Abstract
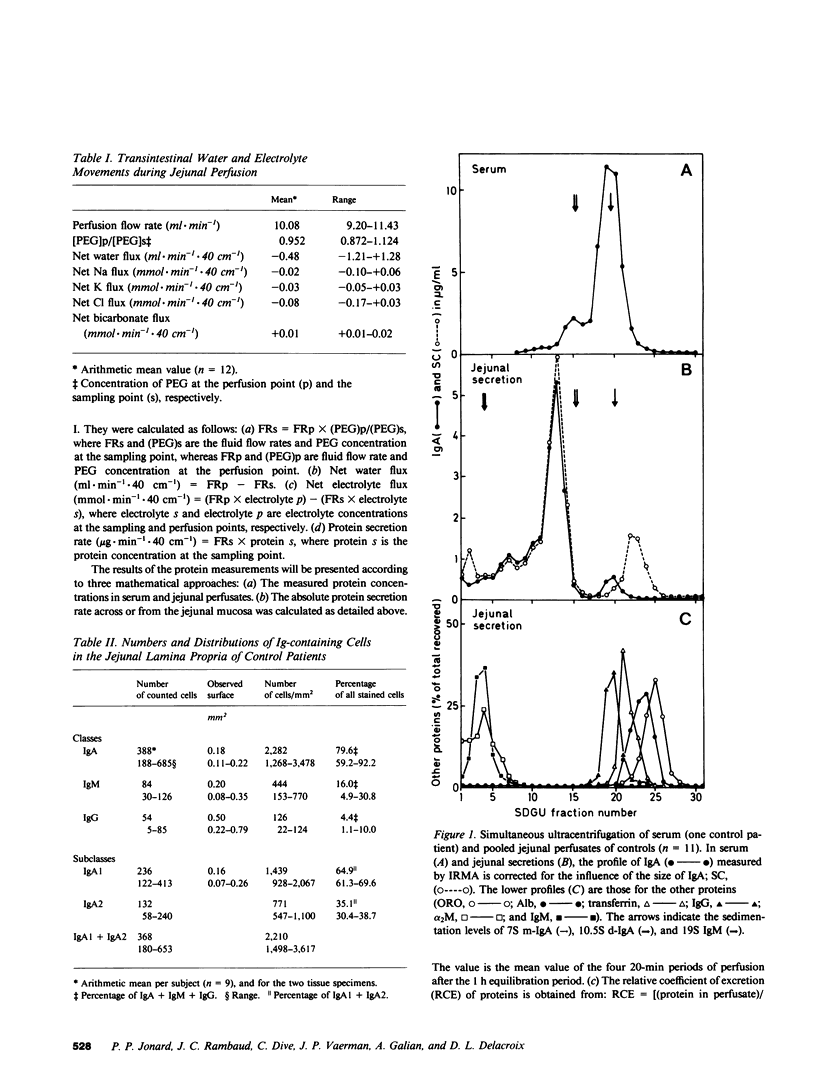
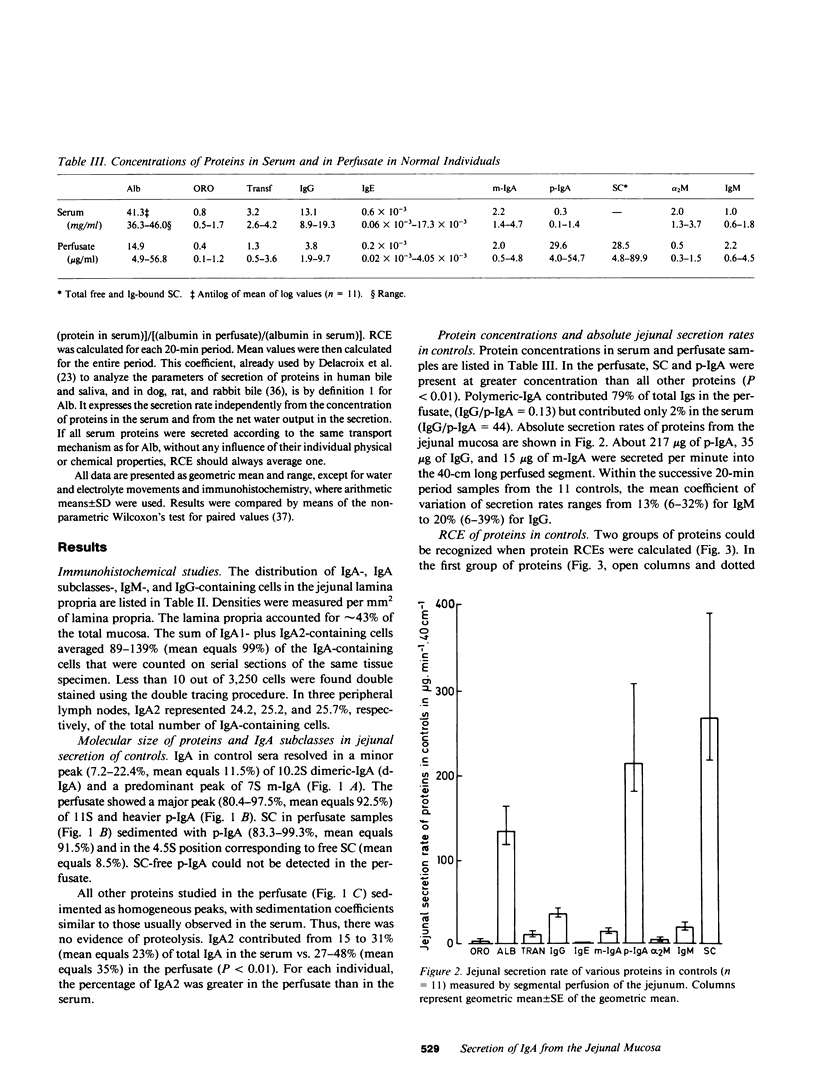
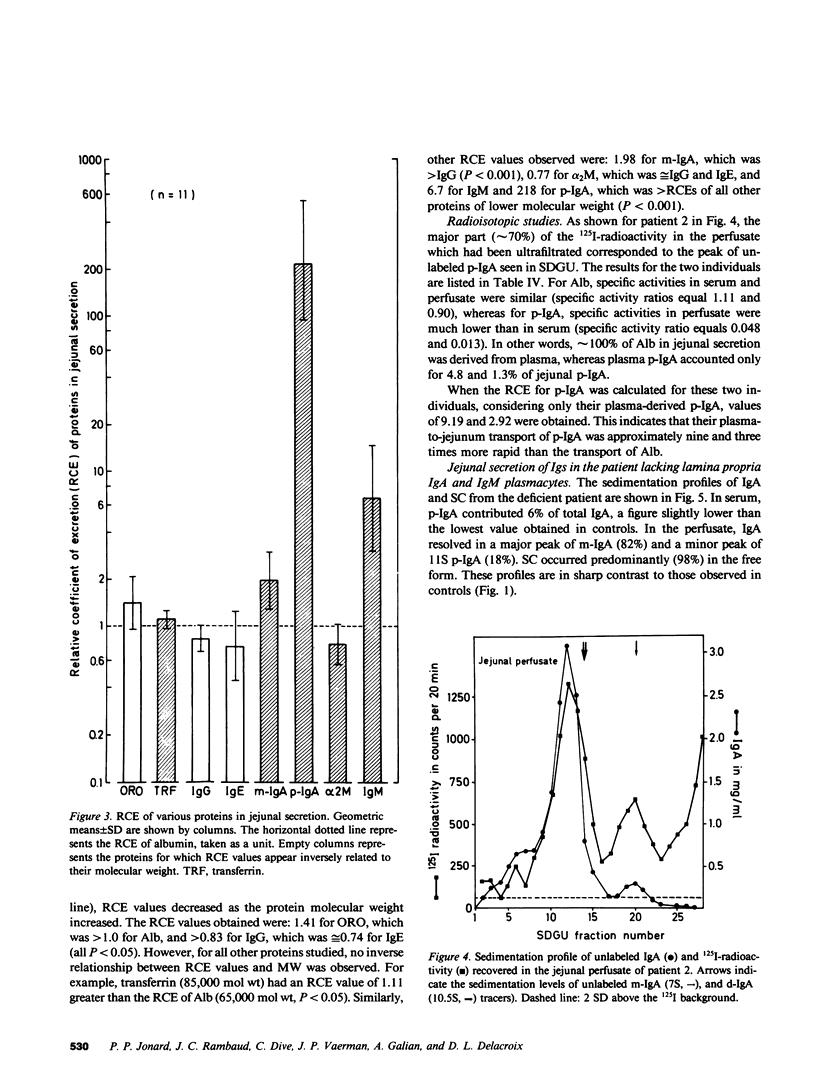
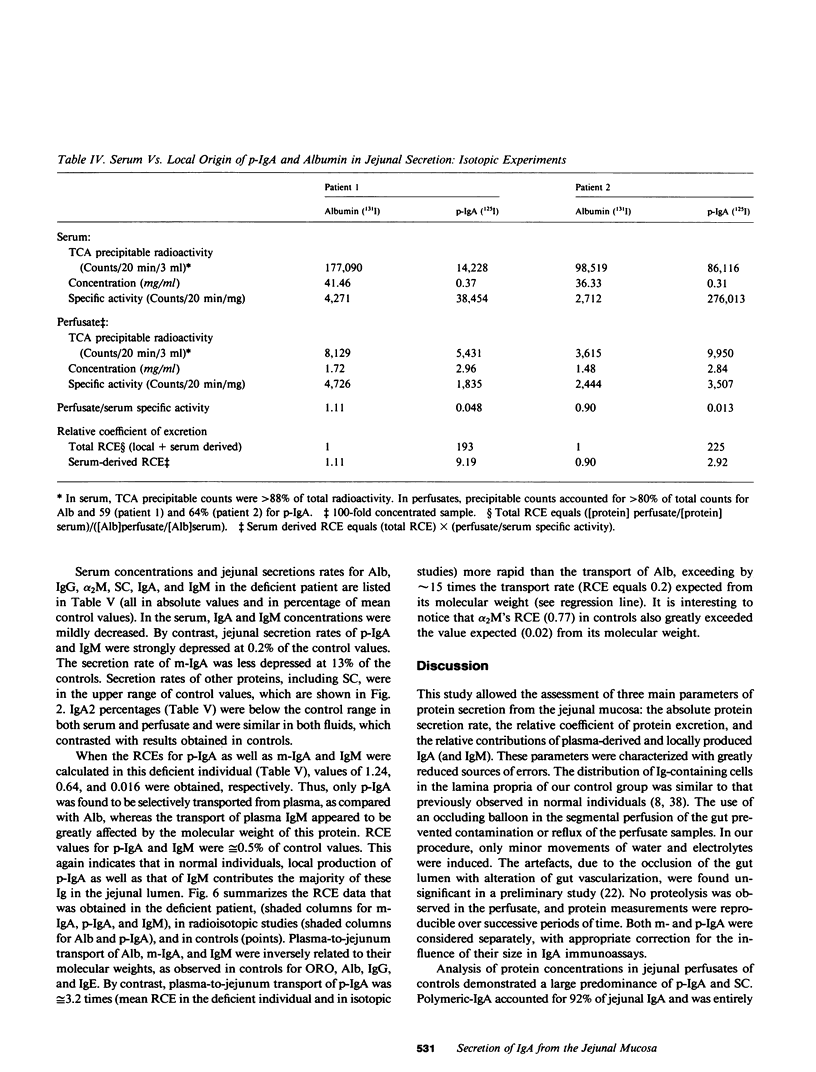
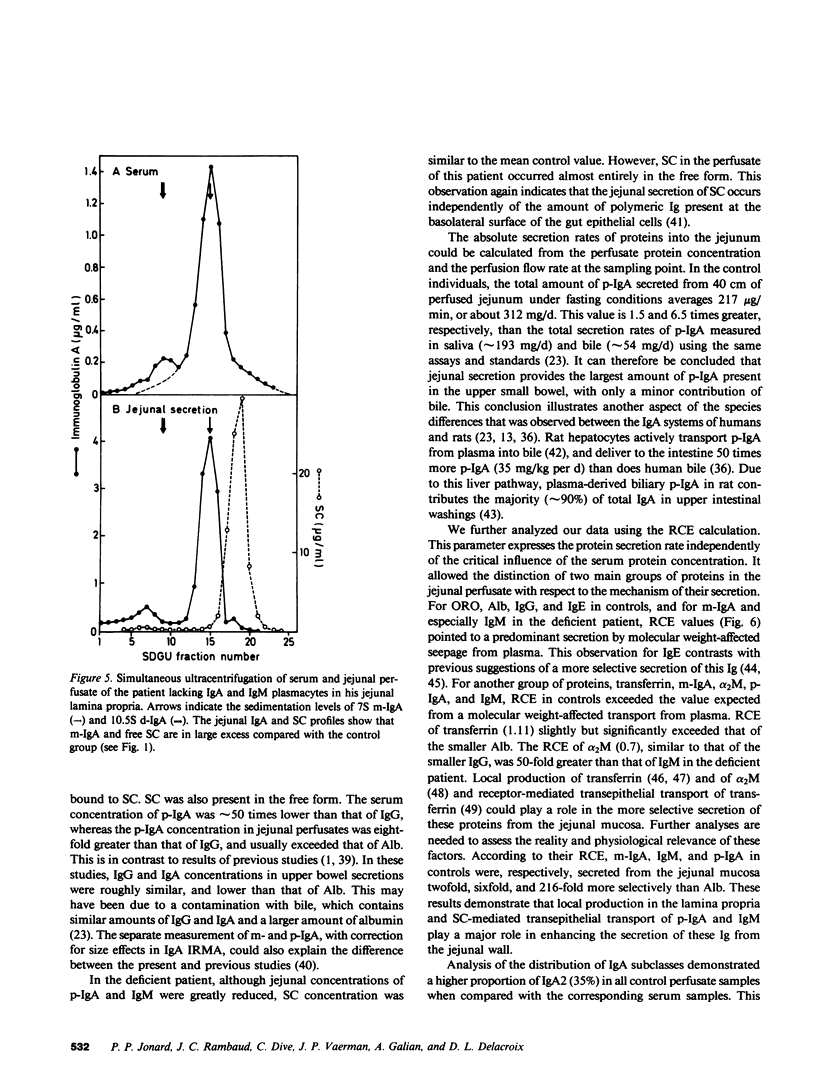
Parameters of secretion of IgA and several other plasma proteins from the jejunal mucosa were investigated in 11 individuals who had a normal distribution of Ig-containing cells in the lamina propria and in one patient who was totally deficient in jejunal IgA and IgM plasmacytes. Jejunal samples were collected during segmental gut perfusion. The following results were obtained: (a) The secretion of polymeric IgA (p-IgA, mean equals 217 micrograms/40 cm per min) exceeded those of albumin (132 micrograms), IgG (35 micrograms), and monomeric IgA (m-IgA, 15 micrograms, or 6.4% of total IgA). About 35% of IgA was IgA2 in the jejunal secretion, compared with approximately 23% in serum. This closely corresponds to the 35 and 24% of IgA2 plasmocytes in jejunal mucosa and peripheral lymph nodes, respectively. (b) For each protein, a relative coefficient of excretion (RCE) was calculated (jejunum to serum concentration ratio expressed relative to that of albumin). RCEs of 1.41 for orosomucoid, 1.0 for albumin, 0.83 for IgG, and 0.74 for IgE and, in the deficient patient, of 0.64 for m-IgA and 0.016 for IgM were obtained. This was inversely related to the molecular weight of these proteins and indicated their predominantly passive transport into the jejunum. However, in normal individuals, the RCE of transferrin (approximately 1.11 greater than 1, P greater than 0.05), alpha 2-macro globulin (approximately 0.77), m-IgA (approximately 1.98), and p-IgA (approximately 218) exceeded the value expected from simple seepage from plasma, thus pointing to an additional role of either local gut synthesis and/or active transepithelial transport. (c) Approximately 98% of p-IgA, approximately 99% of IgM, and approximately 68% of m-IgA in jejunal secretions were derived from local production in the gut wall, as determined by 125I-p-IgA specific activities and/or by comparison between the RCE values of the deficient patient to the values of controls. Therefore, the jejunal production of p-IgA (approximately 312 mg/d per 40 cm vs. approximately 54 mg/d from bile) contributes the majority of upper intestinal IgA in humans. The active transport of plasma p-IgA across the intestinal mucosa (approximately 0.08 mg/40 cm per kg per d) contributes less than 2% of the total amount of p-IgA (4.5 mg/kg per d) that is cleared daily from plasma.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alley C. D., Nash G. S., MacDermott R. P. Marked in vitro spontaneous secretion of IgA by human rib bone marrow mononuclear cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2604–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André C., André F., Fargier C. Distribution of IgA 1 and IgA 2 plasma cells in various normal human tissues and in the jejunum of plasma IgA-deficient patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1978 Aug;33(2):327–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belut D., Moneret-Vautrin D. A., Nicolas J. P., Grilliat J. P. IgE levels in intestinal juice. Dig Dis Sci. 1980 May;25(5):323–332. doi: 10.1007/BF01308055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P., Baklien K. Immunohistochemical studies of the formation and epithelial transport of immunoglobulins in normal and diseased human intestinal mucosa. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1976;36:1–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Human secretory component--VI. Immunoglobulin-binding properities. Immunochemistry. 1977 Mar;14(3):179–188. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(77)90192-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Transport models for secretory IgA and secretory IgM. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 May;44(2):221–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandtzaeg P. Two types of IgA immunocytes in man. Nat New Biol. 1973 May 30;243(126):142–143. doi: 10.1038/newbio243142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Borthistle B. K., Chen S. T. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IgE-containing cells in human gastrointestinal fluids and tissues. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):227–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Isobe K., Nakane P. K., Pacini B. Studies on translocation of immunoglobulins across intestinal epithelium. IV. Evidence for binding of IgA and IgM to secretory component in intestinal epithelium. Gastroenterology. 1977 Dec;73(6):1333–1339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Bienenstock J., Tomasi T. B., Jr Studies on human intestinal immunoglobulin A. Gastroenterology. 1971 Mar;60(3):370–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabbé P. A., Heremans J. F. The distribution of immunoglobulin-containing cells along the human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology. 1966 Sep;51(3):305–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crago S. S., Kulhavy R., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Secretory component of epithelial cells is a surface receptor for polymeric immunoglobulins. J Exp Med. 1978 Jun 1;147(6):1832–1837. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.6.1832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dehennin J. P., Vaerman J. P. Influence of molecular size of IgA on its immunoassay by various techniques. II. Solid-phase radioimmunoassays. J Immunol Methods. 1982;48(3):327–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Denef A. M., Acosta G. A., Montgomery P. C., Vaerman J. P. Immunoglobulins in rabbit hepatic bile: selective secretion of IgA and IgM and active plasma-to-bile transfer of polymeric IgA. Scand J Immunol. 1982 Oct;16(4):343–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1982.tb00733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Dive C., Rambaud J. C., Vaerman J. P. IgA subclasses in various secretions and in serum. Immunology. 1982 Oct;47(2):383–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Elkom K. B., Geubel A. P., Hodgson H. F., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Changes in size, subclass, and metabolic properties of serum immunoglobulin A in liver diseases and in other diseases with high serum immunoglobulin A. J Clin Invest. 1983 Feb;71(2):358–367. doi: 10.1172/JCI110777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Furtado-Barreira G., de Hemptinne B., Goudswaard J., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. The liver in the IgA secretory immune system. Dogs, but not rats and rabbits, are suitable models for human studies. Hepatology. 1983 Nov-Dec;3(6):980–988. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Hodgson H. J., McPherson A., Dive C., Vaerman J. P. Selective transport of polymeric immunoglobulin A in bile. Quantitative relationships of monomeric and polymeric immunoglobulin A, immunoglobulin M, and other proteins in serum, bile, and saliva. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):230–241. doi: 10.1172/JCI110610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Meykens R., Vaerman J. P. Influence of molecular size of IgA on its immunoassay by various techniques--I. Direct and reversed single radial immunodiffusion. Mol Immunol. 1982 Feb;19(2):297–305. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacroix D. L., Vaerman J. P. Influence of molecular size of IgA on its immunoassay by various techniques. III. Immunonephelometry. J Immunol Methods. 1982;51(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Segmental perfusion techniques. Gastroenterology. 1969 May;56(5):987–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Brown G., Trowbridge I. S., Woolston R. E., Mason D. Y. Transferrin receptors in human tissues: their distribution and possible clinical relevance. J Clin Pathol. 1983 May;36(5):539–545. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.5.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey H. M., Abel C. A., Yount W. J., Kunkel H. G. A subclass of human gamma-A-globulins (gamma-A2) which lacks the disulfied bonds linking heavy and light chains. J Exp Med. 1968 Dec 1;128(6):1223–1236. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.6.1223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovi T., Mosher D., Vaheri A. Cultured human monocytes synthesize and secrete alpha2-macroglobulin. J Exp Med. 1977 Jun 1;145(6):1580–1589. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høj L., Oddsson E., Krag E. Secretion rate of intestinal immunoglobulins, complement factor C3, "acute phase" reactants, and albumin in the perfused ileum and jejunum of normal man. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1981 Aug;89(4):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb02692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G., Jacobs P., Purves L. R. Iron binding proteins of iron-absorbing rat intestinal mucosa. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1467–1476. doi: 10.1172/JCI110900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutteh W. H., Prince S. J., Mestecky J. Tissue origins of human polymeric and monomeric IgA. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):990–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaitre-Coelho I., Jackson G. D., Vaerman J. P. Relevance of biliary IgA antibodies in rat intestinal immunity. Scand J Immunol. 1978;8(5):459–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00542.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson C. G., Masson P. L. Particle counting immunoassay of immunoglobulin E antibodies after their elution from allergosorbents by pepsin: an alternative to the radioallergosorbent test. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Nov;70(5):326–336. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90021-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P. L., Cambiaso C. L., Collet-Cassart D., Magnusson C. G., Richards C. B., Sindic C. J. Particle counting immunoassay (PACIA). Methods Enzymol. 1981;74(Pt 100):106–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)74008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K. E., Blobel G. A transmembrane precursor of secretory component. The receptor for transcellular transport of polymeric immunoglobulins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11816–11821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Secretory component in immmunoglobulin deficiency: and immunoelectron microscopic study of intestinal epithelium. Scand J Immunol. 1980;12(4):359–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1980.tb00078.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagura H., Nakane P. K., Brown W. R. Translocation of dimeric IgA through neoplastic colon cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2359–2368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radl J., Schuit H. R., Mestecky J., Hijmans W. The origin of monomeric and polymeric forms of IgA in man. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):57–65. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambaud J. C., Duprey F., Nouel O., Hostein J., Delpech B., Bernier J. J. Assessment of the accuracy of segmental perfusion under an occluding balloon for measuring the intrajejunal secretion of albumin and immunoglobulin A. Gut. 1981 May;22(5):371–375. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.5.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie R. F., Alper C. A., Graves J., Pearson N., Larson C. Automated quantitation of proteins in serum and other biologic fluids. Am J Clin Pathol. 1973 Feb;59(2):151–159. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/59.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skvaril F., Morell A. Distribution of IgA subclasses in sera and bone marrow plasma cells of 21 normal individuals. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):433–435. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Socken D. J., Underdown B. J. Comparison of human, bovine and rabbit secretory component-immunoglobulin interactions. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):499–506. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soltys H. D., Brody J. I. Synthesis of transferrin by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Feb;75(2):250–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOMASI T. B., Jr, TAN E. M., SOLOMON A., PRENDERGAST R. A. CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IMMUNE SYSTEM COMMON TO CERTAIN EXTERNAL SECRETIONS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jan 1;121:101–124. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loghem E., Biewenga J. Allotypic and isotypic aspects of human immunoglobulin A. Mol Immunol. 1983 Sep;20(9):1001–1007. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



