Abstract
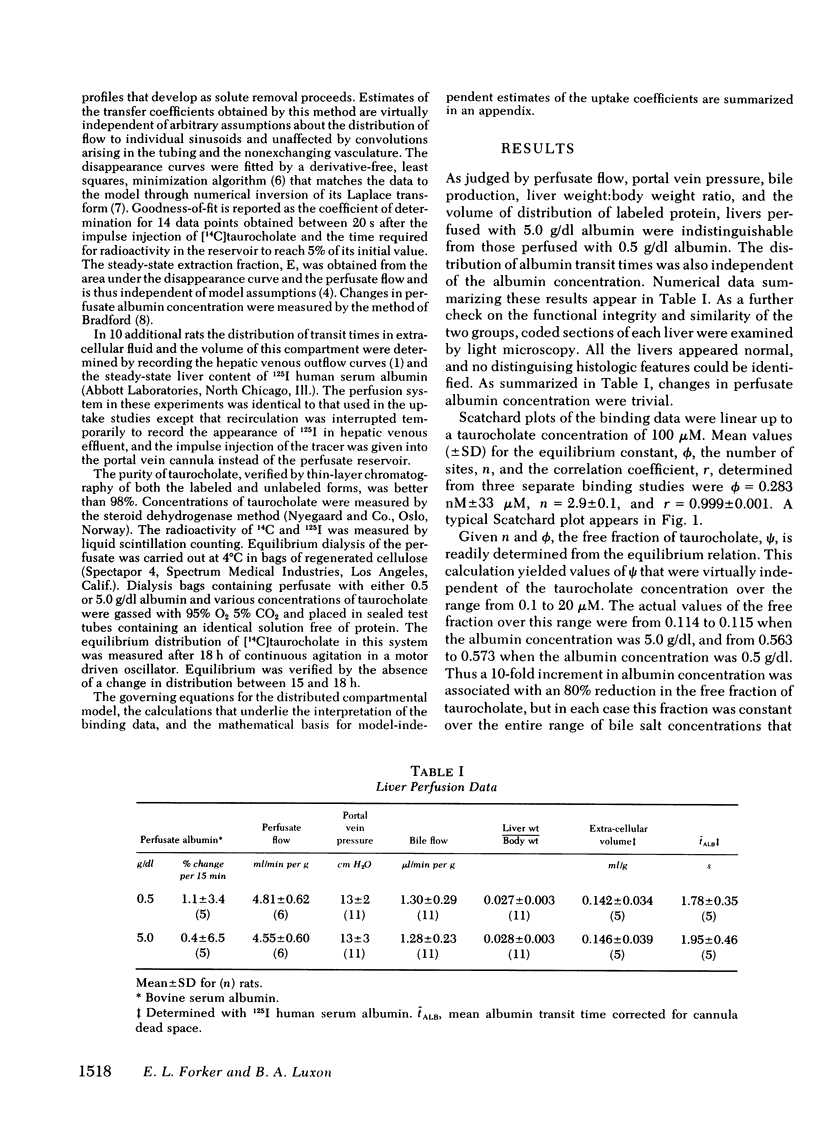
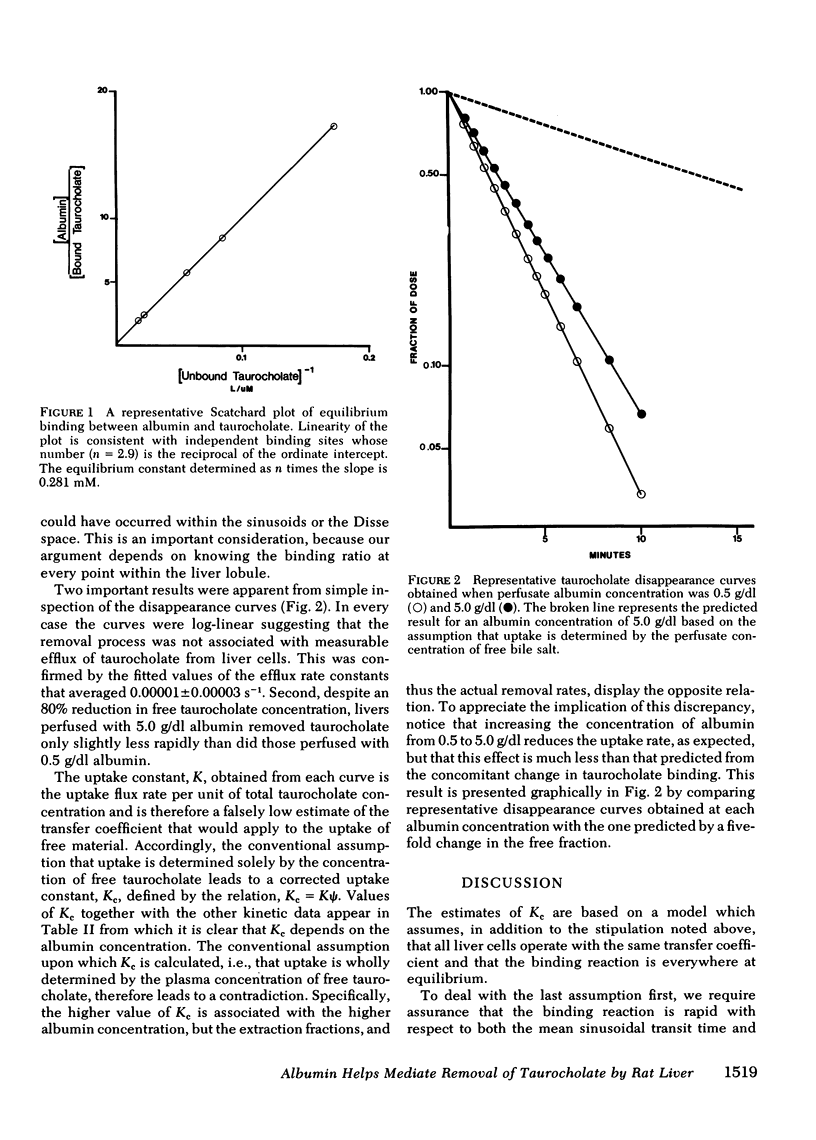
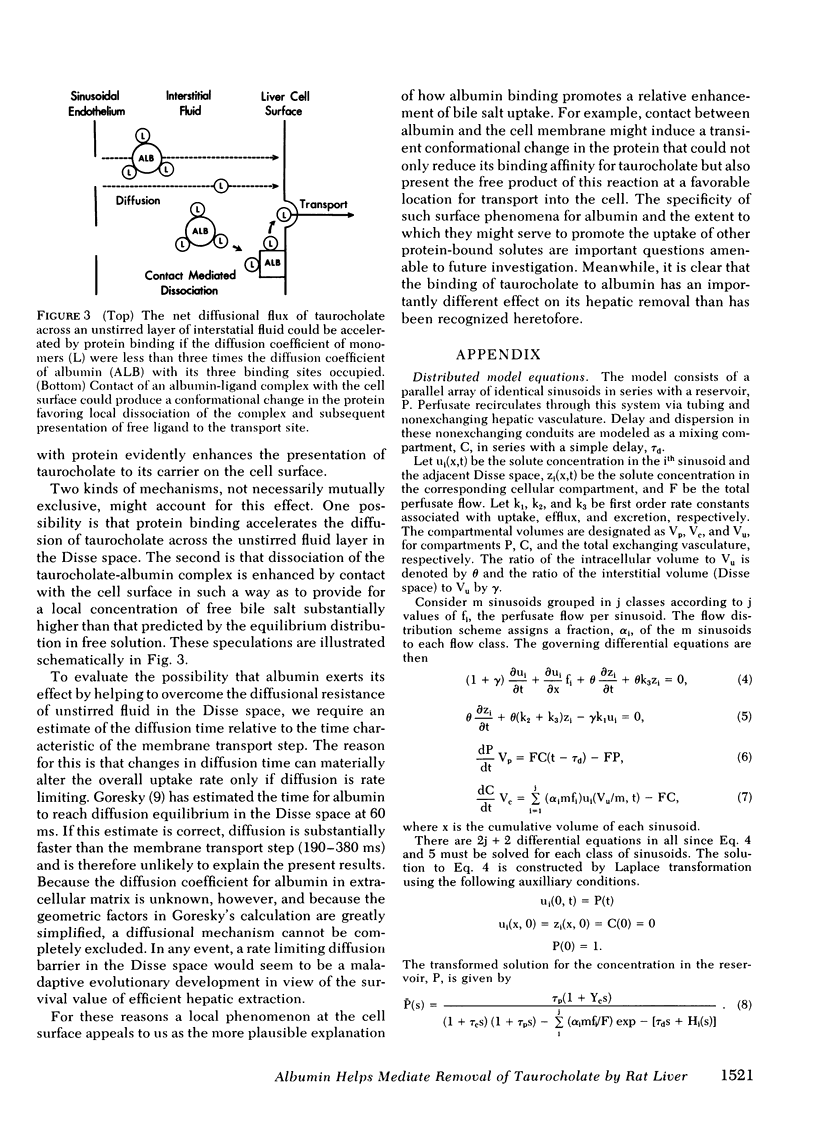
Perfused rat liver removes 97% of the taurocholate from the afferent circulation when the perfusate albumin concentration is 0.5 g/dl. Increasing the albumin concentration 10-fold reduces the concentration of free taurocholate by a factor of five but produces only a 50% reduction in the apparent uptake coefficient. A similar discrepancy is evident from a model-independent analysis of the extraction fractions. From these observations we argue that uptake is not driven solely, or even predominantly, by the plasma concentration of free taurocholate but also depends on interaction between albumin and the cell surface. Nonequilibrium binding, saturation kinetics, and an inhomogeneous population of liver cells are considered as alternative explanations and excluded. The possibility that albumin exerts its effect by enhancing the diffusion of taurocholate across an unstirred layer in the Disse space appears improbable but cannot be eliminated.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EIGEN M., HAMMES G. G. ELEMENTARY STEPS IN ENZYME REACTIONS (AS STUDIED BY RELAXATION SPECTROMETRY). Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1963;25:1–38. doi: 10.1002/9780470122709.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forker E. L., Luxon B. Hepatic transport kinetics and plasma disappearance curves: distributed modeling versus conventional approach. Am J Physiol. 1978 Dec;235(6):E648–E660. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.6.E648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORESKY C. A. A linear method for determining liver sinusoidal and extravascular volumes. Am J Physiol. 1963 Apr;204:626–640. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Kinetics of taurocholate uptake by the perfused rat liver. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):132–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichen J., Paumgartner G. Uptake of bile acids by perfused rat liver. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):734–742. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand D. G., Cotham R. H., Wilkinson G. R. Perfusion-limited of plasma drug binding on hepatic drug extraction. Life Sci. 1976 Jul 1;19(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson G. R., Shand D. G. Commentary: a physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Oct;18(4):377–390. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975184377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



