Abstract
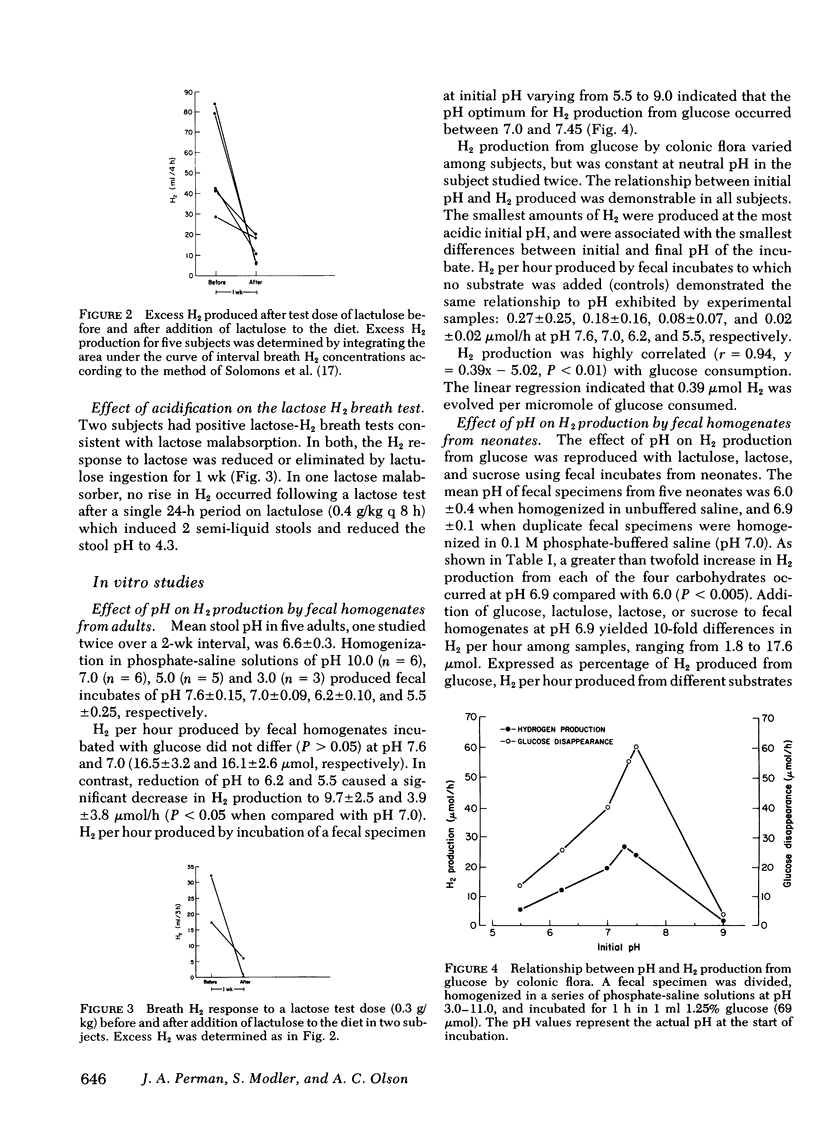
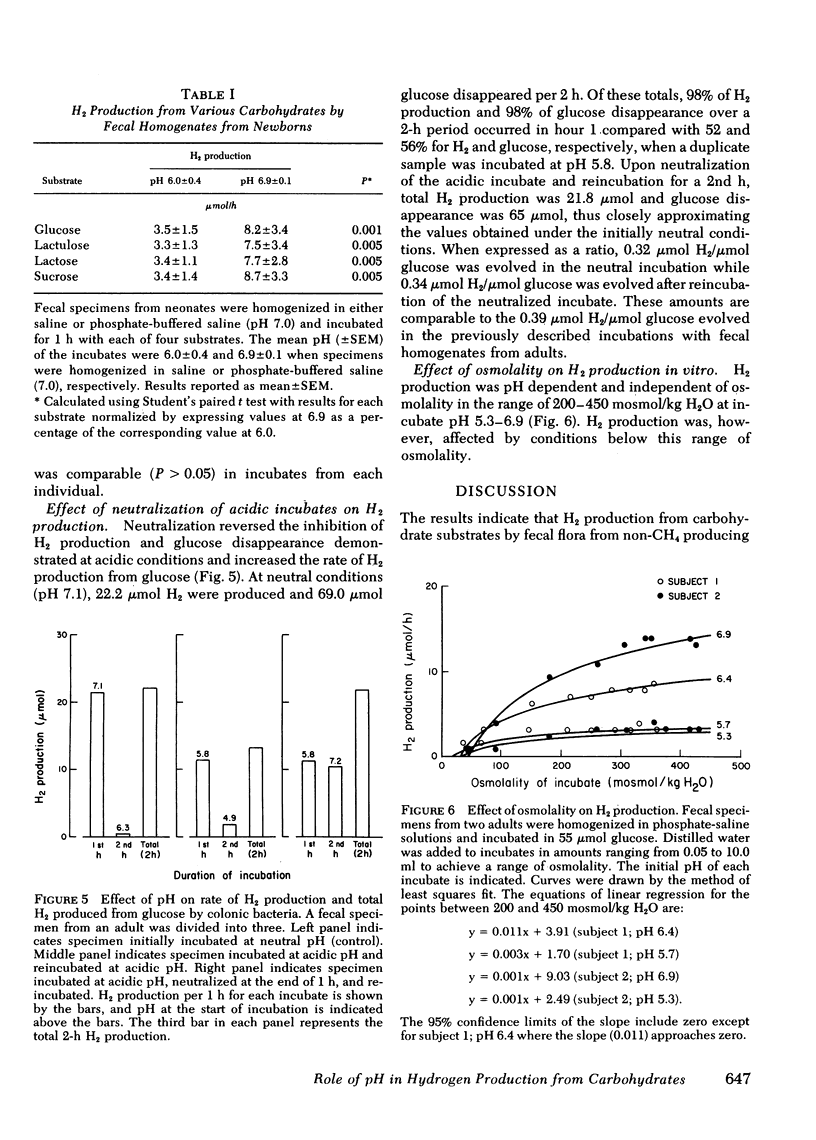
Hydrogen produced by colonic bacteria and excreted in breath is a useful index of carbohydrate malabsorption. Since colonic contents are often acidic in individuals with carbohydrate malabsorption and in normal newborns, we determined the effect of colonic acidification on H2 production. Acidification of colonic contents by dietary means significantly reduced excess breath H2 excretion from 55.4 +/- 11.1 (SEM) to 12.2 +/- 3.1 ml/4 h (P less than 0.05) after administration of 0.3 g/kg of the nonabsorbable sugar lactulose to five normal adult subjects. Similarly, the breath H2 response to lactose was reduced or eliminated in two proven lactose malabsorbers after acidification. The correlation between pH and H2 production from carbohydrate was further investigated in adults and neonates, using an in vitro fecal incubation system. Glucose disappearance and H2 production were pH dependent and highly correlated (r = 0.94) in the pH range 5.5-7.6. Maximal production of H2 from glucose by fecal incubates occurred at pH 7.0-7.45. Inhibition of H2 production from carbohydrate occurred at acid pH. H2 per hour from glucose at pH 6.2 and 5.5 averaged 60.2% and 24.2%, respectively, of that produced at neutral pH. Rapid reversal of pH-induced inhibition by neutralization indicated a metabolic, rather than a bactericidal process. The observations indicate that the breath H2 response to malabsorbed carbohydrate is affected by colonic pH. It appears that the efficiency of bacterial carbohydrate metabolism in the colon is pH dependent.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBERO G. J., RUNGE G., FISCHER D., CRAWFORD M. N., TORRES F. E., GYORGY P. Investigations on the bacterial flora, pH, and sugar content in the intestinal tract of infants. J Pediatr. 1952 Feb;40(2):152–163. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(52)80176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Currier B. E., Buchwald H., Levitt M. D. Colonic conservation of malabsorbed carbohydrate. Gastroenterology. 1980 Mar;78(3):444–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Engel R. R., Levitt M. D. Factors influencing pulmonary methane excretion in man. An indirect method of studying the in situ metabolism of the methane-producing colonic bacteria. J Exp Med. 1971 Mar 1;133(3):572–588. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.3.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D. Fate of soluble carbohydrate in the colon of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1976 May;57(5):1158–1164. doi: 10.1172/JCI108383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Jr, Levitt M. D. Use of pulmonary hydrogen (H 2 ) measurements to quantitate carbohydrate absorption. Study of partially gastrectomized patients. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1219–1225. doi: 10.1172/JCI106916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. H., Levitt M. D. Use of breath hydrogen (H2) in the study of carbohydrate absorption. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Apr;22(4):379–382. doi: 10.1007/BF01072197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bown R. L., Gibson J. A., Sladen G. E., Hicks B., Dawson A. M. Effects of lactulose and other laxatives on ileal and colonic pH as measured by a radiotelemetry device. Gut. 1974 Dec;15(12):999–1004. doi: 10.1136/gut.15.12.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calloway D. H., Murphy E. L., Bauer D. Determination of lactose intolerance by breath analysis. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Nov;14(11):811–815. doi: 10.1007/BF02235972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calloway D. H., Murphy E. L. The use of expired air to measure intestinal gas formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1968 Feb 26;150(1):82–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb19034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher N. L., Bayless T. M. Role of the small bowel and colon in lactose-induced diarrhea. Gastroenterology. 1971 May;60(5):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EL-SHAZLY K., HUNGATE R. E. FERMENTATION CAPACITY AS A MEASURE OF NET GROWTH OF RUMEN MICROORGANISMS. Appl Microbiol. 1965 Jan;13:62–69. doi: 10.1128/am.13.1.62-69.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilat T., Ben Hur H., Gelman-Malachi E., Terdiman R., Peled Y. Alterations of the colonic flora and their effect on the hydrogen breath test. Gut. 1978 Jul;19(7):602–605. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.7.602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumbmann M. R., Williams S. N., Booth A. N. The quantitative collection and determination of hydrogen gas from the rat and factors affecting its production. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Sep;137(4):1171–1175. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Berggren T., Hastings J., Bond J. H. Hydrogen (H2) catabolism in the colon of the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Aug;84(2):163–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D., Donaldson R. M. Use of respiratory hydrogen (H2) excretion to detect carbohydrate malabsorption. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jun;75(6):937–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitt M. D. Production and excretion of hydrogen gas in man. N Engl J Med. 1969 Jul 17;281(3):122–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196907172810303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshitz F., Coello-Ramirez P., Gutierrez-Topete G., Cornado-Cornet M. C. Carbohydrate intolerance in infants with diarrhea. J Pediatr. 1971 Nov;79(5):760–767. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(71)80388-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz G., Jenkins D. J., Peters T. J., Newman A., Blendis L. M. Breath hydrogen as a diagnostic method for hypolactasia. Lancet. 1975 May 24;1(7917):1155–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)93135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomer A. D., McGill D. B., Thomas P. J., Hofmann A. F. Prospective comparison of indirect methods for detecting lactase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1975 Dec 11;293(24):1232–1236. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197512112932405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perman J. A., Barr R. G., Watkins J. B. Sucrose malabsorption in children: noninvasive diagnosis by interval breath hydrogen determination. J Pediatr. 1978 Jul;93(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomons N. W., García R., Schneider R., Viteri F. E., von Kaenel V. A. H2 breath tests during diarrhea. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Mar;68(2):171–172. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1979.tb04984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomons N. W., Viteri F., Rosenberg I. H. Development of an interval sampling hydrogen (H2) breath test for carbohydrate malabsorption in children: evidence for a circadian pattern of breath H2 concentration. Pediatr Res. 1978 Aug;12(8):816–823. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197808000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Pinedo R., Lavastida M., Rivera C. L., Rodrïguez H., Ortiz A. Studies on infant diarrhea. I. A comparison of the effects of milk feeding and intravenous therapy upon the composition and volume of the stool and urine. J Clin Invest. 1966 Apr;45(4):469–480. doi: 10.1172/JCI105361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vince A., Down P. F., Murison J., Twigg F. J., Wrong O. M. Generation of ammonia from non-urea sources in a faecal incubation system. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1976 Sep;51(3):313–322. doi: 10.1042/cs0510313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vince A., Killingley M., Wrong O. M. Effect of lactulose on ammonia production in a fecal incubation system. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):544–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker A. R., Walker B. F., Segal I. Faecal pH value and its modification by dietary means in South African black and white schoolchildren. S Afr Med J. 1979 Mar 24;55(13):495–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



