Abstract
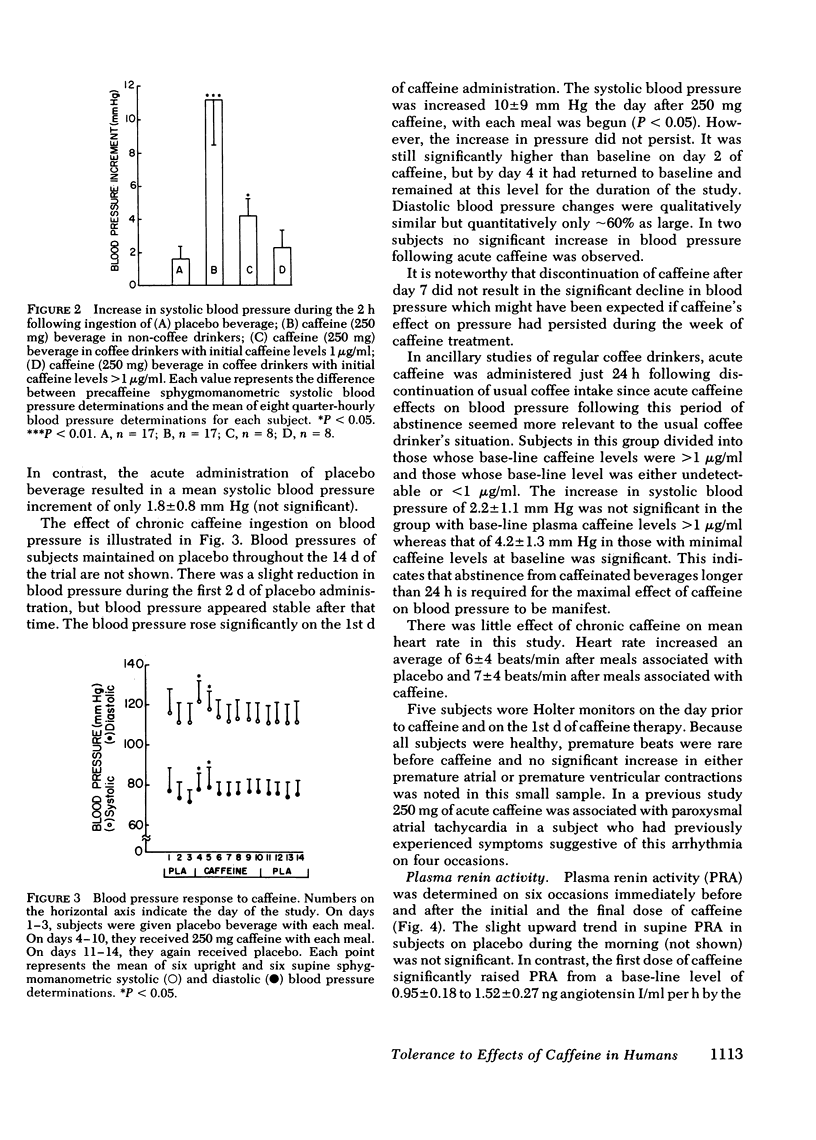
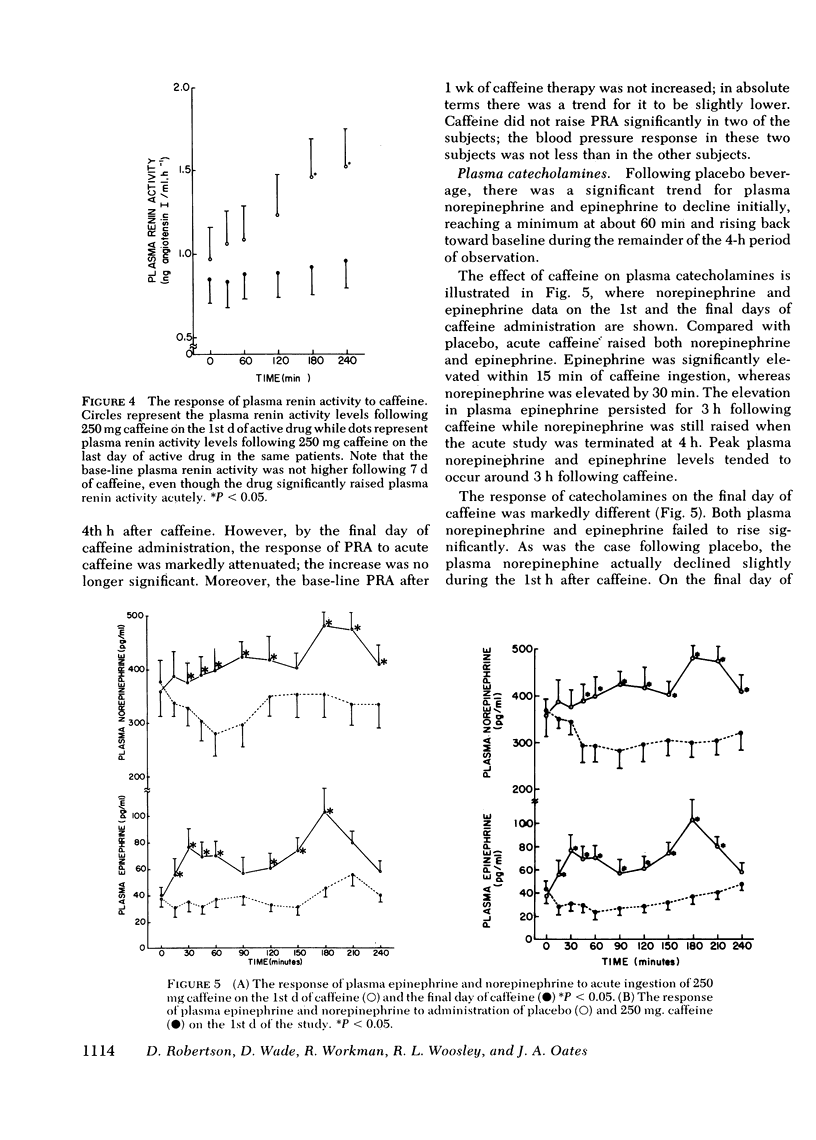
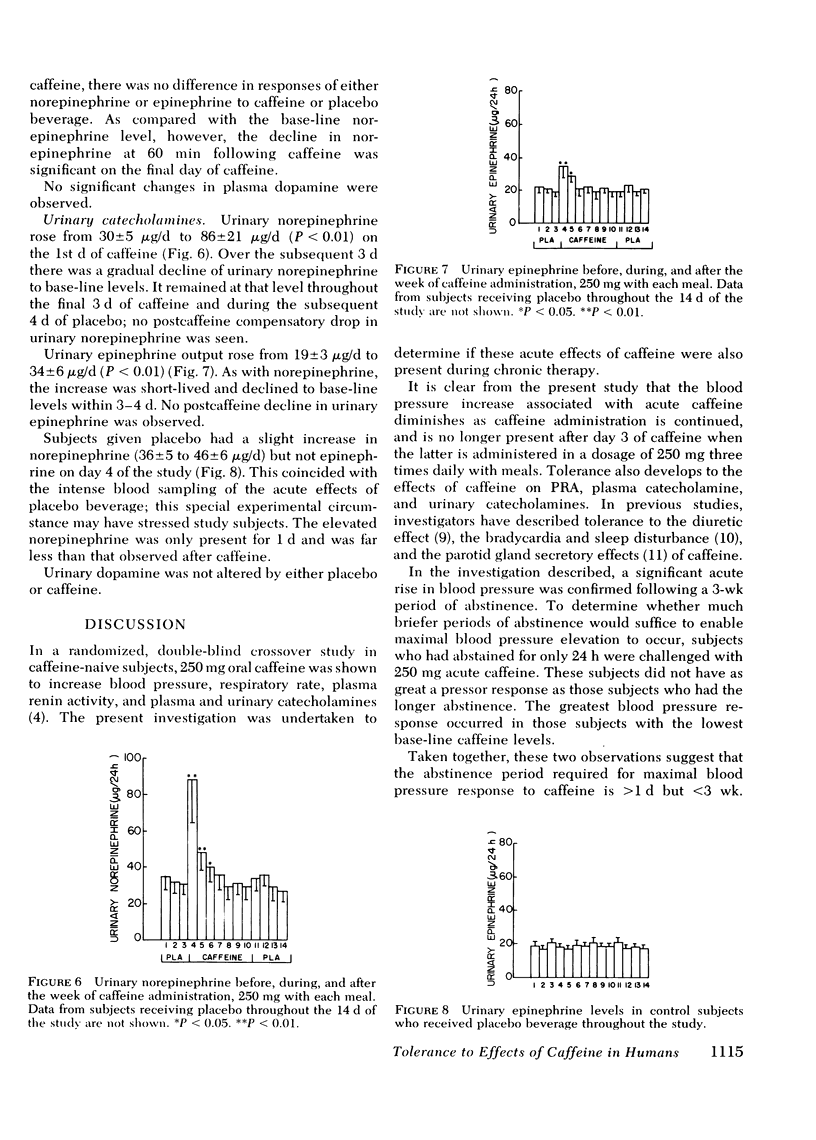
Acute caffeine in subjects who do not normally ingest methylxanthines leads to increases in blood pressure, heart rate, plasma epinephrine, plasma norepinephrine, plasma renin activity, and urinary catecholamines. Using a double-blind design, the effects of chronic caffeine administration on these same variables were assessed. Near complete tolerance, in terms of both humoral and hemodynamic variables, developed over the first 1-4 d of caffeine. No long-term effects of caffeine on blood pressure, heart rate, plasma renin activity, plasma catecholamines, or urinary catecholamines could be demonstrated. Discontinuation of caffeine ingestion after 7 d of administration did not result in a detectable withdrawal phenomenon relating to any of the variables assessed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beavo J. A., Rogers N. L., Crofford O. B., Hardman J. G., Sutherland E. W., Newman E. V. Effects of xanthine derivatives on lipolysis and on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate phosphodiesterase activity. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Nov;6(6):597–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Spector S. Effect of caffeine and theophylline on peripheral catecholamines. Eur J Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;13(2):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(71)90150-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz B. A., Tarver J. H., Spector S. Release of norepinephrine in the central nervous system by theophylline and caffeine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1970 Apr;10(1):64–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(70)90158-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand C. A., Pomper I., Hillman G., Duffy J. C., Micheli I. No relation between coffee and blood pressure. N Engl J Med. 1978 Aug 10;299(6):315–316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197808102990625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondaryóv M. G. The influence of analeptic drugs on the pontine vasomotor center. Nurs Mirror Midwives J. 1967 Apr 28;124(4):171–186. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)62893-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey R. M., Douglas J. G., Schweikert J. R., Liddle G. W. The syndrome of essential hypertension and suppressed plasma renin activity. Normalization of blood pressure with spironolactone. Arch Intern Med. 1972 Dec;130(6):849–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clutter W. E., Bier D. M., Shah S. D., Cryer P. E. Epinephrine plasma metabolic clearance rates and physiologic thresholds for metabolic and hemodynamic actions in man. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):94–101. doi: 10.1172/JCI109840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colton T., Gosselin R. E., Smith R. P. The tolerance of coffee drinkers to caffeine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1968 Jan-Feb;9(1):31–39. doi: 10.1002/cpt19689131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawber T. R., Kannel W. B., Gordon T. Coffee and cardiovascular disease. Observations from the framingham study. N Engl J Med. 1974 Oct 24;291(17):871–874. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197410242911703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald G. A., Hossmann V., Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Davies D. S., Dollery C. T. Interindividual variation in kinetics of infused epinephrine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1979 Dec;26(6):669–675. doi: 10.1002/cpt1979266669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. 3. A questionnaire survey of coffee drinking and its effects in a group of housewives. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Jul-Aug;10(4):477–488. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969104477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Kaizer S., Whitby O. Psychotropic effects of caffeine in man. IV. Quantitative and qualitative differences associated with habituation to coffee. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1969 Jul-Aug;10(4):489–497. doi: 10.1002/cpt1969104489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennekens C. H., Drolette M. E., Jesse M. J., Davies J. E., Hutchison G. B. Coffee drinking and death due to coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1976 Mar 18;294(12):633–636. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197603182941203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jick H., Miettinen O. S., Neff R. K., Shapiro S., Heinonen O. P., Slone D. Coffee and myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1973 Jul 12;289(2):63–67. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197307122890203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalsner S. Mechanism of potentiation of contractor responses to catecholamines by methylxanthines in aortic strips. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Oct;43(2):379–388. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatsky A. L., Friedman G. D., Siegelaub A. B. Coffee drinking prior to acute myocardial infarction. Results from the Kaiser-Permanente Epidemiologic Study of Myocardial Infarction. JAMA. 1973 Oct 29;226(5):540–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passon P. G., Peuler J. D. A simplified radiometric assay for plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):618–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas R. J., Jacobs D. R., Jr, Crow R. S., Blackburn H. Coffee, tea and VPB. J Chronic Dis. 1980;33(2):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(80)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Frölich J. C., Carr R. K., Watson J. T., Hollifield J. W., Shand D. G., Oates J. A. Effects of caffeine on plasma renin activity, catecholamines and blood pressure. N Engl J Med. 1978 Jan 26;298(4):181–186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197801262980403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Heath E. C., Falkner F. C., Hill R. E., Brilis G. M., Watson J. T. A selective and sensitive assay for urinary metanephrine and normetanephrine using gas chromatography mass spectrometry with selected ion monitoring. Biomed Mass Spectrom. 1978 Dec;5(12):704–708. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200051213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Johnson G. A., Robertson R. M., Nies A. S., Shand D. G., Oates J. A. Comparative assessment of stimuli that release neuronal and adrenomedullary catecholamines in man. Circulation. 1979 Apr;59(4):637–643. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.59.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider S. R., Waldeck B. Increased synthesis of adrenomedullary catecholamines induced by caffeine and theophylline. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;281(2):257–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00503502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Somlyo A. P. Electromechanical and pharmacomechanical coupling in vascular smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):129–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



