Abstract
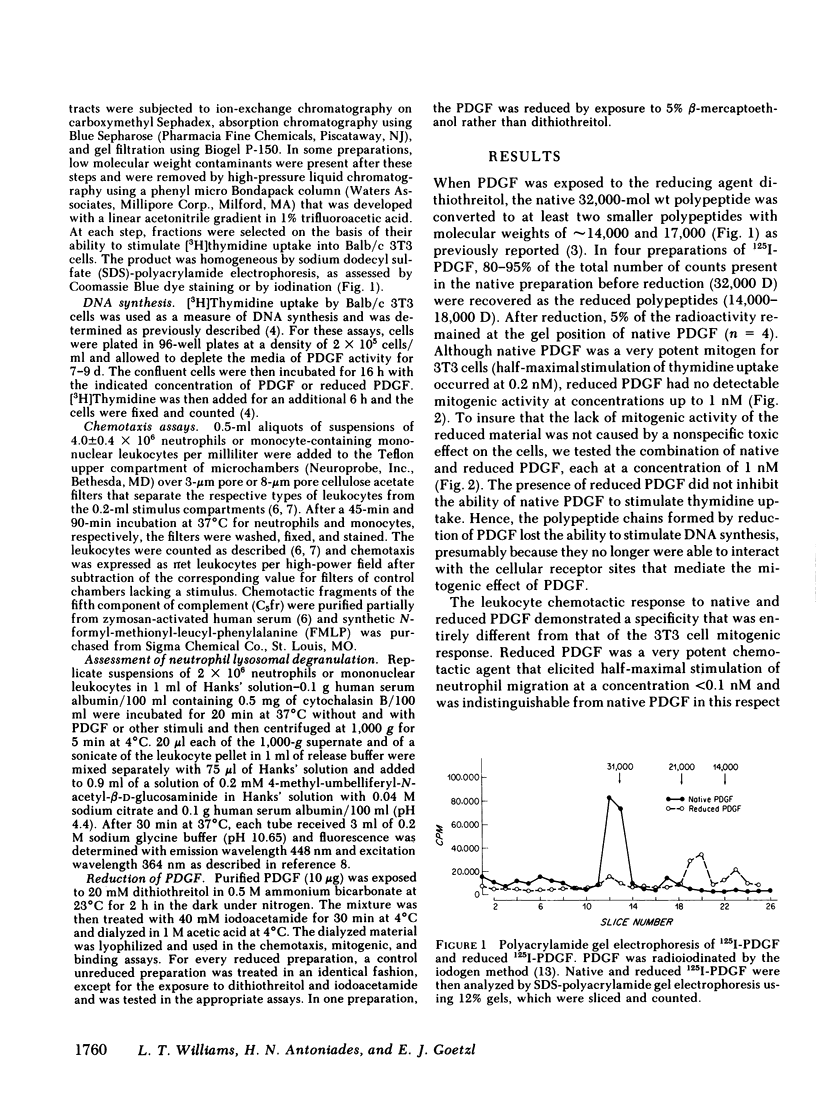
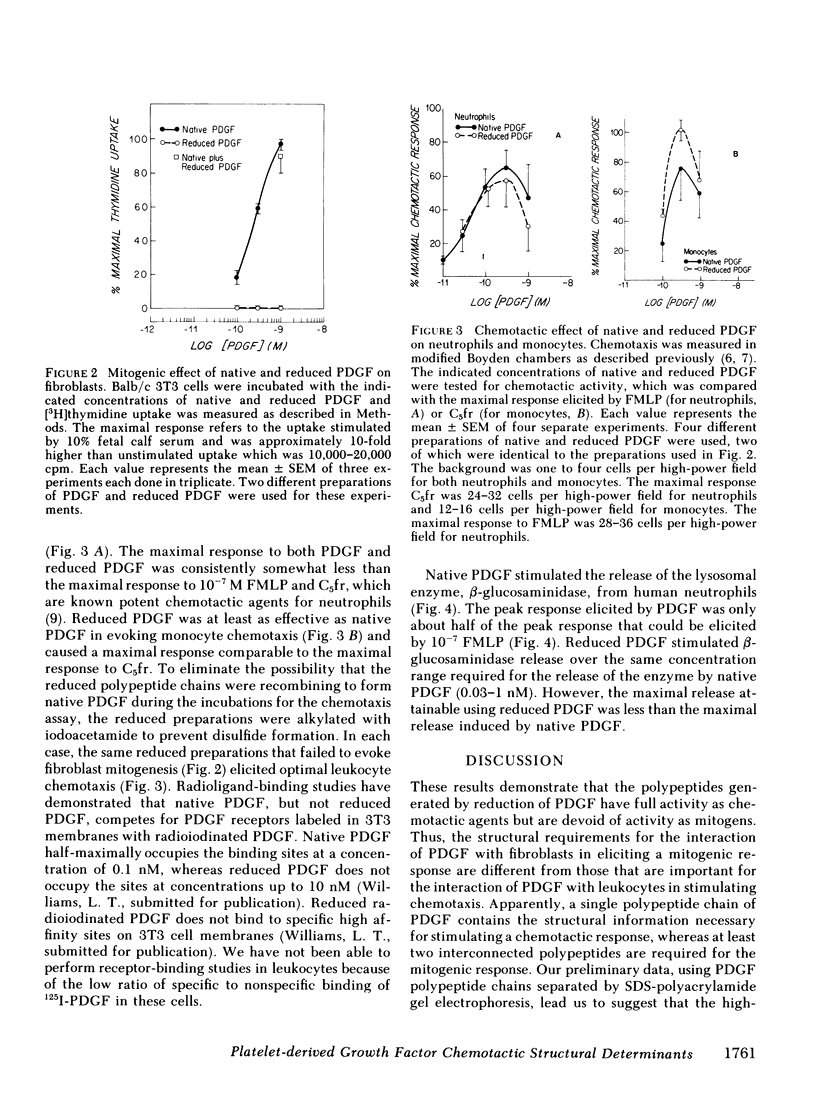
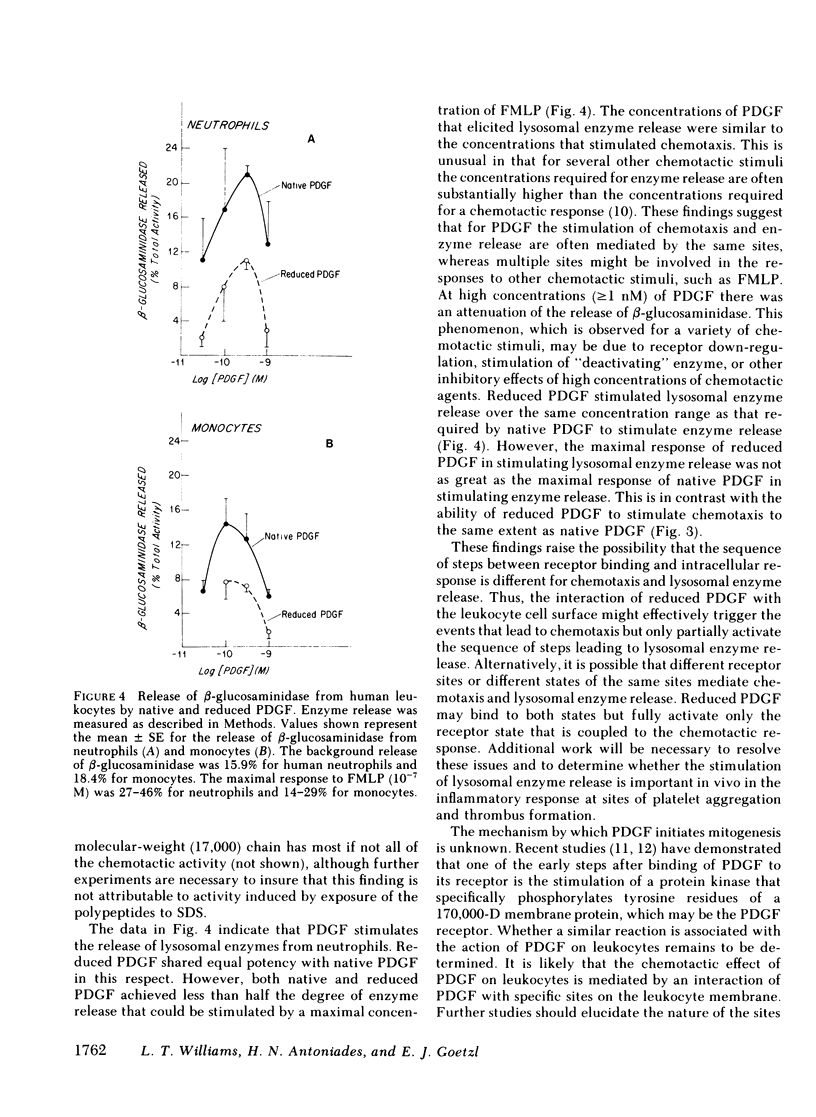
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) stimulates both proliferation of fibroblasts and chemotaxis of leukocytes. In this study we compared the mitogenic and chemotactic activities of native PDGF and reduced PDGF. Reduction of PDGF (Mr = 32,000) to its constituent polypeptides (Mr = 14,000 and 17,000) caused a loss of the ability to stimulate proliferation of Balb/c 3T3 cells. However, reduced PDGF retained virtually all of its activity as a chemotactic agent for human neutrophils and monocytes. A half-maximal chemotactic response to both native and reduced PDGF occurred at a concentration of approximately 0.08 nM for neutrophils and 0.1 nM for monocytes. The maximal chemotactic response to reduced PDGF was at least as great as the maximal response to native PDGF. Both native and reduced PDGF stimulated the release of the lysosomal enzyme, beta-glucosaminidase, from neutrophils with a half-maximal response at less than 0.1 nM. However, the net maximum release of this enzyme by PDGF (and reduced PDGF) was significantly less than that stimulated by a maximal concentration of the chemotactic peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine. These results indicate that different structural determinants are required for the proliferative response of 3T3 cells to PDGF and for the chemotactic response of leukocytes to PDGF.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deuel T. F., Senior R. M., Huang J. S., Griffin G. L. Chemotaxis of monocytes and neutrophils to platelet-derived growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):1046–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI110509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraker P. J., Speck J. C., Jr Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3a,6a-diphrenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. III. Identification of a platelet-derived growth factor receptor by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5172–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Hoe K. Y. Chemotactic factor receptors of human PMN leucocytes. I. Effects on migration of labelling plasma membrane determinants with impermeant covalent reagents and inhibition of labelling by chemotactic factors. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):407–418. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: purification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3722–3726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEABACK D. H., WALKER P. G. Studies on glucosaminidase. 4. The fluorimetric assay of N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78:151–156. doi: 10.1042/bj0780151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity in Swiss mouse 3T3 cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J. A. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1976 Aug 12;295(7):369–377. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197608122950707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Corcoran B. A., Wahl S. M. N-formylmethionyl peptides as chemoattractants for leucocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1059–1062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P., Antoniades H. N. Platelet-derived growth factor binds specifically to receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells and the binding becomes nondissociable. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5867–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



