Abstract
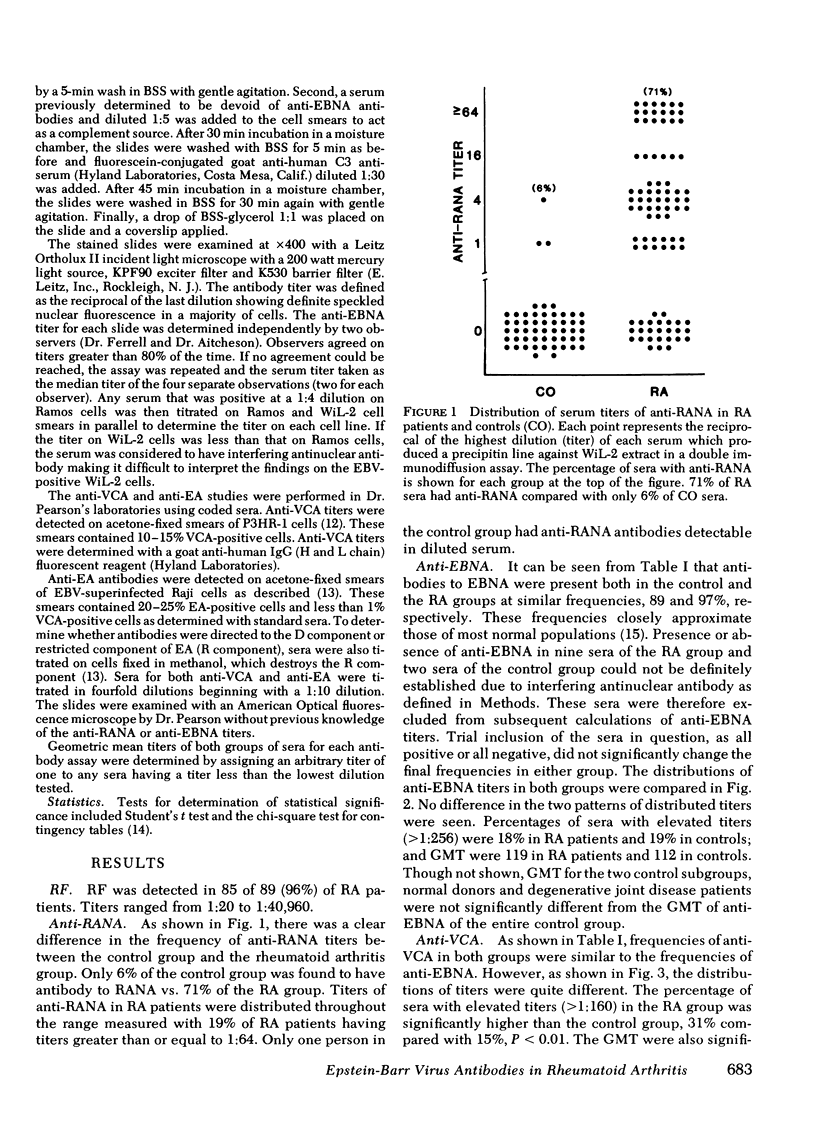
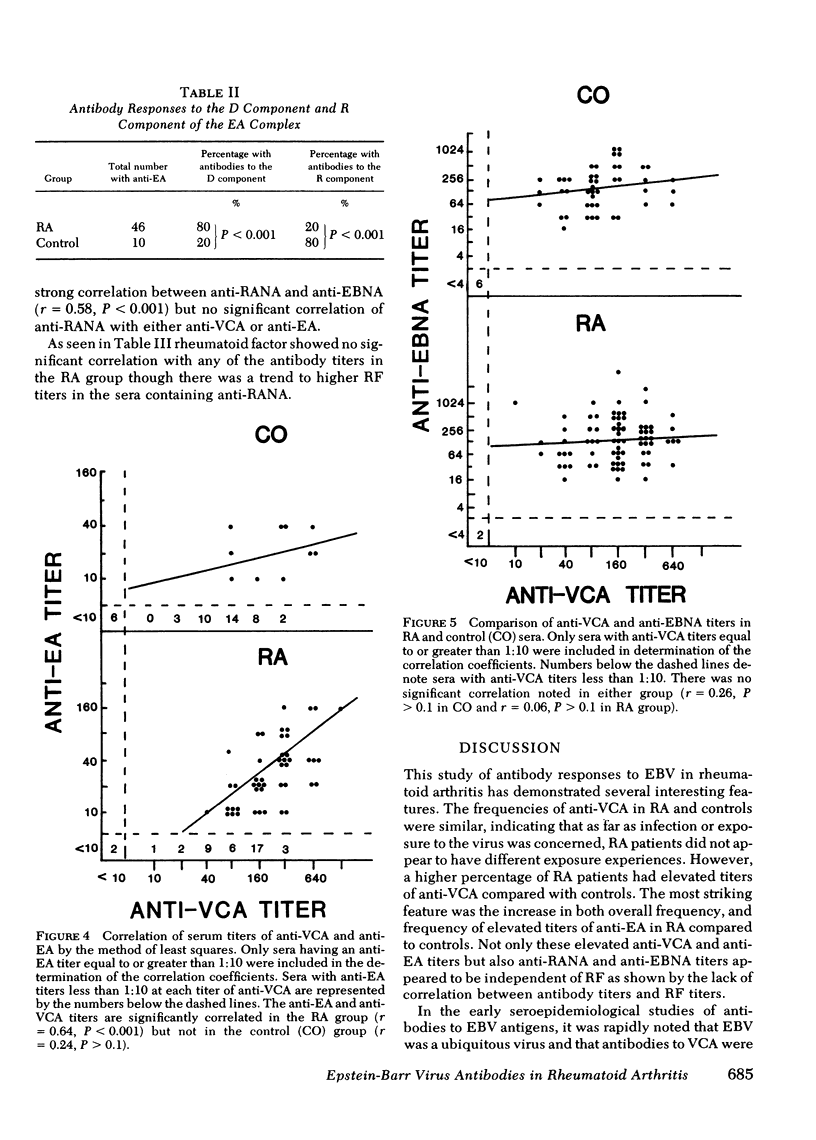
To elucidate the relationship between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA), we measured antibodies to RA-associated nuclear antigen (anti-RANA) and three other EBV-related antigens in the sera of RA patients and controls. Our study groups consisted of 89 patients with definite or classical RA, mean age 56, male/female ratio 47:42; and 53 normal and osteoarthritis controls, mean age 51, male/female ratio 25:28. In addition to anti-RANA, we measured antibodies to viral capsid antigen (anti-VCA), early antigen (anti-EA) and EBV-associated nuclear antigen (anti-EBNA). Anti-RANA was detected in 71% of RA patients but in only 6% of controls. Elevated anti-VCA titers (greater than 1:160) were more common in RA patients than controls, 31% compared with 15%. The geometric mean titer of anti-VCA was significantly higher iun the RA group, 133 compared with 58. Anti-EA was present in 53% of RA patients but only 19% of controls. Anti-EA in elevated titers (greater than 1:20) was present in 26% of RA patients but only 7% of controls. Characterization of the anti-EA antibodies revealed that the RA patients reacted primarily with the diffuse component, whereas the majority of the controls reacted with the restricted component of the EA complex. In contrast, the frequencies, distributions, and geometric mean titers of anti-EBNA were not significantly different between the two groups. Correlative analysis of these antibodies showed highly significant relationships between anti-VCA and anti-EA, and anti-RANA and anti-EBNA in the RA group. These data are compatible with the interpretation that RA patients have either more active EBV infections than controls or an altered regulation of their immune response to this infectious agent.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- 1958 REVISION of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1959 Feb;2(1):16–20. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(195902)2:1<16::aid-art1780020104>3.0.co;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alspaugh M. A., Jensen F. C., Rabin H., Tan E. M. Lymphocytes transformed by Epstein-Barr virus. Induction of nuclear antigen reactive with antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1018–1027. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aslpaugh M. A., Tan E. M. Serum antibody in rheumatoid arthritis reactive with a cell-associated antigen. Demonstration by precipitation and immunofluorescence. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Jul-Aug;19(4):711–719. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(197607/08)19:4<711::aid-art1780190409>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwick P. A., Bluestein H. G., Zvaifler N. J., Depper J. M., Seegmiller J. E. Altered regulation of Epstein-Barr virus induced lymphoblast proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis lymphoid cells. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Jun;23(6):626–632. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkel A. I., Henle W., Henle G., Klein G., Ersoy F., Sanal O. Epstein-Barr virus-related antibody patterns in ataxia-telangiectasia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Feb;35(2):196–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Niederman J. C., Feorino P., Vaughan J. H. Antibody to the rheumatoid arthritis nuclear antigen. Its relationship to in vivo Epstein-Barr virus infection. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1238–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI109779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catalano M. A., Carson D. A., Slovin S. F., Richman D. D., Vaughan J. H. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-determined antigens in normal subjects and in patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5825–5828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henie G., Henle W., Horwitz C. A. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen in infectious mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1974 Sep;130(3):231–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.3.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Klein G. Demonstration of two distinct components in the early antigen complex of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Sep 15;8(2):272–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joncas J., Lapointe N., Gervais F., Leyritz M., Wills A. Unusual prevalence of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus early antigen in ataxia telangiectasia. Lancet. 1977 May 28;1(8022):1160–1160. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Giovanella B., Westman A., Stehlin J. S., Mumford D. An EBV-genome-negative cell line established from an American Burkitt lymphoma; receptor characteristics. EBV infectibility and permanent conversion into EBV-positive sublines by in vitro infection. Intervirology. 1975;5(6):319–334. doi: 10.1159/000149930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Virolainen M., Defendi V. Human lymphoblastoid lines from lymph node and spleen. Cancer. 1968 Sep;22(3):517–524. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196809)22:3<517::aid-cncr2820220305>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng K. C., Brown K. A., Perry J. D., Holborow E. J. Anti-RANA antibody: a marker for seronegative and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1980 Mar 1;1(8166):447–449. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)90997-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Henle G., Henle W. Production of antigens associated with Epstein-Barr virus in experimentally infected lymphoblastoid cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Jun;46(6):1243–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiner M., Klein E., Klein G. Antinuclear reactivity of sera in patients with leukemia and other neoplastic diseases. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Sep;4(3):374–381. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter L., Carson D. A., Jensen F. C., Holbrook T. L., Vaughan J. H. In vitro effects of Epstein-Barr virus on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and normal subjects. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1429–1434. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M., Kunkel H. G. Characteristics of a soluble nuclear antigen precipitating with sera of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 1966 Mar;96(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



