Abstract
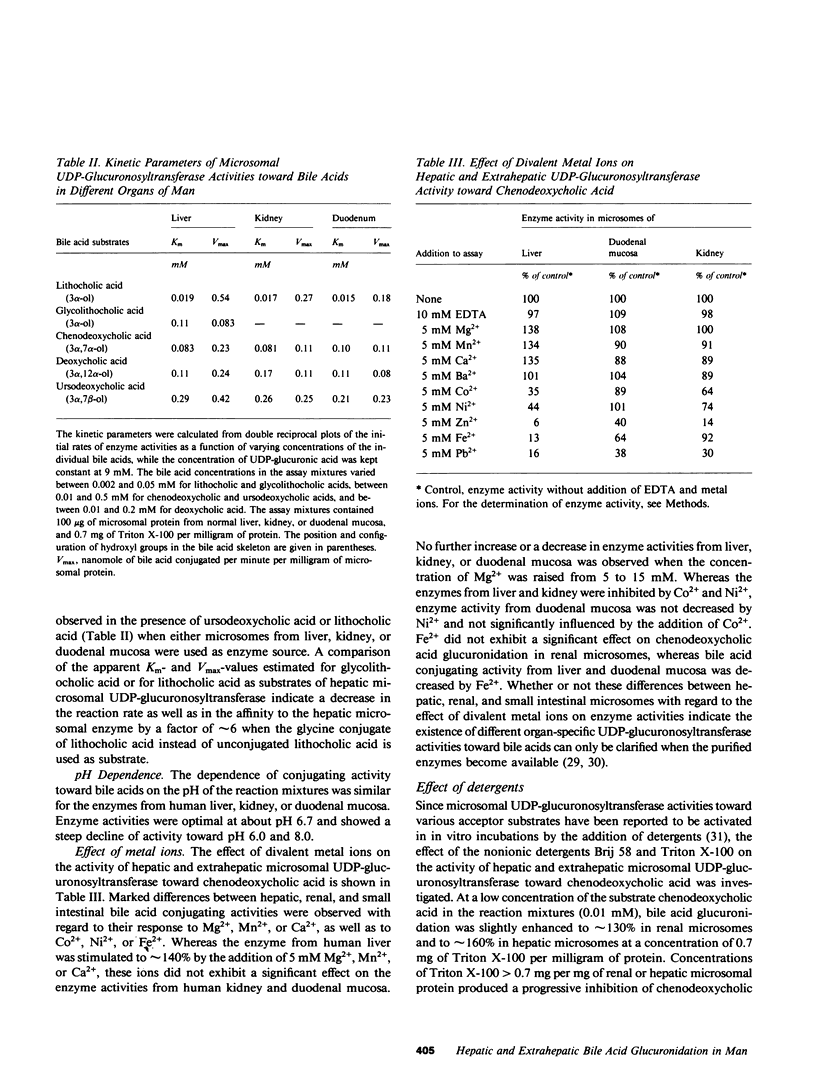
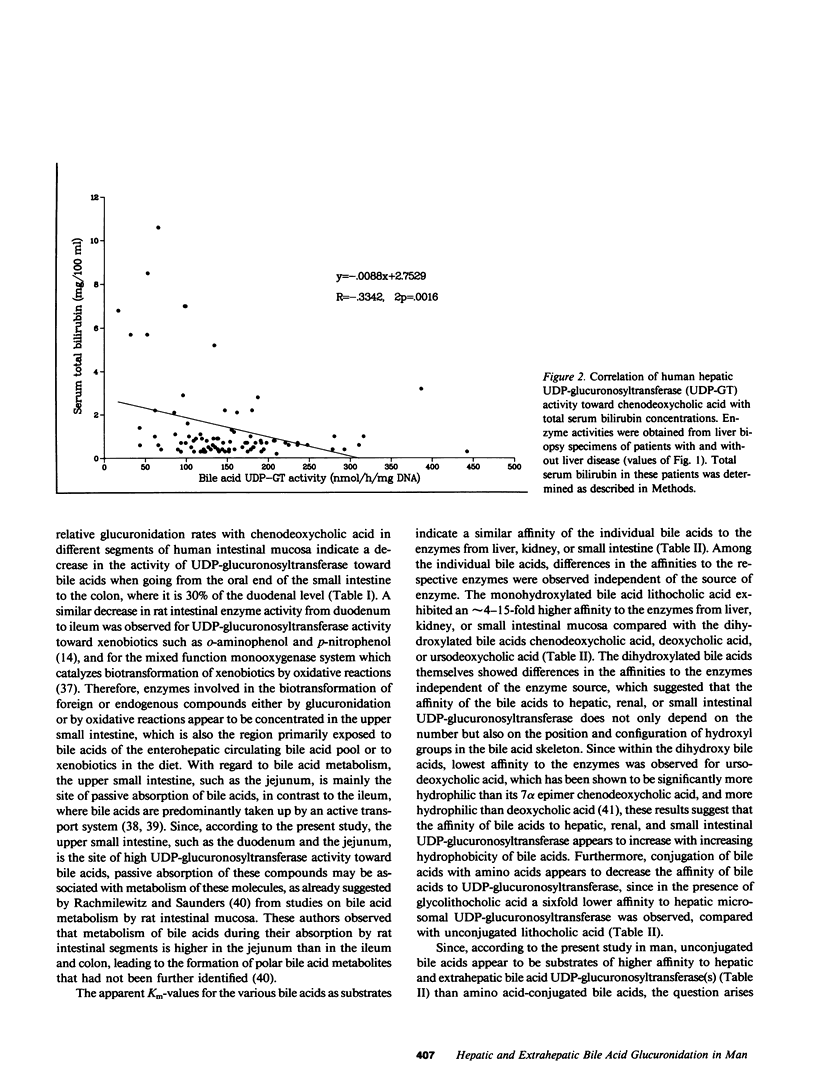
Microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity toward the bile acids (chenodeoxycholic, deoxycholic, ursodeoxycholic, lithocholic, and glycolithocholic) has been detected in human specimens of liver, kidney, and intestinal mucosa. The characteristics of hepatic and extrahepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activities toward these bile acids were compared with respect to kinetic parameters and other catalytic properties. Whereas no organ-specific differences in the affinities of individual bile acids to hepatic and extrahepatic UDP-glucuronosyltransferases were observed, the individual bile acids showed reaction rates in liver that were about twice the rates estimated in kidney and about twice to three times the rates observed in duodenal mucosa. In intestinal mucosa the rate of chenodeoxycholic acid glucuronidation exhibited a progressive decrease from duodenum to colon, where it was 30% of the duodenal level. Comparison of the glucuronidation rates that were estimated with different bile acids in hepatic or extrahepatic tissues showed that for each organ a bile acid structure-activity relationship existed, with highest activity observed for lithocholic and ursodeoxycholic acids, which was about twofold higher compared with chenodeoxycholic or deoxycholic acids. Lowest activity was estimated for glycolithocholic acid. UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity toward chenodeoxycholic acid was studied in biopsy specimens of liver that were obtained from a large group of patients with the following liver diseases: liver cirrhosis, liver fibrosis, granulomatous hepatitis, fatty liver hepatitis, and fatty liver. A significant decrease in enzyme activity was observed in patients with liver cirrhosis and in patients with granulomatous hepatitis compared with patients without liver disease.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almé B., Nordén A., Sjövall J. Glucuronides of unconjugated 6-hydroxylated bile acids in urine of a patient with malabsorption. Clin Chim Acta. 1978 Jun 15;86(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(78)90379-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almé B., Sjövall J. Analysis of bile acid glucuronides in urine. Identification of 3 alpha, 6 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5 beta-cholanoic acid. J Steroid Biochem. 1980 Aug;13(8):907–916. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(80)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong M. J., Carey M. C. The hydrophobic-hydrophilic balance of bile salts. Inverse correlation between reverse-phase high performance liquid chromatographic mobilities and micellar cholesterol-solubilizing capacities. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):70–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachrach W. H., Hofmann A. F. Ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of cholesterol cholelithiasis. part I. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 Aug;27(8):737–761. doi: 10.1007/BF01393771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Back P., Spaczynski K., Gerok W. Bile-salt glucuronides in urine. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jun;355(6):749–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black M., Billing B. H. Hepatic bilirubin udp-glucuronyl transferase activity in liver disease and gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jun 5;280(23):1266–1271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196906052802303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock K. W., Matern S. Immunochemical studies on rat-liver microsomal NAD glycohydrolase. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 21;38(1):20–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danzinger R. G., Hofmann A. F., Schoenfield L. J., Thistle J. L. Dissolution of cholesterol gallstones by chenodeoxycholic acid. N Engl J Med. 1972 Jan 6;286(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197201062860101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENEROTH P. THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1963 Jan;4:11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorowski T., Salen G., Tint G. S., Mosbach E. Transformation of chenodeoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid by human intestinal bacteria. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1068–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobkirk R., Green R. N., Nilsen M., Jennings B. A. Formation of estrogen glucosiduronates by human kidney homogenates. Can J Biochem. 1974 Jan;52(1):9–14. doi: 10.1139/o74-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoensch H. P., Hutt R., Hartmann F. Biotransformation of xenobiotics in human intestinal mucosa. Environ Health Perspect. 1979 Dec;33:71–78. doi: 10.1289/ehp.793371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoensch H., Woo C. H., Raffin S. B., Schmid R. Oxidative metabolism of foreign compounds in rat small intestine: cellular localization and dependence on dietary iron. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jun;70(6):1063–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen O., Aitio A., Hartiala K. Gastrointestinal distribution of glucuronide synthesis and the relevant enzymes in the rat. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1968;3(5):461–464. doi: 10.3109/00365526809179903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis B., Tabaqchali S., Panveliwalla D., Wootton I. D. Serum-bile-acids in the stagnant-loop syndrome. Lancet. 1969 Feb 1;1(7588):219–220. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91238-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H. C., Porter N., Holmes G., Gessner T. Substrate specificity of human UDP-glucuronyltransferase in cultured lymphocytes. Xenobiotica. 1981 Oct;11(10):647–654. doi: 10.3109/00498258109049084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MICHAUELSSON M., NOSSLIN B., SJOELIN S. PLASMA BILIRUBIN DETERMINATION IN THE NEWBORN INFANT. A METHODOLOGICAL STUDY WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO THE INFLUENCE OF HEMOLYSIS. Pediatrics. 1965 Jun;35:925–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino I., Nakagawa S., Mashimo K. Conjugated and unconjugated serum bile acid levels n patients with hepatobiliary diseases. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jun;56(6):1033–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. W., Sue S. O., Pearlman B. J., Bonorris G. G., Varady P., Lachin J. M., Schoenfield L. J. Sulfation of lithocholate as a possible modifier of chenodeoxycholic acid-induced elevations of serum transaminase in patients with gallstones. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1190–1196. doi: 10.1172/JCI110364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Matern S., Gerok W. A rapid and sensitive method for the assay of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity toward bile acids. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):417–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Matern S., Gerok W. Isolation and characterization of rat liver microsomal UDP-glucuronosyltransferase activity toward chenodeoxycholic acid and testosterone as a single form of enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7422–7429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern H., Matern S., Schelzig C., Gerok W. Bile acid UDP-glucoronyltransferase from human liver. Properties and studies on aglycone substrate specificity. FEBS Lett. 1980 Sep 8;118(2):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80231-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matern S., Gerok W. Pathophysiology of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;85:125–204. doi: 10.1007/BFb0036117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. H. The formation of bile acid sulfates: a new pathway of bile acid metabolism in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1047–1050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Saunders D. R. Metabolism of chenodeoxycholate by intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1976 Jul;71(1):82–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEVENSON I. H., DUTTON G. J. Glucuronide synthesis in kidney and gastrointestinal tract. Biochem J. 1962 Feb;82:330–340. doi: 10.1042/bj0820330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff E. R., Small N. C., Dietschy J. M. Characterization of the kinetics of the passive and active transport mechanisms for bile acid absorption in the small intestine and colon of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jun;51(6):1351–1362. doi: 10.1172/JCI106931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senn H. J., Cooper C., Warnke P. C., Wagner M., Decker K. Ganglioside biosynthesis in rat liver. Characterization of UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine -- GM3 acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):59–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05670.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setchell K. D., Lawson A. M., Blackstock E. J., Murphy G. M. Diurnal changes in serum unconjugated bile acids in normal man. Gut. 1982 Aug;23(8):637–642. doi: 10.1136/gut.23.8.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiehl A., Raedsch R., Rudolph G., Czygan P., Walker S. Analysis of bile acid glucuronides in urine: group separation on a lipophilic anion exchanger. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Aug 18;123(3):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Otsuka H., Beppu T., Seyama Y., Yamakawa T. Quantitative determination of bile acid glucuronides in serum by mass fragmentography. J Biochem. 1982 Oct;92(4):985–998. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takikawa H., Otsuka H., Beppu T., Seyama Y., Yamakawa T. Serum concentrations of bile acid glucuronides in hepatobiliary diseases. Digestion. 1983;27(4):189–195. doi: 10.1159/000198952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berge-Henegouwen G. P., Hofmann A. F. Pharmacology of chenodeoxycholic acid. II. Absorption and metabolism. Gastroenterology. 1977 Aug;73(2):300–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



