Abstract
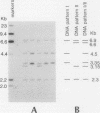
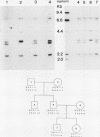
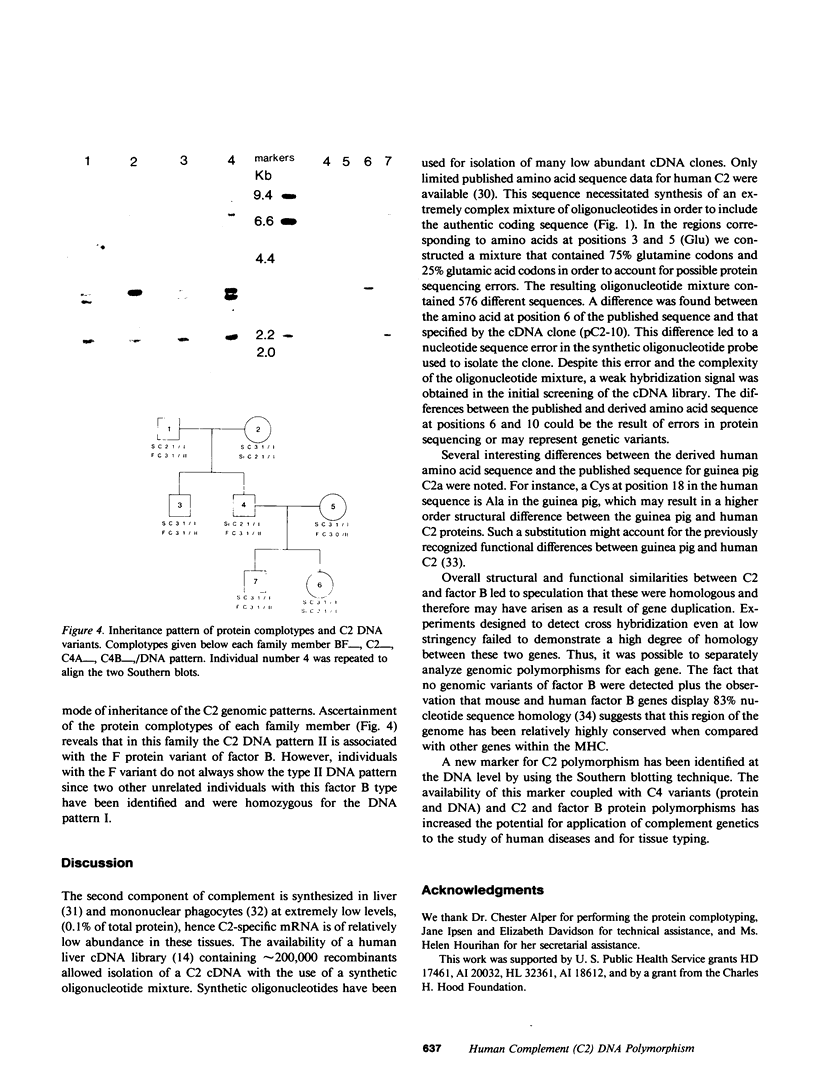
Complementary DNA (cDNA) clones corresponding to the major histocompatibility (MHC) class III antigen, complement protein C2, have been isolated from human liver cDNA libraries with the use of a complex mixture of synthetic oligonucleotides (17 mer) that contains 576 different oligonucleotide sequences. The C2 cDNA were used to identify a DNA restriction enzyme fragment length polymorphism that provides a genetic marker within the MHC that was not detectable at the protein level. An extensive search for genomic polymorphisms using a cDNA clone for another MHC class III gene, factor B, failed to reveal any DNA variants. The genomic variants detected with the C2 cDNA probe provide an additional genetic marker for analysis of MHC-linked diseases.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper C. A., Boenisch T., Watson L. Genetic polymorphism in human glycine-rich beta-glycoprotein. J Exp Med. 1972 Jan;135(1):68–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism in human C2: evidence for genetic linkage between C2 and Bf. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1111–1115. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Korman A. J., Roux-Dosseto M., Bono R., Strominger J. L. cDNA clone for the heavy chain of the human B cell alloantigen DC1: strong sequence homology to the HLA-DR heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awdeh Z. L., Alper C. A. Inherited structural polymorphism of the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3576–3580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa J. A., Kamarck M. E., Biro P. A., Weissman S. M., Ruddle F. H. Identification of human genomic clones coding the major histocompatibility antigens HLA-a2 and HLA-B7 by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsos T., Rapp H. J., Colten H. R. Immune hemolysis and the functional properties of the second (C2) and fourth (C4) components of complement. I. Functional differences among C4 sites on cell surfaces. J Immunol. 1970 Dec;105(6):1439–1446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of the gene coding for human complement protein factor B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Bentley D. R., Porter R. R. A molecular map of the human major histocompatibility complex class III region linking complement genes C4, C2 and factor B. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):237–241. doi: 10.1038/307237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. Cloning of a human complement component C4 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):264–267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaplin D. D., Woods D. E., Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Colten H. R., Seidman J. G. Molecular map of the murine S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6947–6951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einstein L. P., Schneeberger E. E., Colten H. R. Synthesis of the second component of complement by long-term primary cultures of human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):114–126. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götze O., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The alternative pathway of complement activation. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Gagnon J. The purification and properties of the second component of guinea-pig complement. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 1;205(1):59–67. doi: 10.1042/bj2050059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr M. A., Porter R. R. The purification and properties of the second component of human complement. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 1;171(1):99–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1710099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Trowsdale J., Bodmer W. F. cDNA clones coding for the heavy chain of human HLA-DR antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):545–549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malissen M., Malissen B., Jordan B. R. Exon/intron organization and complete nucleotide sequence of an HLA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):893–897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation and DNA sequence of a full-length cDNA clone for human X chromosome-encoded phosphoglycerate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris K. M., Aden D. P., Knowles B. B., Colten H. R. Complement biosynthesis by the human hepatoma-derived cell line HepG2. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):906–913. doi: 10.1172/JCI110687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill G. J., Yang S. Y., Dupont B. Two HLA-linked loci controlling the fourth component of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Shreffler D. C., Sepich D. S., Lilly S. P. cDNA clone spanning the alpha-gamma subunit junction in the precursor of the murine fourth complement component (C4). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5061–5065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palsdottir A., Cross S. J., Edwards J. H., Carroll M. C. Correlation between a DNA restriction fragment length polymorphism and C4A6 protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):615–616. doi: 10.1038/306615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raum D., Awdeh Z., Alper C. A. BF types and the mode of inheritance of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). Immunogenetics. 1981;12(1-2):59–74. doi: 10.1007/BF01561651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. H., Mollenhauer E., Démant P., Rittner C. A molecular basis for the two locus model of human complement component C4. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):854–856. doi: 10.1038/298854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackstein R., Colten H. R., Woods D. E. Phylogenetic conservation of a class III major histocompatibility complex antigen, factor B. Isolation and nucleotide sequencing of mouse factor B cDNA clones. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14693–14697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shows T. B., Alper C. A., Bootsma D., Dorf M., Douglas T., Huisman T., Kit S., Klinger H. P., Kozak C., Lalley P. A. International system for human gene nomenclature (1979) ISGN (1979). Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1979;25(1-4):96–116. doi: 10.1159/000131404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Goldberger G., Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Colten H. R. Use of a cDNA clone for the fourth component of human complement (C4) for analysis of a genetic deficiency of C4 in guinea pig. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5387–5391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead A. S., Woods D. E., Fleischnick E., Chin J. E., Yunis E. J., Katz A. J., Gerald P. S., Alper C. A., Colten H. R. DNA polymorphism of the C4 genes. A new marker for analysis of the major histocompatibility complex. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jan 12;310(2):88–91. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198401123100204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]