Abstract
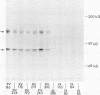
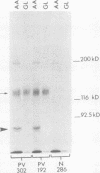
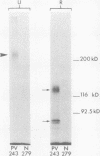
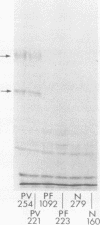
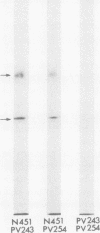
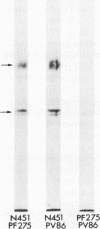
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) and pemphigus foliaceus (PF) are autoimmune blistering diseases in which antibodies develop to the cell surface of epidermal cells. In this study we sought to determine the antigenic specificity of antibodies in the sera of patients with PV and PF. Sera from 12 patients with PV were used to immunoprecipitate extracts of cultured human epidermal cells that were radiolabeled with 14C-amino acids. Immunoprecipitates were identified by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and fluorography. All 12 PV sera precipitated a protein which, when reduced, displayed chains of 130,000 and 80,000 mol wt on SDS-PAGE. Electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions identified a 210,000-mol wt molecule, which was presumably formed by disulfide crosslinking of the 130,000 and 80,000-mol wt chains. Immunoprecipitates of epidermal cell extracts that were labeled with 14C-glucosamine indicated that the 130,000-mol wt chain. Seven of eight PF sera, which were run concurrently with the PV sera in this immunoprecipitation assay, did not precipitate this glycoprotein, nor did they specifically precipitate any protein. To determine if a specific molecule which reacted with antibodies in PF sera could be identified, we used immunoblot analysis of extracts of normal human epidermis. The proteins in these extracts were reduced, separated by SDS-PAGE, and electrophoretically transferred to nitrocellulose sheets or to 2-aminophenylthioether paper. Immunoperoxidase staining of the transferred proteins with PF sera indicated that four of eight PF sera contained antibodies that stained a protein band of 160,000 mol wt. Indirect immunofluorescence, using normal human skin as the substrate, indicated that IgG that was eluted from this protein band stained the epidermis in a cell surface pattern. PV sera did not specifically recognize any bands by immunoblot analysis. Immunoblots performed with PV antigen that was immunoprecipitated from cell culture extracts suggested that, once denatured for SDS-PAGE, PV antigen is no longer immunoreactive. Taken together, these data indicate that: autoantibodies contained in PV sera from various patients have a unique molecular specificity; autoantibodies from most PF sera have a specificity different from that of PV autoantibodies; and autoantibodies from various PF patients may not have identical antigenic specificities. These differences in antigenic specificity between PV and PF sera may account for the clinical and histologic differences between these diseases.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Voorhees J. J., Beals T. F., Diaz L. A. Induction of pemphigus in neonatal mice by passive transfer of IgG from patients with the disease. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 20;306(20):1189–1196. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205203062001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutner E. H., Jordon R. E., Chorzelski T. P. The immunopathology of pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Aug;51(2):63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystryn J. C., Abel E., DeFeo C. Pemphigus foliaceus. Subcorneal intercellular antibodies of unique specificity. Arch Dermatol. 1974 Dec;110(6):857–861. doi: 10.1001/archderm.110.6.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bystryn J. C., Rodriguez J. Absence of intercellular antigens in the deep layers of the epidermis in pemphigus foliaceus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):339–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI108944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng J. S., Beutner E. H., Shu S., Chorzelski T. P. Pemphigus antibody action on skin explants: kinetics of acantholytic changes and stability of antigens in tissue cultures of normal monkey skin explants. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Jul;113(7):923–926. doi: 10.1001/archderm.113.7.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz L. A., Patel H., Calvanico N. J. Isolation of pemphigus antigen from human saliva. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):760–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farb R. M., Dykes R., Lazarus G. S. Anti-epidermal-cell-surface pemphigus antibody detaches viable epidermal cells from culture plates by activation of proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):459–463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Shafran K. M., Webber P. S., Lazarus G. S., Singer K. H. Anti-cell surface pemphigus autoantibody stimulates plasminogen activator activity of human epidermal cells. A mechanism for the loss of epidermal cohesion and blister formation. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):259–272. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Sullivan J. E., Kung M., Hennings H., Yuspa S. H. Optimized conditions for the growth of human epidermal cells in culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Aug;75(2):176–182. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12522602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyagawa S., Hojo T., Ishii H., Yoshioka J., Sakamoto K. Isolation and characterization of soluble epidermal antigens reactive with pemphigus antibodies. Acta Derm Venereol. 1977;57(1):7–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morioka S., Naito K., Ogawa H. The pathogenic role of pemphigus antibodies and proteinase in epidermal acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 May;76(5):337–341. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12519988. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemphigus: current concepts. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):396–405. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):331–343. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(75)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B., Papay R. Appearance of "pemphigus acantholysis factor" in human skin cultured with pemphigus antibody. J Invest Dermatol. 1979 Dec;73(6):575–581. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12541618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B., Papay R. Pemphigus antibody interaction with human epidermal cells in culture. J Clin Invest. 1978 Oct;62(4):778–788. doi: 10.1172/JCI109189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B. Production of epidermal acantholysis in normal human skin in vitro by the IgG fraction from pemphigus serum. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Aug;67(2):254–260. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12513454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shu S. Y., Beutner E. H. Isolation and characterization of antigens reactive with pemphigus antibodies. J Invest Dermatol. 1973 Nov;61(5):270–276. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12676492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Alvarez O. M., Bere E. W., Jr, Eaglstein W. H., Katz S. I. Detection of basement membrane zone antigens during epidermal wound healing in pigs. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Aug;77(2):240–243. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12480082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Hawley-Nelson P., Yuspa S. H., Shevach E. M., Katz S. I. Characterization of bullous pemphigoid antigen: a unique basement membrane protein of stratified squamous epithelia. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Woodley D. T., Katz S. I. Identification and partial characterization of pemphigoid antigen extracted from normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Jan;82(1):108–111. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12259224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley J. R., Yaar M., Hawley-Nelson P., Katz S. I. Pemphigus antibodies identify a cell surface glycoprotein synthesized by human and mouse keratinocytes. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):281–288. doi: 10.1172/JCI110615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thivolet C. H., Hintner H. H., Stanley J. R. The effect of retinoic acid on the expression of pemphigus and pemphigoid antigens in cultured human keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Apr;82(4):329–334. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12260634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo T. Y., Hogan V. A., Patel H., Anhalt G. J., Labib R. S., Voorhees J. J., Diaz L. A. Specificity and inhibition of the epidermal cell detachment induced by pemphigus IgG in vitro. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):115s–121s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. W., Beutner E. H. Blocking-immunofluorescence studies on the specificity of pemphigus autoantibodies. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Mar;7(2):168–175. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]