Abstract
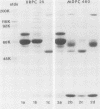
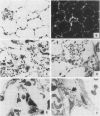
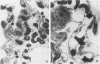
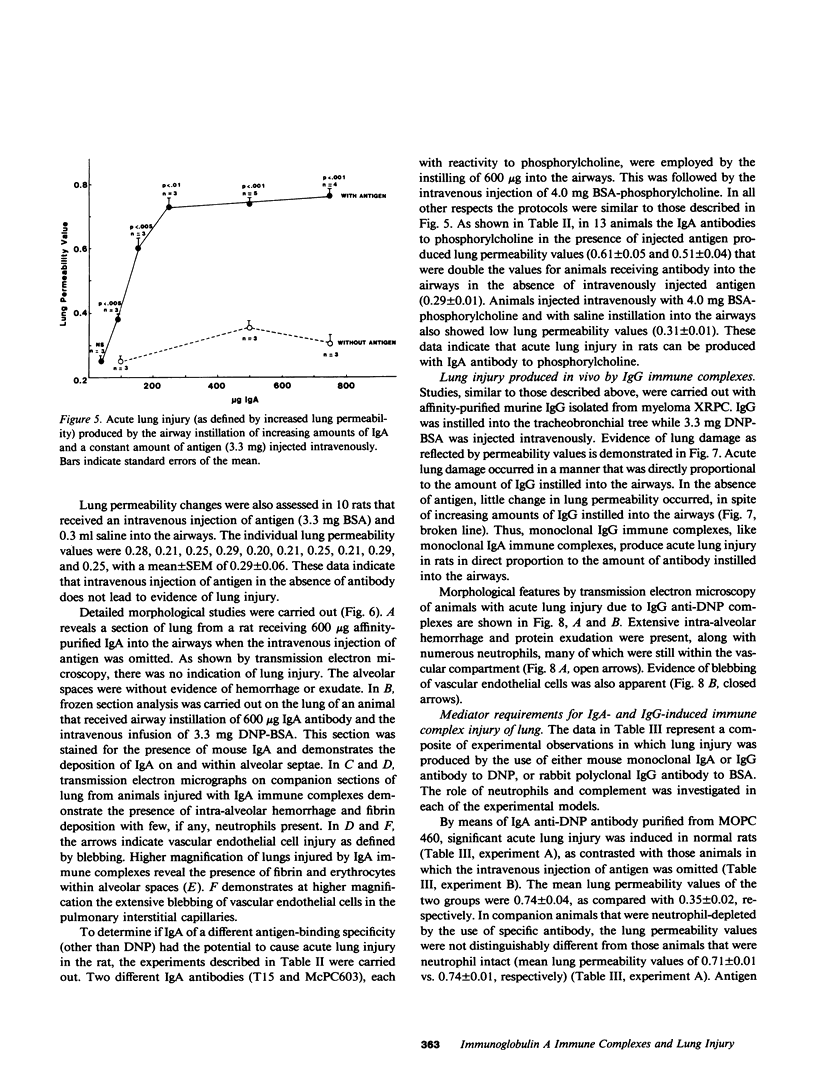
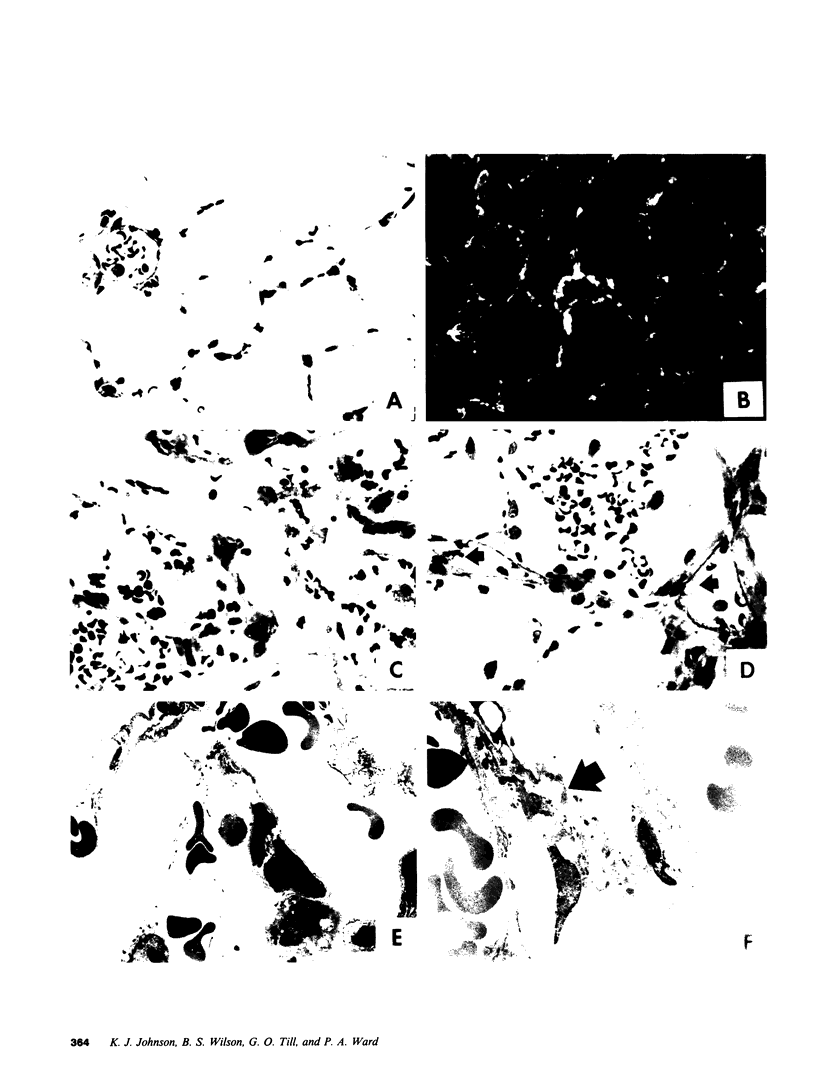
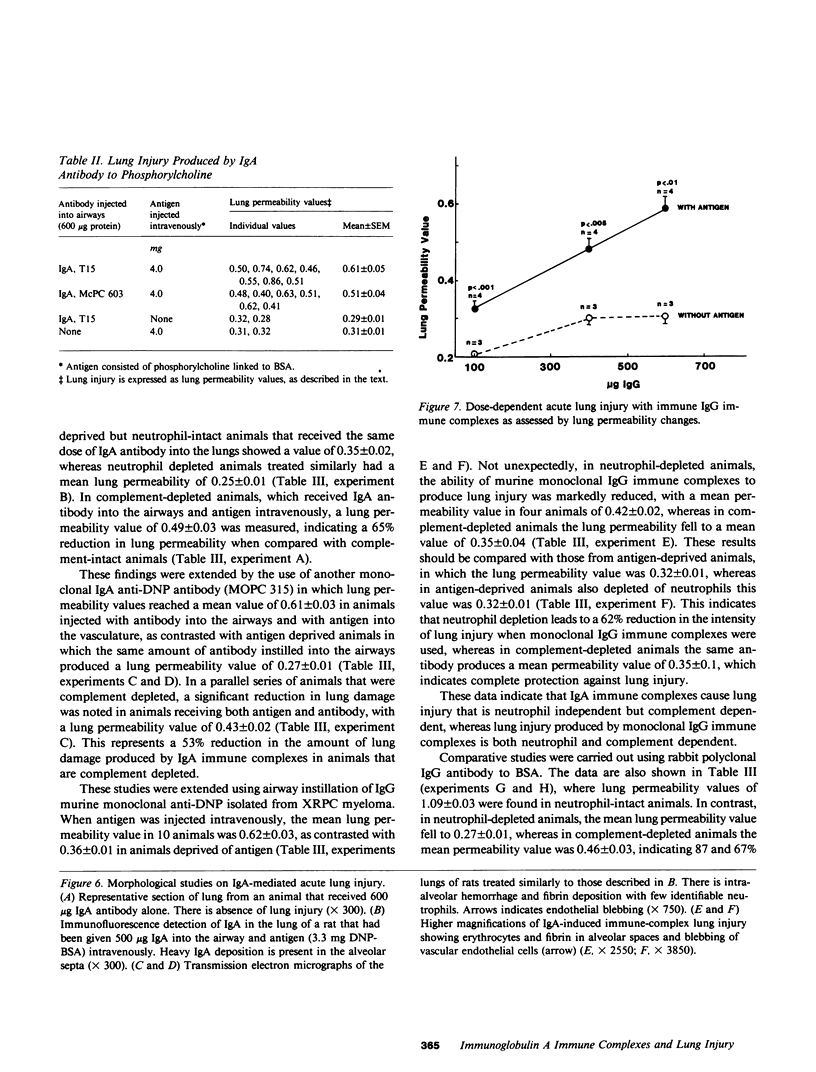
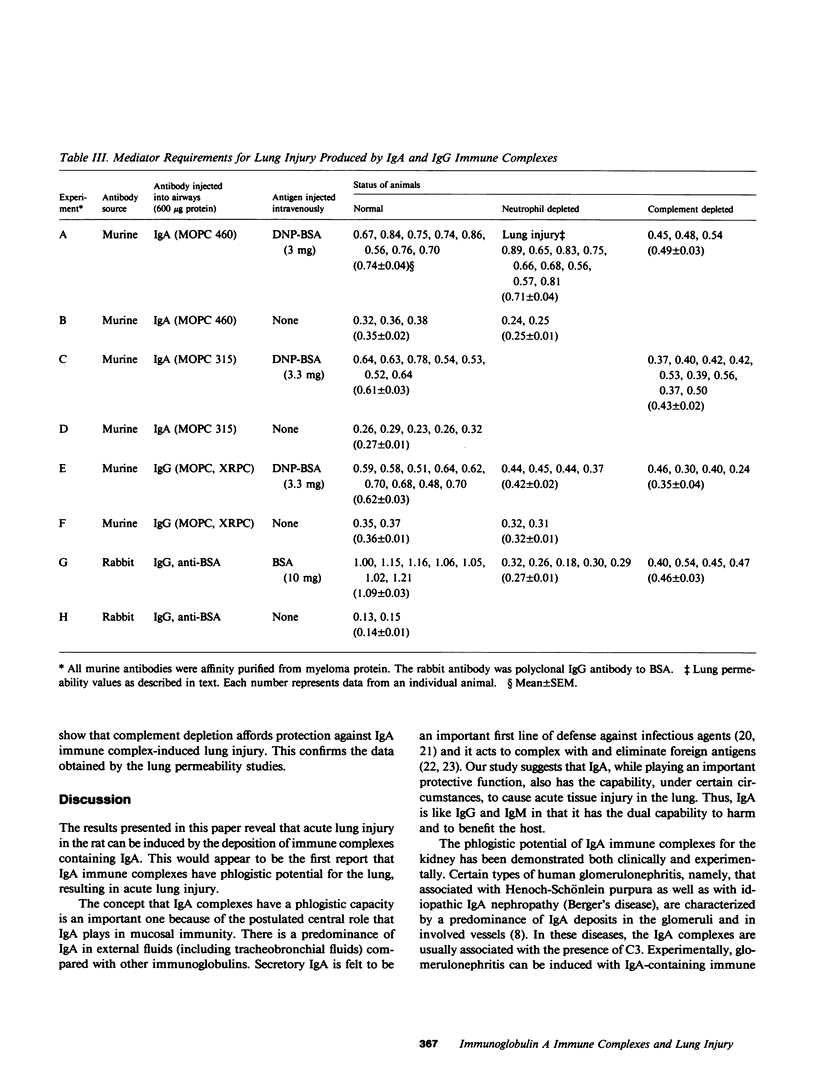
Mouse IgG and IgA, with reactivity to dinitrophenol conjugated to carrier protein, have been isolated from myeloma proteins by means of a variety of affinity techniques. The IgA was predominantly in the dimeric form. The in vitro and in vivo biological activities of IgA-containing immune complexes were assessed in the rat. IgA-containing immune complexes were demonstrated, in a dose-dependent manner in vitro, to activate neutrophils and to generate O.-2. In addition, these immune complexes showed evidence of complement activation in vitro, by the use of immunofixation techniques. When IgA was instilled into the airways of rats and antigen was injected intravenously, acute lung injury occurred, as reflected by increases in lung permeability and morphological changes consisting of blebbing of endothelial cells, intra-alveolar hemorrhage, and fibrin deposition. The lung changes were directly proportional to the amount of IgA instilled into the airways and failed to occur if intravenous injection of antigen was omitted. Lung injury did not occur in animals that received an intravenous injection of antigen in the absence of an airway injection of IgA. Lung injury related to IgA-containing immune complexes was complement dependent but neutrophil independent. In companion studies with mouse IgG-containing immune complexes, acute lung injury also occurred and had morphological features similar to those associated with IgA-induced lung injury except that, in the case of IgG immune complex-induced damage, neutrophils were more evident. Acute lung injury induced by IgG-containing immune complexes, whether of mouse or rabbit origin, was complement and neutrophil dependent. The similarities and differences between IgG- and IgA-associated acute immune complex-induced injury of rat lung were reinforced by the use of morphometry techniques. Studies with another monoclonal IgA antibody-containing antigen-binding activity to phosphorylcholine also demonstrated the ability of IgA antibody to cause acute lung injury in the rat. Neither antibody alone nor antigen (phosphorylcholine linked to bovine serum albumin) alone produced evidence of lung injury. These studies indicate for the first time that immune complexes containing IgA have lung-damaging properties and that the pathogenic mechanisms are different from those associated with IgG-associated immune complex-induced acute lung injury.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berger J. IgA glomerular deposits in renal disease. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):939–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G., Müller-Eberhard H. J., Aikin B. S. Depletion of plasma complement in vivo by a protein of cobra venom: its effect on various immunologic reactions. J Immunol. 1970 Jul;105(1):55–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colten H. R., Bienenstock J. Lack of C3 activation through classical or alternate pathways by human secretory IgA anti blood group A antibody. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):305–308. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreisin R. B., Schwarz M. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Stanford R. E. Circulating immune complexes in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. N Engl J Med. 1978 Feb 16;298(7):353–357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197802162980701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N. PREPARATION OF PURIFIED ANTI-2,4-DINITROPHENYL ANTIBODIES. Methods Med Res. 1964;10:94–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emancipator S. N., Gallo G. R., Lamm M. E. IgA-immune complex renal disease induced by mucosal immunization. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:171–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faille-Kuyber E. H., Kater L., Kooiker C. J., Dorhout Mees E. J. IgA-deposits in cutaneous blood-vessel walls and mesangium in Henoch-Schönlein syndrome. Lancet. 1973 Apr 21;1(7808):892–893. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Goldstine S. N., Shen L. The properties and role of receptors for IgA on human leukocytes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983 Jun 30;409:552–563. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb26898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Richards C., Lamontagne L. Fc receptors for IgA and other immunoglobulins on resident and activated alveolar macrophages. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1029–1037. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U. Induction of thromboxane release from macrophages by anaphylatoxic peptide C3a of complement and synthetic hexapeptide C3a 72-77. J Immunol. 1983 Mar;130(3):1345–1349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartung H. P., Hadding U., Bitter-Suermann D., Gemsa D. Stimulation of prostaglandin E and thromboxane synthesis in macrophages by purified C3b. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2861–2865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Kanayama Y., Ohe A., Kato N., Horiguchi T., Ishii M., Shiota K. Immunopathologic studies of pneumonitis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Jul;91(1):30–34. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-1-30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Acute immunologic pulmonary alveolitis. J Clin Invest. 1974 Aug;54(2):349–357. doi: 10.1172/JCI107770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. J., Ward P. A. Role of oxygen metabolites in immune complex injury of lung. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2365–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffenbach G., Lamm M. E., Gigli I. Activation of the guinea pig alternative complement pathway by mouse IgA immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):231–247. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. Antigen-binding myeloma proteins of mice. Adv Immunol. 1977;25:141–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifai A., Small P. A., Jr, Teague P. O., Ayoub E. M. Experimental IgA nephropathy. J Exp Med. 1979 Nov 1;150(5):1161–1173. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.5.1161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. F., Smith R. Immunofixation. I. General principles and application to agarose gel electrophoresis. Clin Chem. 1976 Apr;22(4):497–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roska A. K., Garancis J. C., Moore V. L., Abramoff P. Immune-complex disease in guinea pig lungs. I. Elicitation by aerosol challenge, suppression with cobra venom factor, and passive transfer with serum. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1977 Sep;8(2):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(77)90111-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherzer H., Ward P. A. Lung injury produced by immune complexes of varying composition. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):947–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz M. I., Dreisin R. B., Pratt D. S., Stanford R. E. Immunofluorescent patterns in the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Jun;91(6):929–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Epps D. E., Williams R. C., Jr Suppression of leukocyte chemotaxis by human IgA myeloma components. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1227–1242. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Duque R. E., Sulavik M. C., Johnson K. J. In vitro and in vivo stimulation of rat neutrophils and alveolar macrophages by immune complexes. Production of O-2 and H2O2. Am J Pathol. 1983 Mar;110(3):297–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Duque R. E., Sulavik M. C., Johnson K. J. In vitro and in vivo stimulation of rat neutrophils and alveolar macrophages by immune complexes. Production of O-2 and H2O2. Am J Pathol. 1983 Mar;110(3):297–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Till G. O., Kunkel R., Beauchamp C. Evidence for role of hydroxyl radical in complement and neutrophil-dependent tissue injury. J Clin Invest. 1983 Sep;72(3):789–801. doi: 10.1172/JCI111050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]