Abstract
The pathogenesis of liver disease in protoporphyria has been presumed to result from the hepatic deposition of protoporphyrin. To examine the effects of protoporphyrin on hepatic bile flow and histopathology, studies were performed employing an isolated, in situ, rat liver perfusion system. Rat livers in the control group were perfused with 0-80 μmol sodium taurocholate/h. Rat livers in the experimental group were perfused with sodium taurocholate and (a) sufficient quantities of protoporphyrin to produce maximal canalicular secretion and (b) perfusate protoporphyrin concentrations of 0.01, 0.1, and 1 μM.
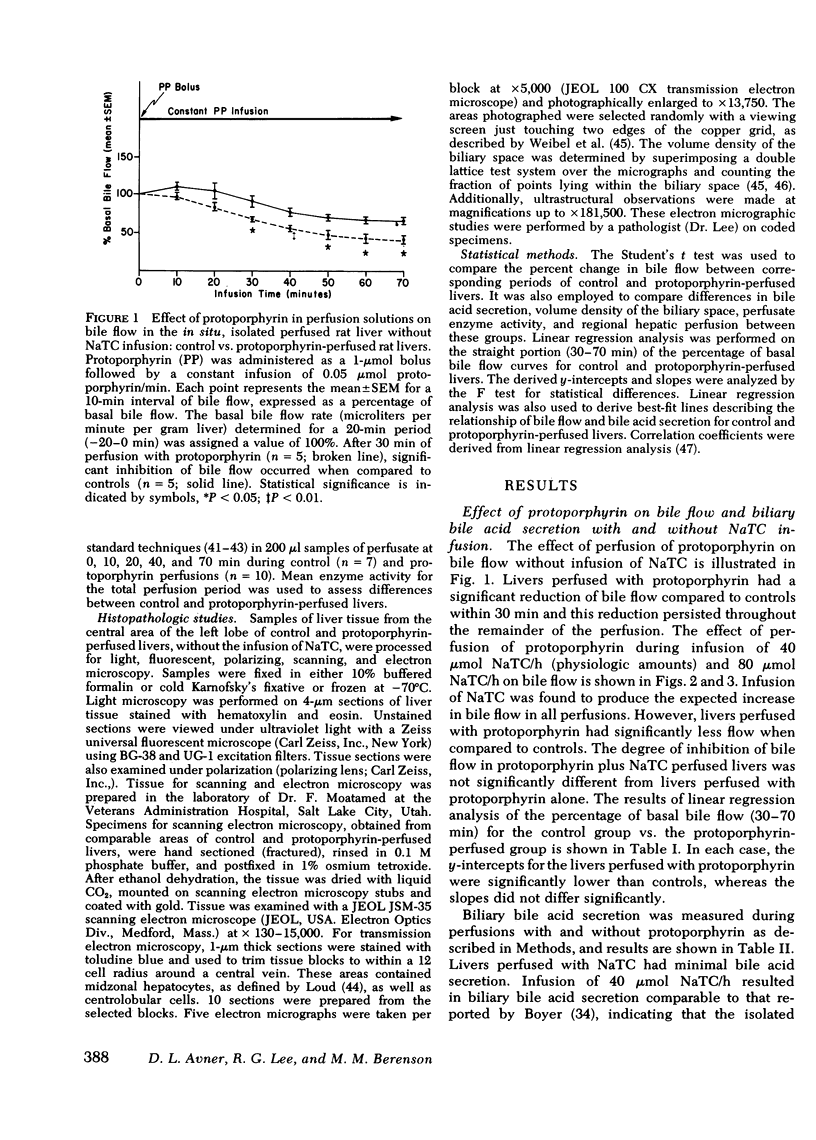
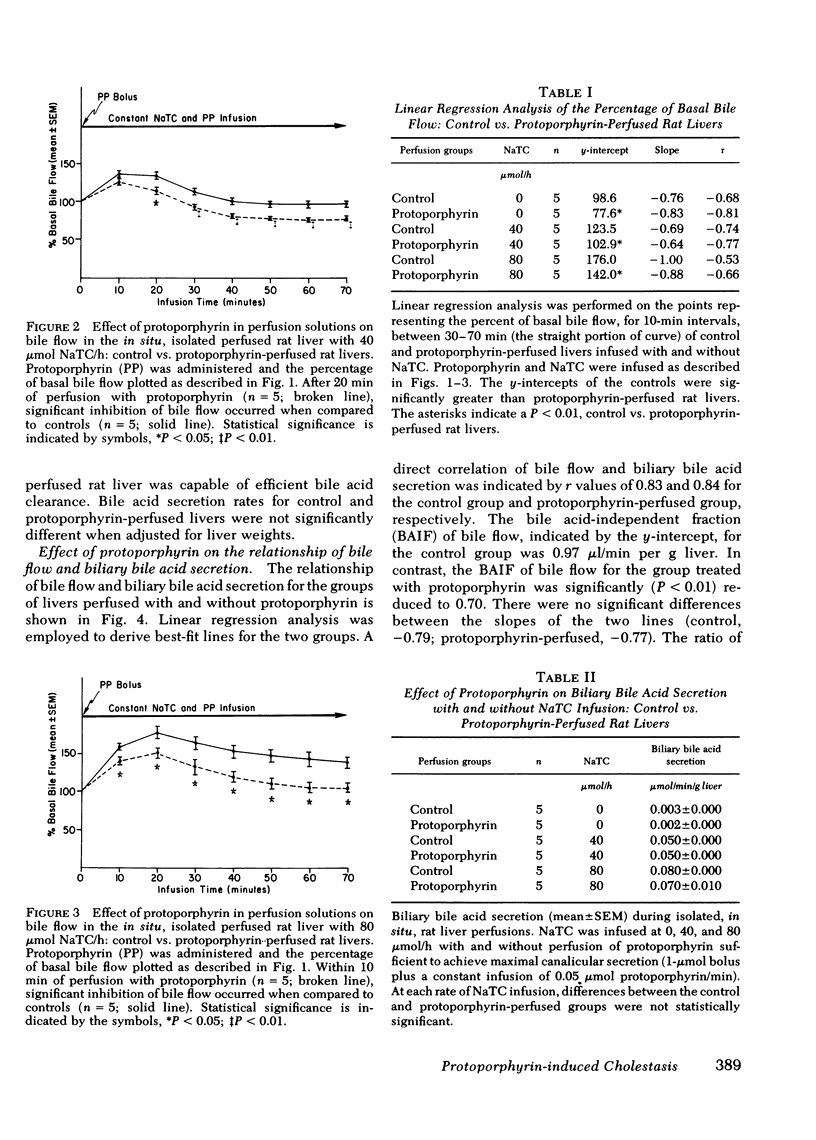
The administration of protoporphyrin sufficient to achieve maximal canalicular secretion was found to significantly reduce bile flow in rats infused with 0, 40, and 80 μmol sodium taurocholate/h. Linear regression analysis defined the relationship between bile flow and biliary bile acid secretion and showed that the bile acid-independent fraction of bile flow was reduced (P < 0.01). Bile acid-dependent flow was unaffected and there was no significant difference in biliary bile acid secretion rates between control and protoporphyrin-perfused livers. Perfusion of rat livers with varying concentrations of protoporphyrin demonstrated the reduction of bile flow was dose-related. Analysis of perfusate enzyme activity did not reveal abnormalities that could account for the cholestasis. Studies to evaluate the effect of protoporphyrin on regional hepatic hemodynamics were inconclusive.
Histopathological studies of control and protoporphyrin-perfused rat livers did not show abnormalities on light microscopy. However, canalicular dilatation, distortion, and loss of microvilli were present in the protoporphyrin-perfused livers examined by transmission electron microscopy. Although ultraviolet microscopy showed diffuse fluorescence of the hepatocytes and canaliculi of protoporphyrin-perfused livers, the deposition of protoporphyrin in amorphous or crystalline forms was notably absent in studies with polarizing and transmission electron microscopy.
These studies provide evidence that protoporphyrin has hepatotoxic properties that affect the canalicular secretory apparatus. The mechanism(s) responsible for the injury require further clarification.
Full text
PDF


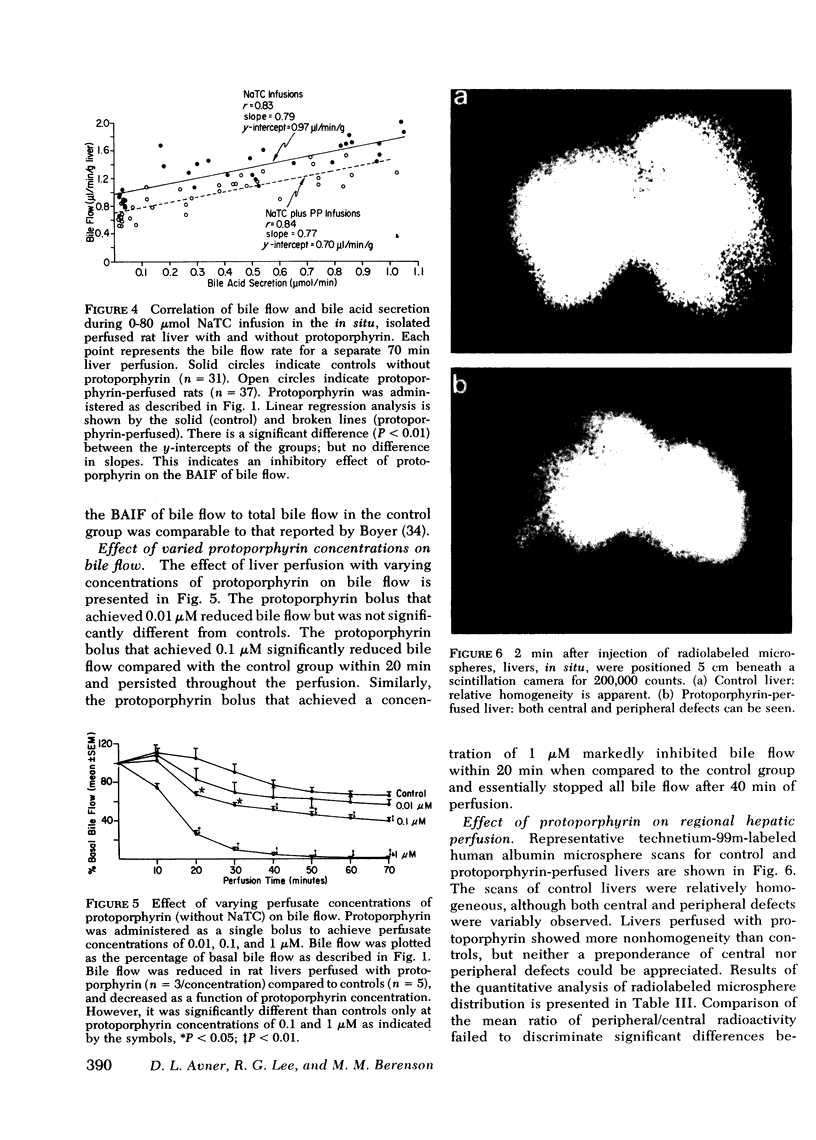




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMADOR E., DORFMAN L. E., WACKER W. E. SERUM LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE ACTIVITY: AN ANALYTICAL ASSESSMENT OF CURRENT ASSAYS. Clin Chem. 1963 Aug;12:391–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AMADOR E., WACKER W. E. Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase activity. A new modification and an anaytical assessment of current assay technics. Clin Chem. 1962 Aug;8:343–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Bonkowsky H. L., Ebert P. S., Mahoney M. J. Inheritance in protoporphyria. Comparison of haem synthetase activity in skin fibroblasts with clinical features. Lancet. 1976 Jul 31;2(7979):226–228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Brenner D. A., Mahoney M. J. Study of factors causing excess protoporphyrin accumulation in cultured skin fibroblasts from patients with protoporphyria. J Clin Invest. 1977 Dec;60(6):1354–1361. doi: 10.1172/JCI108895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R. Pathogenesis and therapy of liver disease in protoporphyria. Yale J Biol Med. 1979 Jan-Feb;52(1):39–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloomer J. R., Phillips M. J., Davidson D. L., Klatskin G., Bloomer Hepatic disease in erythropoietic protoporphyria. Am J Med. 1975 Jun;58(6):869–882. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(75)90644-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkowsky H. L., Bloomer J. R., Ebert P. S., Mahoney M. J. Heme synthetase deficiency in human protoporphyria. Demonstration of the defect in liver and cultured skin fibroblasts. J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov;56(5):1139–1148. doi: 10.1172/JCI108189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottomley S. S., Tanaka M., Everett M. A. Diminished erythroid ferrochelatase activity in protoporphyria. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Jul;86(1):126–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. Canalicular bile formation in the isolated perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1971 Oct;221(4):1156–1163. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1971.221.4.1156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruguera M., Esquerda J. E., Mascaró J. M., Piñol J. Erythropoietic protoporphyria. A light, electron, and polarization microscopical study of the liver in three patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1976 Nov;100(11):587–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps D. J., Gilbert L. A., Goldfarb S. S. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: juvenile protoporphyrin hepatopathy cirrhosis and death. J Pediatr. 1977 Nov;91(5):744–748. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(77)81027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps D. J., Goldfarb S. S. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: hepatic cirrhosis. Br J Dermatol. 1978 Mar;98(3):349–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1978.tb06163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cripps D. J., Scheuer P. J. Hepatobiliary changes in erythropoietic protoporphyria. Arch Pathol. 1965 Nov;80(5):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIEL P. M., PRICHARD M. M. L. Variations in the circulation of the portal venous blood within the liver. J Physiol. 1951 Aug;114(4):521–537. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Kern F., Jr, Showalter R., Sutherland E., Sinensky M., Simon F. R. Alterations of hepatic Na+,K+-atpase and bile flow by estrogen: effects on liver surface membrane lipid structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4130–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo V. A., Poh-Fitzpatrick M., Mathews-Roth M., Harber L. C. Erythropoietic protoporphyria. 10 years experience. Am J Med. 1976 Jan;60(1):8–22. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90528-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson E. M., McCall A. J., Magnus I. A., Simpson J. R., Caldwell R. A., Hargreaves T. Erythropoietic protoporphyria: two deaths from hepatic cirrhosis. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Jan;84(1):14–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb14191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eales L., Day R. S., Pimstones N. R. Protoporphyrin (proto)-determined hepatopathy in a South African Jewish family. Ann Clin Res. 1978 Aug;10(4):205–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias E., Boyer J. L. Chlorpromazine and its metabolites alter polymerization and gelation of actin. Science. 1979 Dec 21;206(4425):1404–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.574316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S., Dhumeaux D. Mechanisms and control of secretion of bile water and electrolytes. Gastroenterology. 1974 Feb;66(2):281–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham J. W., Nopanitaya W., Compagno J., Nägel A. E. Scanning electron microscopy of normal rat liver: the surface structure of its cells and tissue components. Am J Anat. 1975 Nov;144(3):295–321. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001440304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschnait F., Konrad K., Hönigsmann H., Denk H., Wolff K. Mouse model for protoporphyria. I. The liver and hepatic protoporphyrin crystals. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Sep;65(3):290–299. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12598357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENRY R. J., CHIAMORI N., GOLUB O. J., BERKMAN S. Revised spectrophotometric methods for the determination of glutamic-oxalacetic transaminase, glutamic-pyruvic transaminase, and lactic acid dehydrogenase. Am J Clin Pathol. 1960 Oct;34:381–398. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/34.4_ts.381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hems R., Ross B. D., Berry M. N., Krebs H. A. Gluconeogenesis in the perfused rat liver. Biochem J. 1966 Nov;101(2):284–292. doi: 10.1042/bj1010284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruban Z., Tavoloni N., Reed J. S., Boyer J. L. Ultrastructural changes during cholestasis induced by chlorpromazine in the isolated perfused rat liver. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1978 Feb 14;26(4):289–305. doi: 10.1007/BF02889557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. L., Schmucker D. L., Mooney J. S., Adler R. D., Ockner R. K. Morphometric analysis of rat hepatocytes after total billary obstruction. Gastroenterology. 1976 Dec;71(6):1050–1060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keefee E. B., Scharschmidt B. F., Blankenship N. M., Ockner R. K. Studies of relationship among bile flow, liver plasma membrane NaK-ATPase, and membrane microviscosity in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1590–1598. doi: 10.1172/JCI109620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatskin G., Bloomer J. R. Birefringence of hepatic pigment deposits in erythropoietic protoporphyria. Specificity of polarization microscopy in the identification of hepatic protoporphyrin deposits. Gastroenterology. 1974 Aug;67(2):294–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Boyer J. L. The effect of thyroid hormone on bile salt-independent bile flow and Na+, K+ -ATPase activity in liver plasma membranes enriched in bile canaliculi. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):1009–1018. doi: 10.1172/JCI108342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loud A. V. A quantitative stereological description of the ultrastructure of normal rat liver parenchymal cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):27–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGNUS I. A., JARRETT A., PRANKERD T. A., RIMINGTON C. Erythropoietic protoporphyria. A new porphyria syndrome with solar urticaria due to protoporphyrinaemia. Lancet. 1961 Aug 26;2(7200):448–451. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92427-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER L. L., BLY C. G., WATSON M. L., BALE W. F. The dominant role of the liver in plasma protein synthesis; a direct study of the isolated perfused rat liver with the aid of lysine-epsilon-C14. J Exp Med. 1951 Nov;94(5):431–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.94.5.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matilla A., Molland E. A. A light and electron microscopic study of the liver in case of erythrohepatic protoporphyria and in griseofulvin-induced porphyria in mice. J Clin Pathol. 1974 Sep;27(9):698–709. doi: 10.1136/jcp.27.9.698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimstone N. R., Webber B. L., Blekkenhorst G. H., Eales L. The hepatic lesion in protoporphyria (PP): preliminary studies of haem metabolism, liver structure and ultrastructure. Ann Clin Res. 1976;8 (Suppl 17):122–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh-Fitzpatrick M. B. Erythropoietic porphyrias: current mechanistic, diagnostic, and therapeutic considerations. Semin Hematol. 1977 Apr;14(2):211–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poh-Fitzpatrick M. B., Lamola A. A. Comparative study of protoporphyrins in erythropoietic protoporphyria and griseofulvin-induced murine protoporphyria. Binding affinities, distribution, and fluorescence spectra in various blood fractions. J Clin Invest. 1977 Aug;60(2):380–389. doi: 10.1172/JCI108787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUTH G. R., Schwartz S., Stephenson B. Bovine protoporphyria: the first nonhuman model of this hereditary photosensitizing disease. Science. 1977 Oct 14;198(4313):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.905823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER F. MORPHOLOGIC STUDIES ON BILE SECRETION. Am J Dig Dis. 1965 Feb;10:99–115. doi: 10.1007/BF02236658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER F., POPPER H., PEREZ V. Changes in bile canaliculi produced by norethandrolone: electron microscopic study of human and rat liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Oct;56:623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon F. R., Sutherland E., Accatino L. Stimulation of hepatic sodium and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase activity by phenobarbital. Its possible role in regulation of bile flow. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):849–861. doi: 10.1172/JCI108707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer J. A., Plaut A. G., Kaplan M. M. Hepatic failure and death from erythropoietic protoporphyria. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):588–591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenhagen E., Rideal E. K. The interaction between porphyrins and lipoid and protein monolayers. Biochem J. 1939 Oct;33(10):1591–1598. doi: 10.1042/bj0331591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavoloni N., Reed J. S., Boyer J. L. Hemodynamic effects on determinants of bile secretion in isolated rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1978 Jun;234(6):E584–E592. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.234.6.E584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavoloni N., Reed J. S., Hruban Z., Boyer J. L. Effect of chlorpromazine on hepatic perfusion and bile secretory function in the isolated perfused rat liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Nov;94(5):726–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wannagat R. J., Adler R. D., Ockner R. K. Bile acid-induced increase in bile acid-independent flow and plasma membrane NaK-ATPase activity in rat liver. J Clin Invest. 1978 Feb;61(2):297–307. doi: 10.1172/JCI108939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Kistler G. S., Scherle W. F. Practical stereological methods for morphometric cytology. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):23–38. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R., Stäubli W., Gnägi H. R., Hess F. A. Correlated morphometric and biochemical studies on the liver cell. I. Morphometric model, stereologic methods, and normal morphometric data for rat liver. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jul;42(1):68–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoo H., Craig R. M., Harwood T. R., Cochrane C. Griseofulvin-induced cholestasis in Swiss albino mice. Gastroenterology. 1979 Nov;77(5):1082–1087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]