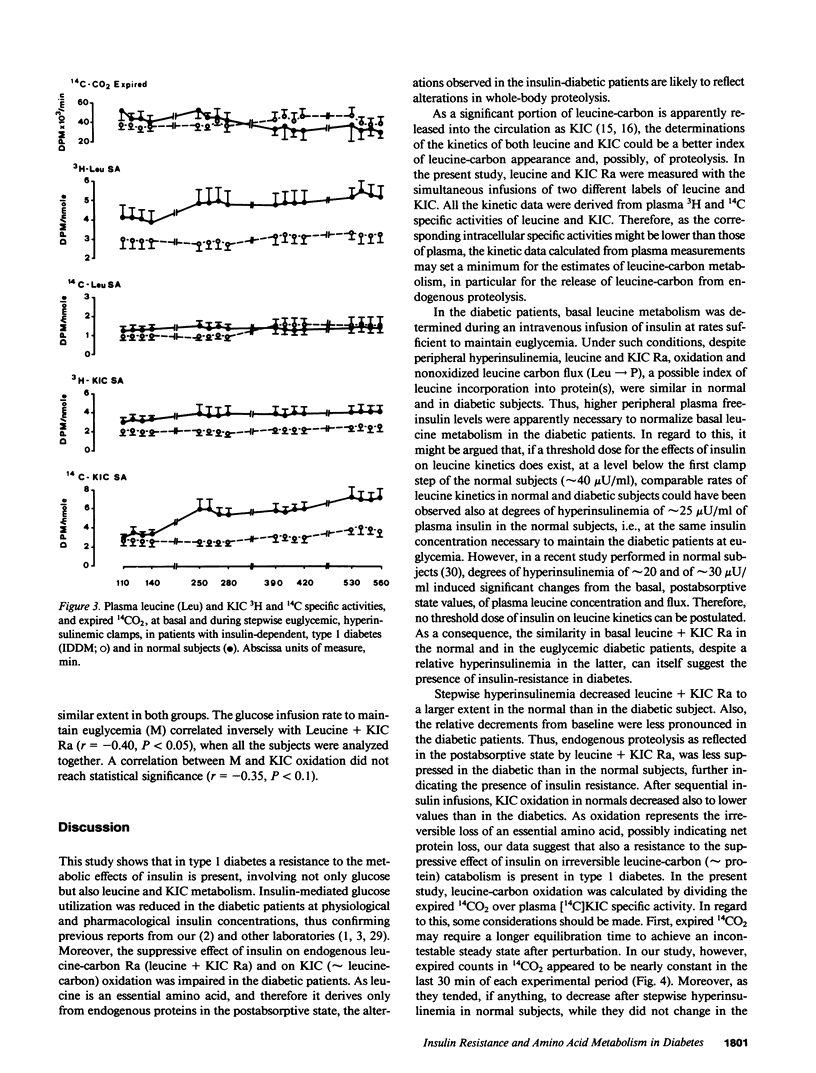
Abstract
To determine whether a resistance to insulin in type 1, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) is extended to both glucose and amino acid metabolism, six normal subjects and five patients with IDDM, maintained in euglycemia with intravenous insulin administration, were infused with L-[4,5-3H]leucine (Leu) and [1-14C]alpha ketoisocaproate (KIC). Steady-state rates of leucine-carbon appearance derived from protein breakdown (Leu + KIC Ra) and KIC (approximately leucine) oxidation were determined at basal and during sequential euglycemic, hyperinsulinemic (approximately 40, approximately 90 and approximately 1,300 microU/ml) clamps. In the euglycemic postabsorptive diabetic patients, despite basal hyperinsulinemia (24 +/- 6 microU/ml vs. 9 +/- 1 microU/ml in normals, P less than 0.05), Leu + KIC Ra (2.90 +/- 0.18 mumol/kg X min), and KIC oxidation (0.22 +/- 0.03 mumol/kg X min) were similar to normal values (Leu + KIC Ra = 2.74 +/- 0.25 mumol/kg X min) (oxidation = 0.20 +/- 0.02 mumol/kg X min). During stepwise hyperinsulinemia, Leu + KIC Ra in normals decreased to 2.08 +/- 0.19, to 2.00 +/- 0.17, and to 1.81 +/- 0.16 mumol/kg X min, but only to 2.77 +/- 0.16, to 2.63 +/- 0.16, and to 2.39 +/- 0.08 mumol/kg X min in the diabetic patients (P less than 0.05 or less vs. normals at each clamp step). KIC oxidation decreased in normal subjects to a larger extent than in the diabetic subjects. Glucose disposal was reduced at all insulin levels in the patients. In summary, in IDDM: (a) Peripheral hyperinsulinemia is required to normalize both fasting leucine metabolism and blood glucose concentrations. (b) At euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamps, lower glucose disposal rates and a defective suppression of leucine-carbon appearance and oxidation were observed. We conclude that in type 1 diabetes a resistance to the metabolic effects of insulin on both glucose and amino acid metabolism is present.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abumrad N. N., Jefferson L. S., Rannels S. R., Williams P. E., Cherrington A. D., Lacy W. W. Role of insulin in the regulation of leucine kinetics in the conscious dog. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1031–1041. doi: 10.1172/JCI110690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abumrad N. N., Rabin D., Diamond M. P., Lacy W. W. Use of a heated superficial hand vein as an alternative site for the measurement of amino acid concentrations and for the study of glucose and alanine kinetics in man. Metabolism. 1981 Sep;30(9):936–940. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90074-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsop J. R., Wolfe R. R., Burke J. F. Tracer priming the bicarbonate pool. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Jul;45(1):137–139. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., Reid S. S. Leucine. A possible regulator of protein turnover in muscle. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1250–1261. doi: 10.1172/JCI108201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr The Banting Memorial Lecture 1971. Physiology of insulin in man. Diabetes. 1971 Dec;20(12):785–799. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.12.785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens A. H., Hough D. L., D'Orazio P. A. Development of the Biostator Glucose clamping algorithm. Clin Chem. 1982 Sep;28(9):1899–1904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Hendler R., Simonson D. Insulin resistance is a prominent feature of insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):795–801. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Prato S., Nosadini R., Tiengo A., Tessari P., Avogaro A., Trevisan R., Valerio A., Muggeo M., Cobelli C., Toffolo G. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal in type I diabetes: evidence for insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):904–910. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Schulz B., Reaven G. M. Enhanced glucose utilization during prolonged glucose clamp studies. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):829–835. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garlick P. J., Albertse E. C., McNurlan M. A., Pain V. M. Protein turnover in tissues of diabetic rats. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1301–1307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutson S. M., Zapalowski C., Cree T. C., Harper A. E. Regulation of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproic acid metabolism in skeletal muscle. Effects of starvation and insulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2418–2426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James W. P., Garlick P. J., Sender P. M., Waterlow J. C. Studies of amino acid and protein metabolism in normal man with L-[U-14C]tyrosine. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Jun;50(6):525–532. doi: 10.1042/cs0500525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson L. S., Li J. B., Rannels S. R. Regulation by insulin of amino acid release and protein turnover in the perfused rat hemicorpus. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1476–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuya T., Saito T., Yoshida S., Matsuda A. Human C-peptide immunoreactivity (CPR) in blood and urine - evaluation of a radioimmunoassay method and its clinical applications. Diabetologia. 1976 Oct;12(5):511–518. doi: 10.1007/BF01219516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews D. E., Schwarz H. P., Yang R. D., Motil K. J., Young V. R., Bier D. M. Relationship of plasma leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate during a L-[1-13C]leucine infusion in man: a method for measuring human intracellular leucine tracer enrichment. Metabolism. 1982 Nov;31(11):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90160-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May M. E., Mancusi V. J., Aftring R. P., Buse M. G. Effects of diabetes on oxidative decarboxylation of branched-chain keto acids. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):E215–E222. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.3.E215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimore G. E., Mondon C. E. Inhibition by insulin of valine turnover in liver. Evidence for a general control of proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1970 May 10;245(9):2375–2383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa S., Nakayama H., Sasaki T., Yoshino K., Yu Y. Y. A simple method for the determination of serum free insulin levels in insulin-treated patients. Diabetes. 1973 Aug;22(8):590–600. doi: 10.2337/diab.22.8.590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhooda A. F., Wei C. N., Marliss E. B. Muscle protein catabolism in diabetes: 3-methylhistidine excretion in the spontaneously diabetic "BB" rat. Metabolism. 1980 Dec;29(12):1272–1277. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen S. L., Van Huysen C., Haymond M. W. Measurement of branched chain amino acids and branched chain alpha-ketoacids in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1982 Oct 8;232(1):170–175. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)86021-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen S., Haymond M. W. Effects of fasting on flux and interconversion of leucine and alpha-ketoisocaproate in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):E72–E75. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1981.241.1.E72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M., Garlick P. J. Effect of streptozotocin diabetes and insulin treatment on the rate of protein synthesis in tissues of the rat in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4510–4514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernet A., Trimble E. R., Kuntschen F., Damoiseaux P., Assal J. P., Hahn C., Renold A. E. Insulin resistance in Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes: dependence on plasma insulin concentration. Diabetologia. 1984 Apr;26(4):255–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00283646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozefsky T., Felig P., Tobin J. D., Soeldner J. S., Cahill G. F., Jr Amino acid balance across tissues of the forearm in postabsorptive man. Effects of insulin at two dose levels. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2273–2282. doi: 10.1172/JCI106193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert J. J., Bier D. M., Zhao X. H., Matthews D. E., Young V. R. Glucose and insulin effects on the novo amino acid synthesis in young men: studies with stable isotope labeled alanine, glycine, leucine, and lysine. Metabolism. 1982 Dec;31(12):1210–1218. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90006-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdiger H. W., Langenbeck U., Goedde H. W. A simplified method for the preparation of 14 C-labelled branched-chain -oxo acids. Biochem J. 1972 Jan;126(2):445–446. doi: 10.1042/bj1260445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacca L., Hendler R., Sherwin R. S. Hyperglycemia inhibits glucose production in man independent of changes in glucoregulatory hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Nov;47(5):1160–1163. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-5-1160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Inchiostro S., Biolo G., Duner E., Nosadini R., Tiengo A., Crepaldi G. Hyperaminoacidaemia reduces insulin-mediated glucose disposal in healthy man. Diabetologia. 1985 Nov;28(11):870–872. doi: 10.1007/BF00291080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tessari P., Tsalikian E., Schwenk W. F., Nissen S. L., Haymond M. W. Effects of [15N]leucine infused at low rates on leucine metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jul;249(1 Pt 1):E121–E130. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.249.1.E121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsalikian E., Howard C., Gerich J. E., Haymond M. W. Increased leucine flux in short-term fasted human subjects: evidence for increased proteolysis. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E323–E327. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Koivisto V. A. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy decreases insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):659–666. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



