Abstract
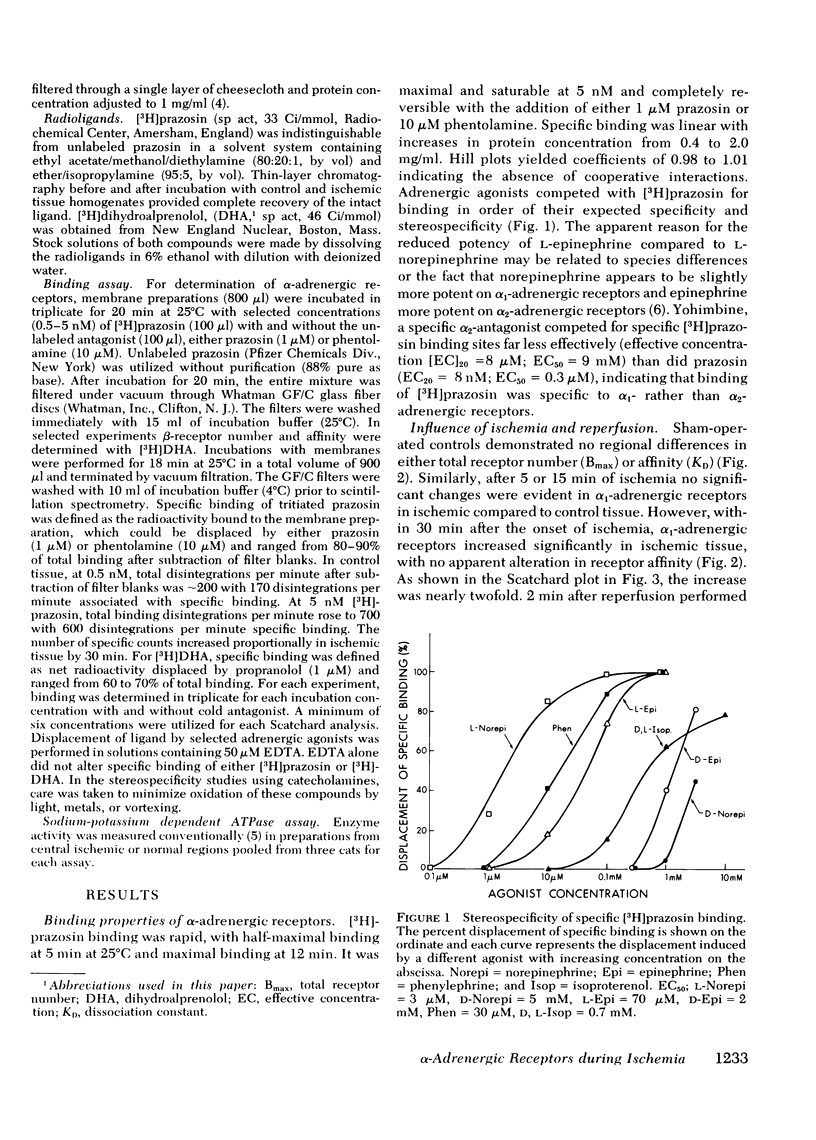
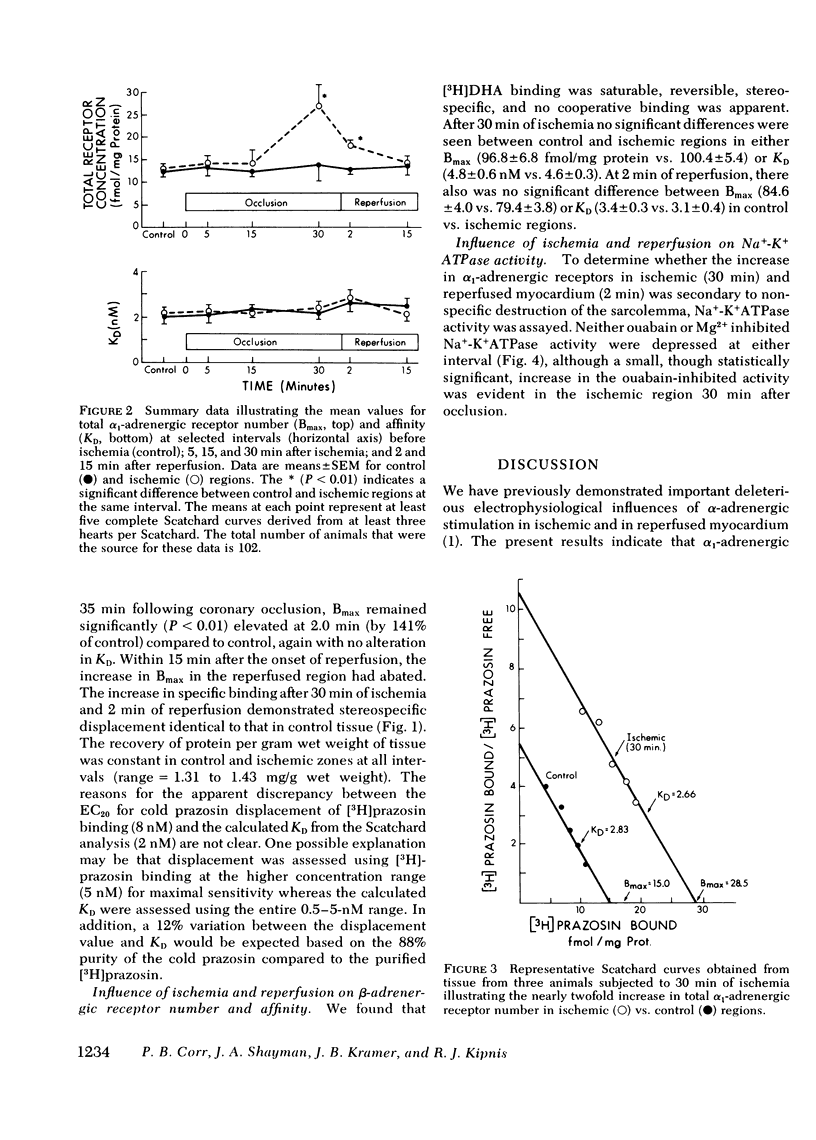
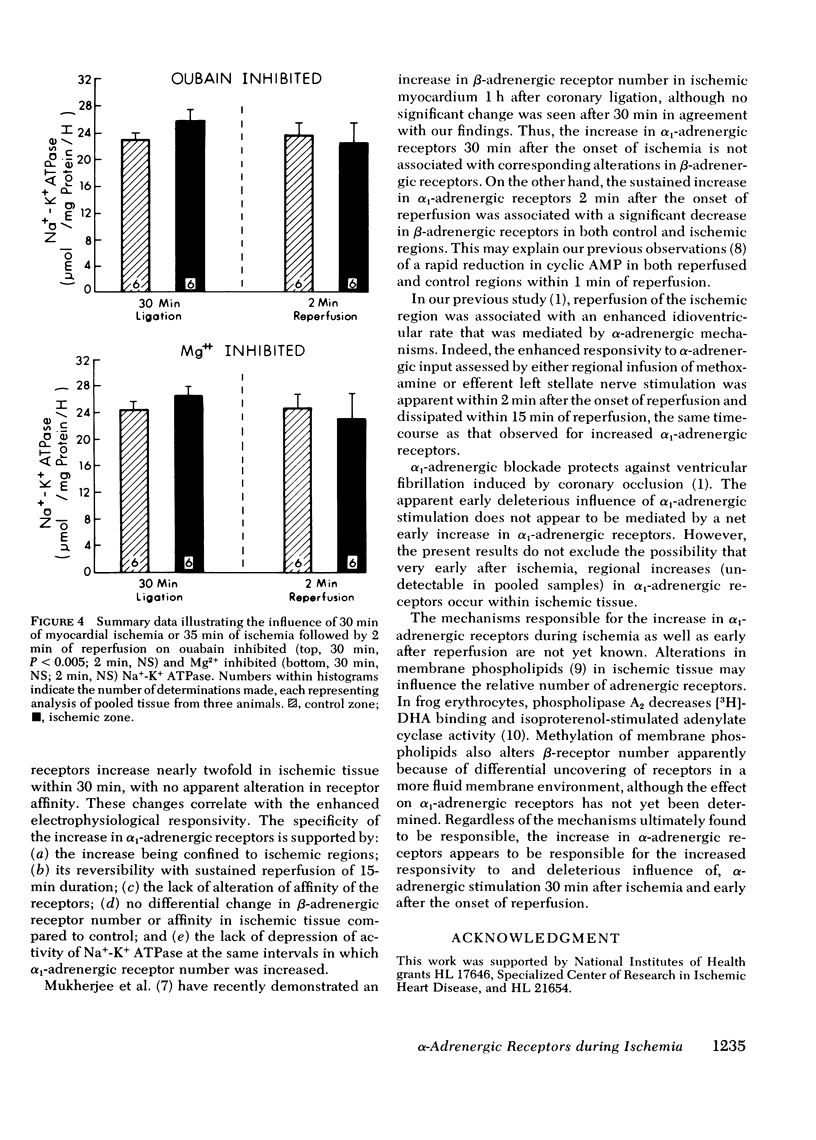
We have recently demonstrated enhanced alpha-adrenergic responsiveness assessed electrophysiologically in ischemic and reperfused myocardium. This study was performed to determine whether ischemia alters alpha 1-adrenergic receptor number (Bmax) of affinity (KD) based on [3H]prazosin binding. Within 30 min after occlusion, Bmax increased in ischemic regions to 207% of control to 27 +/- 2 fmol/mg protein, with the increase persisting (+ 141% of control) during early reperfusion (2 min), before returning to control base-line values (13 +/- 1.6) after 15 min of reperfusion. KD was not altered at any interval studied. Beta receptor number of ([3H]dihydroalprenolol) and Na+-K+ ATPase activity were comparable in control compared to ischemic myocardium although beta-receptor Bmax and KD in both regions decreased during early reperfusion. Thus, the enhanced alpha-adrenergic responsivity previously recognized with ischemia and reperfusion is correlated with an increase in alpha 1-adrenergic receptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller G. A., Conroy J., Smith T. W. Ischemia-induced alterations in myocardial (Na+ + K+)-ATPase and cardiac glycoside binding. J Clin Invest. 1976 Feb;57(2):341–350. doi: 10.1172/JCI108285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthelsen S., Pettinger W. A. A functional basis for classification of alpha-adrenergic receptors. Life Sci. 1977 Sep 1;21(5):595–606. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karliner J. S., Barnes P., Hamilton C. A., Dollery C. T. alpha 1-Adrenergic receptors in guinea pig myocardium: identification by binding of a new radioligand, (3H)-prazosin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Sep 12;90(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91601-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Adenylate cyclase-coupled beta adrenergic receptors effect of membrane lipid-perturbing agents on receptor binding and enzyme stimulation by catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A., Wong T. M., Buja L. M., Lefkowitz R. J., Willerson J. T. Beta adrenergic and muscarinic cholinergic receptors in canine myocardium. Effects of ischemia. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1423–1428. doi: 10.1172/JCI109600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penkoske P. A., Sobel B. E., Corr P. B. Disparate electrophysiological alterations accompanying dysrhythmia due to coronary occlusion and reperfusion in the cat. Circulation. 1978 Dec;58(6):1023–1035. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.6.1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan D. J., Penkoske P. A., Sobel B. E., Corr P. B. Alpha adrenergic contributions to dysrhythmia during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in cats. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):161–171. doi: 10.1172/JCI109647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel B. E., Corr P. B., Robison A. K., Goldstein R. A., Witkowski F. X., Klein M. S. Accumulation of lysophosphoglycerides with arrhythmogenic properties in ischemic myocardium. J Clin Invest. 1978 Sep;62(3):546–553. doi: 10.1172/JCI109159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



