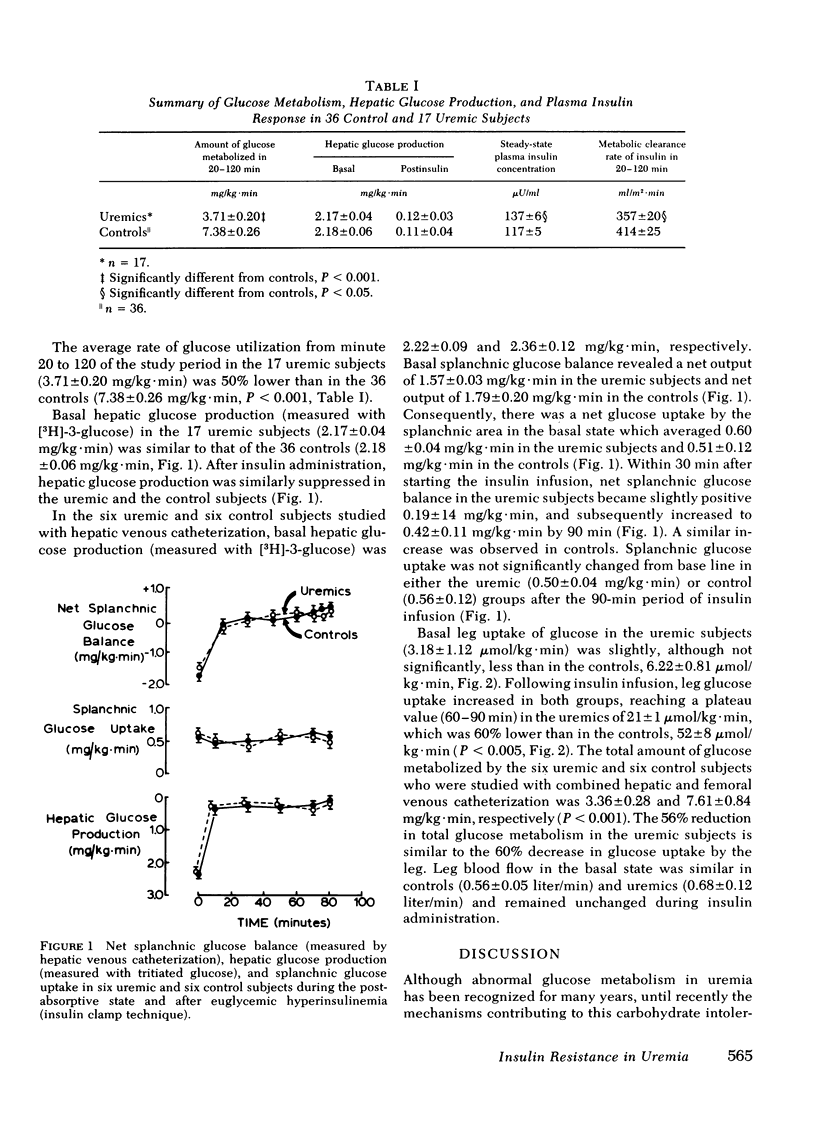
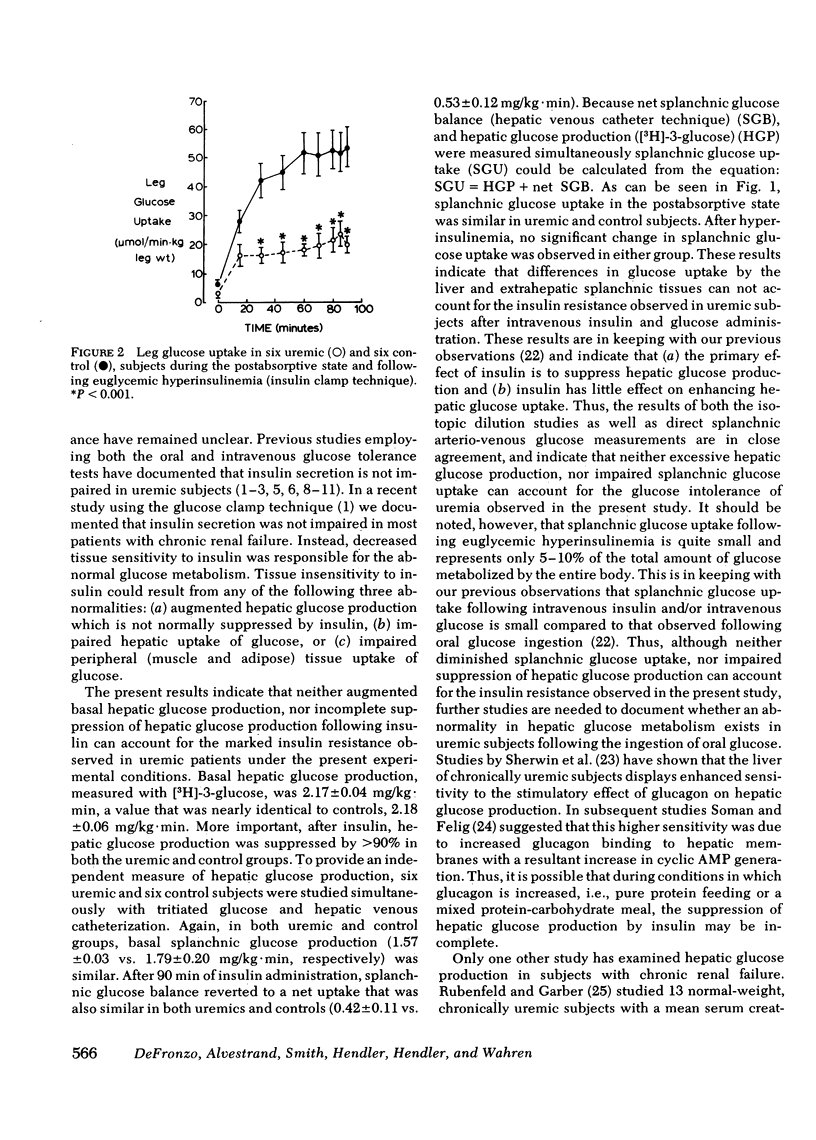
Abstract
Tissue sensitivity to insulin was examined with the euglycemic insulin clamp technique in 17 chronically uremic and 36 control subjects. The plasma insulin concentration was raised by approximately 100 microU/ml and the plasma glucose concentration was maintained at the basal level with a variable glucose infusion. Under these steady-state conditions of euglycemia, the glucose infusion rate is a measure of the amount of glucose taken up by the entire body. In uremic subjects insulin-mediated glucose metabolism was reduced by 47% compared with controls (3.71 +/- 0.20 vs. 7.38 +/- 0.26 mg/kg . min; P less than 0.001). Basal hepatic glucose production (measured with [3H]-3-glucose) was normal in uremic subjects (2.17 +/- 0.04 mg/kg . min) and suppressed normally by 94 +/- 2% following insulin administration. In six uremic and six control subjects, net splanchnic glucose balance was also measured directly by the hepatic venous catheterization technique. In the postabsorptive state splanchnic glucose production was similar in uremics (1.57 +/- 0.03 mg/kg . min) and controls (1.79 +/- 0.20 mg/kg . min). After 90 min of sustained hyperinsulinemia, splanchnic glucose balance reverted to a net uptake which was similar in uremics (0.42 +/- 0.11 mg/kg . min) and controls (0.53 +/- 0.12 mg/kg . min). In contrast, glucose uptake by the leg was reduced by 60% in the uremic group (21 +/- 1 vs. 52 +/- 8 mumol/min . kg of leg wt; P less than 0.005) and this decrease closely paralleled the decrease in total glucose metabolism by the entire body. These results indicate that: (a) suppression of hepatic glucose production by physiologic hyperinsulinemia is not impaired by uremia, (b) insulin-mediated glucose uptake by the liver is normal in uremic subjects, and (c) tissue insensitivity to insulin is the primary cause of insulin resistance in uremia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerletty J. M., Engbring N. H. Azotemia and glucose intolerance. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Jun;66(6):1097–1108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-6-1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain M. J., Stimmler L. The renal handling of insulin. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jun;46(6):911–919. doi: 10.1172/JCI105597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. D., Horowitz H. I. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia: inhibition of phosphate release. Am J Clin Nutr. 1968 May;21(5):407–413. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/21.5.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan J. S., Hetenyi G., Jr Glucoregulatory responses in normal and diabetic dogs recorded by a new tracer method. Metabolism. 1971 Apr;20(4):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Wahren J., Felig P. Influence of hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and the route of glucose administration on splanchnic glucose exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Soman V., Sherwin R. S., Hendler R., Felig P. Insulin binding to monocytes and insulin action in human obesity, starvation, and refeeding. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):204–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI109108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Rowe J. W., Andres R. Glucose intolerance in uremia. Quantification of pancreatic beta cell sensitivity to glucose and tissue sensitivity to insulin. J Clin Invest. 1978 Aug;62(2):425–435. doi: 10.1172/JCI109144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampers C. L., Soeldner J. S., Doak P. B., Merrill J. P. Effect of chronic renal failure and hemodialysis on carbohydrate metabolism. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1719–1731. doi: 10.1172/JCI105478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E. S., Johnson C., Lebovitz H. E. Carbohydrate metabolism in uremia. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Jan;68(1):63–74. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-68-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorfeldt L., Wahren J. Leg blood flow during exercise in man. Clin Sci. 1971 Nov;41(5):459–473. doi: 10.1042/cs0410459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire E. A., Helderman J. H., Tobin J. D., Andres R., Berman M. Effects of arterial versus venous sampling on analysis of glucose kinetics in man. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Oct;41(4):565–573. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.4.565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. The site of insulin resistance in acute uremia. Diabetes. 1978 May;27(5):571–576. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.5.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKOFF G. T., THOMAS C. L., NEWTON J. D., SELLMAN J. C., TYLER F. H. Mechanism of impaired glucose tolerance in uremia and experimental hyperazotemia. Diabetes. 1958 Sep-Oct;7(5):375–383. doi: 10.2337/diab.7.5.375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenfeld S., Garber A. J. Abnormal carbohydrate metabolism in chronic renal failure. The potential role of accelerated glucose production, increased gluconeogenesis, and impaired glucose disposal. J Clin Invest. 1978 Jul;62(1):20–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI109107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin R. S., Bastl C., Finkelstein F. O., Fisher M., Black H., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of uremia and hemodialysis on the turnover and metabolic effects of glucagon. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):722–731. doi: 10.1172/JCI108330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V., Felig P. Glucagon and insulin binding to liver membranes in a partially nephrectomized uremic rat model. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):224–232. doi: 10.1172/JCI108759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Spitz I. M., Rubenstein A. H., Bersohn I., Abrahams C., Lowy C. Carbohydrate metabolism in renal disease. Q J Med. 1970 Apr;39(154):201–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEUSCHER A. BEURTEILUNG DER BLUTZUCKERWERTE UND DER GLUKOSETOLERANZ BEI URAEMIE. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1964 Jan 18;94:69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEUSCHER A., FANKHAUSER S., KUFFER F. R. [Studies on carbohydrate metabolism in renal insufficiency]. Klin Wochenschr. 1963 Jul 15;41:706–715. doi: 10.1007/BF01478416. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTERVELT F. B., Jr, SCHREINER G. E. The carbohydrate intolerance of uremic patients. Ann Intern Med. 1962 Aug;57:266–276. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-57-2-266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Felig P., Hagenfeldt L. Effect of protein ingestion on splanchnic and leg metabolism in normal man and in patients with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Apr;57(4):987–999. doi: 10.1172/JCI108375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B. Insulin effect in uremia. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Jul;74(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt F. B., Jr Uremia and insulin response. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Nov;126(5):865–869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. K., Hendler R., Felig P. Influence of glucocorticoids on glucagon secretion and plasma amino acid concentrations in man. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2774–2782. doi: 10.1172/JCI107473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



