Abstract
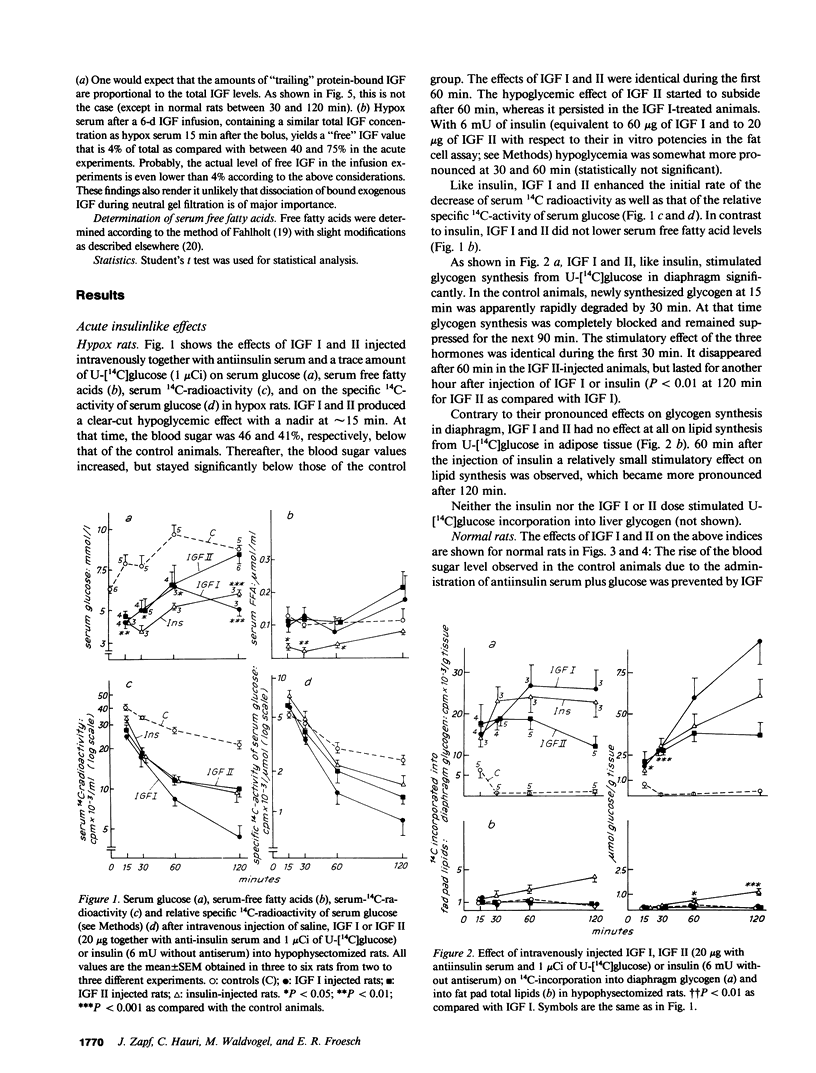
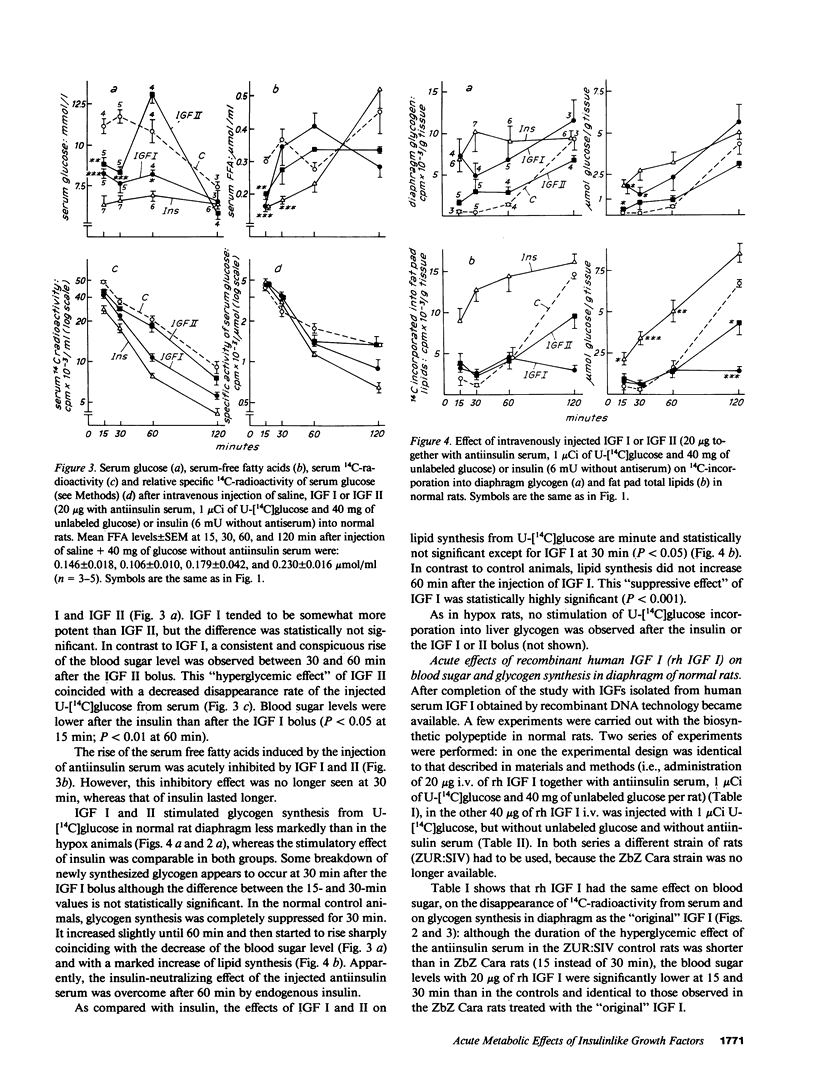
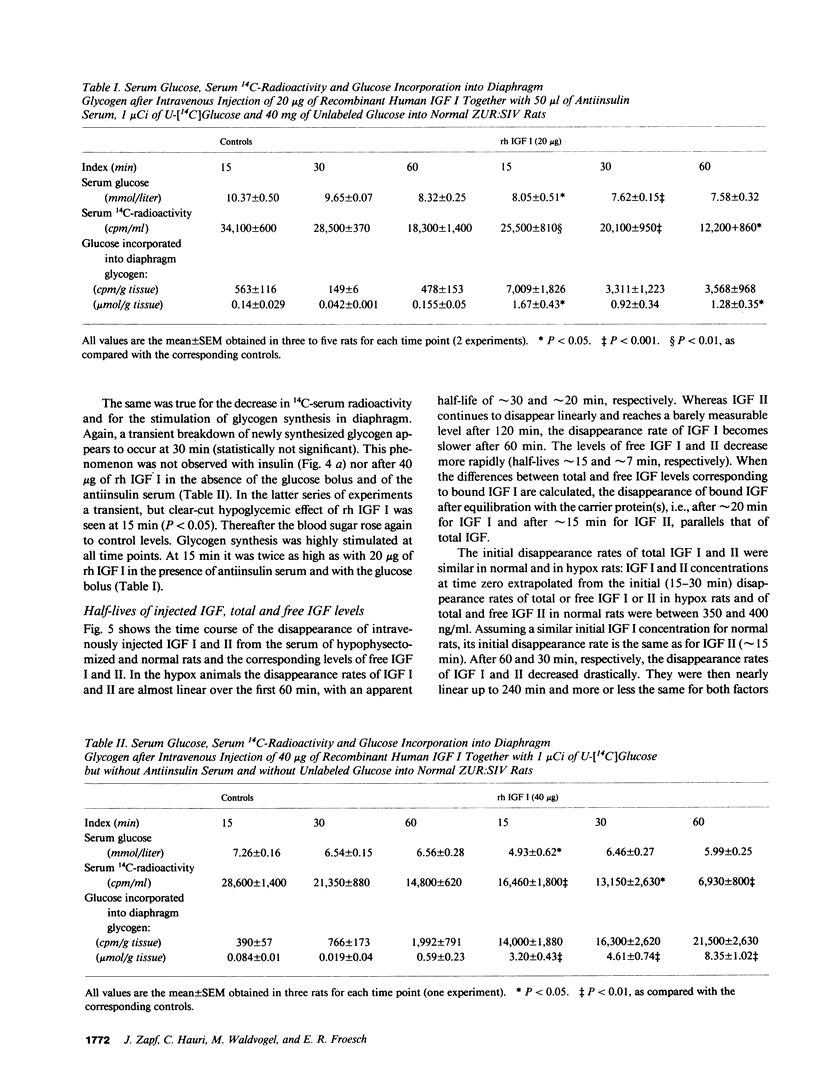
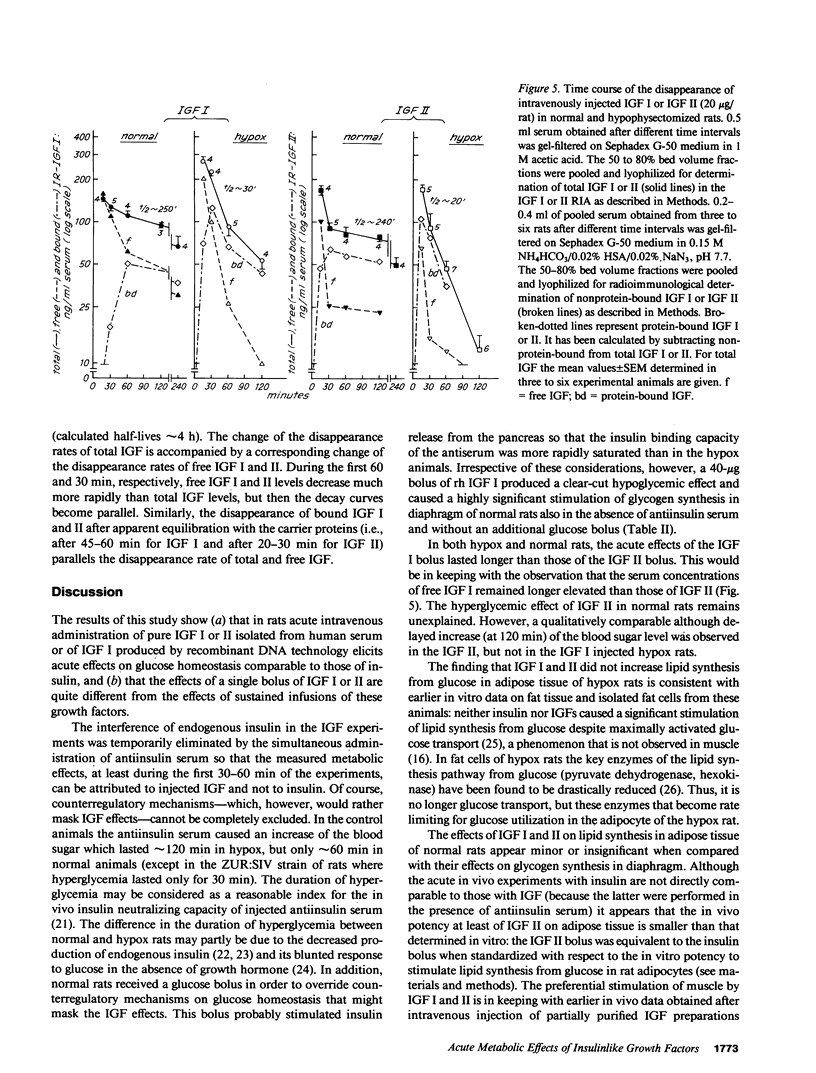
Insulinlike growth factors (IGF) act qualitatively like insulin on insulin target tissues in vitro. In the circulation in vivo they are bound to specific carrier proteins. In this form or when continuously infused into hypophysectomized (hypox) rats they do not exert acute insulinlike effects on glucose homeostasis. This study definitively shows that intravenous bolus injections of pure IGF I or II act acutely on glucose homeostasis: they lower the blood sugar, enhance the disappearance of U-[14C]glucose from serum and increase its incorporation into diaphragm glycogen in normal and hypox rats in the presence of antiinsulin serum. The same effects were obtained with recombinant human IGF I injected intravenously either with or without antiinsulin serum into normal rats. Free fatty acid levels decreased transiently only in normal animals. Lipid synthesis from glucose in adipose tissue was not stimulated in hypox and barely stimulated in normal rats. The half-life of injected IGF I or II in normal rats (approximately 4 h) is strikingly different from that in hypophysectomized rats (20-30 min) and appears to depend on the growth hormone-induced 150,000-200,000-mol wt IGF carrier protein that is lacking in hypophysectomized rats. 15 min after the bolus serum IGF I and II concentrations were similar to steady state levels during long-term infusion in hypox rats. Free IGF was barely detectable, however, in the infused animals, whereas 40-100% was found free 15 min after the bolus. These observations for the first time confirm the hypothesis that only free IGF, but not the IGF carrier protein complex, is bioavailable to insulin target tissues.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER N., SHIPLEY R. A., CLARK R. E., INCEFY G. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism: glucose pool size and rate of turnover in the normal rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):245–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Krotkiewski M., Larsson B., Somlo-Szücs Z. Effects of feeding states on lipid radioactivity in liver, muscle and adipose tissue after injection of labelled glucose in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970 Sep;80(1):29–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1970.tb04766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen K. L., Nissley S. P. The serum half-life of somatomedin activity: evidence for growth hormone dependence. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1976 Oct;83(2):243–258. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0830243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Wilkins J. R. Affinity labeled somatomedin-C-binding proteins in rat sera. Endocrinology. 1984 Apr;114(4):1141–1144. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-4-1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enberg G., Carlquist M., Jörnvall H., Hall K. The characterization of somatomedin A, isolated by microcomputer-controlled chromatography, reveals an apparent identity to insulin-like growth factor 1. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):117–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROESCH E. R., BUERGI H., RAMSEIER E. B., BALLY P., LABHART A. ANTIBODY-SUPPRESSIBLE AND NONSUPPRESSIBLE INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITIES IN HUMAN SERUM AND THEIR PHYSIOLOGIC SIGNIFICANCE. AN INSULIN ASSAY WITH ADIPOSE TISSUE OF INCREASED PRECISION AND SPECIFICITY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1816–1834. doi: 10.1172/JCI104866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falholt K., Lund B., Falholt W. An easy colorimetric micromethod for routine determination of free fatty acids in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1973 Jun 28;46(2):105–111. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(73)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Müller W. A., Bürgi H., Waldvogel M., Labhart A. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. II. Biological properties of plasma extracts with non-suppressible insulin-like activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 29;121(2):360–374. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90125-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze E., Kleinert W., Voigt K. H. Insulin release in rats 1 and 5 days after hypophysectomy. Horm Res. 1981;14(4):243–249. doi: 10.1159/000179394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Mar;13(1):31–42. doi: 10.1016/s0300-595x(84)80007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann U., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Growth-hormone dependence of non-suppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) and of NSILA-carrier protein in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1978 Apr;87(4):716–727. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0870716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapper D. G., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J. Sequence analysis of somatomedin-C: confirmation of identity with insulin-like growth factor I. Endocrinology. 1983 Jun;112(6):2215–2217. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-6-2215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merimee T. J., Rimoin D. L., Rabinowitz D., Cavalli-Sforza L. L., McKusick V. A. Metabolic studies in the African pygmy. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1968;81:221–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuli C., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. NSILA-carrier protein abolishes the action of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S) on perfused rat heart. Diabetologia. 1978 Apr;14(4):255–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01219425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nessley S. P., Cohen K. L., Rechler M. M. Specific binding of a somatomedin-like polypeptide in rat serum depends on growth hormone. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):137–140. doi: 10.1038/263137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. C., Nissley S. P., Passamani J., White R. M. Further characterization of growth hormone-dependent somatomedin-binding proteins in rat serum and demonstration of somatomedin-binding proteins produced by rat liver cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1979 Feb;104(2):536–546. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-2-536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelz O., Jakob A., Froesch E. R. Nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA) of human serum. V. Hypoglycaemia and preferential metabolic stimulation of muscle by NSILA-S. Eur J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;1(1):48–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1970.tb00596.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poggi C., Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Freychet P. Effects and binding of insulin-like growth factor I in the isolated soleus muscle of lean and obese mice: comparison with insulin. Endocrinology. 1979 Sep;105(3):723–730. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-3-723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON B. H., WRIGHT P. H. Guinea-pig anti-insulin serum. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:302–310. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Zapf J., Nissley S. P., Froesch E. R., Moses A. C., Podskalny J. M., Schilling E. E., Humbel R. E. Interactions of insulin-like growth factors I and II and multiplication-stimulating activity with receptors and serum carrier proteins. Endocrinology. 1980 Nov;107(5):1451–1459. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-5-1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. Primary structure of human insulin-like growth factor II. FEBS Lett. 1978 May 15;89(2):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., Humbel R. E. The amino acid sequence of human insulin-like growth factor I and its structural homology with proinsulin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Apr 25;253(8):2769–2776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Froesch E. R. Receptor binding and effects of insulin and NSILA-S on glucose transport and metabolism in adipocytes from hypophysectomized rats. Diabetologia. 1979 Jan;16(1):41–46. doi: 10.1007/BF00423149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Hauri C., Steiner T., Froesch E. R. Comparison of in vivo effects of insulin-like growth factors I and II and of growth hormone in hypophysectomized rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1985 Feb;108(2):167–174. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1080167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenle E., Zapf J., Humbel R. E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factor I stimulates growth in hypophysectomized rats. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):252–253. doi: 10.1038/296252a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lan V., Yamaguchi N., Garcia M. J., Ramey E. R., Penhos J. C. Effect of hypophysectomy and adrenalectomy on glucagon and insulin concentration. Endocrinology. 1974 Mar;94(3):671–675. doi: 10.1210/endo-94-3-671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Froesch E. R., Humbel R. E. The insulin-like growth factors (IGF) of human serum: chemical and biological characterization and aspects of their possible physiological role. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;19:257–309. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152819-5.50024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Insulin-like growth factors I and II: some biological actions and receptor binding characteristics of two purified constituents of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):285–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Schoenle E., Waldvogel M., Sand I., Froesch E. R. Effect of trypsin treatment of rat adipocytes on biological effects and binding of insulin and insulin-like growth factors: further evidence for the action of insulin-like growth factors through the insulin receptor. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jan;113(3):605–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Waldvogel M., Schoenle E., Froesch E. R. Effect of insulin on glucose transport and metabolism in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle of hypophysectomized rats. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 30;135(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80976-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapf J., Walter H., Froesch E. R. Radioimmunological determination of insulinlike growth factors I and II in normal subjects and in patients with growth disorders and extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1172/JCI110379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



