Abstract
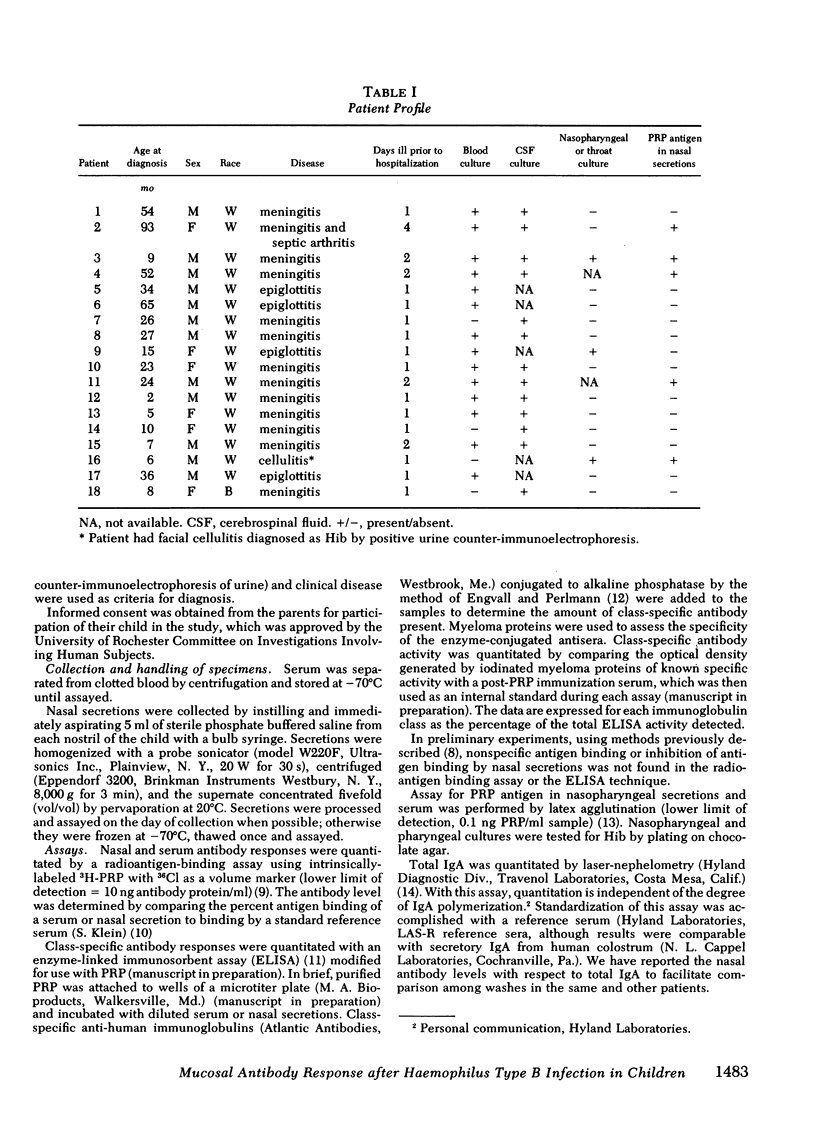
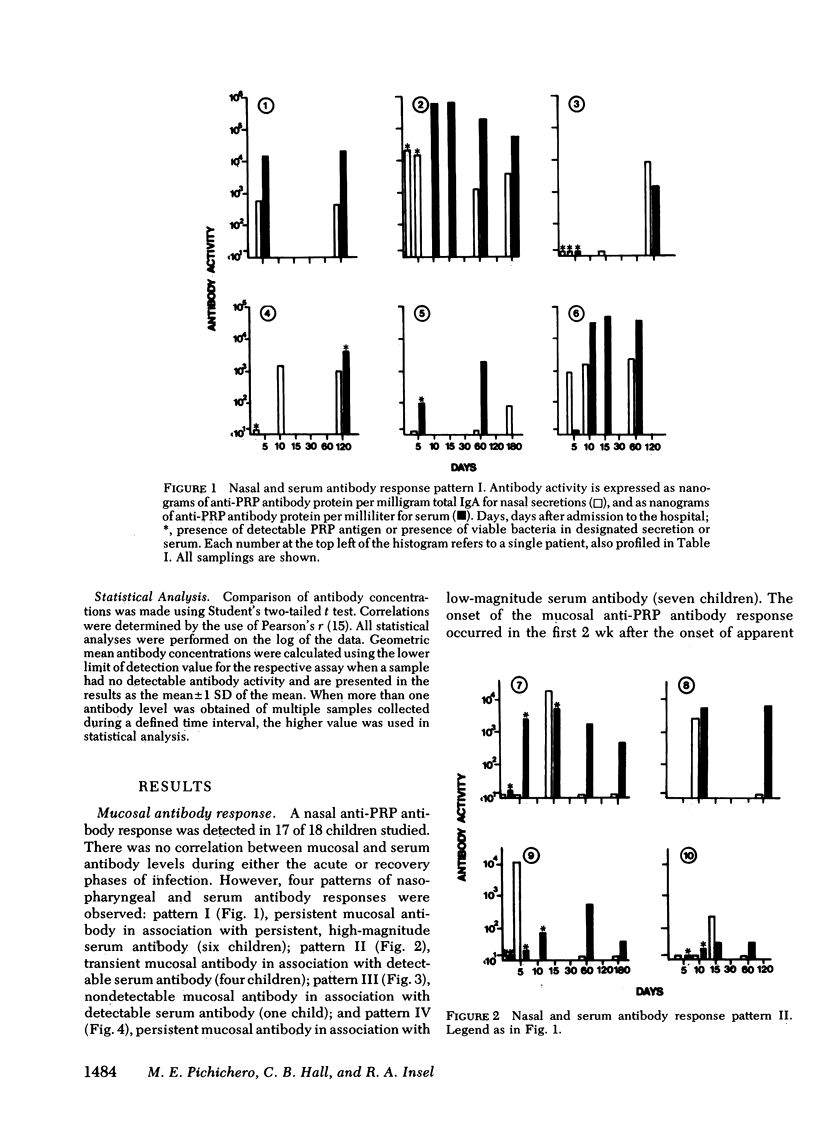
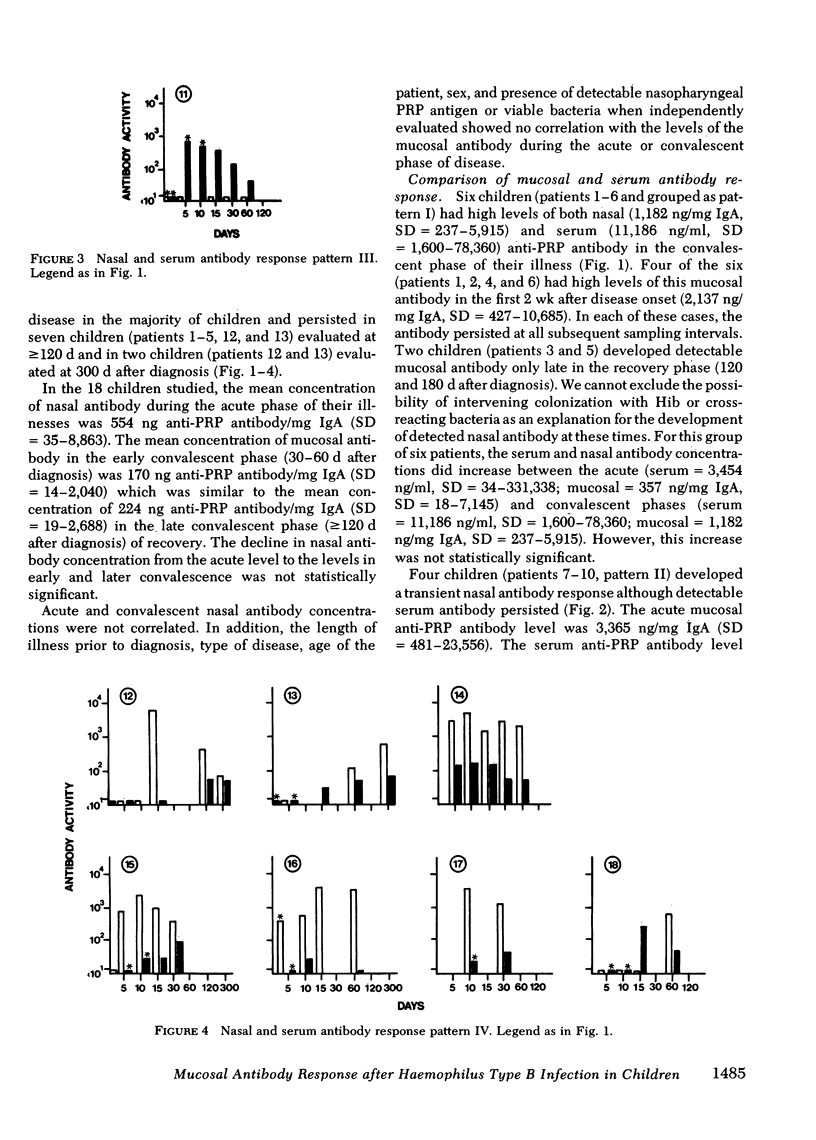
The possibility that mucosal antibody is produced as a host response to Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) infection was examined in this study. 17 of 18 prospectively evaluated children ranging in age from 2 mo to 7 yr developed a detectable level of anticapsular antibody in their nasopharyngeal secretions after systemic Hib infection. The mean concentration of nasal anti-capsular antibody of the 18 children was 554 ng/mg IgA (SD = 35-8,863) during the acute phase of illness and declined to 224 ng/mg IgA (SD = 19-2,688) in convalescence. Some children had mucosal antibody detectable at least 10 mo after infection. The mucosal antibody levels were not affected by the length of illness before diagnosis, type of disease, age of the patient, sex, or presence of detectable capsular antigen or viable bacteria in the nasopharynx. The mucosal antibody was predominantly of the IgA class and occurred independent of the serum antibody. Six of the children aged less than 1 yr who did not produce and/or sustain a serum antibody level correlated with protection demonstrated a persistent mucosal antibody response. These findings suggest that the mucosal immune system may have the ability to respond at an earlier age than the serum immune system and lead us to postulate that protective secretory antibodies to prevent systemic Hib disease may be inducible in young infants in spite of the poor serum antibody response occurring at this age.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson P. Intrinsic tritium labeling of the capsular polysaccharide antigen of Haemophilus influenzae type B. J Immunol. 1978 Mar;120(3):866–870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson P., Peter G., Johnston R. B., Jr, Wetterlow L. H., Smith D. H. Immunization of humans with polyribophosphate, the capsular antigen of Hemophilus influenzae, type b. J Clin Invest. 1972 Jan;51(1):39–44. doi: 10.1172/JCI106794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantey J. R. Prevention of bacterial infections of mucosal surfaces by immune secretory IgA. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:461–470. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanock R. M., Wyatt R. G., Kapikian A. Z. Immunization of infants and young children against rotaviral gastroenteritis--prospects and problems. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):570–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa. 3. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol. 1972 Jul;109(1):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fubara E. S., Freter R. Protection against enteric bacterial infection by secretory IgA antibodies. J Immunol. 1973 Aug;111(2):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneberg B., Tonder O. Immunoglobulins and other serum proteins in feces from infants and children. Scand J Immunol. 1973;2(4):375–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb02046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth J. C., Dilling L. Concentration of gamma-A-globulin in serum, saliva, and nasopharyngeal secretions of infants and children. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jun;67(6):922–933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S., Holmgren J. Protective antitoxic cholera immunity in mice: influence of route and number of immunizations and mode of action of protective antibodies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand C. 1978 Aug;86C(4):145–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1978.tb02572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland D. B., Samson R. R., Parkin D. M., Shearman D. J. Bacterial agglutination studies with secretory IgA prepared from human gastrointestinal secretions and colostrum. Gut. 1972 Jun;13(6):450–458. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.6.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDermott M. R., Bienenstock J. Evidence for a common mucosal immunologic system. I. Migration of B immunoblasts into intestinal, respiratory, and genital tissues. J Immunol. 1979 May;122(5):1892–1898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay E., Thom H. Observations on neonatal tears. J Pediatr. 1969 Dec;75(6):1245–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(69)80380-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery P. C., Connelly K. M., Cohn J., Skandera C. A. Remote-site stimulation of secretory IgA antibodies following bronchial and gastric stimulation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;107:113–122. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3369-2_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Anderson P. Meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae in infant rats: protective immunity and antibody priming by gastrointestinal colonization with Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):471–478. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxon E. R., Smith A. L., Averill D. R., Smith D. H. Haemophilus influenzae meningitis in infant rats after intranasal inoculation. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):154–162. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman R. B., Stevens R. W., Gaafar H. A. Latex agglutination test for the diagnosis of Haemophilus influenzae meningitis. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Jul;76(1):107–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Anderson P., Ingram D. L., Peter G., Smith D. H. Circulating polyribophosphate in Hemophilus influenzae, type b meningitis. Correlation with clinical course and antibody response. J Clin Invest. 1975 Oct;56(4):1012–1022. doi: 10.1172/JCI108148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peltola H., Käyhty H., Sivonen A., Mäkelä H. Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide vaccine in children: a double-blind field study of 100,000 vaccinees 3 months to 5 years of age in Finland. Pediatrics. 1977 Nov;60(5):730–737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichichero M. E., Sommerfelt A. E., Steinhoff M. C., Insel R. A. Breast milk antibody to the capsular polysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):694–698. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Gowans J. L. Cellular kinetics of the intestinal immune response to cholera toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1550–1563. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Parke J. C., Jr, Schneerson R., Whisnant J. K. Quantitative measurement of "natural" and immunization-induced Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Pediatr Res. 1973 Mar;7(3):103–110. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197303000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliep G., Felgenhauer K. Rapid determination of proteins in serum and cerebrospinal fluid by laser-nephelometry. J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 1978 Nov;16(11):631–635. doi: 10.1515/cclm.1978.16.11.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Robbins J. B. Induction of serum Haemophilus influenzae type B capsular antibodies in adult volunteers fed cross-reacting Escherichia coli 075:K100:H5. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 22;292(21):1093–1096. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505222922103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneerson R., Rodrigues L. P., Parke J. C., Jr, Robbins J. B. Immunity to disease caused by Hemophilus influenzae type b. II. Specificity and some biologic characteristics of "natural," infection-acquired, and immunization-induced antibodies to the capsular polysaccharide of Hemophilus influenzae type b. J Immunol. 1971 Oct;107(4):1081–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selner J. C., Merrill D. A., Claman H. N. Salivary immunoglobulin and albumin: development during the newborn period. J Pediatr. 1968 May;72(5):685–689. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(68)80014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Potter C. W., McLaren C. Immunity to influenza in ferrets. IV. Antibody in nasal secretions. J Infect Dis. 1972 Oct;126(4):394–400. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.4.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svennerholm A. M., Holmgren J., Hanson L. A., Lindblad B. S., Quereshi F., Rahimtoola R. J. Boosting of secretory IgA antibody responses in man by parenteral cholera vaccination. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(12):1345–1349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Larson L., Challacombe S., McNabb P. Mucosal immunity: The origin and migration patterns of cells in the secretory system. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1980 Jan;65(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(80)90171-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Ganguly R. The role of the secretory immune system in protection against agents which infect the respiratory tract. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1974;45(0):283–294. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-4550-3_34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz-Carrington P., Roux M. E., McWilliams M., PHILLIPS-Quagliata J. M., Lamm M. E. Organ and isotype distribution of plasma cells producing specific antibody after oral immunization: evidence for a generalized secretory immune system. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1705–1708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Gibbons R. J. Inhibition of bacterial adherence by secretory immunoglobulin A: a mechanism of antigen disposal. Science. 1972 Aug 25;177(4050):697–699. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4050.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



