Abstract
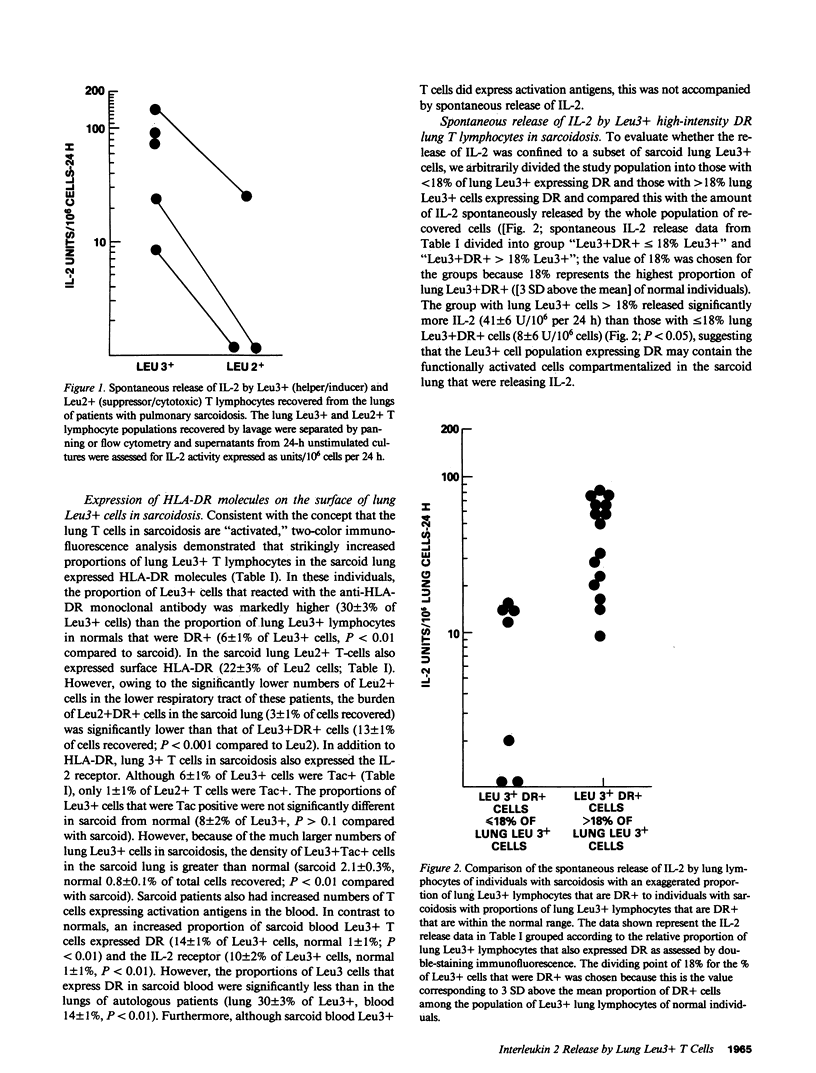
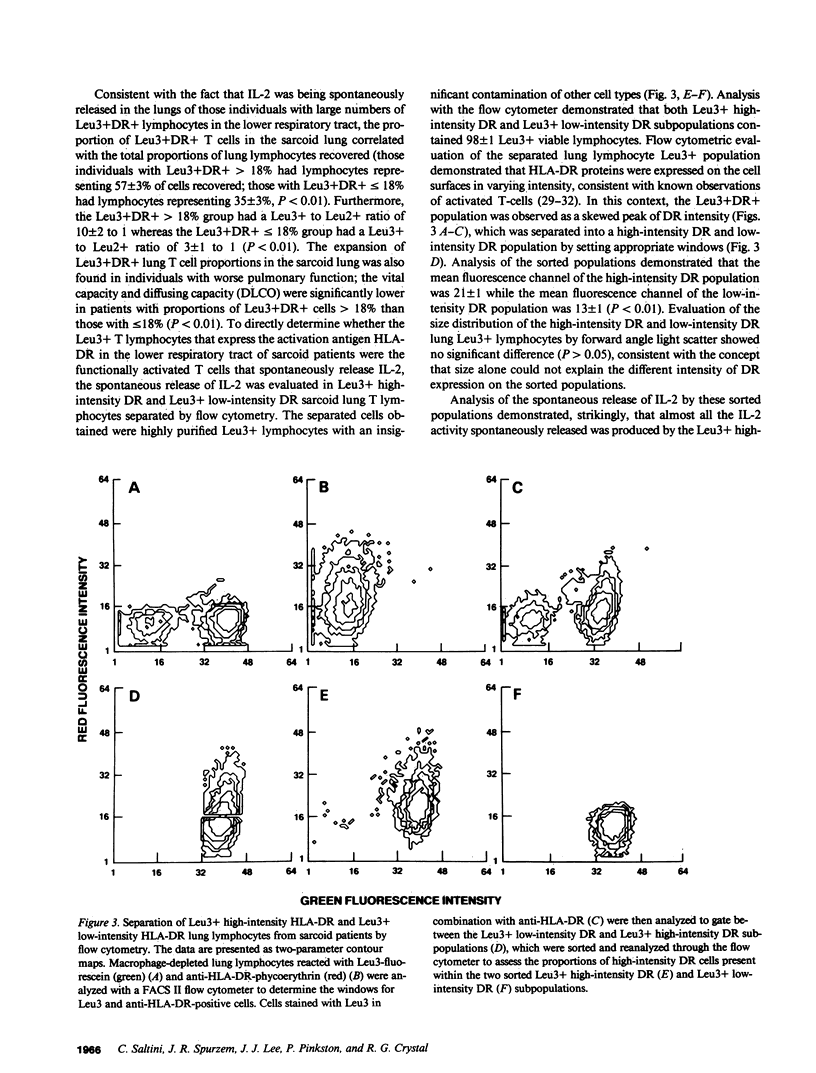
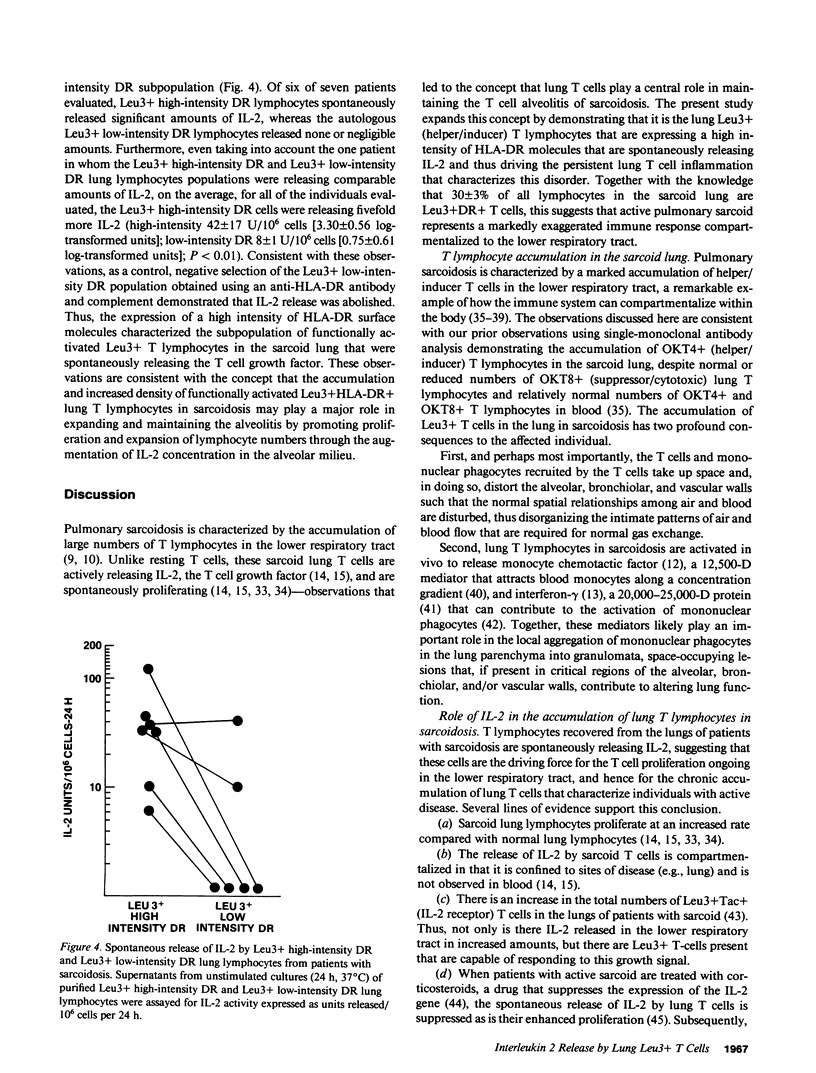
The inflammation within the lower respiratory tract of individuals with pulmonary sarcoidosis is dominated by large numbers of helper T lymphocytes that proliferate and spontaneously release interleukin 2 (IL-2). To identify the lymphocyte subpopulation that releases IL-2 in this disorder, lung lymphocytes recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage were characterized using the monoclonal antibodies Leu4 (T lymphocyte), Leu3 (helper/inducer), Leu2 (suppressor/cytotoxic), and anti-HLA-DR, and separated by panning and flow cytometry. The majority of the IL-2 spontaneously released by T cells in the sarcoid lung was contributed by the Leu3+ cell population (Leu3+65 +/- 23 IL-2 units released/10(6) cells per 24 h; Leu2+ 9 +/- 8, P less than 0.04). Further characterization of the lung Leu3+ T cells in sarcoid demonstrated that 30 +/- 3% were expressing HLA-DR molecules on their surface compared with 6 +/- 1% in normals (P less than 0.01). Importantly, the subpopulation of Leu3+ lung T lymphocytes expressing a high intensity of HLA-DR molecules on their surface was responsible for the majority of the release of IL-2 in the sarcoid lung (Leu3+ high-intensity DR 42 +/- 17 U/10(6) cells per 24 h, Leu3+ low-intensity DR 8 +/- 1 U/10(6) cells per 24 h; P less than 0.01). Thus, the spontaneous release of IL-2 in the lung of sarcoid patients appears to be localized to a subset of Leu3+ high-intensity DR ("activated" lung helper/inducer) T lymphocytes. Because the sarcoid lung is characterized by markedly increased numbers of these cells, it is likely that this compartmentalized T cell population plays a major role in sustaining the exaggerated localized immune processes of this disorder.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman L. C., Snyderman R., Oppenheim J. J., Mergenhagen S. E. A human mononuclear leukocyte chemotactic factor: characterization, specificity and kinetics of production by homologous leukocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):801–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arya S. K., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Dexamethasone-mediated inhibition of human T cell growth factor and gamma-interferon messenger RNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):273–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmester G. R., Jahn B., Gramatzki M., Zacher J., Kalden J. R. Activated T cells in vivo and in vitro: divergence in expression of Tac and Ia antigens in the nonblastoid small T cells of inflammation and normal T cells activated in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1230–1234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceuppens J. L., Lacquet L. M., Mariën G., Demedts M., van den Eeckhout A., Stevens E. Alveolar T-cell subsets in pulmonary sarcoidosis. Correlation with disease activity and effect of steroid treatment. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Apr;129(4):563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costabel U., Bross K. J., Rühle K. H., Löhr G. W., Matthys H. Ia-like antigens on T-cells and their subpopulations in pulmonary sarcoidosis and in hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Analysis of bronchoalveolar and blood lymphocytes. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):337–342. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crystal R. G., Gadek J. E., Ferrans V. J., Fulmer J. D., Line B. R., Hunninghake G. W. Interstitial lung disease: current concepts of pathogenesis, staging and therapy. Am J Med. 1981 Mar;70(3):542–568. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniele R. P., Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D. Immunologic abnormalities in sarcoidosis. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):406–416. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWolf W. C., Schlossman S. F., Yunis E. J. DRw antisera react with activated T cells. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1780–1784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. E., Dauber J. H., Rossman M. D., Daniele R. P. Bronchoalveolar lavage in a patient with chronic berylliosis: evidence for hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Aug;97(2):213–216. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-97-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Wall D. W., Platsoucas C. D., Siegal F. P., Fikrig S. M., Testa C. M., Good R. A. Thymus-dependent membrane antigens in man: inhibition of cell-mediated lympholysis by monoclonal antibodies to TH2 antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):544–548. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishbein E., Alcocer-Varela J., Alarcón-Segovia D. Cellular bases of the production of and response to interleukin-2 in man: role of autologous rosette-forming T-cell subsets defined with monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 1983 Oct;50(2):223–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox R. I., Theofilopoulos A. N., Altman A. Production of interleukin 2 (IL 2) by salivary gland lymphocytes in Sjögren's syndrome. Detection of reactive cells by using antibody directed to synthetic peptides of IL 2. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3109–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerne P. A., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. Production of interleukin 2, interleukin 3, and interferon by mouse T lymphocyte clones of Lyt-2+ and -2- phenotype. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1869–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafler D. A., Fox D. A., Manning M. E., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L., Weiner H. L. In vivo activated T lymphocytes in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 30;312(22):1405–1411. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505303122201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. T., Heurich A. E., Rosen Y., Moon S., Lyons H. A. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: roentgenographic, functional, and pathologic correlations. Respiration. 1979;37(6):337–345. doi: 10.1159/000194046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Bedell G. N., Zavala D. C., Monick M., Brady M. Role of interleukin-2 release by lung T-cells in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Oct;128(4):634–638. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.4.634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Crystal R. G. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disorder mediated by excess helper T-lymphocyte activity at sites of disease activity. N Engl J Med. 1981 Aug 20;305(8):429–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198108203050804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Fulmer J. D., Young R. C., Jr, Gadek J. E., Crystal R. G. Localization of the immune response in sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Jul;120(1):49–57. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.120.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Gadek J. E., Young R. C., Jr, Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Maintenance of granuloma formation in pulmonary sarcoidosis by T lymphocytes within the lung. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 13;302(11):594–598. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003133021102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Kawanami O., Ferrans V. J., Young R. C., Jr, Roberts W. C., Crystal R. G. Characterization of the inflammatory and immune effector cells in the lung parenchyma of patients with interstitial lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 Apr;123(4 Pt 1):407–412. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelso A., Macdonald H. R. Precursor frequency analysis of lymphokine-secreting alloreactive T lymphocytes. Dissociation of subsets producing interleukin 2, macrophage-activating factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on the basis of Lyt-2 phenotype. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1366–1379. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Hunninghake G. W., Line B. R., Crystal R. G. The alveolitis of pulmonary sarcoidosis. Evaluation of natural history and alveolitis-dependent changes in lung function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Aug;128(2):256–265. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.128.2.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keogh B. A., Lakatos E., Price D., Crystal R. G. Importance of the lower respiratory tract in oxygen transfer. Exercise testing in patients with interstitial and destructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Feb;129(2 Pt 2):S76–S80. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.129.2P2.S76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko H. S., Fu S. M., Winchester R. J., Yu D. T., Kunkel H. G. Ia determinants on stimulated human T lymphocytes. Occurrence on mitogen- and antigen-activated T cells. J Exp Med. 1979 Aug 1;150(2):246–255. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld H., Berman J. S., Beer D. J., Center D. M. Induction of human T lymphocyte motility by interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3887–3890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Levy R. Two populations of Ia-like molecules on a human B cell line. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Evans R. L., Lipinski M., Cunningham-Rundles C., Good R. A., Herzenberg L. A. Evolutionary conservation of surface molecules that distinguish T lymphocyte helper/inducer and cytotoxic/suppressor subpopulations in mouse and man. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):310–323. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Uchiyama T., Smith K. A., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. A monoclonal antibody that appears to recognize the receptor for human T-cell growth factor; partial characterization of the receptor. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):267–269. doi: 10.1038/300267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger T. A., Smolen J. S., Chused T. M., Steinberg A. D., Oppenheim J. J. Human lymphocytes with either the OKT4 or OKT8 phenotype produce interleukin 2 in culture. J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):470–473. doi: 10.1172/JCI110637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maceira J. M., Fukuyama K., Epstein W. L. Appearance of T-cell subpopulations during the time course of beryllium-induced granulomas. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Nov;83(5):314–316. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12264096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. L., Sharrow S. O. HLA-DRw alloantigens can be detected on peripheral blood T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1980 Nov;125(5):1889–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Cantrell D. A., Hodgdon J. C., Schlossman S. F., Smith K. A., Reinherz E. L. Triggering of the T3-Ti antigen-receptor complex results in clonal T-cell proliferation through an interleukin 2-dependent autocrine pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Penta A. C., Fitzgerald K. A., Stadler B. M., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Cellular origin of interleukin 2 (IL 2) in man: evidence for stimulus-restricted IL 2 production by T4+ and T8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Sep;129(3):1076–1079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. N., Scadding J. G. Sarcoidosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1974 Dec;110(6):774–802. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1974.110.6P1.774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Horwitz D. A., Husmann L. A., Gillis S., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ identification of cells in human leprosy granulomas with monoclonal antibodies to interleukin 2 and its receptor. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3085–3090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modlin R. L., Hofman F. M., Meyer P. R., Sharma O. P., Taylor C. R., Rea T. H. In situ demonstration of T lymphocyte subsets in granulomatous inflammation: leprosy, rhinoscleroma and sarcoidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Mar;51(3):430–438. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIH conference. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: a disease characterized and perpetuated by activated lung T-lymphocytes. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jan;94(1):73–94. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-94-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco Y., Cordier G., Perrin-Fayolle M., Revillard J. P. Flow cytometry analysis of T lymphocytes in sarcoidosis. Am J Med. 1982 Jul;73(1):82–88. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90930-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkston P., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Spontaneous release of interleukin-2 by lung T lymphocytes in active pulmonary sarcoidosis. N Engl J Med. 1983 Apr 7;308(14):793–800. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198304073081401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Kung P. C., Pesando J. M., Ritz J., Goldstein G., Schlossman S. F. Ia determinants on human T-cell subsets defined by monoclonal antibody. Activation stimuli required for expression. J Exp Med. 1979 Dec 1;150(6):1472–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.6.1472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Morimoto C., Penta A. C., Schlossman S. F. Subpopulations of the T4+ inducer T cell subset in man: evidence for an amplifier population preferentially expressing Ia antigen upon activation. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., O'Connor B. H., Rodriguez H. Natural human interferon-gamma. Complete amino acid sequence and determination of sites of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6790–6797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. W., McLemore T. L., Crystal R. G. Gamma interferon is spontaneously released by alveolar macrophages and lung T lymphocytes in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1488–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen Y., Athanassiades T. J., Moon S., Lyons H. A. Nongranulomatous interstitial pneumonitis in sarcoidosis. Relationship to development of epithelioid granulomas. Chest. 1978 Aug;74(2):122–125. doi: 10.1378/chest.74.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Di Negro G. B., Balzano E., Cerri E., Sacco O., Balbi B., Venturini A., Ramoino R., Ravazzoni C. Suppression of the alveolitis in pulmonary sarcoidosis by oral corticosteroids. Lung. 1985;163(2):83–93. doi: 10.1007/BF02713810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G. A., Sacco O., Cosulich E., Damiani G., Corte G., Bargellesi A., Ravazzoni C. Pulmonary sarcoidosis: excess of helper T lymphocytes and T cell subset imbalance at sites of disease activity. Thorax. 1984 Feb;39(2):143–149. doi: 10.1136/thx.39.2.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Gallo R. C. Human T-lymphocyte growth factor: regulation of growth and function of T lymphocytes. Blood. 1981 Mar;57(3):379–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltini C., Hance A. J., Ferrans V. J., Basset F., Bitterman P. B., Crystal R. G. Accurate quantification of cells recovered by bronchoalveolar lavage. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Oct;130(4):650–658. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasazuki T., Nishimura Y., Muto M., Ohta N. HLA-linked genes controlling immune response and disease susceptibility. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:51–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Agostini C., Trentin L., Zambello R., Chilosi M., Cipriani A., Ossi E., Angi M. R., Morittu L., Pizzolo G. Evidence of cells bearing interleukin-2 receptor at sites of disease activity in sarcoid patients. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Aug;57(2):331–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semenzato G., Pezzutto A., Pizzolo G., Chilosi M., Ossi E., Angi M. R., Cipriani A. Immunohistological study in sarcoidosis: evaluation at different sites of disease activity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1984 Jan;30(1):29–40. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(84)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siltzbach L. E. Sarcoidosis: clinical features and management. Med Clin North Am. 1967 Mar;51(2):483–502. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)33069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venet A., Hance A. J., Saltini C., Robinson B. W., Crystal R. G. Enhanced alveolar macrophage-mediated antigen-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation in sarcoidosis. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jan;75(1):293–301. doi: 10.1172/JCI111688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger S. E., Kelman J. A., Elson N. A., Young R. C., Jr, Reynolds H. Y., Fulmer J. D., Crystal R. G. Bronchoalveolar lavage in interstitial lung disease. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Oct;89(4):459–466. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-89-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welte K., Platzer E., Wang C. Y., Rinnooy Kan E. A., Moore M. A., Mertelsmann R. OKT8 antibody inhibits OKT3-induced IL 2 production and proliferation in OKT8+ cells. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2356–2361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. The family of human T-lymphotropic leukemia viruses: HTLV-I as the cause of adult T cell leukemia and HTLV-III as the cause of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Blood. 1985 Feb;65(2):253–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Sato V. L. "Panning" for lymphocytes: a method for cell selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2844–2848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yachie A., Miyawaki T., Uwadana N., Ohzeki S., Taniguchi N. Sequential expression of T cell activation (Tac) antigen and Ia determinants on circulating human T cells after immunization with tetanus toxoid. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



