Abstract
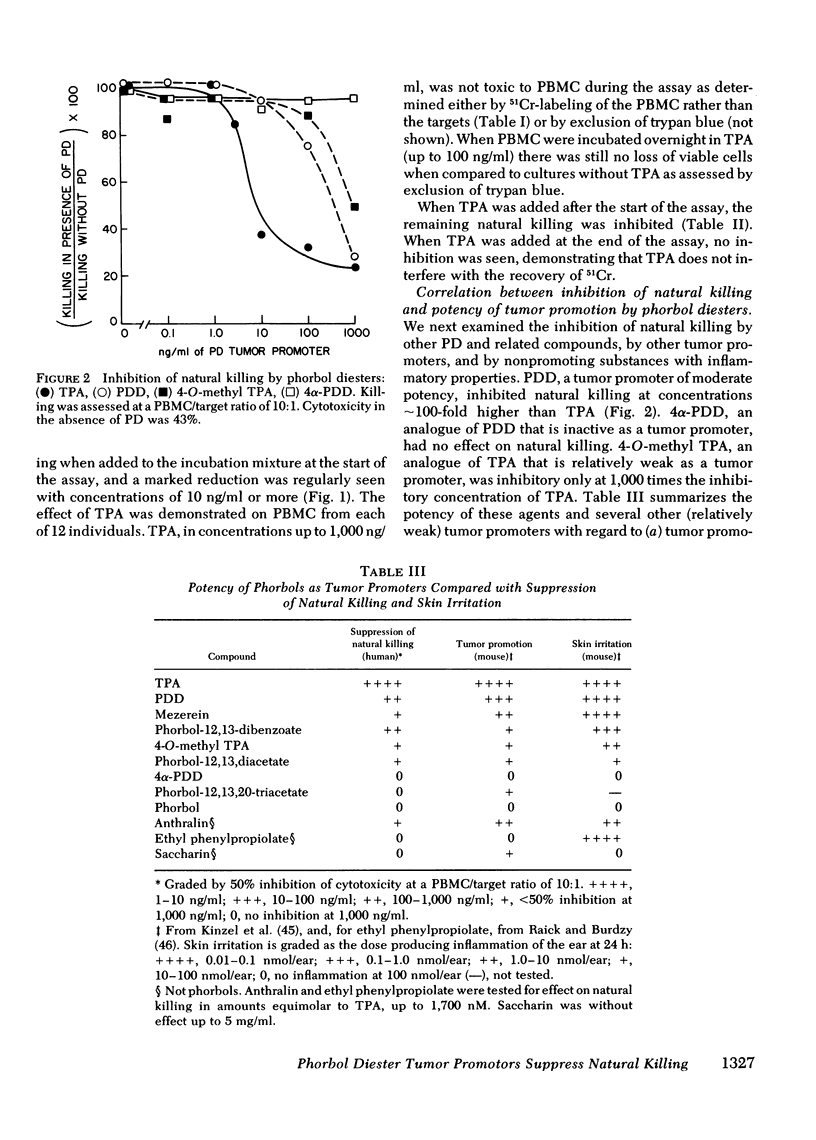
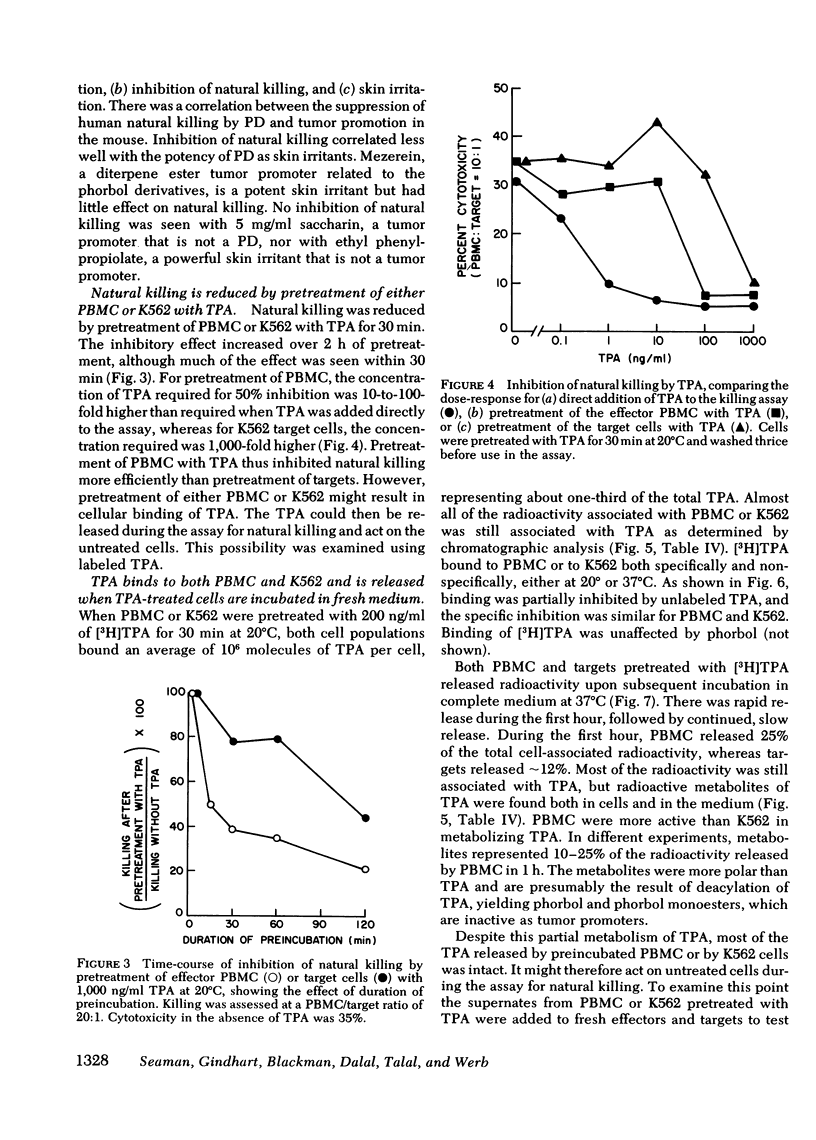
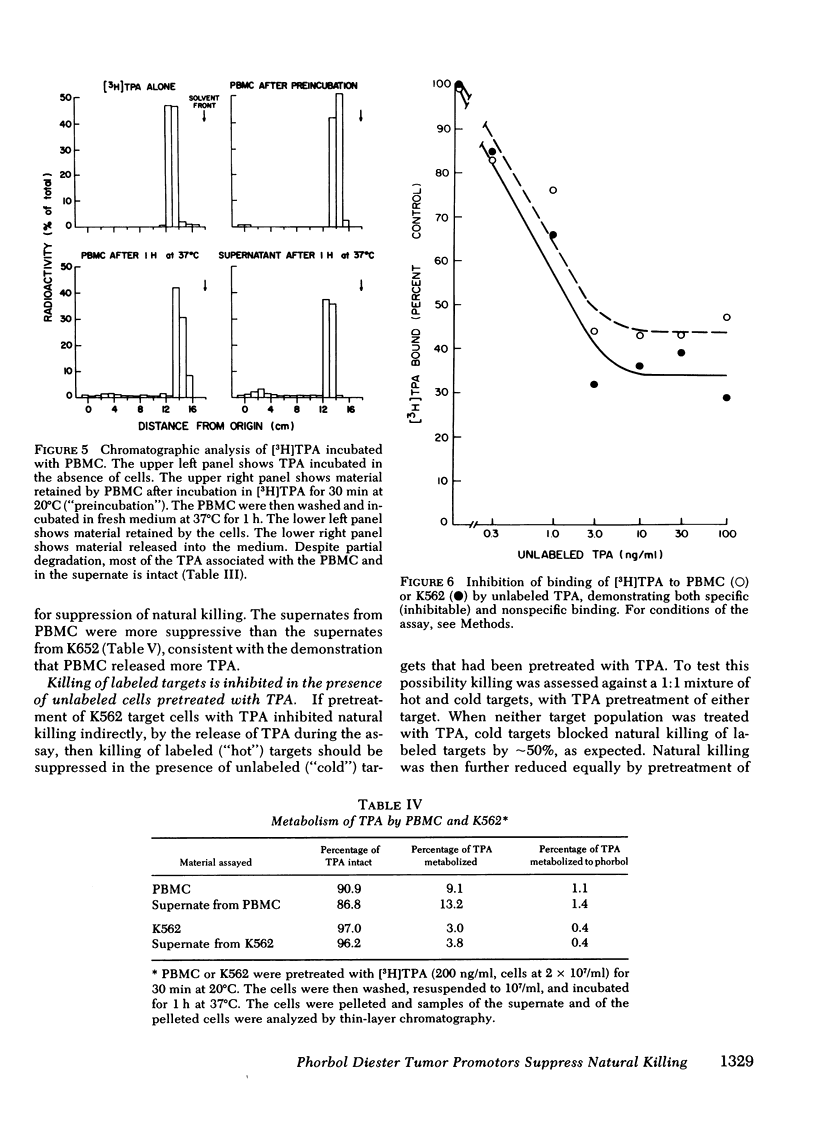
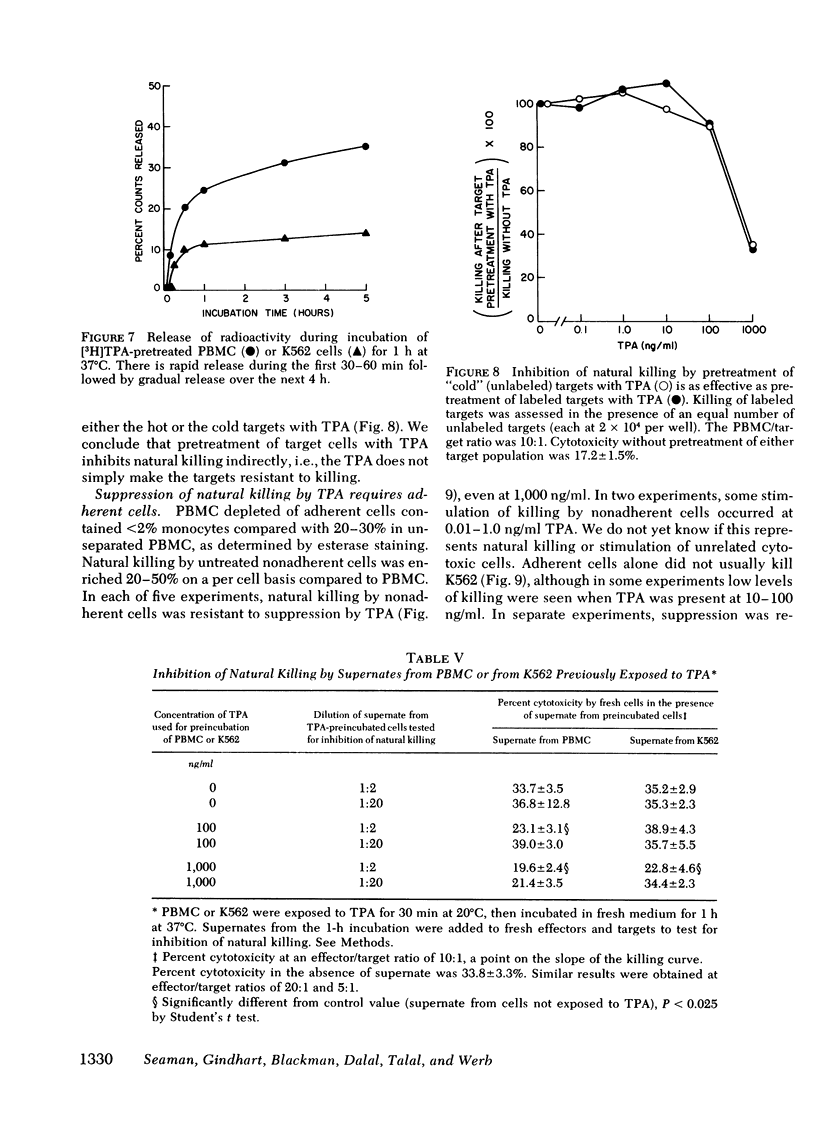
Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters were shown to suppress natural killing in vitro by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The inhibitory effect of different phorbol diesters and their analogues correlated with their potency as tumor promoters, the most effective agent being 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). Both peripheral blood cells and targets specifically bound TPA, and natural killing could be inhibited by pretreatment of either cell population with TPA, though this was less effective than direct addition of TPA to the assay. Cells that had been pretreated with TPA released TPA and metabolites of tPA during subsequent incubation in fresh medium. This release of tPA was evidently responsible for the inhibition of natural killing by pretreated target cells; in experiments where labeled and unlabeled target cells were mixed, pretreatment of unlabeled targets with TPA inhibited killing of labeled targets. Suppression of natural killing by TPA was greatly reduced when adherent cells were removed from the peripheral blood cells, suggesting that monocytes mediate suppression. Inhibition of natural killing by TPA provides a model for examining the regulation of natural killing. Suppression of natural killing by phorbol diesters may contribute to their activity as tumor promoters.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. K., Douglas S. D. Purification of human monocytes on microexudate-coated surfaces. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1372–1374. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENBLUM I. A speculative review; the probable nature of promoting action and its significance in the understanding of the mechanism of carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1954 Aug;14(7):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Driedger P. E., Rossow P. W. Effect of a phorbol ester on a transformation-sensitive surface protein of chick fibroblasts. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):446–447. doi: 10.1038/264446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutwell R. K. The function and mechanism of promoters of carcinogenesis. CRC Crit Rev Toxicol. 1974 Jan;2(4):419–443. doi: 10.3109/10408447309025704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Hochman P. S. Do natural killer cells engage in regulated reactions against self to ensure homeostasis? Immunol Rev. 1979;44:13–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R., Shirley P. S., Johnston R. B., Jr Effect of phorbol myristate acetate on the oxidative metabolism of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Blood. 1976 Apr;47(4):545–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger P. E., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of phorbol ester tumor promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):567–571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., DeHoogh D. K., Cole C. F. Binding of [3H]12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate to intact human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1980 Apr;40(4):1119–1124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidlund M., Ojo E. A., Orn A., Wigzell H., Murgita R. A. Severe suppression of the B-cell system has no impact on the maturation of natural killer cells in mice. Scand J Immunol. 1979;9(2):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. G., Weigle W. O. Modulation of lymphocyte activation. I. Inhibition by an oxidation product of arachidonic acid. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):593–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliotis T., Roder J., Klein M., Ortaldo J., Fauci A. S., Herberman R. B. Chédiak-Higashi gene in humans I. Impairment of natural-killer function. J Exp Med. 1980 May 1;151(5):1039–1048. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.5.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller O., Hansson M., Kiessling R., Wigzell H. Role of non-conventional natural killer cells in resistance against syngeneic tumour cells in vivo. Nature. 1977 Dec 15;270(5638):609–611. doi: 10.1038/270609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker E. Cocarcinogenic principles from the seed oil of Croton tiglium and from other Euphorbiaceae. Cancer Res. 1968 Nov;28(11):2338–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Holden H. T., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. II. Characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):230–239. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Godzik C. A., Cohn Z. A. Increased superoxide anion production by immunologically activated and chemically elicited macrophages. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):115–127. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller R. Suppression of natural antitumour defence mechanisms by phorbol esters. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):729–731. doi: 10.1038/282729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Pross H., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):117–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzel V., Kreibich G., Hecker E., Süss R. Stimulation of choline incorporation in cell cultures by phorbol derivatives and its correlation with their irritant and tumor-promoting activity. Cancer Res. 1979 Jul;39(7 Pt 1):2743–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopelovich L., Bias N. E., Helson L. Tumour promoter alone induces neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts from humans genetically predisposed to cancer. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):619–621. doi: 10.1038/282619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasne C., Gentil A., Chouroulinkov I. Two-stage malignant transformation of rat fibroblasts in tissue culture. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):490–491. doi: 10.1038/247490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. K., Schmied R., Waxman S. 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate release of glycosyltransferases from human blood cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jun;65(6):1365–1371. doi: 10.1172/JCI109800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotem J., Sachs L. Regulation of normal differentiation in mouse and human myeloid leukemic cells by phorbol esters and the mechanism of tumor promotion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondal S., Heidelberger C. Transformation of C3H/10T1/2CL8 mouse embryo fibroblasts by ultraviolet irradiation and a phorbol ester. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):710–711. doi: 10.1038/260710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Brukner L. H., Silverstein S. C., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. I. Pharmacologic triggering of effector cells and the release of hydrogen peroxide. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):84–99. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Root R. K. Hydrogen peroxide release from mouse peritoneal macrophages: dependence on sequential activation and triggering. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1648–1662. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Silverstein S. C., Brukner L. H., Cohn Z. A. Extracellular cytolysis by activated macrophages and granulocytes. II. Hydrogen peroxide as a mediator of cytotoxicity. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):100–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Metabolism of tritium-labeled 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate by cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2562–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape G. R., Moretta L., Troye M., Perlmann P. Natural cytotoxicity of human Fc gamma-receptor-positive T lymphocytes after surface modulation with immune complexes. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):291–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02734.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raick A. N., Burdzy K. Ultrastructural and biochemical changes induced in mouse epidermis by a hyperplastic agent, ethylphenylpropiolate. Cancer Res. 1973 Oct;33(10):2221–2230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkin D. B., Crowe R. M., Pollack R. Tumor promoters induce changes in the chick embryo fibroblast cytoskeleton. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Tumor promoters inhibit spontaneous differentiation of Friend erythroleukemia cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2894–2898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela E., Timonen T., Ranki A., Häyry P. Morphological and functional characterization of isolated effector cells responsible for human natural killer activity to fetal fibroblasts and to cultured cell line targets. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:71–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of activation of human natural killer cells against tumor and virus-infected cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:125–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seaman W. E., Blackman M. A., Gindhart T. D., Roubinian J. R., Loeb J. M., Talal N. beta-Estradiol reduces natural killer cells in mice. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2193–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talmadge J. E., Meyers K. M., Prieur D. J., Starkey J. R. Role of NK cells in tumour growth and metastasis in beige mice. Nature. 1980 Apr 17;284(5757):622–624. doi: 10.1038/284622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touraine J. L., Hadden J. W., Touraine F., Hadden E. M., Estensen R., Good R. A. Phorbol myristate acetate: a mitogen selective for a T-lymphocyte subpopulation. J Exp Med. 1977 Feb 1;145(2):460–465. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.2.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trosko J. E., Chang C. C. Environmental carcinogenesis: an integrative model. Q Rev Biol. 1978 Jun;53(2):115–141. doi: 10.1086/410451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West W. H., Cannon G. B., Kay H. D., Bonnard G. D., Herberman R. B. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of human lymphocytes against a myeloid cell line: characterization of effector cells. J Immunol. 1977 Jan;118(1):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., zur Hausen H. Tumour promoter TPA enhances transformation of human leukocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):244–245. doi: 10.1038/280244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotti L. P., Chang C. C., Trosko J. E. Elimination of metabolic cooperation in Chinese hamster cells by a tumor promoter. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.493994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


