Abstract
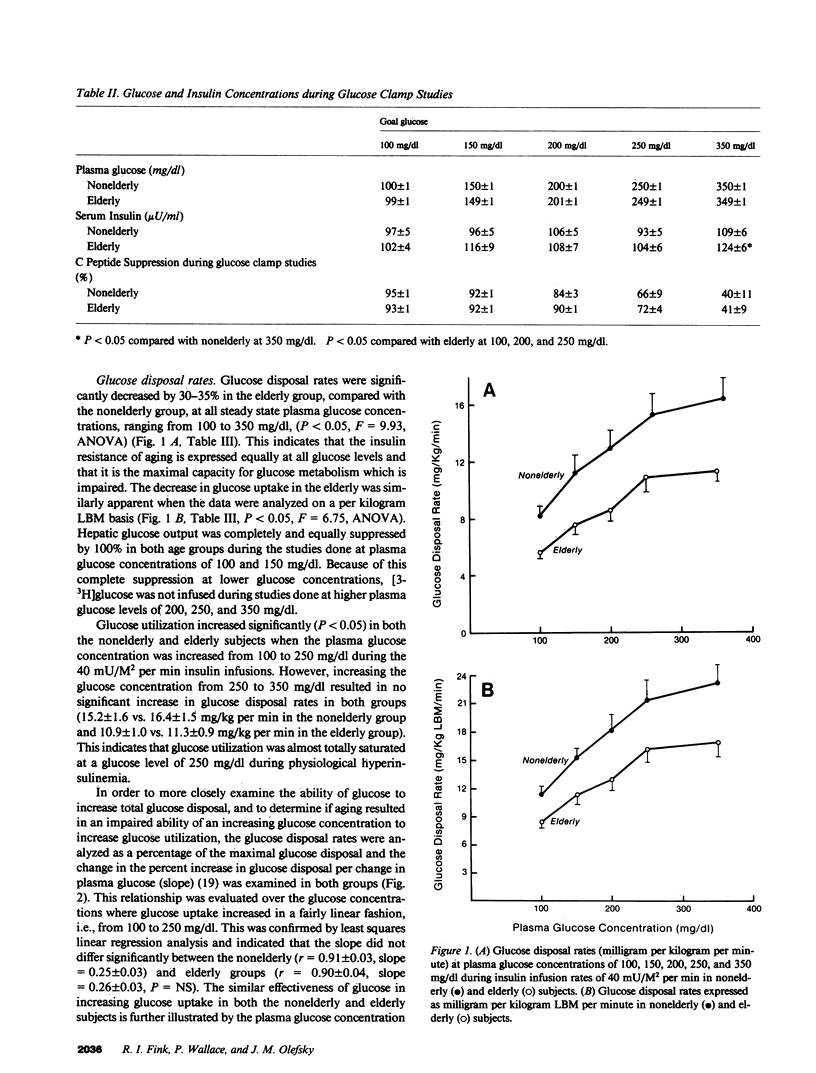
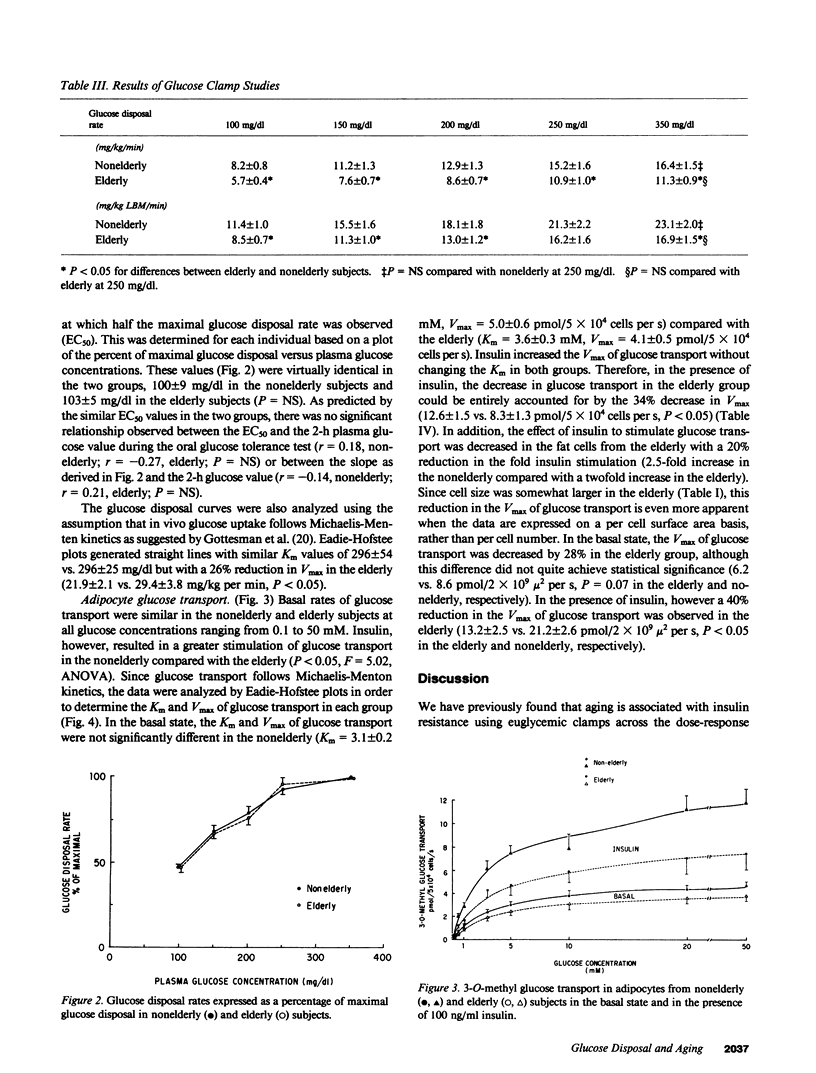
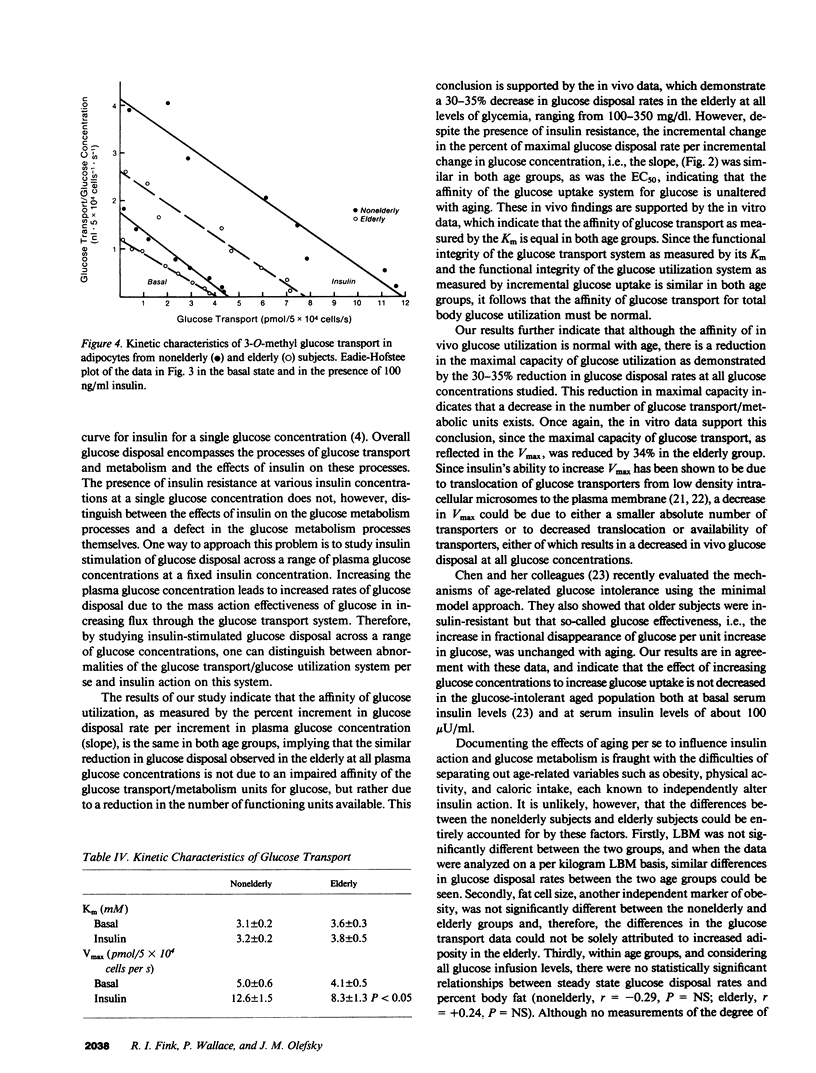
To assess the effects of aging on glucose-mediated glucose disposal and glucose transport, glucose disposal rates were measured in 10 nonelderly (32 +/- 4 yr) and 11 elderly (64 +/- 4 yr) subjects at five different plasma glucose concentrations. Glucose disposal was decreased by 30-35% in the elderly at each level of glycemia (100-350 mg/dl) in the presence of similar levels of hyperinsulinemia (approximately 100 microU/ml), and the 50% effective concentration (EC50) was similar in both the nonelderly (100 +/- 9) and elderly (103 +/- 5 mg/dl). The Michaelis constant (Km) of 3-O-methyl glucose transport in adipocytes was unchanged with aging (3.8 +/- 0.5 vs. 3.2 +/- 0.2 mM) while the maximum velocity of insulin stimulated transport was reduced by 34% in the elderly (8.3 +/- 1.3 vs. 12.6 +/- 1.5 pmol/5 X 10(4) cells per s, P less than 0.05). The insulin resistance of aging is therefore due to a reduction in the capacity of the glucose uptake system, while the affinity of glucose utilization (EC50 and Km) is unchanged. This supports the hypothesis that a reduction in the number of glucose transport and metabolic units occurs with aging, but that each unit functions normally.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron A. D., Kolterman O. G., Bell J., Mandarino L. J., Olefsky J. M. Rates of noninsulin-mediated glucose uptake are elevated in type II diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1782–1788. doi: 10.1172/JCI112169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman R. N., Ader M., Finegood D. T., Pacini G. Extrapancreatic effect of somatostatin infusion to increase glucose clearance. Am J Physiol. 1984 Sep;247(3 Pt 1):E370–E379. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.3.E370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best J. D., Taborsky G. J., Jr, Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr Glucose disposal is not proportional to plasma glucose level in man. Diabetes. 1981 Oct;30(10):847–850. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.10.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolinder J., Ostman J., Arner P. Influence of aging on insulin receptor binding and metabolic effects of insulin on human adipose tissue. Diabetes. 1983 Oct;32(10):959–964. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.10.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Bergman R. N., Pacini G., Porte D., Jr Pathogenesis of age-related glucose intolerance in man: insulin resistance and decreased beta-cell function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985 Jan;60(1):13–20. doi: 10.1210/jcem-60-1-13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B. The effect of aging on carbohydrate metabolism: a review of the English literature and a practical approach to the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Metabolism. 1979 Jun;28(6):688–705. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E. Influence of plasma glucose and insulin concentration on plasma glucose clearance in man. Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):683–688. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defronzo R. A. Glucose intolerance and aging: evidence for tissue insensitivity to insulin. Diabetes. 1979 Dec;28(12):1095–1101. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.12.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Mendlinger S., Fertig J. W. A simple method to determine fat cell size and number in four mammalian species. Am J Physiol. 1971 Sep;221(3):850–858. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.3.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doberne L., Greenfield M. S., Rosenthal M., Widstrom A., Reaven G. Effect of variations in basal plasma glucose concentration on glucose utilization (M) and metabolic clearance (MCR) rates during insulin clamp studies in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1982 May;31(5 Pt 1):396–400. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.5.396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber O. K., Binder C., Markussen J., Heding L. G., Naithani V. K., Kuzuya H., Blix P., Horwitz D. L., Rubenstein A. H. Characterization of seven C-peptide antisera. Diabetes. 1978;27 (Suppl 1):170–177. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.1.s170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. I., Kolterman O. G., Griffin J., Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of insulin resistance in aging. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1523–1535. doi: 10.1172/JCI110908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. I., Kolterman O. G., Kao M., Olefsky J. M. The role of the glucose transport system in the postreceptor defect in insulin action associated with human aging. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):721–725. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink R. I., Revers R. R., Kolterman O. G., Olefsky J. M. The metabolic clearance of insulin and the feedback inhibition of insulin secretion are altered with aging. Diabetes. 1985 Mar;34(3):275–280. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.3.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Minaker K. L., Landsberg L., Young J. B., Pallotta J., Rowe J. W. Impaired in vivo insulin clearance in patients with severe target-cell resistance to insulin. Diabetes. 1982 Feb;31(2):132–135. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.2.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerich J. E., Lorenzi M., Bier D. M., Tsalikian E., Schneider V., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Effects of physiologic levels of glucagon and growth hormone on human carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Studies involving administration of exogenous hormone during suppression of endogenous hormone secretion with somatostatin. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):875–884. doi: 10.1172/JCI108364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I., Mandarino L., Verdonk C., Rizza R., Gerich J. Insulin increases the maximum velocity for glucose uptake without altering the Michaelis constant in man. Evidence that insulin increases glucose uptake merely by providing additional transport sites. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1310–1314. doi: 10.1172/JCI110731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen I. L., Cryer P. E., Rizza R. A. Comparison of insulin-mediated and glucose-mediated glucose disposal in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and in nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34(8):751–755. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.8.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J., Gallian E. Methods for the determination of adipose cell size in man and animals. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jan;9(1):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hom F. G., Goodner C. J. Insulin dose-response characteristics among individual muscle and adipose tissues measured in the rat in vivo with 3[H]2-deoxyglucose. Diabetes. 1984 Feb;33(2):153–159. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.2.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. A., Blix P. M., Matthews J. A., Hamling J. B., Din B. M., Brown D. C., Belin J., Rubenstein A. H., Nabarro J. D. Influence of ageing on glucose homeostasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Nov;55(5):840–848. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-5-840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwagi A., Foley J. E. Opposite effects of a beta-adrenergic agonist and a phosphodiesterase inhibitor on glucose transport in isolated human adipocytes: isoproterenol increases Vmax and IBMX increases Ks. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Aug;107(3):1151–1157. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)90642-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Robinson F. W., Blevins T. L., Ezaki O. Evidence that translocation of the glucose transport activity is the major mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10942–10947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Chisholm D. J. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E353–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Jen P., Reaven G. M., Alto P. Insulin binding to isolated human adipocytes. Diabetes. 1974 Jul;23(7):565–571. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.7.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano G., Cassader M., Cavallo-Perin P., Bruno A., Masciola P., Ozzello A., Dall'Omo A. M., Foco A. Insulin resistance in the aged: a quantitative evaluation of in vivo insulin sensitivity and in vitro glucose transport. Metabolism. 1984 Nov;33(11):976–981. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90223-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Greenfield M. S., Mondon C. E., Rosenthal M., Wright D., Reaven E. P. Does insulin removal rate from plasma decline with age? Diabetes. 1982 Aug;31(8 Pt 1):670–673. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.8.670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizza R., Verdonk C., Miles J., Service F. J., Gerich J. Effect of intermittent endogenous hyperglucagonemia on glucose homeostasis in normal and diabetic man. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jun;63(6):1119–1123. doi: 10.1172/JCI109404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Minaker K. L., Pallotta J. A., Flier J. S. Characterization of the insulin resistance of aging. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1581–1587. doi: 10.1172/JCI110914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdonk C. A., Rizza R. A., Gerich J. E. Effects of plasma glucose concentration on glucose utilization and glucose clearance in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Jun;30(6):535–537. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.6.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell R. R., Gliemann J. Kinetic parameters of transport of 3-O-methylglucose and glucose in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):5276–5283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



