Abstract
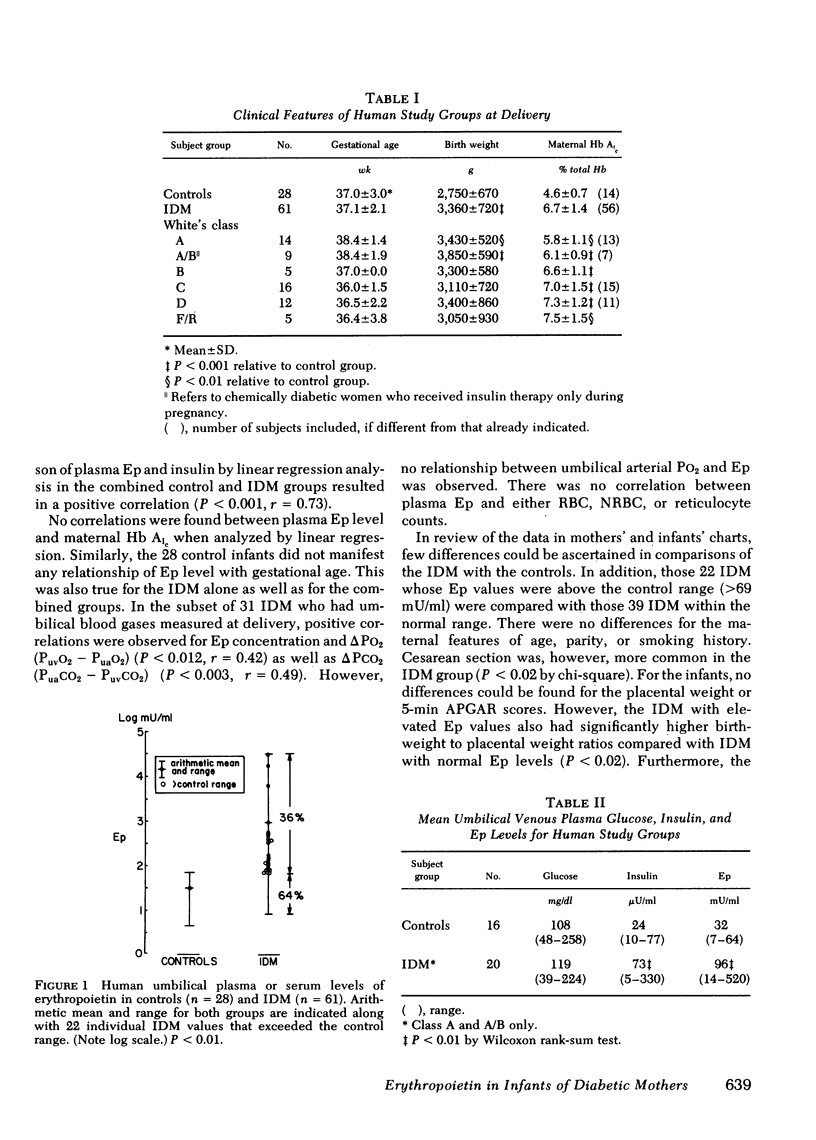
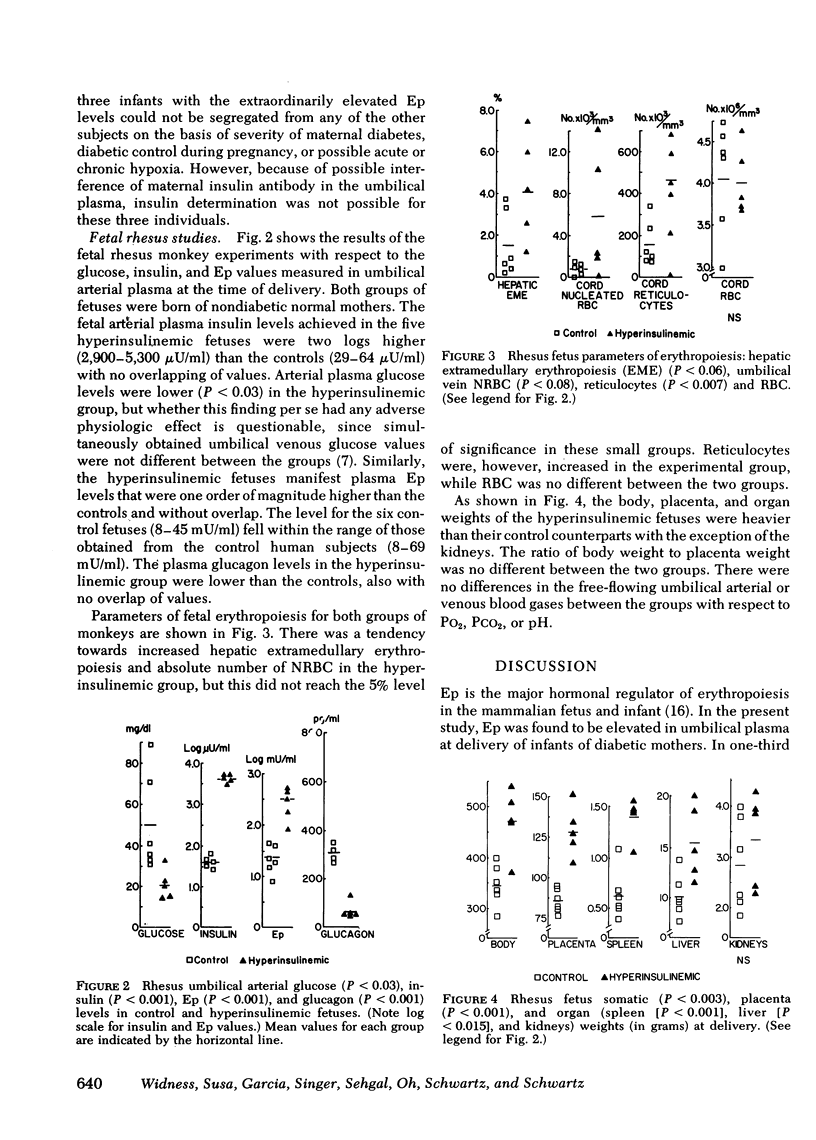
The pathogenesis of the increased erythrocytosis and extramedullary erythropoiesis observed in infants of diabetic mothers (IDM) has been obscure. In the present studies, IDM were found to have elevated umbilical plasma erythropoietin (Ep) concentrations by radioimmunoassay. 22 of 61 IDM (36%) had levels above the range of 28 nonasphyxiated, appropriately grown normal infants. In 16 controls and 20 IDM, plasma Ep correlated directly with plasma insulin (P less than 0.001, r = 0.73). To investigate this relationship further, a chronic rhesus model was studied with continuous fetal hyperinsulinemia for 21 d in utero in the last third of pregnancy. In five experimental fetuses, plasma insulin levels averaged 4,210 microU/ml at delivery, whereas plasma Ep was above the range of six controls. In addition, the experimental fetuses had elevated reticulocyte counts in umbilical cord blood. The mechanism for the increased plasma Ep associated with hyperinsulinemia in the fetus is unexplained but may be mediated by fetal hypoxia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babson S. G., Behrman R. E., Lessel R. Fetal growth. Liveborn birth weights for gestational age of white middle class infants. Pediatrics. 1970 Jun;45(6):937–944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson B. S., Philipps A. F., Simmons M. A., Battaglia F. C., Meschia G. Effects of a sustained insulin infusion upon glucose uptake and oxygenation of the ovine fetus. Pediatr Res. 1980 Feb;14(2):147–152. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198002000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erslev A. J., Caro J., Kansu E., Silver R. Renal and extrarenal erythropoietin production in anaemic rats. Br J Haematol. 1980 May;45(1):65–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1980.tb03811.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne P. H. Erythropoietin levels in cord blood as an indicator of intrauterine hypoxia. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1966 Sep;55(5):478–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1966.tb15239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finne P. H., Halvorsen S. Regulation of erythropoiesis in the fetus and newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1972 Oct;47(255):683–687. doi: 10.1136/adc.47.255.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. F., Schooley J. C. Dissociation of erythropoietin from erythropoietin-antierythropoietin complex. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):213–215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. F., Sherwood J., Goldwasser E. Radioimmunoassay of erythropoietin. Blood Cells. 1979 Aug;5(3):405–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G. P., Hathaway W. E., McGaughey H. R. Hyperviscosity in the neonate. J Pediatr. 1973 Jun;82(6):1004–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(73)80433-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin antibody preciptate. Lancet. 1963 Jan 26;1(7274):200–200. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY R. B. Observations of the oxygenation of the foetus in normal and abnormal pregnancy. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Emp. 1957 Apr;64(2):185–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1957.tb02619.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAEYE R. L. INFANTS OF DIABETIC MOTHERS: A QUANTITATIVE, MORPHOLOGIC STUDY. Pediatrics. 1965 Jun;35:980–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naets J. P., Guns M. Inhibitory effect of glucagon on erythropoiesis. Blood. 1980 Jun;55(6):997–1002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schooley J. C., Mahlmann L. J. Extrarenal erythropoietin production by the liver in the weanling rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 Mar;145(3):1081–1083. doi: 10.3181/00379727-145-37957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson D. K., Bartoletti A. L., Ostrander C. R., Johnson J. D. Pulmonary excretion of carbon monoxide in the human infant as an index of bilirubin production. II. Infants of diabetic mothers. J Pediatr. 1979 Jun;94(6):956–958. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(79)80232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susa J. B., McCormick K. L., Widness J. A., Singer D. B., Oh W., Adamsons K., Schwartz R. Chronic hyperinsulinemia in the fetal rhesus monkey: effects on fetal growth and composition. Diabetes. 1979 Dec;28(12):1058–1063. doi: 10.2337/diab.28.12.1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. Diabetes mellitus in pregnancy. Clin Perinatol. 1974 Sep;1(2):331–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widness J. A., Rogler-Brown T. L., McCormick K. L., Petzold K. S., Susa J. B., Schwartz H. C., Schwartz R. Rapid fluctuations in glycohemoglobin (hemoglobin Alc) related to acute changes in glucose. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Mar;95(3):386–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZETTERSTROM R., STRINDBERG B., ARNHOLD R. G. Hyperbilirubinemia and ABO hemolytic disease in newborn infants of diabetic mothers. Acta Paediatr. 1958 May;47(3):238–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1958.tb07880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanjani E. D., Banisadre M. Hormonal stimulation of erythropoietin production and erythropoiesis in anephric sheep fetuses. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1181–1187. doi: 10.1172/JCI109571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanjani E. D., Poster J., Burlington H., Mann L. I., Wasserman L. R. Liver as the primary site of erythropoietin formation in the fetus. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Mar;89(3):640–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



