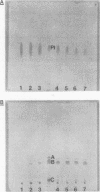
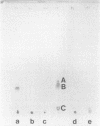
Abstract
An assay procedure was developed in which phosphatidyl[2-3H]inositol was employed as substrate for the measurement of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity. Employing this assay, phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in human fetal membranes and uterine decidua was identified and characterized. The specific activity of this enzyme in amnion (4.4 μmol × mg−1 protein × h−1) was three times that in uterine decidua and more than five times that in chorion laeve. No difference was found between the specific activity of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in placental amnion and that in reflected amnion. The products of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis in short-term incubations were stoichiometric amounts of diacylglycerol and inositol-1,2-cyclic-phosphate plus inositol-1-phosphate. After longer periods of incubation, monoacylglycerol also was detected. Diacylglycerol lipase activity also was demonstrated in these tissues. More than 90% of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity of amnion tissue was recovered in the 105,000-g supernatant fraction, and optimal enzymatic activity in vitro was observed at pH 6.5-7.5 in the presence of Ca2+ (8 mM) and mercaptoethanol (4 mM). Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity was stimulated by fatty acids in low concentrations, but was inhibited by lysophosphatidylcholine and a variety of detergents. No effect of labor on the specific activity of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in either fetal membranes or uterine decidua could be detected. The finding of an active phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity in human fetal membranes and uterine decidua is complementary to our previous finding of a selective loss of arachidonic acid from phosphatidylinositol of human fetal membranes during labor. The action of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, coupled to diacylglycerol lipase action, could provide a mechanism for the release of arachidonic acid for prostaglandin biosynthesis during parturition.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan D., Michell R. H. Phosphatidylinositol cleavage catalysed by the soluble fraction from lymphocytes. Activity at pH5.5 and pH7.0. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):591–597. doi: 10.1042/bj1420591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton R. S., Hawthorne J. N. The phosphoinositide inositolphosphohydrolase of guinea-pig intestinal mucosa. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Mar;4(1):68–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. L., Kennerly D. A., Stanford N., Majerus P. W. Diglyceride lipase: a pathway for arachidonate release from human platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3238–3241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M., Lapetina E. G., Cuatrecasas P. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase-C of platelets: association with 1,2-diacyglycerol-kinase and inhibition by cyclic-AMP. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91594-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleasdale J. E., Wallis P., MacDonald P. C., Johnston J. M. Characterization of the forward and reverse reactions catalyzed by CDP-diacylglycerol:inositol transferase in rabbit lung tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 26;575(1):135–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. M., Clarke N. D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate 2-phosphohydrolase. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;127(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj1270113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hokin-Neaverson M., Sadeghian K., Majumder A. L., Eisenberg F., Jr Inositol is the water-soluble product of acetylcholine-stimulated breakdown of phosphatidylinositol in mouse pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Dec 15;67(4):1537–1544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90201-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Hemington N., Dawson R. M. Phosphatidylinositol-degrading enzymes in liver lysosomes. Biochem J. 1977 Apr 15;164(1):277–280. doi: 10.1042/bj1640277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Letcher A. J., Dawson R. M. Fatty acid stimulation of membrane phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis by brain phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase. Biochem J. 1979 Feb 15;178(2):497–500. doi: 10.1042/bj1780497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEMP P., HUBSCHER G., HAWTHORNE J. N. Phosphoinositides. 3. Enzymic hydrolysis of inositol-containing phospholipids. Biochem J. 1961 Apr;79:193–200. doi: 10.1042/bj0790193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lands W. E., Samuelsson B. Phospholipid precursors of prostaglandins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 22;164(2):426–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Grosman M., Canessa de Scarnati O. Phosphatidylinositol-cleaving activity in smooth muscle from rat vas deferens. Int J Biochem. 1976;7(9-10):507–513. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(76)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. A membrane-bound activity catalysing phosphatidylinositol breakdown to 1,2-diacylglycerol, D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate an D-myoinositol 1-phosphate. Properties and subcellular distribution in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1310433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. The action of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipases C on membranes. Biochem J. 1976 Jan 15;154(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1540203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. C., Porter J. C., Schwarz B. E., Johnston J. M. Initiation of parturition in the human female. Semin Perinatol. 1978 Jul;2(3):273–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald P. C., Schultz F. M., Duenhoelter J. H., Gant N. F., Jimenez J. M., Pritchard J. A., Porter J. C., Johnston J. M. Initiation of human parturition. I. Mechanism of action of arachidonic acid. Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Nov;44(5):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majumder A. L., Eisenberg F., Jr The formation of cyclic inositol 1,2-monophosphate, inositol 1-phosphate, and glucose 6-phosphate by brain preparations stimulated with deoxycholate and calcium: a gas chromatographic study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa Y., Hostetler K. Y. Properties of phospholipase C isolated from rat liver lysosomes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):646–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Douste-Blazy L. Characterization and properties of a phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C) from platelet cytosol. FEBS Lett. 1979 Apr 15;100(2):367–370. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80371-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauco G., Chap H., Simon M. F., Douste-Blazy L. Phosphatidic and lysophosphatidic acid production in phospholipase C-and thrombin-treated platelets. Possible involvement of a platelet lipase. Biochimie. 1978 Sep 29;60(6-7):653–661. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(78)80784-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell M. D., Keirse M. J., Brunt J. D., Anderson A. B., Turnbull A. C. Concentrations of the prostacyclin metabolite, 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha, in amniotic fluid during late pregnancy and labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1979 May;86(5):350–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1979.tb10609.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Okita J. R., MacDonald P. C., Johnston J. M. Initiation of human parturition. X. Substrate specificity of phospholipase A2 in human fetal membranes. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1978 Feb 15;130(4):432–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J. The association between phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase activity and a specific subunit of microtubular protein in rat brain. Biochem J. 1973 Jun;133(2):273–281. doi: 10.1042/bj1330273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Indomethacin-induced accumulation of diglyceride in activated human platelets. The role of diglyceride lipase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2259–2262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelsson B., Granström E., Green K., Hamberg M., Hammarström S. Prostaglandins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:669–695. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz B. E., Schultz F. M., Macdonald P. C., Johnston J. M. Initiation of human parturition. III. Fetal membrane content of prostaglandin E2 and F2alpha precursor. Obstet Gynecol. 1975 Nov;46(5):564–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. The hydrolysis of monophosphoinositide by extracts of brain. Can J Biochem. 1967 Jun;45(6):853–861. doi: 10.1139/o67-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waite M., van Deenen L. L. Hydrolysis of phospholipids and glycerides by rat-liver preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Jun 6;137(3):498–517. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90131-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yavin E., Zutra A. Separation and analysis of 32P-labeled phospholipids by a simple and rapid thin-layer chromatographic procedure and its application to cultured neuroblastoma cells. Anal Biochem. 1977 Jun;80(2):430–437. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90665-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]