Abstract
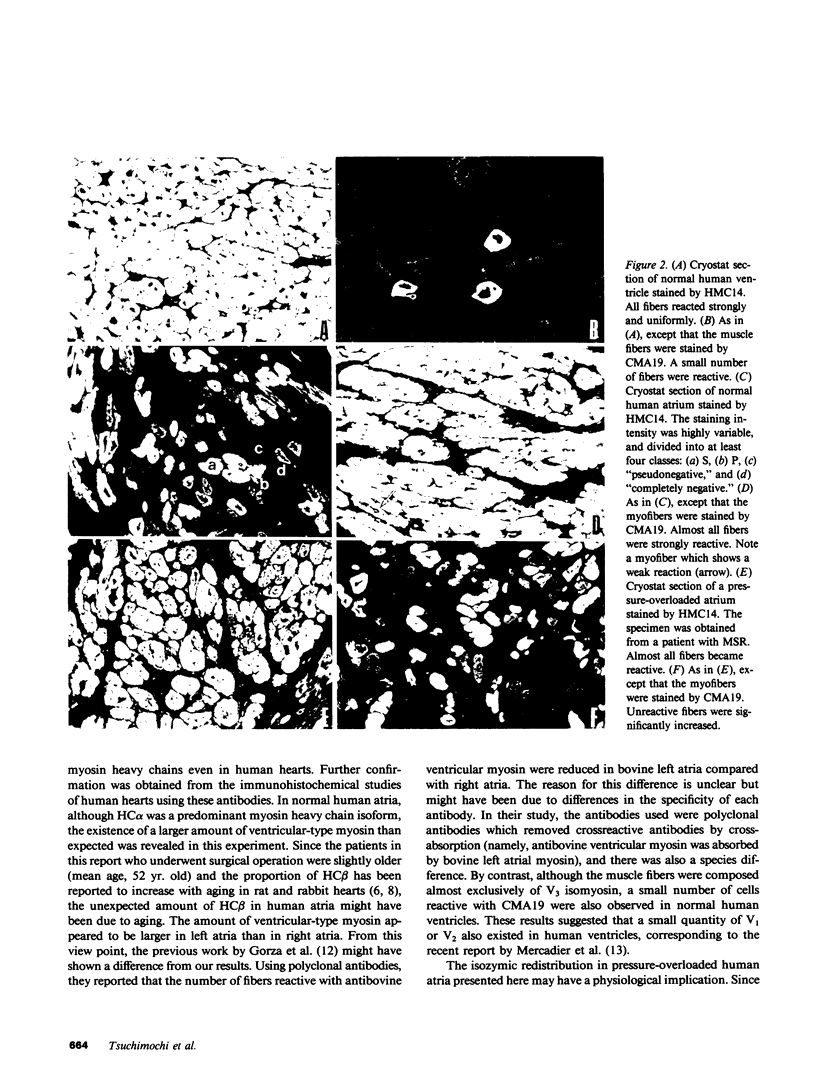
An immunohistochemical study using monoclonal antibodies specific for the heavy chains of either human atrial (HC alpha) or ventricular (HC beta) myosin was performed to clarify the distribution of each isozyme in normal as well as pressure-overloaded human hearts. In normal human ventricles, all muscle fibers were stained by a monoclonal antibody (HMC14) specific for HC beta, whereas a small number of fibers reacted with a monoclonal antibody (CMA19) specific for HC alpha. In contrast, in normal human atria, almost all muscle fibers were stained by CMA19, and a relatively larger number of muscle fibers also reacted with HMC14. Furthermore, in pressure-overloaded atria, muscle fibers reactive with HMC14 were strikingly increased while those reactive with CMA19 showed a corresponding decrease. The extent of this isozymic redistribution was in good correlation with atrial pressure. These results not only confirmed the existence of isoforms of myosin heavy chain in human hearts, but also demonstrated that redistribution of iso-myosins could occur as an adaptation to pressure overload.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpert N. R., Mulieri L. A. Increased myothermal economy of isometric force generation in compensated cardiac hypertrophy induced by pulmonary artery constriction in the rabbit. A characterization of heat liberation in normal and hypertrophied right ventricular papillary muscles. Circ Res. 1982 Apr;50(4):491–500. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chizzonite R. A., Everett A. W., Clark W. A., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M., Zak R. Isolation and characterization of two molecular variants of myosin heavy chain from rabbit ventricle. Change in their content during normal growth and after treatment with thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2056–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins P. Transitions in human atrial and ventricular myosin light-chain isoenzymes in response to cardiac-pressure-overload-induced hypertrophy. Biochem J. 1982 Jul 1;205(1):195–204. doi: 10.1042/bj2050195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorza L., Pauletto P., Pessina A. C., Sartore S., Schiaffino S. Isomyosin distribution in normal and pressure-overloaded rat ventricular myocardium. An immunohistochemical study. Circ Res. 1981 Oct;49(4):1003–1009. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.4.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorza L., Sartore S., Schiaffino S. Myosin types and fiber types in cardiac muscle. II. Atrial myocardium. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):838–845. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Ternynck T., Avrameas S. The use of avidin-biotin interaction in immunoenzymatic techniques. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Aug;27(8):1131–1139. doi: 10.1177/27.8.90074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. F., McGrath P. A., Hale P. T. Electrophoretic analysis of multiple forms of rat cardiac myosin: effects of hypophysectomy and thyroxine replacement. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1978 Nov;10(11):1053–1076. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(78)90401-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lompre A. M., Schwartz K., d'Albis A., Lacombe G., Van Thiem N., Swynghedauw B. Myosin isoenzyme redistribution in chronic heart overload. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):105–107. doi: 10.1038/282105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercadier J. J., Bouveret P., Gorza L., Schiaffino S., Clark W. A., Zak R., Swynghedauw B., Schwartz K. Myosin isoenzymes in normal and hypertrophied human ventricular myocardium. Circ Res. 1983 Jul;53(1):52–62. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.1.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartore S., Gorza L., Pierobon Bormioli S., Dalla Libera L., Schiaffino S. Myosin types and fiber types in cardiac muscle. I. Ventricular myocardium. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):226–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki Y., Mochinaga S., Raben M. S. Fractionation of the light chains from rat and rabbit cardiac myosin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 6;328(2):464–469. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki Y., Raben M. S. Cardiac myosin adenosinetriphosphatase of rat and mouse. Distinctive enzymatic properties compared with rabbit and dog cardiac myosin. Circ Res. 1974 Jul;35(1):15–23. doi: 10.1161/01.res.35.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki Y., Raben M. S. Effect of the thyroid state on the enzymatic characteristics of cardiac myosin. A difference in behavior of rat and rabbit cardiac myosin. Circ Res. 1975 Jan;36(1):208–215. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.1.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazaki Y., Ueda S., Nagai R., Shimada K. Cardiac atrial myosin adenosine triphosphatase of animals and humans: distinctive enzymatic properties compared with cardiac ventricular myosin. Circ Res. 1979 Oct;45(4):522–527. doi: 10.1161/01.res.45.4.522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]