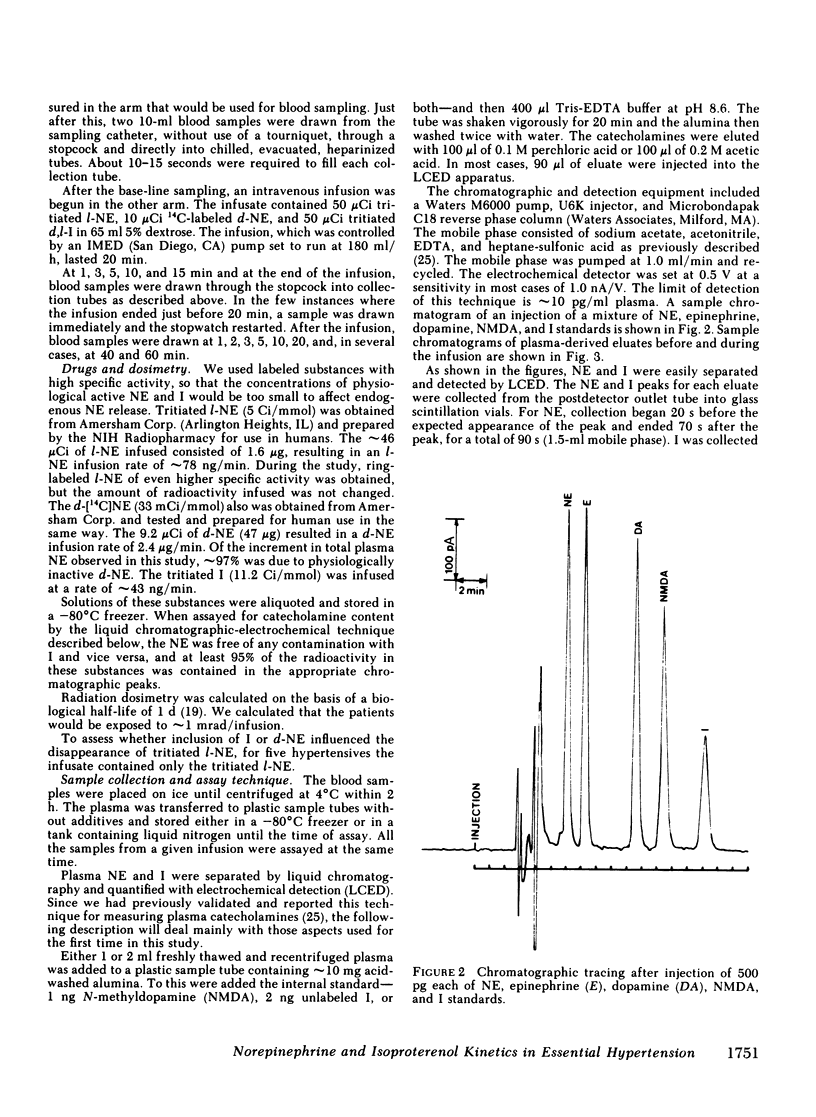
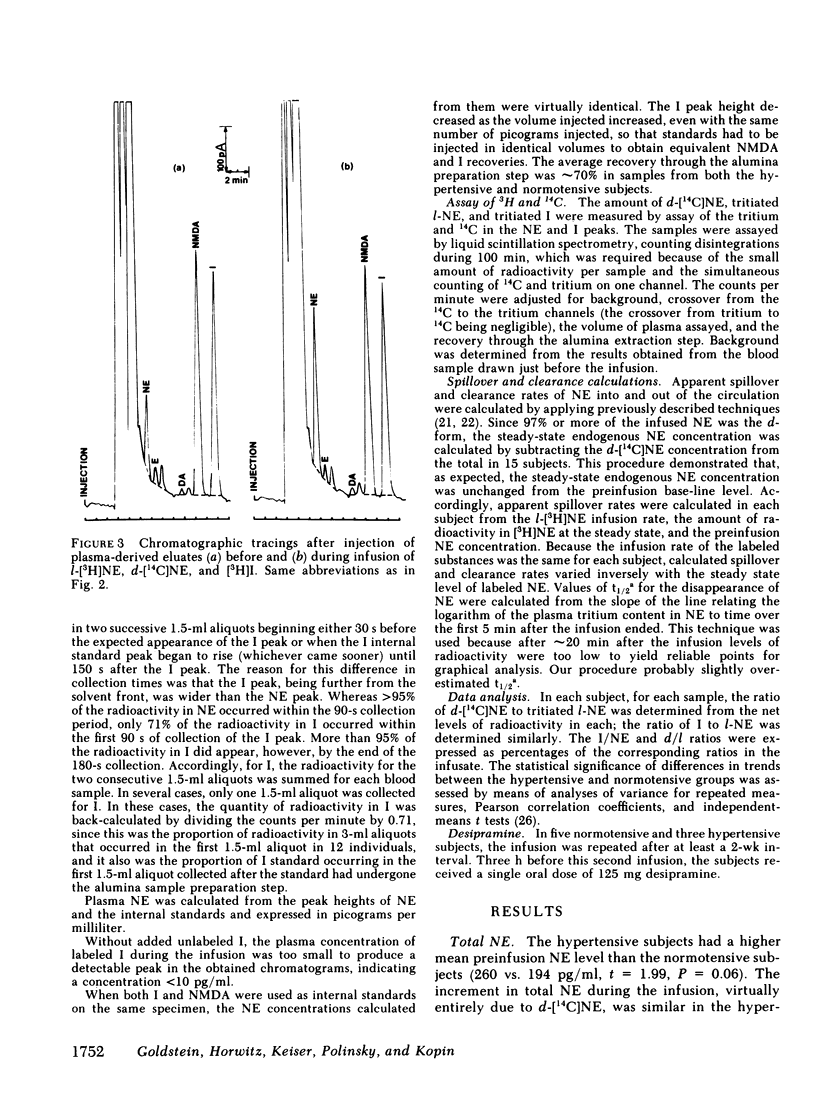
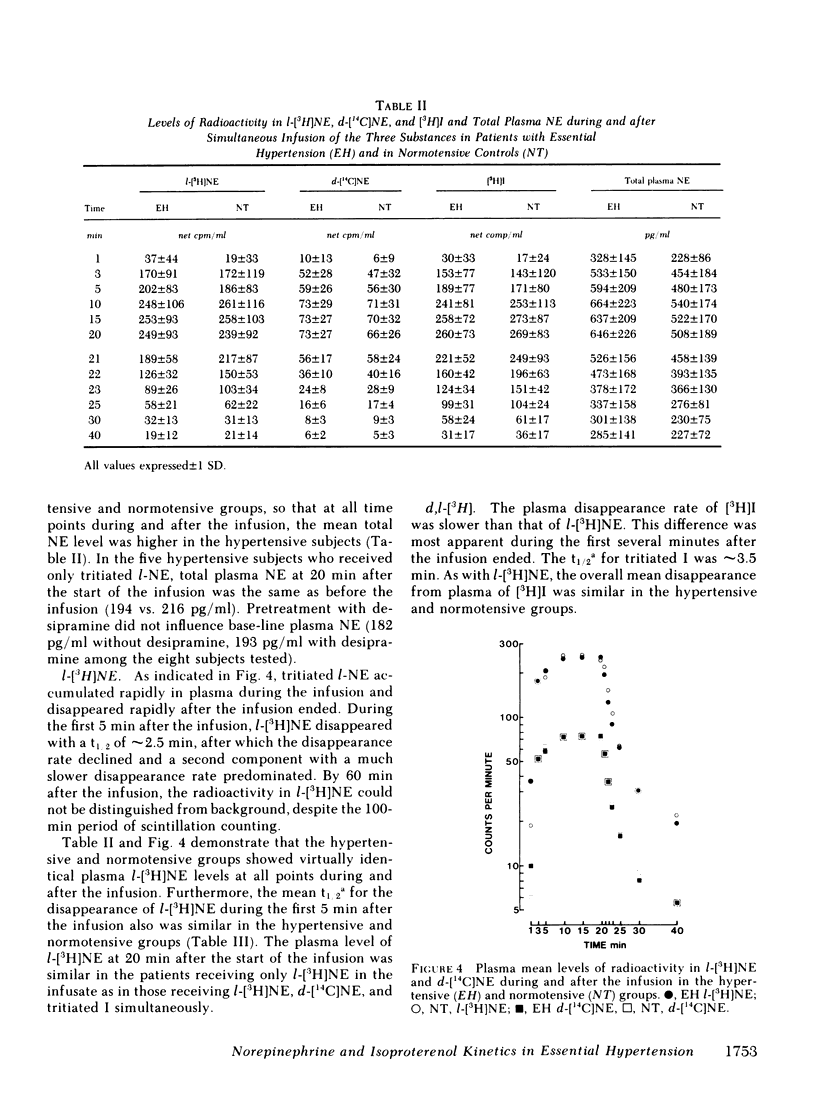
Abstract
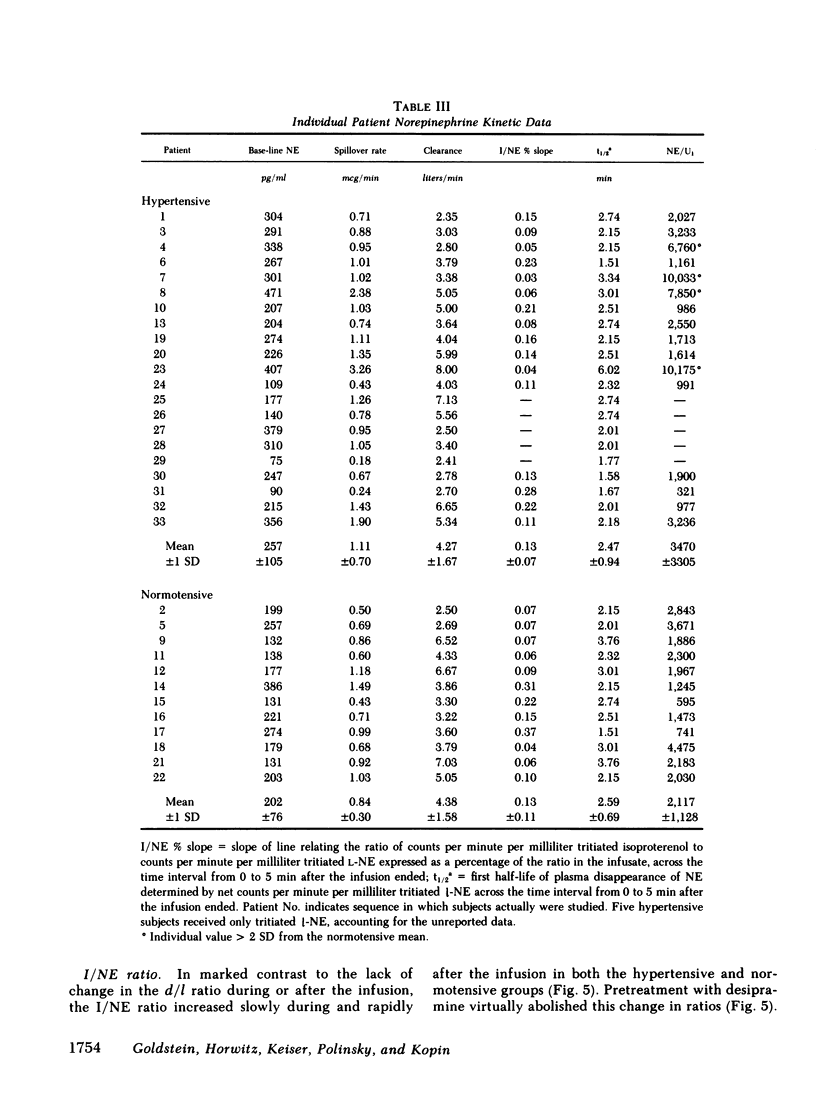
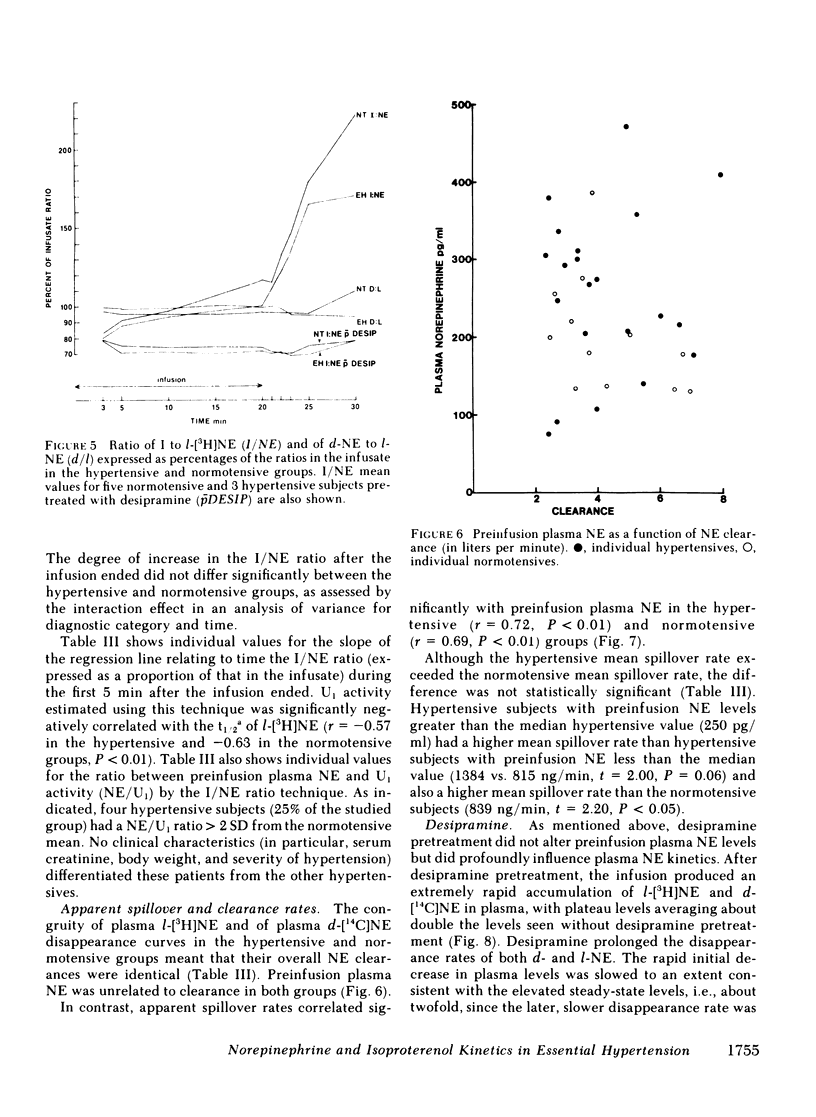
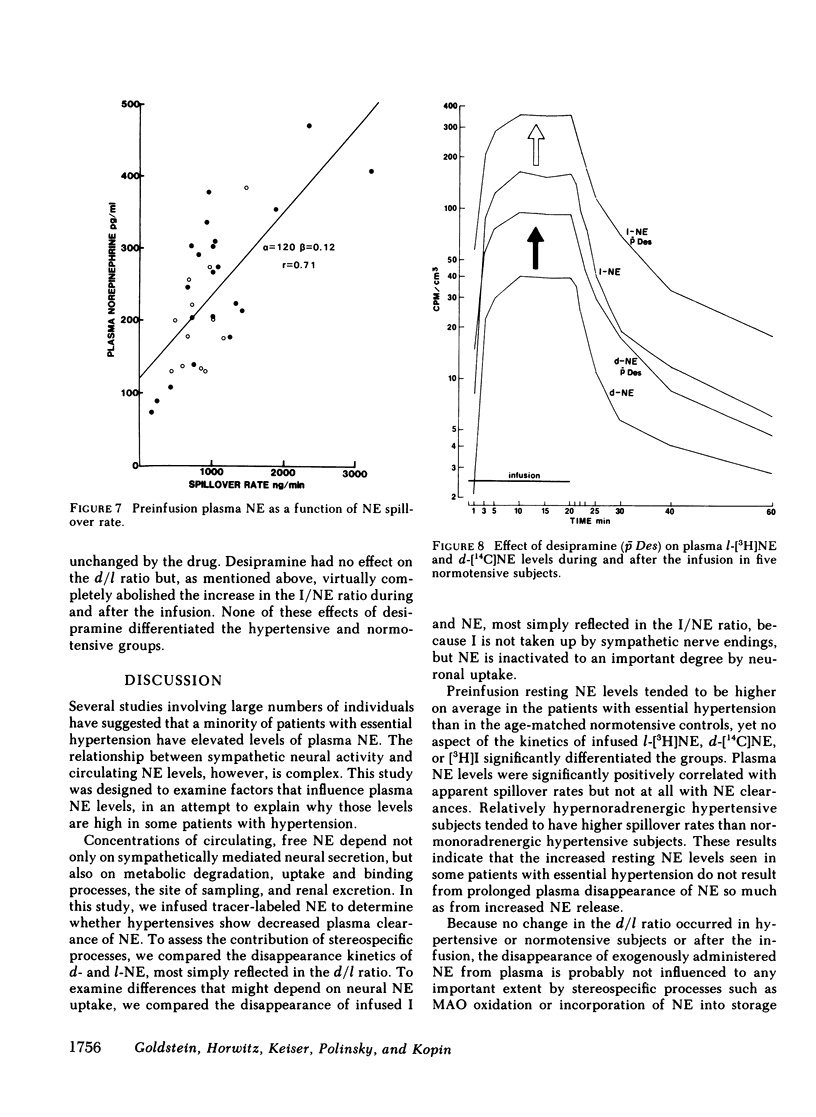
We infused tracer-labeled l-[3H]-norepinephrine, d-[14C]norepinephrine, and d,l-[3H]-isoproterenol simultaneously into patients with essential hypertension and into normotensive control subjects, in order to determine whether abnormalities in the disappearance kinetics of these substances characterized the hypertensive patients. The mean preinfusion venous plasma norepinephrine concentration was somewhat higher in the hypertensive group (260 vs. 194 pg/ml, P = 0.06), but the groups did not differ in the disappearance kinetics of l- or d-norepinephrine or of isoproterenol. Preinfusion plasma norepinephrine was significantly positively correlated with calculated spillover rates in both the hypertensive and normotensive groups, but not with norepinephrine clearances. The d/l ratio in plasma norepinephrine was the same as in the infusate during and after the infusion, even after pretreatment with the neuronal norepinephrine uptake blocker, desipramine. Because isoproterenol is not taken up by nerve endings, the ratio of [3H]isoproterenol to l-[3H]norepinephrine increased after the infusion ended. This increase was almost completely abolished by pretreatment with desipramine. These results indicate that (a) increased plasma norepinephrine levels seen in some patients with essential hypertension result from increased sympathetic neural activity and not from decreased clearance of norepinephrine, (b) changes in the isoproterenol/norepinephrine ratio after simultaneous infusion of both provide an index of neuronal norepinephrine uptake in man, and (c) neuronal norepinephrine uptake is not stereospecific.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertel O., Bühler F. R., Kiowski W., Lütold B. E. Decreased Beta-adrenoreceptor responsiveness as related to age, blood pressure, and plasma catecholamines in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1980 Mar-Apr;2(2):130–138. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.2.2.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callingham B. A., Burgen A. S. The uptake of isoprenaline and noradrenaline by the perfused rat heart. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 Jan;2(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Plasma catecholamines in long-term diabetics with and without neuropathy and in hypophysectomized subjects. J Clin Invest. 1972 Apr;51(4):779–787. doi: 10.1172/JCI106872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert E., Henseling M., Gescher A., Trendelenburg U. Stereoselectivity of the distribution of labelled noradrenaline in rabbit aortic strips after inhibition of the noradrenaline-metabolizing enzymes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1976;292(3):219–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00517382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Bobik A., Kelleher D., Jennings G., Leonard P., Skews H., Korner P. Determination of norepinephrine apparent release rate and clearance in humans. Life Sci. 1979 Oct 22;25(17):1461–1470. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90371-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Bobik A., Leonard P., Kelleher D., Skews H., Jennings G., Korner P. Norepinephrine kinetics in essential hypertension. Defective neuronal uptake of norepinephrine in some patients. Hypertension. 1981 Mar-Apr;3(2):149–156. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.2.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Leonard P., Bobik A., Skews H., Jennings G., Kelleher D., Korner P. Determination of noradrenaline uptake, spillover to plasma and plasma concentration in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59 (Suppl 6):311s–313s. doi: 10.1042/cs059311s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esler M., Jackman G., Leonard P., Skews H., Bobik A., Korner P. Effect of norepinephrine uptake blockers on norepinephrine kinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Jan;29(1):12–20. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald G. A., Hossmann V., Dollery C. T. Norepinephrine release in essential hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1981 Aug;30(2):164–171. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1981.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlow S., Dziedzic S., Dziedzic L., Roubein I. Metabolism of D, L-3H-norepinephrine in essential hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens. 1981;3(5):897–918. doi: 10.3109/10641968109033711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S., Feuerstein G., Izzo J. L., Jr, Kopin I. J., Keiser H. R. Validity and reliability of liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection for measuring plasma levels of norepinephrine and epinephrine in man. Life Sci. 1981 Feb 2;28(5):467–475. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S. Plasma norepinephrine during stress in essential hypertension. Hypertension. 1981 Sep-Oct;3(5):551–556. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.5.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. S. Plasma norepinephrine in essential hypertension. A study of the studies. Hypertension. 1981 Jan-Feb;3(1):48–52. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.3.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm M., Weidmann P., Keusch G., Meier A., Glück Z. Norepinephrine clearance and pressor effect in normal and hypertensive man. Klin Wochenschr. 1980 Nov 3;58(21):1175–1181. doi: 10.1007/BF01478873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halter J. B., Pflug A. E., Tolas A. G. Arterial-venous differences of plasma catecholamines in man. Metabolism. 1980 Jan;29(1):9–12. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90090-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henseling M., Trendelenburg U. Stereoselectivity of the accumulation and metabolism of noradrenaline in rabbit aortic strips. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1978 Apr;302(2):195–206. doi: 10.1007/BF00517986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchel O., Buu N. T., Unger T., Genest J. Free and conjugated catecholamines in human hypertension. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1978 Dec;4:77s–80s. doi: 10.1042/cs055077s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R. Relationship of sympathetic nervous system tone and blood pressure. Nephron. 1979;23(2-3):84–90. doi: 10.1159/000181614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake C. R., Ziegler M. G., Coleman M. D., Kopin I. J. Age-adjusted plasma norepinephrine levels are similar in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. N Engl J Med. 1977 Jan 27;296(4):208–209. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197701272960408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattiasson I., Hood B. Efflux of noradrenaline from platelets in normotensive members of hypertensive families. Clin Sci (Lond) 1982 Feb;62(2):151–155. doi: 10.1042/cs0620151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen S. L., Christensen N. J., Olsen N., Lassen N. A. Raynaud's phenomenon: peripheral catecholamine concentration and effect of sympathectomy. Acta Chir Scand Suppl. 1980;502:57–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa K., Matsuno T., Tsuchiya S., Ban M., Minaguchi K. Plasma level of norepinephrine, cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in essential hypertension. Jpn Circ J. 1981 Jun;45(6):654–660. doi: 10.1253/jcj.45.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickar D., Lake C. R., Cohen R. M., Jimerson D. C., Murphy D. L. Alterations in noradrenergic function during clorgyline treatment. Commun Psychopharmacol. 1980;4(5):379–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sever P. S., Osikowska B., Birch M., Tunbridge R. D. Plasma-noradrenaline in essential hypertension. Lancet. 1977 May 21;1(8021):1078–1081. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallin B. G., Sundlöf G., Eriksson B. M., Dominiak P., Grobecker H., Lindblad L. E. Plasma noradrenaline correlates to sympathetic muscle nerve activity in normotensive man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1981 Jan;111(1):69–73. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1981.tb06706.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler M. G., Lake C. R., Kopin I. J. The sympathetic-nervous-system defect in primary orthostatic hypotension. N Engl J Med. 1977 Feb 10;296(6):293–297. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197702102960601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



