Abstract
It has been suggested that the phorbol ester tumor promoters act via the receptor-effector system for epidermal growth factor (EGF), since they interact with the EGF receptor system and mimic many of the effects of EGF in cultured cells. We have studied the interaction of phorbol esters with the EGF-responsive MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Similar to other systems, phorbol esters inhibit EGF binding in MCF-7 cells in a manner paralleling their potency as tumor promoters in mice. The effect is specific for EGF since the membrane binding of insulin is unaffected. Like EGF, the potent phorbol ester 12-O-tetradecanoyl-13-phorbol acetate (TPA) stimulates protein synthesis as indicated by a twofold increase in [3H]leucine incorporation into protein after 24 h in TPA. Cell morphology, however, is significantly different with TPA treatment. After 24-48 h in TPA, cells become markedly enlarged with increased cytoplasmic vacuolization and increased membrane microvilli. This is reflected in a fourfold increase in the protein/DNA ratio (control 13.1; TPA 55.9). Furthermore, TPA inhibits cell division in media with or without serum, and prevents growth stimulation by EGF. Low TPA concentrations (1.0 ng/ml) are active, and 10 ng/ml results in maximal inhibition of cell replication. Other phorbol esters inhibit MCF-7 cells relative to their tumor promoting activity in vivo and their ability to inhibit EGF binding in these cells. After 24 h in TPA, incorporation of [3H]thymidine into DNA is markedly reduced and the thymidine labeling index falls (33% to 2%) indicating very few S-phase cells. Growth inhibition is reversible by removing TPA from the medium. Similar inhibitory effects are seen with the two other human breast cancer cell lines studied, ZR75-1 and MDA-MB-231. In conclusion, phorbol esters may interact with the EGF receptor domain in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells, but they have distinct effects on cell morphology and growth suggesting alternative pathways of action. The antineoplastic activity of these compounds needs further investigation.
Full text
PDF

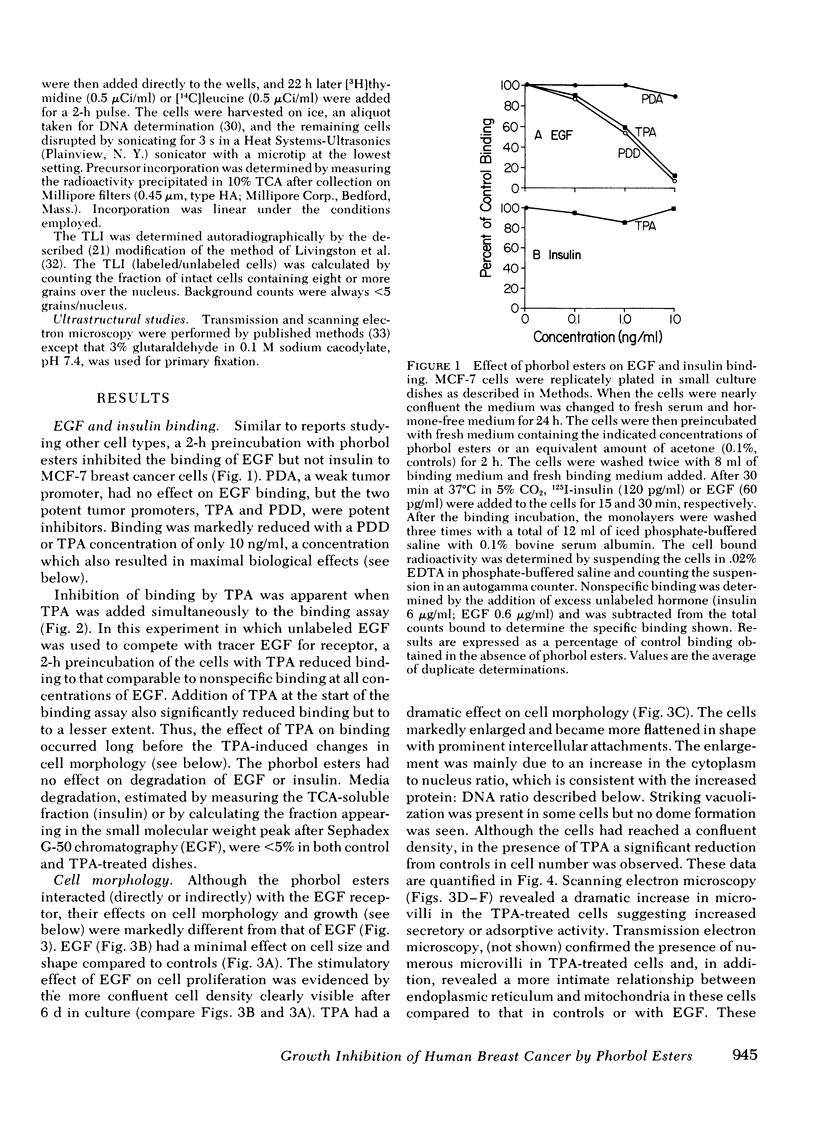
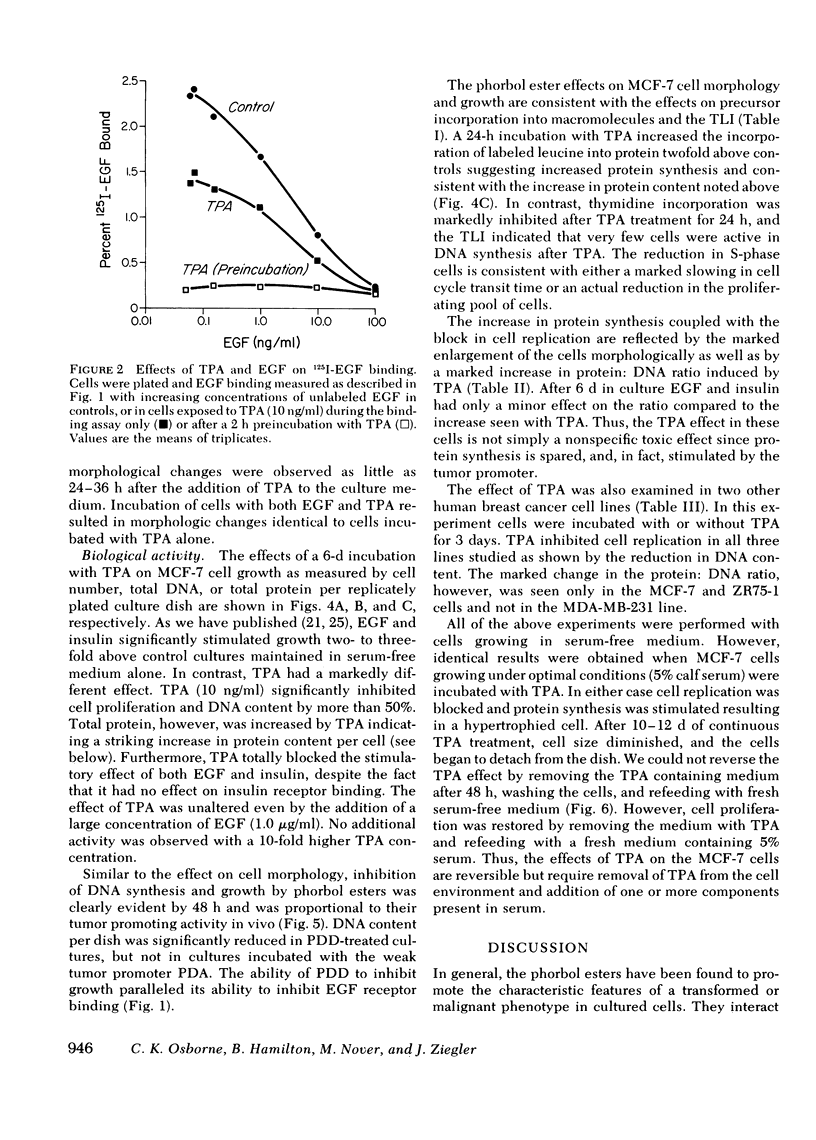
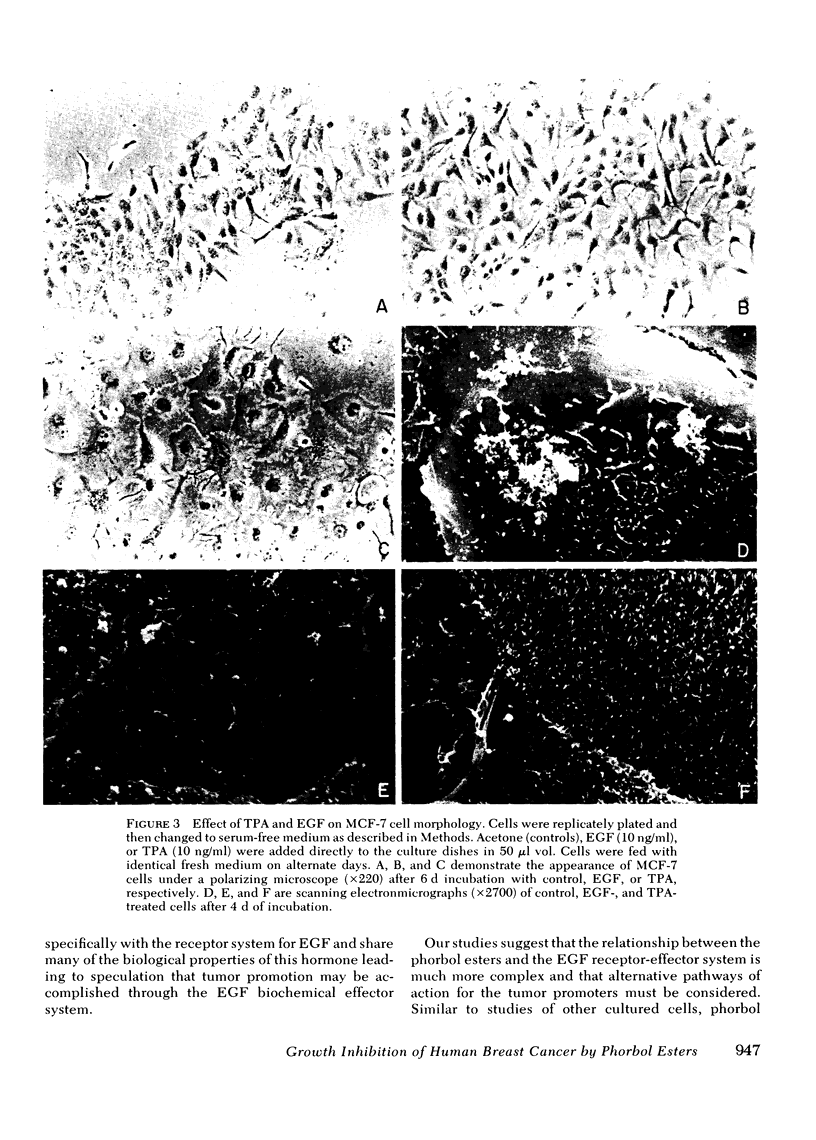
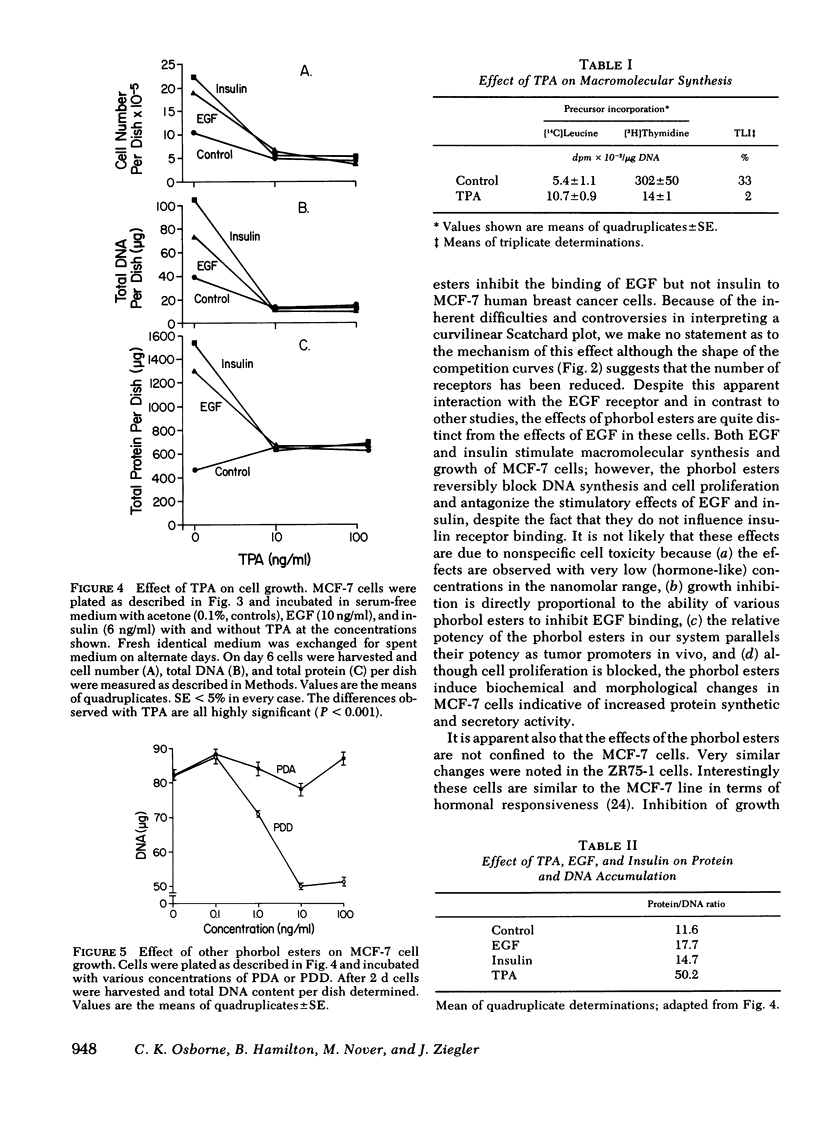
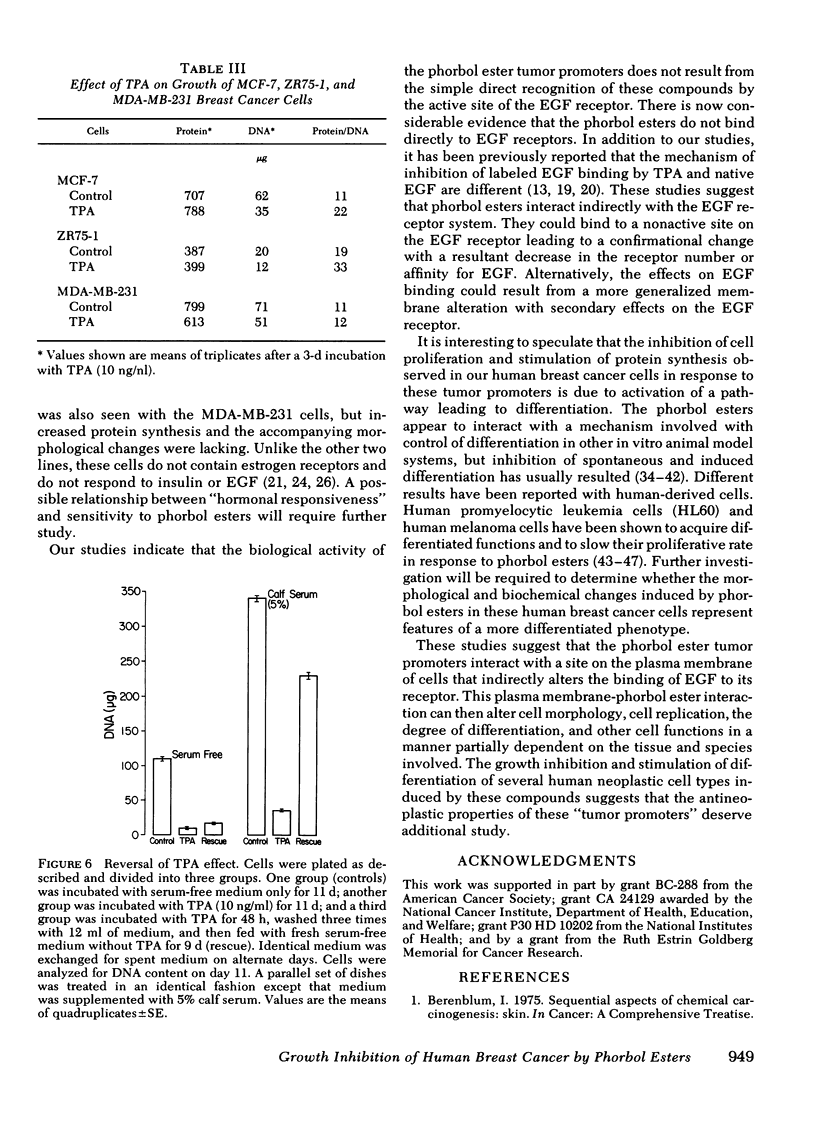


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes D., Sato G. Growth of a human mammary tumour cell line in a serum-free medium. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):388–389. doi: 10.1038/281388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K. D., Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor binding to surface receptors by tumor promotors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90221-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. Biological and molecular studies of the mitogenic effects of human epidermal growth factor. Symp Soc Dev Biol. 1978;(35):13–31. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-612981-6.50007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Pacifici M., Rubinstein N., Biehl J., Holtzer H. Effect of a tumour promoter on myogenesis. Nature. 1977 Apr 7;266(5602):538–540. doi: 10.1038/266538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Rovera G. Inhibition of adipose conversion of 3T3 fibroblasts by tumour promoters. Nature. 1977 Sep 15;269(5625):247–249. doi: 10.1038/269247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Rovera G. Tumor promoters: effects on proliferation and differentiation of cells in culture. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):1979–1988. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dicker P., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis by tumour promoter and pure mitogenic factors. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):723–726. doi: 10.1038/276723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. The effect of phorbol diesters on chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):3257–3265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibach E., Gambari R., Shaw P. A., Maniatis G., Reuben R. C., Sassa S., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Tumor promoter-mediated inhibition of cell differentiation: suppression of the expression of erythroid functions in murine erythroleukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Flamm M., Schachter D., Weinstein I. B. Tumor promoters induce membrane changes detected by fluorescence polarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Feb 28;86(4):1063–1068. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90225-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz C. N., Stiles C. D., Scher C. D. The tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate enhances the proliferative response of Balb/c-3T3 cells to hormonal growth factors. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Sep;100(3):413–424. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Kahn R., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin interactions with liver plasma membranes. Independence of binding of the hormone and its degradation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3953–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürstenberger G., Marks F. Indomethacin inhibition of cell proliferation induced by the phorbolester TPA is reversed by prostaglandin E2 in mouse epidermis in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 30;84(4):1103–1111. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91697-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Callaham M. F. Induction of terminal differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor-promoting agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Heckman C., Langenbach R. Stimulation of differentiated functions in human melanoma cells by tumor-promoting agents and dimethyl sulfoxide. Cancer Res. 1979 Jul;39(7 Pt 1):2618–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N. Effect of tumor promoters on the response of cultured embryonic chick ganglia to nerve growth factor. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 1):3886–3893. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Fibach E., Yamasaki H., Weinstein I. B. Tumor promoters inhibit morphological differentiation in cultured mouse neuroblastoma cells. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):556–559. doi: 10.1126/science.644318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Epidermal growth factor, like phorbol esters, induces plasminogen activator in HeLa cells. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):696–697. doi: 10.1038/274696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Mechanism of tumor promoter inhibition of cellular binding of epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5168–5172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. S., Weinstein I. B. Tumor-promoting phorbol esters inhibit binding of epidermal growth factor to cellular receptors. Science. 1978 Oct 20;202(4365):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.308698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston R. B., Ambus U., George S. L., Freireich E. J., Hart J. S. In vitro determination of thymidine-3H labeling index in human solid tumors. Cancer Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):1376–1380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation of normal differentiation in mouse and human myeloid leukemic cells by phorbol esters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe M. E., Pacifici M., Holtzer H. Effects of phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate on the phenotypic program of cultured chondroblasts and fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2350–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima S., Morisawa Y., Petterborg L. J., Zeagler J. W., Reiter R. J. Ultrastructure of pinealocytes of the cotton rat, Sigmodon hispidus. Cell Tissue Res. 1979;204(3):407–416. doi: 10.1007/BF00233652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal S., Heidelberger C. Inhibition of induced differentiation of C3H/10T 1/2 clone 8 mouse embryo cells by tumor promoters. Cancer Res. 1980 Feb;40(2):334–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mufson R. A., Fisher P. B., Weinstein I. B. Effect of phorbol ester tumor promoters on the expression of melanogenesis in B-16 melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1979 Oct;39(10):3915–3919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Fusenig N. E. Binding of epidermal growth factor to primary and permanent cultures of mouse epidermal cells: inhibition by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. Cancer Lett. 1979 Jul;7(2-3):71–77. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(79)80098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Ornithine decarboxylase induction and DNA synthesis in hamster embryo cell cultures treated with tumor-promoting phorbol diesters. Cancer Res. 1977 Nov;37(11):3895–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne C. K., Bolan G., Monaco M. E., Lippman M. E. Hormone responsive human breast cancer in long-term tissue culture: effect of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4536–4540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne C. K., Hamilton B., Titus G., Livingston R. B. Epidermal growth factor stimulation of human breast cancer cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1980 Jul;40(7):2361–2366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne C. K., Monaco M. E., Lippman M. E., Kahn C. R. Correlation among insulin binding, degradation, and biological activity in human breast cancer cells in long-term tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1978 Jan;38(1):94–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Herschman H. R. Variants of 3T3 cells lacking mitogenic response to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3918–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose S. P., Stahn R., Passovoy D. S., Herschman H. Epidermal growth factor enhancement of skin tumor induction in mice. Experientia. 1976;32(7):913–915. doi: 10.1007/BF02003764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Induction of differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor promoters. Science. 1979 May 25;204(4395):868–870. doi: 10.1126/science.286421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Tumor promoters inhibit spontaneous differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2894–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soule H. D., Vazguez J., Long A., Albert S., Brennan M. A human cell line from a pleural effusion derived from a breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Nov;51(5):1409–1416. doi: 10.1093/jnci/51.5.1409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma A. K., Ashendel C. L., Boutwell R. K. Inhibition by prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors of the induction of epidermal ornithine decarboxylase activity, the accumulation of prostaglandins, and tumor promotion caused by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1980 Feb;40(2):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenner C. E., Hackney J., Kimelberg H. K., Mayhew E. Membrane effects of phorbol esters. Cancer Res. 1974 Jul;34(7):1731–1737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Weinstein I. B. Tumour promotor induces plasminogen activator. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):232–233. doi: 10.1038/259232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




