Abstract
Forty four marine actinomycetes of the family Microccocaceae isolated from sponges collected primarily in Florida Keys (USA) were selected from our strain collection to be studied as new sources for the production of bioactive natural products. A 16S rRNA gene based phylogenetic analysis showed that the strains are members of the genera Kocuria and Micrococcus. To assess their biosynthetic potential, the strains were PCR screened for the presence of secondary metabolite genes encoding nonribosomal synthetase (NRPS) and polyketide synthases (PKS). A small extract collection of 528 crude extracts generated from nutritional microfermentation arrays was tested for the production of bioactive secondary metabolites against clinically relevant strains (Bacillus subtilis, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Acinetobacter baumannii and Candida albicans). Three independent isolates were shown to produce a new anti-MRSA bioactive compound that was identified as kocurin, a new member of the thiazolyl peptide family of antibiotics emphasizing the role of this family as a prolific resource for novel drugs.
Keywords: marine actinomycete, sponge, Kocuria, Microccocus, antibiotic, MRSA, thiazolyl peptide, NRPS, PKS
1. Introduction
Marine sponges (phylum Porifera) are abundant multicellular invertebrates with a broad distribution in the oceans. As filter feeders they harbor a large density and diversity of bacterial populations and they are considered as “microbial fermenters” capable of producing a broad range of bioactive secondary metabolites with pharmaceutical application [1,2]. Inter-cellular signaling mechanisms modulate and control the exchange of primary metabolites within these microbial symbiotic communities, and these bacterial symbionts have been proposed to play roles in digestion, waste removal, chemical defense for the sponge host against infectious agents or predators, and the colonization of microbial niches [1,2,3].
Sponge-associated Actinobacteria represent only a small fraction of the sponge bacterial communities (3%–20%) with abundant uncultured lineages detected in clone libraries identified as true symbionts. The class Actinobacteria is one of the most prolific bacterial groups as producers of bioactive metabolites and the source of almost 50% of all known bioactive microbial metabolites [4]. The recent discovery of new groups of marine bacteria from unexplored or underexploited habitats, particularly sponges and marine soils, has led to intensively exploit this bacterial community as an untapped source of new bioactive compounds [5,6,7]. Among them are included novel strains of Streptomyces and Micromonospora [8,9] as well as the first obligate marine actinomycetes, Salinispora tropica and Salinispora arenicola [5,10]. There is currently high interest to investigate the potential of these actinobacterial communities, and especially those assemblages associated to sponges, as producers of novel bioactive compounds [11,12].
The biosynthesis of large number of bioactive natural products is dependent on nonribosomal synthetase (NRPS) and type I and type II polyketide synthases (PKS-I, PKS-II). These biosynthetic systems are broadly distributed among actinomycetes, cyanobacteria, myxobacteria and fungi and molecular tools derived from conserved domain genes sequences have been useful for screening the biosynthetic potential of these microorganisms [13,14,15]. Natural products derived from these biosynthetic pathways have been extensively described for cultured and uncultured marine strains. These marine metabolites include among others the polyketide synthase-derived bryostatin, a cytotoxic compound produced by a bryozoan bacterial symbiont [16]; abyssomicin C, a unique polycyclic polyketide from a marine Verrucosispora [6], salinisporamide A, a potent cytotoxic proteasome inhibitor from S. tropica, and promising new antitumor candidate in Phase I clinical trials [17,18], and the antitumor onnamides and theopederins, mixed polyketide-non ribosomal peptides produced by an uncultured Pseudomonas sp. symbiont of the marine sponge Theonella swinhoei [19,20].
Members of the family Micrococcaceae have been reported from a broad diversity of terrestrial and marine sources including cyanobacterial mats and marine sediments [21,22], and especially among the cultured Actinobacteria isolated from diverse sponge specimens [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Despite the broad distribution of Micrococcaceae in sponges, very little is known about the occurrence of natural products biosynthetic pathways and the production of bioactive compounds, especially by species of the sponge-associated genera Kocuria and Micrococcus. We report a first insight into the occurrence of these biosynthetic systems and the production of new bioactive compounds by sponge-associated bacteria of the Micrococcaceae family.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Identification and Diversity of Microccocaceae Sponge Isolates
Forty-four marine actinomycetes of the family Micrococcaceae originally isolated from Florida Keys, Fort Lauderdale and Maryland sponges (USA) were selected from our marine strain collection to be evaluated as potential sources of new bioactive natural products. The strains were isolated from fresh sponge specimens on marine-based conditions as previously described [11]. Once purified, the strains were characterized morphologically and identified based on 16S rRNA gene sequences as members of the genera Micrococccus (15 strains) and Kocuria (29 strains) (Supplementary Table S1). All Micrococcus strains were assigned to the same species M. yunnanensis whereas Kocuria strains were distributed among seven different species (K. flava, K. marina, K. palustris, K. rhizophila, K. rosea, K. sediminis and K. turfanensis).
To confirm the taxonomic assignment and the existing phylogenetic relationships between the different isolates and the type strains, a phylogenetic tree was built based on the 16S rRNA genes partial sequences alignments. The phylogenetic analysis, based on the Neighbor-Joining method using matrix pairwise comparisons of sequences corrected with Jukes and Cantor algorithm [24,25], showed that the 44 strains were clearly divided in two groups corresponding to the genera Kocuria and Micrococcus. The strains of Kocuria are distributed in two large clusters encompassing 11 and 18 strains. The first cluster contains 7 isolates closely related to the type strain K. turfanensis HO-9042T and 2 closely related to K. sediminis FCS-11T. The remaining two strains cluster with the strains K. flava HO-9041T and K. rosea DSM20447T respectively suggesting relatedness with these species.
The second cluster of Kocuria spp. contains 18 isolates with 11 strains closely related to the type strains K. palustris DSM 11925T, four isolates clustering with K. marina KMM 3905T and three strains with K. rhizophila DSM 11926T. Only two strains were associated to the marine species K. sediminis FCS-11T isolated from marine environments (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
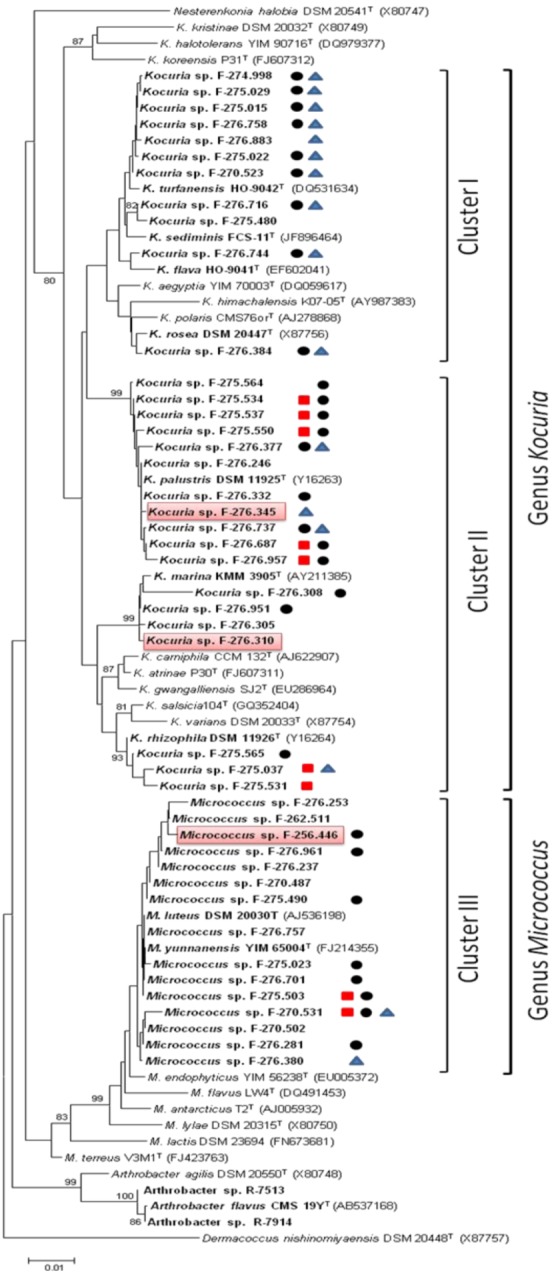
Phylogenetic diversity of sponge Micrococcaceae. Neighbor-Joining (NJ) tree built with MEGA 5.1 based on partial 16S rRNA gene sequences of 44 strains belonging to the genera Kocuria and Micrococcus (family Micrococcaceae) and the type strains of closely related genera. The numbers at the nodes indicate bootstrap support (%) based on a NJ analysis of 1.000 replicates; only values ≥75% are given. The scale bar indicates 0.01 substitutions per nucleotide position. Biosynthetic gene sequences detected: polyketide synthases PKS-I  , PKS-II
, PKS-II  or NRPS
or NRPS  . Strains with antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant S. aureus MB5393 are highlighted in red.
. Strains with antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant S. aureus MB5393 are highlighted in red.
All 15 Micrococcus strains clustered with the type strains M. luteus DSM 20030T (AJ536198) and M. yunnanensis YIM 65004T (FJ214355), two species that have been reported to be closely related phylogenetically with 100% similarity.
Fatty acid composition of the isolates, a chemotaxonomic marker used to assess the strain intraspecific diversity, was used to confirm the presence of two clearly distinguished taxonomic groups. All isolates were characterized by the presence of saturated branched fatty acids with a predominance of 12-methyl-tetradecanoic acid (anteiso-C15:0) as the major component, and smaller amounts of 13-methyl-tetradecanoic acid (iso-C15:0). These fatty acid compositions are consistent with members of the genera Arthrobacter, Kocuria and Micrococcus, which are characterized by the presence of saturated branched fatty acids (anteiso-C15:0 as the major component) in their cell envelopes [26,27,28,29,30]. In addition the species of the genera Kocuria and Micrococcus were clearly distinguished from each other by the different amounts of some diagnostic fatty acids such as the presence in Kocuria strains of larger amounts of iso-C16:0, C16:0, iso-C17:0 and smaller amounts of iso-C15:0 (see Supplementary Table S2).
2.2. Detection of PKS and NRPS Genes
Type I and Type II polyketide synthases (PKS-I and PKS-II) and nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) are biosynthetic systems involved in the synthesis of an important number of microbial natural products classes including important drugs with antibiotic, antifungal or anticancer activity. Whereas the diversity of new chemical structures with biological activities produced by sponges supports their significance as reservoir of new therapeutic agents, today sponge-associated microbial communities are considered to be responsible for the biosynthesis of many of these agents. The presence of PKS and NRPS genes has been previously used to reveal the biosynthetic potential of natural products in bacterial isolates [13]. We evaluated their occurrence in the genomes of the 44 bacteria using degenerate PCR primers targeting conserved motifs in these genes to infer their biosynthetic potential (Table 1).
Table 1.
Detection of PKS and nonribosomal synthetase (NRPS) sequences.
| Genera | Strains | PKS-I | PKS-II | NRPS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | (%) | Total | (%) | Total | % | ||
| Kocuria spp. | 29 | 7 | 24.1 | 21 | 72.4 | 14 | 48.3 |
| Micrococcus spp. | 15 | 2 | 13.3 | 8 | 53.3 | 2 | 13.3 |
| Total | 44 | 9 | 20.5 | 29 | 65.9 | 16 | 36.4 |
Gene sequences corresponding to PKS-II were the most frequent and were detected in 29 of the 44 strains (66%), whereas NRPS and PKS-I sequences were only identified in 16 (36.4%) and 9 strains (20.5%) respectively. The strains of Kocuria stand out in their relative richness in these biosynthetic systems compared to those detected in Micrococccus.
The observed frequencies of NRPS and PKS-I gene sequences detected in marine Micrococcaceae (36.4% NRPS and 20.5% PKS-I) are lower than those observed in our previous studies with other terrestrial actinobacteria groups such as lichen Pseudonocardiaceae (68.2% PKS-II; 86.4% NRPS and PKS-I) or tropical soil Micromonosporaceae (42% NRPS, 77% PKS-I). Despite these results, NRPS and PKS sequences have been reported in marine actinobacteria isolated from a wide variety of environments ranging from marine caves, coral reef sediments, the deep sea Mariana Trench to north sea sediments, and with a high occurrence variability reaching up to 94% of the strains [31,32,33]. When comparing our results with other reports including all lineages of sponge-associated actinomycetes, our strains differ in the reduced number of PKS and NRPS gene sequences detected. In fact 70%–87% of the actinomycetes isolated from Norwegian marine sponges, Antarctic deep-sea sponges or the marine sponge Iotrochota sp. collected in the South China Sea contained PKS-I and NRPS genes [33,34,35].
So far, few Micrococcaceae strains have been reported for their capacity to produce natural products with biopharmaceutical potential. Li et al., (2012) reported actimicrobial activities produced by two endophytic actinobacteria from Artemisia annua, a Kocuria strain with type I PKS and NRPS gene sequences and one Micrococcus strain with type II PKS [36]. Similarly Gontang et al. (2010) detected the presence of NRPS genes in 2 of the 5 Kocuria strains isolated from marine sediments [14]. On the contrary, none of the Kocuria strains isolated from the Challenger Deep sediments from the Mariana Trench or the M. luteus isolated from the marine sponge Halichondria panacea gave any positive PKS or NRPS amplification products [12,32]. In our study, it is interesting to show that 86% and 60% of the Kocuria and Micrococcus isolates possess at least one of these biosynthetic pathways classes. These results are remarkable because K. rhizophila DC2201 has been shown to contain one of the smallest actinomycetes genomes (2.7 Mb). Genome annotation has shown that it encodes only a limited number of secondary metabolite pathways, including a type III polyketide synthase and a nonribosomal peptide synthetase, but does not contain genes for typical bacterial type I or type II PKS [37].
The detection of genes associated to these biosynthetic clusters does not guarantee the expression of genes involved in the production of secondary metabolites. The absence of PCR products in some of the isolates may reflect the lack of biosynthetic genes or the presence of less conserved domains sequences with low homology with the primers. Furthermore, PCR products can reflect the presence of genes involved in the biosynthesis of other types of metabolites, such as pigments or structural components of the microbial cell such as fatty acids [38], and an involvement in quorum sensing or iron metabolism has also been proposed for these gene products [31,32,39,40].
2.3. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activities
To evaluate the production of bioactive secondary metabolites the 44 marine isolates were cultivated in nutritional arrays of 12 different liquid media using Duetz 96-deep well plates. Applying this micro-cultivation system, all steps in the screening procedure, including the fermentation, solvent extraction of fermentation broths, storage of extracts and bioassays, could be efficiently performed in a standard 96-well format. In total, 528 crude extracts were analyzed for the production of antibacterial and antifungal activities in whole-cell agar-based growth inhibition assays against Bacillus subtilis MB964, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) MB5393, Acinetobacter baumannii MB5973 and the yeast Candida albicans MY1055.
The frequency of microbiological activities against bacterial human pathogens was considered to be an indicator of their ability to produce anti-infective molecules with potential therapeutic properties [41]. Three out of the 528 extracts that were tested in these bioassays inhibited the growth of MRSA. The producer actinobacteria strains correspond to two Kocuria spp. and one Micrococcus sp., that have been identified after phylogenetic analysis as the strains Kocuria marina F-276,310, Kocuria palustris F-276,345, and Micrococcus yunnanensis F-256,446 (Figure 1).
The preliminary inhibitory activity observed with 10 μL extracts in the agar well-based assay format was confirmed in a second agar assay directly using 10 μL and 20 μL extracts spotted on Nunc plates (24 × 24 cm) containing the reporter strains. The bioactivity was confirmed in both formats and the diameters of the zones of inhibition recorded, observing a 2 mm increase of the inhibition zone upon duplication of the extract volume used (Table 2).
Table 2.
Antimicrobial activities of the extracts against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA).
| Antibacterial activities in agar diffusion assays (mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract volume | Extract volume | |||
| Strain code | Identification | 10 μL | 10 μL | 20 μL |
| (96 well plate format) | (Nunc plate) | |||
| F-276,310 | Kocuria marina | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| F-276,345 | Kocuria palustris | 5 | 6 | 8 |
| F-256,446 | Micrococcus sp. | 4 | 5 | 7 |
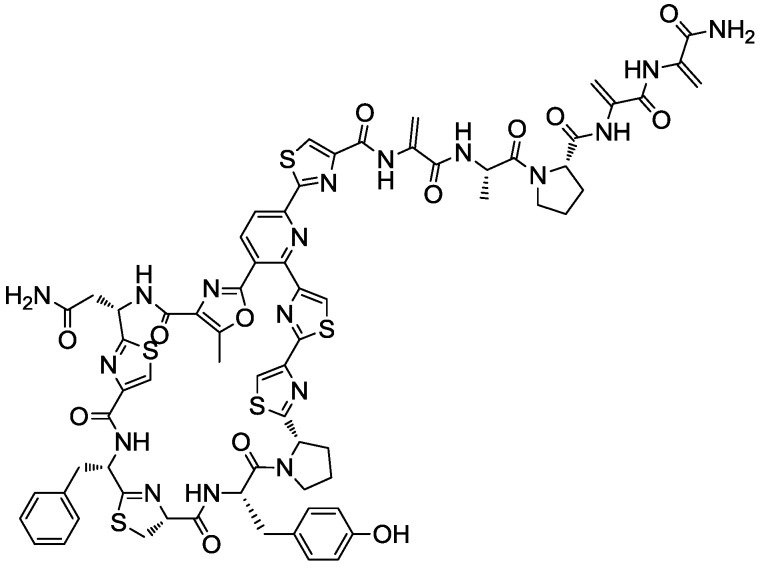
The anti-MRSA activity was confirmed in new 10 mL fermentations and a preliminary LC-MS analysis showed similar profiles in the three extracts, with a principal component (UV absorption maxima at 218, 307 and 349 (sh) nm) of 1514.366 Da and others minor components. The strain Kocuria sp. F-276,345 was then selected for further studies on the production and characterization of this antibacterial compound that was later identified by Martín et al. (2012) [42] as kocurin, a new member of the thiazolyl peptide family of antibiotics (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Chemical structure of thiazolyl peptide kocurin.
2.4. Production Conditions of the Thiazolyl Peptide Kocurin
The production of the new thiazolyl peptide kocurin by the strains of Kocuria and Micrococcus was detected in short fermentations in only one of the 12 production conditions tested, the medium R358, previously described by Jensen et al. (2007) [43] as providing enough amounts of bromide and iron, elements frequently observed in halogenated marine-derived compounds or of limited access in marine environments [39,44]. As previously observed with other examples of the family Microccocaceae, the compound was only produced in this medium in the absence of marine salts, conditions that were used to scale up the production for the isolation of the molecule. In fact, our group had already described two related strains of Microccocaceae corresponding to the species Arthrobacter, R-7513 and R-7914 (Figure 1), which were isolated in a previous study from Antarctic microbial mats. Both strains produced a potent anti-MRSA compound characterized by a major LCMS peak of 1514 Da proposed at that time as a new thiazolyl peptide [21] that we confirmed to correspond to kocurin (data not shown). In contrast to the Kocuria and Micrococcus strains, both strains of Arthrobacter produce kocurin in the medium CGY [21], a medium also used in our study without success.
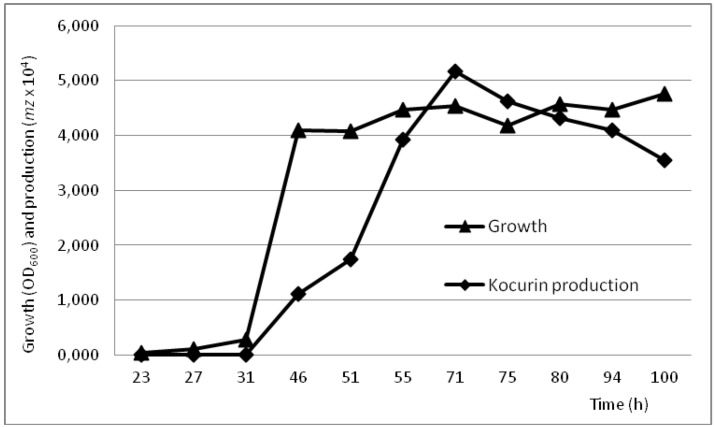
The production conditions of kocurin by the Kocuria strain F-276,345 were analyzed with a time course study monitoring the growth and kocurin production in the medium R358 during 4 days. Given that our preliminary experiments using standard seed ratios of 5% had shown a rapid exponential growth and production of the compound in concentrations of 0.2 μg/mL within the first 24 h of cultivation, the experiment was established using diluted seed conditions ensuring initial optical densities as low as OD600 0.015. Using this approach we have confirmed that whereas the strain reached the stationary phase within the first 48 h, kocurin production, estimated as the intensity of the ion M + 2Na+ with m/z = 780, was initiated during the exponential growth reaching its maximal production 24 h after the establishment of the stationary phase to fall afterwards as the incubation proceeds up to 4 days (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Time course production of kocurin by Kocuria palustris F-276,345. Growth levels (OD600) (▲) and kocurin production (■) (estimated as the m/z = 780 intensity) were followed during 100 h of cultivation at 28 °C in medium R358; all samples points were analyzed in triplicate.
2.5. Detection of Biosynthetic Pathways and Production of Bioactivities in Micrococcaceae
Whereas 77% of the marine Micrococcaceae in our study were shown to contain at least one class of NRPS and PKS “gene clusters” involved with the production of secondary metabolites, antimicrobial activity was detected from only 7% of the strains. It is accepted that the detection of secondary metabolites biosynthetic pathways may be used only as an indicator of the metabolic potential, and that the right cultivation conditions are still needed to express most of these pathways as well as the use of the appropriate targets to reveal the biological activity of the compounds [38]. In the experimental conditions used in our study, it has not been possible to establish any direct relationship between the presence of these specific secondary pathways and the production of antimicrobial activities. We cannot discard that distinct production conditions may be required for the expression of these cryptic genes in these strains or that other screening targets could reveal new activities for their products. The compound detected, the new thiazolyl peptide kocurin, is expected to be produced by ribosomal synthesis as for other molecules of the same class [45,46,47].
The antimicrobial activity profile of kocurin has shown that the compound has extremely potent activity against Gram-positive bacteria with MIC values of 0.25–0.5 μg/mL against MRSA and no activity against the Gram-negative bacterial pathogens A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa and E. coli [42]. Since the discovery of micrococcin, the first compound of this class isolated from a strain of Micrococcus, many other thiazolyl peptides also isolated from actinobacteria have been shown to act as potent inhibitors of protein synthesis in Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VRE), with molecular targets including the L11 binding region of the 23S rRNA and the bacterial elongation factor (EF-Tu) [33,45]. Kocurin is closely related to two known thiazolyl peptide antibiotics with similar mode of action, GE37468A [47,48,49] produced by a soil strain of Streptomyces and antibiotic GE2270 [45,50] obtained from a strain of Planobispora rosea, the only thiazolyl peptide in clinical trials for human use (as a tropical treatment for acne) [47].
Despite the emerging role of marine actinomycetes as a new resource for novel drugs, antimicrobial activities have not been reported so far for Micrococacceae species collected from sediment and marine sponges [12,14,32,51], and only some Kocuria isolates have been shown to exhibit an anti-parasitic activity against T. brucei [52].
Furthermore there is not a clear-cut correlation between the antimicrobial activity and the taxonomic position of the active bacterial strains, given that representatives of two distinct species of the genus Kocuria and another one of the genus Micrococcus produce the same compound. In spite of the common geographical origin of their sponge host, the three strains producing kocurin present different secondary metabolite gene amplification patterns: the Micrococcus sp. F-256,446 contains PKS-II genes whereas only NRPS genes can be detected in Kocuria palustris F-276,345 and no NRPS and PKS-related secondary metabolite genes were detected in the strain Kocuria marina F-276,310.
This is the first report of the production of a new potent thiazolyl peptide antibiotic by marine derived species of the genera Kocuria and Microccocus. The production of this compound by unrelated Antarctic Arthrobacter species suggest the broad distribution of the biosynthetic clusters involved in the synthesis of this thiazolyl peptide among the different lineages of the family Micrococcaceae.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Environmental Sampling
The 44 wild-type marine actinomycetes used in this study were isolated from sponges during a research trip to the Florida Keys and Maryland (USA) and preserved at Fundación Medina in the culture collection. Sponge collection and processing as well as actinomycetes isolation procedures were performed as described by Montalvo et al. (2005) [11].
3.2. Strain Culture and DNA Extraction
All strains were grown on R2A agar medium (BD) and MY liquid medium (10 g/L glucose, 3 g/L yeast extract, 5 g/L proteose-peptone, 3 g/L malt extract) both supplemented with 3% (w/v) sea salts (Sigma Aldrich). Plates were incubated in a humidified chamber at 28 °C for 2–4 weeks. Following incubation, selected cultures were incubated in MY liquid medium at 28 °C in an orbital shaker at 220 rpm for 4 days. For long-term storage, pure cultures were frozen in 20% glycerol at −80 °C. Total genomic DNA from marine actinomycetes was recovered and purified as described elsewhere [53].
3.3. Analysis of Fatty Acid by Gas Chromatography
Bacterial cultures were grown on TSB (Trypticase Soy Broth BBL 30 g/L, agar 15 g/L and 30 g/L sea salts) at 28 °C for 24 h. Vegetative growth was scraped and fatty acid methyl esters (FAMEs) were prepared using a modified sample preparation [54]. Analysis of FAMEs was carried out by capillary gas chromatography using a Hewlett-Packard Model 5890 gas chromatograph/MIDI system (Microbial ID, Inc., Newark, DE, USA) equipped with phenyl-methyl silicon column (0.2 mm × 25 m). Chromatography conditions were performed as recommended by the manufacturer. Individual FAMEs were identified using the Microbial Identification Software (MIS).
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
The 16S rRNA gene (approximately 900 bp) was partially PCR-amplified from the purified genomic DNA obtained from bacterial cultures [11]. Nucleotide sequences were analyzed and edited using MEGA (5.1 version) [55]. The partial 16S rRNA gene sequences from cultivable isolates were compared to 16S rRNA genes in the Eztaxon database [56] to determine the closest phylogenetic positions. Sequences (averaging 900 nucleotides) were aligned using ClustalW [57] including representative actinomycete 16S rRNA gene sequences from the family Micrococcaeae. Phylogenetic tree was constructed generating a complete alignment of 16S rRNA gene sequences of selected members of each genus within the family Micrococcaceae. Trees were generated using the Neighbor-Joining and Jukes-Cantor algorithms [24,25]. Bootstrap values were calculated from 1000 resampled datasets.
3.5. PCR Amplification
Ketosynthase (KS) domains of type I polyketide synthase (PKS) gene were PCR amplified from genomic DNA using the primers K1F (5′-TSAAGTCSAACATCGGBCA-3′) and M6R (5′-CGCAGGTTSCSGTACCAGTA-3′). Type II PKS sequences were amplified specifically using KSαF (5′-TSGRCTACRTCAACGCSCACGG-3′) and KSβR (5′-TACSAGTCSWTCGCCTGGTTC-3′). Degenerate PCR primers targeting specifically NRPS adenylation domains were A3F (5′-GCSTACSYSATS TACACSTCSGG-3′) and A7R (5′-SASGTCVCCSGTSCGGTAS-3′). The bands correspond to KS domains (≈1250–1400 bp), conserved sequences KSα and KSβ (≈800–900 bp) and adenylation domains (≈700 bp). These degenerated primers were designed by Ayuso and Genilloud (2005), and Ayuso et al. (2005) [13,38]. PCR amplifications were performed in a iCycler Bio-Rad thermal cycler in a final volume of 50 μL PCR mixture contained 0.5 μM of each primer, 0.2 mM of each of the four dNTPS (Applied Biosystems), 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase (5 U/μL) (with its recommended reaction buffer) (MP) and 5 μL of template DNA. The PCR protocol for PKS-I amplifications consisted of a 5 min denaturation step at 95 °C and 35 cycles of 30 s at 95 °C, 2 min at 57 °C for K1F/M6R, 58 °C for KSαF/KSβR and 61 °C for A3F/A7R and 4 min extension at 72 °C; followed by 10 min at 72 °C. The amplified products were analyzed by electrophoresis in 2% (w/v) agarose gels stained with ethidium bromide (Invitrogen).
3.6. Microfermentation and Extraction of Marine Microbial Secondary Metabolites
Marine actinomycetes were cultivated for the production of secondary metabolites in 96-deep well plate fermentations using different nutritional arrays in the presence and absence of sea salts [58]. Seeds were prepared inoculating 0.5 mL of a frozen inoculum stock of each strain in 12 mL of MY seed medium supplemented with 3% Sigma Aldrich sea salts. Fermentations in 96-deep well plates were performed in 800 μL of production medium and incubated for four days at 28 °C in a rotary shaker at 330 rpm and 70% humidity. Production conditions included the following six media prepared in parallel with 3% (w/v) sea salts or without sea salts: Antibiotic Assay Medium No. 3 (Assay Broth) (FLUKA); medium CGY (5 g/L bacto casitone, 5 g/L glycerol, 1 g/L bacto yeast extract, adjusted to pH 7) [21]; medium DEF-15 (40 g/L sucrose, 2 g/L NH4Cl, 2 g/L Na2SO4, 1 g/L K2HPO4, 1 g/L MgCl2·6H2O, 1 g/L NaCl, 2 g/L CaCO3, 1 mL trace elements solution (100 mg/L MnCl2·4H2O, 100 mg/L ZnCl2, 100 mg/L FeCl2·4H2O, 50 mg/L NaI, adjusted to pH 7); medium IN (2 g/L dl-serine, 2 g/L dl-alanine, 8.6 g/L K2SO4, 1.4 g/L KCl, 1.4 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, 10 g/L sucrose, 30 g/L yeast extract, adjusted to pH 7) [59]; Marine Broth (BD); medium R358 (10 g/L starch from potato, 4 g/L yeast extract, 2 g/L peptone, 5 mL of a 20 g/L stock solution KBr and 5 mL of a stock solution of 8 g/L FeSO4·7H2O, adjusted to pH 7) [43]. Plates were incubated for four days at 28 °C in a rotary shaker at 330 rpm and 70% humidity. After four days of incubation, broths were extracted with 800 μL acetone and 40 μL DMSO. Each extract was shaken at 200 rpm for 1 h, the acetone evaporated and the sample concentrated under vacuum, to be finally reconstituted in 200 μL of water. The resulting crude extracts were transferred to a 96-well plate for storage at −20 °C.
3.7. Production of Thiazolyl Peptides
Scale-up fermentation conditions to reproduce the production of the bioactive compounds in microfermentations were initially performed in 40 mL EPA vials. Each vial containing 10 mL of production medium R358 was seeded with 5% inoculum in MY prepared as described previously and incubated 24 to 96 h at 28 °C in a rotary shaker at 220 rpm and 70% humidity. Acetone extraction and preparation of crude extracts was performed as described previously.
The production conditions of the active compound were studied on the basis of the initial results obtained with the Kocuria strain F-276,345. A first seed culture of strain F-276,345 was prepared in MY medium with 3% artificial sea salts (3 days at 28 °C and in a rotary shaker at 220 rpm and 70% humidity) and 2 L volume of medium R358 were inoculated to obtain a final OD600 of 0.015 measured with a Eppendorf BioPhotometer. 10 mL aliquots of the seeded medium were then distributed in 40-mL EPA vials, and incubated during 4 days at 28 °C in a rotary shaker at 220 rpm and 70% humidity. Samples were taken by triplicate to evaluate the growth rate as derived from the DO600 estimation and the production of the compound determined by mass spectrometry as the intensity of the kocurin fragmentation ion with m/z = 780.
3.8. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activity
Evaluation of antimicrobial activity of the extracts was performed by agar diffusion test against clinically relevant strains in solid agar plates: Gram-positive Bacillus subtilis MB964 and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus MB5393, Gram-negative Acinetobacter baumannii MB5973, and Candida albicans MY1055, all from Fundación Medina’s collection. The seeds and assay plates were prepared as described previously [41]. Marine crude extracts were dispensed both in wells (10 μL) onto agar plates (12 cm × 8 cm) or as 10 μL and 20 μL drops on the surface of Nunc agar plates (24 cm × 24 cm). Inhibition zones were measured in mm after 24 h incubation at 37 °C.
4. Conclusions
This survey supports previous reports showing that marine environments, and especially sponges, are sources for novel bioactive metabolite producers with biotechnological use, and that geographic and environmental factors may affect the occurrence of these biochemical pathways and bioactivities. In fact, our data currently suggest that marine sponges support a diverse community of Kocuria species distributed among seven taxa in contrast with the single lineage observed for members of the genus Micrococcus. The pre-screening methodology implemented in this survey, developed in a framework of enhanced understanding of microbial and chemical ecology associated to the marine environment, will certainly increase the discovery and development of novel natural products from marine sources. Our results provide an initial study of the scale-up production conditions of kocurin as well as new insights into the metabolism of these sponge symbionts, that so far has been limited to the production of this molecule, a new thiazolyl peptide from a family of compounds well represented among different lineages of terrestrial actinomycetes. The presence of type I and type II PKS and NRPS pathways in this family of actinomycetes has not been translated into the production of any bioactive compound that could be revealed with our screening approach. The synthesis of kocurin is unrelated with any these biosynthetic systems and additional experiments would be necessary to confirm if they are being expressed and involved in the synthesis of additional molecules. The fact that the same thiazolyl peptide was found in bacterial isolates independently of their geographic location (marine sponges and Antarctic mats), suggests a wide geographic distribution of this antibacterial compound. Kocurin is a new antibiotic molecule with unique chemical structure and biological activity facing the rise in drug-resistant pathogens.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the assistance of Catalina Moreno in the preparation of the extracts. Some of these results were presented by S.P. to obtain her Diploma of Advanced Studies from the Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Spain. This is contribution no. 13105 from the Institute of Marine and Environmental Technology and contribution number 4746 from the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science.
Supplementary Files
Supplementary Information (PDF, 122 KB)
References
- 1.Hentschel U., Usher K.M., Taylor M.W. Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006;55:167–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2005.00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Taylor M.W., Hill R.T., Piel J., Thacker R.W., Hentschel U. Soaking it up: The complex lives of marine sponges and their microbial associates. ISME J. 2007;1:187–190. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2007.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Webster N.S., Taylor M.W. Marine sponges and their microbial symbionts: Love and other relationships. Environ. Microbiol. 2012;14:335–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02460.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Berdy J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005;58:1–26. doi: 10.1038/ja.2005.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mincer T.J., Jensen P.R., Kauffman C.A., Fenical W. Widespread and persistent populations of a major new marine actinomycete taxon in ocean sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002;68:5005–5011. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.10.5005-5011.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fenical W., Jensen P.R. Developing a new resource for drug discovery: Marine actinomycete bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006;2:666–673. doi: 10.1038/nchembio841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lam K.S. Discovery of novel metabolites from marine actinomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006;9:245–251. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2006.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gontang E.A., Fenical W., Jensen P.R. Phylogenetic diversity of Gram-positive bacteria cultured from marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:3272–3282. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02811-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Maldonado L.A., Stach J.E., Ward A.C., Bull A.T., Goodfellow M. Characterization of Micromonosporae from aquatic environments using molecular taxonomic methods. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2008;94:289–298. doi: 10.1007/s10482-008-9244-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Maldonado L.A., Fenical W., Jensen P.R., Kauffman C.A., Mincer T.J., Ward A.C., Bull A.T., Goodfellow M. Goodfellow, M. Salinispora arenicola gen. nov., sp. nov. and Salinispora tropica sp. nov., obligate marine actinomycetes belonging to the family Micromonosporaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2005;55:1759–1766. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.63625-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Montalvo N., Mohamed N., Enticknap J., Hill R. Novel actinobacteria from marine sponges. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2005;87:29–36. doi: 10.1007/s10482-004-6536-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schneemann I., Nagel K., Kajahn I., Labes A., Wiese J., Imhoff J.F. Comprehensive investigation of marine actinobacteria associated with the sponge Halichondria panicea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;76:3702–3714. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00780-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ayuso-Sacido A., Genilloud O. New PCR primers for the screening of NRPS and PKS-I systems in actinomycetes: Detection and distribution of these biosynthetic gene sequences in major taxonomic groups. Microb. Ecol. 2005;49:10–24. doi: 10.1007/s00248-004-0249-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gontang E.A., Gaudencio S.P., Fenical W., Jensen P.R. Sequence-based analysis of secondary-metabolite biosynthesis in marine actinobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010;76:2487–2499. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02852-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Metsa-Ketela M., Halo L., Munukka E., Hakala J., Mantsala P., Ylihonko K. Molecular evolution of aromatic polyketides and comparative sequence analysis of polyketide ketosynthase and 16S ribosomal DNA genes from various Streptomyces species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002;68:4472–4479. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.9.4472-4479.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Penesyan A., Kjelleberg S., Egan S. Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Mar. Drugs. 2010;8:438–459. doi: 10.3390/md8030438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Freel K.C., Nam S.-J., Fenical W., Jensen P.R. Evolution of secondary metabolite genes in three closely related marine actinomycete species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011;77:7261–7270. doi: 10.1128/AEM.05943-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fenical W., Jensen P.R., Palladino M.A., Lam K.S., Lloyd G.K., Potts B.C. Discovery and development of the anticancer agent salinosporamide A (NPI-0052) Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009;17:2175–2180. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.10.075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lane A.L., Moore B.S. A sea of biosynthesis: Marine natural products meet the molecular age. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011;28:411–428. doi: 10.1039/c0np90032j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhao X.Q. Genome-based studies of marine microorganisms to maximize the diversity of natural products discovery for medical treatments. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011;2011:384572. doi: 10.1155/2011/384572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rojas J.L., Martín J., Tormo J.R., Vicente F., Brunati M., Ciciliato I., Losi D., van Trappen S., Mergaert J., Swings J., et al. Bacterial diversity from benthic mats of Antarctic lakes as a source of new bioactive metabolites. Mar. Genomics. 2009;2:33–41. doi: 10.1016/j.margen.2009.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bala M., Kaur C., Kaur I., Khan F., Mayilraj S. Kocuria sediminis sp. nov., isolated from a marine sediment sample. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2012;101:469–478. doi: 10.1007/s10482-011-9654-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hentschel U., Schmid M., Wagner M., Fieseler L., Gernert C., Hacker J. Isolation and phylogenetic analysis of bacteria with antimicrobial activities from the Mediterranean sponges Aplysina aerophoba and Aplysina cavernicola. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2001;35:305–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2001.tb00816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jukes T.H., Cantor C. Evolution of Protein Molecules. In: Munro H.N., Allison J.B., editors. Mammalian Protein Metabolism. Academic Press; New York, NY, USA: 1969. pp. 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987;4:406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Stackebrandt E., Koch C., Gvozdiak O., Schumann P. Taxonomic dissection of the genus Micrococcus: Kocuria gen. nov., Nesterenkonia gen. nov., Kytococcus gen. nov., Dermacoccus gen. nov., and Micrococcus Cohn 1872 gen. emend. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1995;45:682–692. doi: 10.1099/00207713-45-4-682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kovacs G., Burghardt J., Pradella S., Schumann P., Stackebrandt E., Marialigeti K. Kocuria palustris sp. nov. and Kocuria rhizophila sp. nov., isolated from the rhizoplane of the narrow-leaved cattail (Typha angustifolia) Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1999;49:167–173. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Reddy G.S.N., Prakash J.S.S., Prabahar V., Matsumoto G.I., Stackebrandt E., Shivaji S. Kocuria polaris sp. nov., an orange-pigmented psychrophilic bacterium isolated from an Antarctic cyanobacterial mat sample. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2003;53:183–187. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02336-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kim S.B., Nedashkovskaya O.I., Mikhailov V.V., Han S.K., Kim K.O., Rhee M.S., Bae K.S. Kocuria marina sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from marine sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2004;54:1617–1620. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.02742-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Liu H., Xu Y., Ma Y., Zhou P. Characterization of Micrococcus antarcticus sp. nov., a psychrophilic bacterium from Antarctica. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2000;50:715–719. doi: 10.1099/00207713-50-2-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hodges T., Slattery M., Olson J. Unique actinomycetes from marine caves and coral reef sediments provide novel pks and nrps biosynthetic gene clusters. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012;14:270–280. doi: 10.1007/s10126-011-9410-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Pathom-aree W., Stach J., Ward A., Horikoshi K., Bull A., Goodfellow M. Diversity of actinomycetes isolated from Challenger Deep sediment (10,898 m) from the Mariana Trench. Extremophiles. 2006;10:181–189. doi: 10.1007/s00792-005-0482-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Engelhardt K. Ph.D. Thesis. Norwegian University of Science and Technology; Trondheim, Norway: Oct, 2010. Assessment of the Antibiotic Production Potential of Marine Derived Actinomycetes via Bioactivity Screening and Targeted Genetic Analysis. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jiang S., Li X., Zhang L., Sun W., Dai S., Xie L., Liu Y., Lee K. Culturable actinobacteria isolated from marine sponge Iotrochota sp. Mar. Biol. 2008;153:945–952. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Xin Y., Kanagasabhapathy M., Janussen D., Xue S., Zhang W. Phylogenetic diversity of Gram-positive bacteria cultured from Antarctic deep-sea sponges. Polar Biol. 2011;34:1501–1512. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li J., Zhao G.-Z., Huang H.-Y., Qin S., Zhu W.-Y., Zhao L.-X., Xu L.-H., Zhang S., Li W.-J., Strobel G. Isolation and characterization of culturable endophytic actinobacteria associated with Artemisia annua L. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2012;101:515–527. doi: 10.1007/s10482-011-9661-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Takarada H., Sekine M., Kosugi H., Matsuo Y., Fujisawa T., Omata S., Kishi E., Shimizu A., Tsukatani N., Tanikawa S., et al. Complete genome sequence of the soil actinomycete Kocuria rhizophila. J. Bacteriol. 2008;190:4139–4146. doi: 10.1128/JB.01853-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Ayuso A., Clark D., Gonzalez I., Salazar O., Anderson A., Genilloud O. A novel actinomycete strain de-replication approach based on the diversity of polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase biosynthetic pathways. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005;67:795–806. doi: 10.1007/s00253-004-1828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fenical W. Chemical studies of marine bacteria: Developing a new resource. Chem. Rev. 1993;93:1673–1683. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Selvin J. Exploring the antagonistic producer streptomyces MSI051: Implications of polyketide synthase gene type II and a ubiquitous defense enzyme phospholipase A2 in the host sponge Dendrilla nigra. Curr. Microbiol. 2009;58:459–463. doi: 10.1007/s00284-008-9343-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Suay I., Arenal F., Asensio F.J., Basilio A., Angeles Cabello M., Teresa Díez M., García J.B., González del Val A., Gorrochategui J., Hernández P., Peláez F., Vicente M.F. Screening of basidiomycetes for antimicrobial activities. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2000;78:129–140. doi: 10.1023/a:1026552024021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Martín J., Sousa T., Crespo G., Palomo S., González I., Tormo J.R., de la Cruz M., Anderson M., Hill R.T., Vicente F., et al. Kocurin, the true structure of PM 181104, an anti-MRSA thiazolyl peptide from the marine-derived bacterium Kocuria palustris. Mar. Drugs. 2013;11:387–398. doi: 10.3390/md11020387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Jensen P.R., Williams P.G., Oh D.-C., Zeigler L., Fenical W. Species-specific secondary metabolite production in marine actinomycetes of the genus Salinispora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007;73:1146–1152. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01891-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Marwick J.D., Wright P.C., Burgess J. Grant, Bioprocess intensification for production of novel marine bacterial antibiotics through bioreactor operation and design. Mar. Biotechnol. 1999;1:495–507. doi: 10.1007/pl00011806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bagley M.C., Dale J.W., Merritt E.A., Xiong X. Thiopeptide antibiotics. Chem. Rev. 2005;105:685–714. doi: 10.1021/cr0300441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Morris R.P., Leeds J.A., Naegeli H.U., Oberer L., Memmert K., Weber E., LaMarche M.J., Parker C.N., Burrer N., Esterow S., et al. Ribosomally synthesized thiopeptide antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009;131:5946–5955. doi: 10.1021/ja900488a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Young T.S., Walsh C.T. Identification of the thiazolyl peptide GE37468 gene cluster from Streptomyces ATCC 55365 and heterologous expression in Streptomyces lividans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:13053–13058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1110435108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ferrari P., Colombo L., Stella S., Selva E., Zerilli L.F. Antibiotic GE37468 A: A novel inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis II. Structure elucidation. J. Antibiot. 1995;48:1304–1311. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.48.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Marinelli F., Gastaldo L., Toppo G., Quarta C. Antibiotic GE37468 A: A new inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. III. Strain and fermentation study. J. Antibiot. 1996;49:880–885. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.49.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Selva E., Beretta G., Montanini N., Saddler G.S., Gastaldo L., Ferrari P., Ripamonti F., Goldstein B.P., Berti M., Montanaro L., et al. Antibiotic GE2270 a: A novel inhibitor of bacterial protein synthesis. I. Isolation and characterization. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1991;44:693–701. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.44.693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xi L., Ruan J., Huang Y. Diversity and biosynthetic potential of culturable actinomycetes associated with marine sponges in the China seas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012;13:5917–5932. doi: 10.3390/ijms13055917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Abdelmohsen U.R., Pimentel-Elardo S.M., Hanora A., Radwan M., Abou-El-Ela S.H., Ahmed S., Hentschel U. Isolation, phylogenetic analysis and anti-infective activity screening of marine sponge-associated actinomycetes. Mar. Drugs. 2010;8:399–412. doi: 10.3390/md8030399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Innis M.A., Gelfand D.H., Sninsky J.J., White T.J. PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Amplifications. Academic Press; San Diego, CA, USA: 1990. pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Miller L.T. Single derivatization method for routine analysis of bacterial whole-cell fatty acid methyl esters, including hydroxy acids. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1982;16:584–586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.3.584-586.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M., Kumar S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011;28:2731–2739. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chun J., Lee J.-H., Jung Y., Kim M., Kim S., Kim B.K., Lim Y.-W. EzTaxon: A web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2007;57:2259–2261. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.64915-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Higgins D.G. CLUSTAL W: Multiple alignment of DNA and protein sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 1994;25:307–318. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-276-0:307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Duetz W.A., Ruedi L., Hermann R., O’Connor K., Buchs J., Witholt B. Methods for intense aeration, growth, storage, and replication of bacterial strains in microtiter plates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000;66:2641–2646. doi: 10.1128/aem.66.6.2641-2646.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Obata H., Muryoi N., Kawahara H., Yamade K., Nishikawa J. Identification of a novel ice-nucleating bacterium of Antarctic origin and its ice nucleation properties. Cryobiology. 1999;38:131–139. doi: 10.1006/cryo.1999.2156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Information (PDF, 122 KB)