Abstract
Anterioposterior vertebrate limb patterning is controlled by opposing action between Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) and the Gli3 transcriptional repressor. Unexpectedly, Gli3Δ699 mutant mice, which are thought to express only a Gli3 repressor and not the full-length activator, exhibit limb phenotypes inconsistent with those of Shh mutant mice. Therefore, it remains debatable whether Shh patterns the anterioposterior limb primarily by inhibiting generation of the Gli3 repressor. However, one caveat is that Gli3Δ699 may not be as potent as the natural form of Gli3 repressor because of the nature of the mutant allele. In the present study, we created a conditional Gli3 mutant allele that exclusively expresses Gli3 repressor in the presence of Cre recombinase. Using this mutant, we show that the phenotypes of mouse limbs expressing only the Gli3 repressor exhibit no or single digit, resembling those of Shh mutant limbs. Consistent with the limb phenotypes, the expression of genes dependent on Shh signaling is also inhibited in both mutants. This inhibition by the Gli3 repressor is independent of Shh. Thus, our study clarifies the current controversy and provides important genetic evidence to support the hypothesis that Shh patterns the anterioposterior limb primarily through the inhibition of Gli3 repressor formation.
Keywords: Hedgehog, Gli3, limb patterning
Introduction
Anterioposterior (A/P) patterning of the vertebrate limb is controlled by Sonic Hedgehog (Shh). Shh is expressed in the posterior margin of the developing vertebrate limb bud, known as the zone of polarizing activity (ZPA). The secreted Shh is transported away from the ZPA and forms a gradient along the A/P axis of the limb (Riddle et al., 1993). This Shh protein gradient is thought to determine limb digit number and identity. Consistent with this view, Shh mutant mouse embryos have no digits in the forelimb and lack all but the first digit in the hind limb (Chiang et al., 2001; Chiang et al., 1996; Kraus et al., 2001). Conversely, either the graft of ZPA, or implantation of cells expressing Shh or a Sepharose bead soaked in Shh to the anterior region of chicken limb buds produces mirror-image duplicated limb digits (Lopez-Martinez et al., 1995; Riddle et al., 1993; Yang et al., 1997).
In vertebrates, Shh signaling is mediated by three Gli transcriptional factors: Gli1, Gli2, and Gli3. In the absence of Hh signaling, the majority of Gli3 full-length protein, Gli3FL, is proteolytically processed into a C-terminally truncated repressor, Gli3R, whereas only a small fraction of Gli2 full-length protein, Gli2FL, is processed into a repressor, Gli2R (Pan et al., 2006; Wang et al., 2000). Both Gli2 and Gli3 processing is triggered by the phosphorylation of four serine/threonine residues at their C-termini by protein kinase A (PKA). Shh signaling suppresses Gli2 and Gli3 processing and converts them into activators, Gli2A and Gli3A, in a concentration-dependent manner (Tempe et al., 2006; Wang and Li, 2006). Thus, in the developing vertebrate limbs, Gli3R levels, presumably as well as Gli2R levels, are graded from the highest in the anterior to the lowest in the posterior, while Gli3A and Gli2A levels or activities form a reverse gradient along the A/P axis (Wang et al., 2000). Perturbation of Gli3A and/or Gli3R gradients results in abnormal limb patterning (Wang et al., 2007a; Wang et al., 2007b).
Gli1 gene function is dispensable for mouse embryogenesis (Park et al., 2000). Despite severe defects in central nervous system patterning, mice homozygous for Gli2 null mutation exhibit normal limb patterning (Ding et al., 1998; Matise et al., 1998; Mo et al., 1997). In contrast, mice homozygous for a Gli3 null mutant allele, Extratoe or Gli3Xt, are characterized by polysyndactylous and abnormal craniofacial phenotypes (Hui and Joyner, 1993). Several mutations in the human Gli3 gene are also associated with various defects in limb patterning (Biesecker, 1997; Vortkamp et al., 1991). Interestingly, mice lacking both Gli3 and Shh gene functions exhibit limb phenotypes indistinguishable from those of mice lacking Gli3 gene function alone (Litingtung et al., 2002; te Welscher et al., 2002b). These observations have led to the prevailing model that the regulation of A/P limb patterning by Shh signaling is mostly through Gli3. The Gli3R is to restrict the pattern formation of polydactylous digits, while Shh serves to promote the patterning of multiple digits by inhibiting Gli3 processing and creating Gli3A. A precisely balanced counteraction between Shh and Gli3 establishes normal patterning of vertebrate limb digit number and identity. Based on this model, mice that express Gli3R alone are expected to develop limbs with a single digit, reminiscent of Shh mutant limb phenotypes. Unexpectedly, Gli3Δ699 homozygous mice, which are thought to express only a Gli3 repressor, display limbs with four to six digits (Hill et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2007a). However, the interpretation of Gli3Δ699 mutant limb phenotypes requires caution. The Gli3Δ699 expresses a fusion protein containing the first 699 amino acid residues of the Gli3 protein and extra 21 residues from the thymidine kinase (TK) gene sequence used for generating the mutant allele (Bose et al., 2002). Thus, it is possible that the repressing activity of Gli3Δ699 protein may not be as potent as that of the natural Gli3R. By design, Gli3Δ699 mutant may also potentially express more than one protein product, and insertion of the pGKneo cassette may affect the levels of Gli3 gene expression. Therefore, it remains to be determined whether Shh does in fact pattern the A/P limb by inhibiting generation of Gli3R.
To address this important question, we generated a conditional Gli3 repressor mutant allele called Gli3Δ701C (see below). This allele is likely to be ‘cleaner’ than the Gli3Δ699 allele, since it expresses a predicted Gli3R and does not contain the pGKneo cassette initially used for gene targeting. When bred with transgenic animals expressing Cre in the developing limbs, mice heterozygous for Gli3Δ701C displayed oligosyndactylous phenotypes in both the forelimbs and hindlimbs. Surprisingly, Gli3Δ701C homozygous forelimb autopods expressing only the Gli3Δ701 repressor failed to generate any digits, and they instead presented with a single distal cartilage element. Meanwhile the mutant hindlimb autopods were composed of three digits due to inefficient Cre expression (see explanation below). Thus, the mutant forelimb phenotypes resemble those of the Shh mutant. In addition, in situ hybridization analysis revealed that the expression of several known limb-patterning genes dependent on Shh was inhibited in the Gli3Δ701 mutant limb, similar to that of the Shh mutant. Therefore, these results indicate that Shh mutant limb phenotype results from the expression of Gli3R, which supports the hypothesis that Shh directs A/P limb patterning by inhibiting Gli3R generation.
Materials and Methods
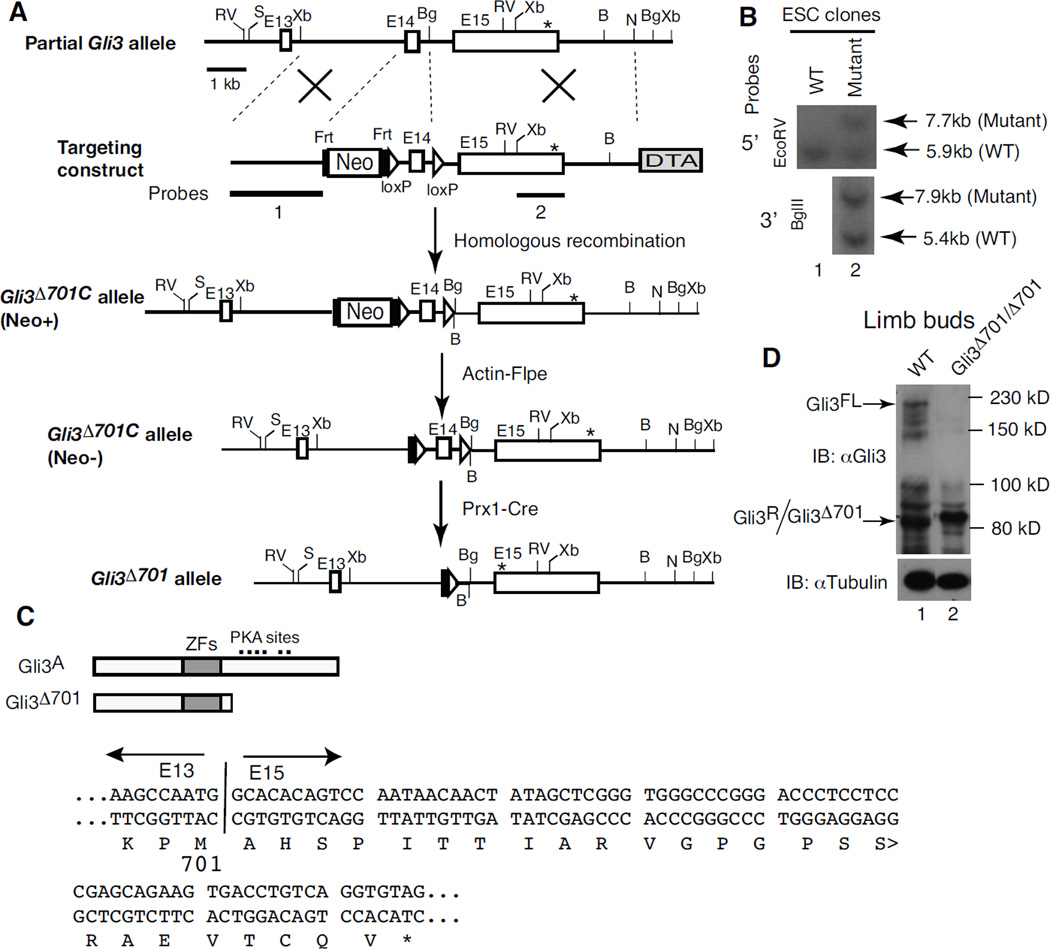
Mouse strains and the generation of Gli3Δ701C mutant mice
A BAC clone containing mouse Gli3 genomic DNA sequences was purchased from Genome Systems Inc, UK. The Gli3Δ701C targeting construct was generated by using the relevant Gli3 genomic sequence from the BAC clone and the pGKneo2frt.loxP.DTA.2 vector, which was constructed from the pGKneoloxP2.DTA.2 vector (Soriano, 1997). The Gli3Δ701C targeting construct included the pGKneo2frt.loxP cassette and a loxP site inserted into the two introns flanking exon 14 of the mouse Gli3 gene. The Gli3Δ701C construct was then introduced into W4 ES cells (Taconic Farms, Inc.) (Auerbach et al., 2000) by electroporation, and neomycin-resistant clones were selected by incubating cells in ES cell growth medium containing G418 (150 µg/ml). Targeted ES cell clones were identified by restriction enzyme digestion, followed by Southern blot analysis of ES cell DNA using a 5' and a 3' probes. The 5' probe identified a 7.7 kb fragment in the targeted allele and a 5.9 kb fragment in the wild type (wt) allele following EcoRV digestion. The 3' probe identified a 7.9 kb fragment in the targeted allele and a 5.4 kb fragment in the wt allele following BglII digestion. Several targeted clones were obtained, two of which were injected into C57BL/6 blastocysts to generate chimeric founders. These mice were then bred with C57BL/6 to establish F1 Gli3Δ701C(+neo) heterozygotes. The pGKneo cassette was removed by breeding the mice with Actin-Flpe transgenic mice (obtained from Licia Selleri). This resulted in the Gli3Δ701C allele used in this study. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis was used for routine genotyping with the following primers: BW892F, 5’-AATGGAATGTTTCCAAGACTG -3’, and BW892R, 5’-ATAAAACCAAGGGTTCCAGATC-3’, each of which flanks the second loxP site. The predicted size of the PCR fragments was 180 bp for the wt allele and about 250 bp for the mutant.
Shh and Gli3Δ699 mutant mice were originally obtained from Philip Beachy and Ulrich Ruther, respectively, and Prx1-Cre mice were purchased from Jackson laboratories and genotyped as described (Bose et al., 2002; Chiang et al., 1996; Logan et al., 2002). All mice used in this study were in a 129sve and C57BL/6 mixed background and were manipulated according to NIH regulation.
Immunoblotting, whole mount in situ hybridization, and skeleton preparation
Immunoblotting was performed using the Gli3 antibody, which recognizes Gli3-396-495aa, as described (Wang et al., 2000). Whole mount in situ hybridization was carried out according to a published protocol (Wilkinson, 1992), and the skeletons were prepared as described (Nagy et al., 2003).
Results and Discussion
Generation of a conditional Gli3 mutant allele expressing only the Gli3 repressor
Based on the hypothesis that the counteraction between Shh and Gli3 controls A/P limb patterning, one would predict that mouse limbs expressing only the Gli3R should exhibit phenotypes that resemble those of Shh mutant limbs, that is, either a single or no digit. Unexpectedly, Gli3Δ699 mutant mice, which are thought to express a Gli3 repressor, exhibit variably four to six digits (Hill et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2007b). To clarify this controversy, we used a targeted gene knock-in approach to create the conditional Gli3Δ701C mutant allele, in which exon 14 of the Gli3 gene is flanked by two loxP sites in introns (Fig. 1A, B). Thus, exon 14 is deleted only in the presence of Cre protein, causing a reading frame shift expected to result in premature termination of protein translation. Consequently, the protein product of the mutant allele is expected to contain the first 701 residues of Gli3 protein and additional 25 artificial residues (Fig. 1C).
Figure 1. The generation of a conditional Gli3 allele (Gli3Δ701C) expressing only the Gli3 repressor.
(A) The gene targeting strategy used to create the Gli3Δ701C allele and screen for mutant ES cell clones. Exons are represented by open rectangles and introns by lines. Exons are numbered based on the full-length Gli3 RNA transcript. pGKneo, Frt, loxP, and DTA sequences are indicated. The asterisk represents a stop codon. The relevant restriction sites are: Bg, BglII; RV, EcoRV; N, NheI; S, SacII; Xb, XbaI. (B) Southern blot analysis of representative ES cell (ESC) clones using the 5'- and 3'-probes shown in A. (C) Diagrams of the predicted full-length Gli3 and Gli3Δ701 mutant proteins. The zinc finger DNA-binding domain (ZFs) is represented by grey rectangles, and protein kinase A (PKA) phosphorylation sites by dots. The sequences of the predicted Gli3Δ701 cDNA and amino acid residues are shown below. Amino acid residues starting from exon 15 (E15) are artificial and caused by an open reading frame shift. The junction between exons 13 and 15 upon deletion of exon 14 and the stop codon are marked by a vertical line and an asterisk, respectively. (D) Immunoblots showing that the mutant limb buds expressed only Gli3Δ701 repressor, as predicted. Protein lysates were made from limb buds of E10.5 wt or Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre embryos and immunoblotted with a Gli3 antibody, with α–tubulin as a loading control. Gli3FL, Gli3R, and Gli3Δ701 are indicated by arrows, with molecular weight markers to the right.
To test whether the mutant allele worked as designed, the Gli3Δ701C mutant mice were crossed with Prx1-Cre transgenic mice, which express Cre protein in developing limbs and craniofacial areas and has been widely used for the study of limb patterning (Kmita et al., 2005; Logan et al., 2002). Exon 14 of the Gli3 gene was therefore deleted in the Cre-expressing tissues of the resulting Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre mice, hereafter referred to as Gli3Δ701/Δ701. Limb buds were then collected from Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and wild type (wt) mouse embryos at stage E10.5 and subjected to immunoblotting analysis using a Gli3 antibody (Wang et al., 2000). As expected, while the wt limb buds expressed both Gli3FL and Gli3R, the mutant limb buds expressed only a Gli3 repressor slightly larger than the Gli3R in size and is designated as Gli3Δ701 (Fig.1D). Therefore, the Gli3Δ701C allele behaved as designed.
Gli3+/Δ701 mutant limb phenotypes
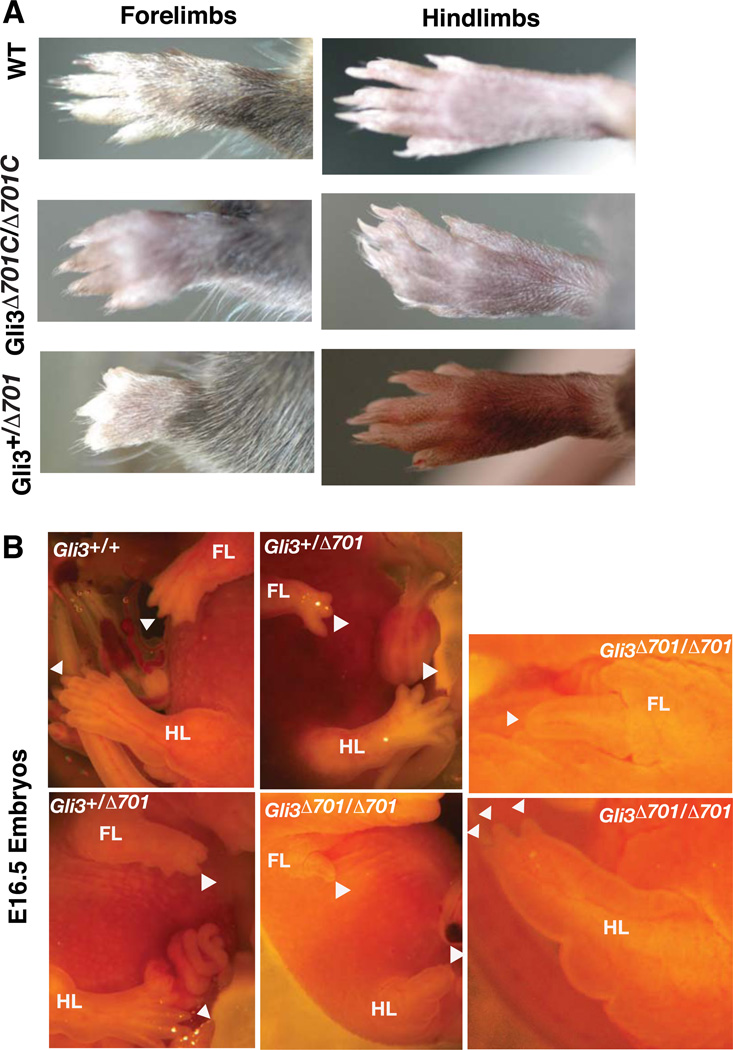
Adult mice homozygous for Gli3Δ701C were alive, fertile, and without any noticeable abnormal phenotypes. These mice were crossed with Prx1-Cre transgenic mice to produce Gli3+/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre animals, hereafter referred to as Gli3+/Δ701. Surprisingly, Gli3+/Δ701 forelimbs were significantly shorter with consistently smaller autopods than those of wt or Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C mice. The digits appeared fused (or syndactylous) and shorter, making it difficult to accurately determine digit number. Unlike the forelimb autopods, the hindlimb autopods of about half of the Gli3+/Δ701 mice (16 out of 30) were normal, and the other half exhibited fused digits. No significant changes in the hindlimb length were noticed (Fig. 2A). These adult limb phenotypes were also found in E16.5 or older mouse embryos (Fig. 2B). The difference between forelimb and hindlimb phenotypes is unlikely to be caused by differential dependencies on Gli3 function, but rather by the differential Cre expression. It has been shown that Cre expression in the forelimbs of Prx1-Cre embryos begins to strengthen at E9.5 and is detected throughout the mesenchymal cells at this stage onward. However, Cre expression in the hindlimb buds of E9.5 embryos is barely detectable. By 10.5, weak expression is only detected in some of mesenchymal cells. By E11.5 and onward, Cre expression is increased and detected throughout mesenchymal cells (Logan et al., 2002).
Figure 2. The limb phenotypes of Gli3Δ701 mutant mice.
(A) The limb phenotypes of adult mice with the genotypes indicated to the left. Gli3Δ701C refers to the conditional allele prior to the deletion of exon 14, while Gli3Δ701 refers to the same allele in the presence of Prx1-Cre. Only left limbs are shown with the anterior at the top and the posterior at the bottom. Note that the Gli3+/Δ701 forelimb appears short and the autopod is oligosyndactylous, while the hindlimb appears normal. The same magnification is applied to all panels. (B) The limb phenotypes of E16.5 embryos with the indicated genotypes. Limb autopods are indicated by arrowheads. An enlargement of the forelimb (FL) and hindlimb (HL) appears two panels to the right. Note the very short limbs with a single (in FL) or seemingly three digits (in HL) in Gli3Δ701 homozygotes.
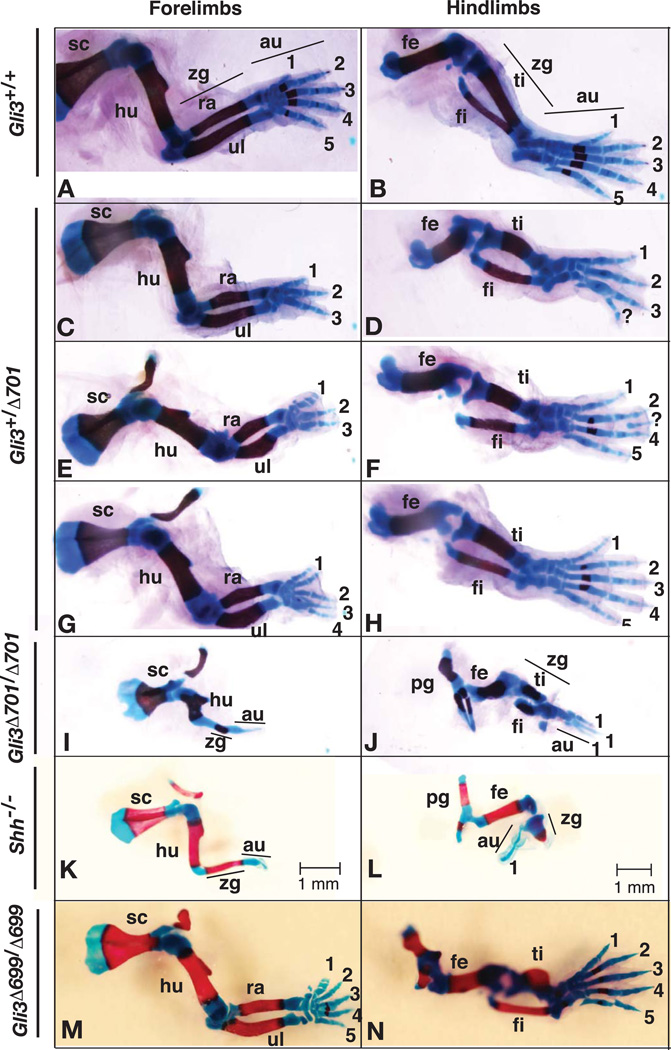
To determine the digit number and patterning of Gli3+/Δ701 limbs, the skeletons of mouse embryos at E16.5 (n = 4) were prepared and analyzed in order to match developmental stages of Shh mutants (see below). As predicted, the Gli3+/Δ701 mutant forelimb autopods were much smaller than those of wt animals. Digit number varied from three to five, some of which were fused. Most, if not all of the digits, were identifiable. Ossification was barely noticeable as digits were made up of cartilage. In addition, the forelimb zeugopod elements, the radius and ulna, were bent and much shorter than those of wt. Similarly, both the distal scapula and humerus appeared slightly shorter than those of wt (Fig. 3, compare C, E, G to A). On the other hand, the hindlimb autopods of about half of Gli3+/Δ701 mice (2 out of 5) were normal, and the rest exhibited three to five digits, some of which were fused or partial. The femur, tibia, and fibula of Gli3+/Δ701 embryos were all slightly shorter than those of wt, but their patterning appeared normal (Fig. 3, compare D, F, H to B).
Figure 3. Skeletal stains of wt, Gli3Δ701, Gli3Δ699, and Shh mutant limbs.
Skeletons were prepared from E16.5 embryos. The right limbs are shown with the anterior at the top and posterior at the bottom. Genotypes are indicated to the left, and Gli3+/Δ701 and Gli3Δ701/Δ701 are referred to as Gli3+/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre and Gli3Δ701/Δ701; Prx1-Cre, respectively. In Gli3Δ701 heterozygous limbs (C, E, G), the scapula (sc) is slightly shorter than that of wt limbs (A), and the radius (ra) and ulna (ul) are much shorter and bent. The femur (fe), tibia (ti), and fibula (fi) are also significantly shorter (compare D, F, H to B). Digit number in both the forelimbs and hindlimbs varies, and syndactyly is often found in the forelimbs. Forelimb autopods (au) often lack ossification (red). All bone elements of Gli3Δ701 homozygous forelimbs (I) are much shorter than those of Shh mutant forelimbs (K). The forelimb zeugopod (zg) and autopod are presented by a single bone element and cartilage (blue), respectively. All bone structures of Gli3Δ701 homozygous hindlimbs (J) are much or slightly shorter than those of wt (B) or Shh mutant (L) hindlimbs, respectively. The tibia and fibula are formed. Digit number varies from one to four. The autopod lacks ossification. The Shh mutant forelimb has a single zeugopod element and a single autopod cartilage element. The hindlimb zeugopod is presented by a single small cartilage with a single digit. The forelimb autopods of Gli3Δ699/Δ699 mice exhibit an additional digit and lack ossification (M). The tibia is significantly shorter (N). Sc, scapula; hu, humerus; pg, pelvic girdle; number, digit identity. Scale bars for forelimb and hindlimbs are shown.
The severe limb phenotypes of Gli3+/Δ701 mice were unexpected, since mice heterozygous for Gli3Δ699, which are also thought to express a Gli3 repressor form, are generally normal (Bose et al., 2002). In order to directly compare gene activity between Gli3Δ701 and Gli3Δ699, generation of Gli3+/Δ701C; Actin-Cre was attempted by crossing Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C or Gli3+/Δ701C with Actin-Cre transgenic animals. Since Cre is ubiquitously expressed in Actin-Cre animals, exon 14 of the Gli3 gene would then be deleted in the entire organism. Unfortunately, no Gli3+/Δ701C; Actin-Cre animals were recovered from the crosses (at least 70 mice genotyped), indicating that Gli3Δ701 heterozygotes are embryonically lethal. These results together demonstrate that the Gli3Δ701 allele produces a much more potent form of Gli3 repressor than the Gli3Δ699 allele.
There are at least three explanations for this difference. First, Gli3Δ701 and Gli3Δ699 may exhibit different transcriptional repressing activities, given the extra different amino acid residues in their C-termini. Second, the Gli3Δ699 allele may produce more than one protein. That is because the Gli3Δ699 allele was engineered by inserting a pGkneoNTRtkpA cassette into exon 14 of the Gli3 gene. By design, the allele was not originally predicted to express Gli3Δ699, but rather the first 744 amino acid residues of Gli3 plus some sequence from the cassette (Bose et al., 2002). Therefore, the Gli3Δ699 allele may express not only Gli3Δ699 that has been determined but also Gli3Δ744, which has not been determined. These two proteins are unlikely to be resolved by Western blot, as their predicted sizes are very similar (720 versus 744 residues). Gli3Δ744 may have less repressing activity than either Gli3Δ701 or Gli3Δ699, given its size greater than the naturally processed Gli3R. Third, the presence of the pGkneo cassette in exon 14 could potentially affect Gli3Δ699 expression level, while the cassette has been removed from the Gli3Δ701C allele.
The limb phenotypes of Gli3Δ701/Δ701 mice resemble those of Shh mutants
Having shown that Gli3Δ701 exhibits potent repressor function, we next used the Gli3Δ701 allele to test the hypothesis that Shh mutant limb phenotypes result from expression of Gli3 repressor. Based on this hypothesis, mouse limbs homozygous for Gli3Δ701 are expected to exhibit phenotypes reminiscent of those of Shh mutant limbs. We thus crossed Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C mice with Gli3+/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre animals to generate Gli3Δ701C/Δ701C; Prx1-Cre, or Gli3Δ701/Δ701 mice. All but two Gli3Δ701/Δ701 animals died before or immediately after birth. The lethality is likely to be attributed to the expression of Prx1-Cre transgene in tissues not in the limb such as those in the craniofacial region (Logan et al., 2002) and/or the mutant newborns’ inability to compete with their littermates for milk. The two that survived had extremely short limbs with a single digit in the forelimbs and one or three digits in the hindlimbs (data not shown). Similar limb phenotypes were also consistently observed in all embryos collected during late gestation stages. We thus decided to collect and prepare the skeletons of E16.5 embryos. This stage was also chosen because Shh mutant embryos, the control, die at various late gestation stages.
Gli3Δ701/Δ701 mutant forelimbs were consistently very short without obvious digit structure, regardless of the age of the embryos and newborns. The hindlimbs were also short, though not as significantly as the forelimbs. Most hindlimbs appeared to exhibit three digits, or occasionally only one (Fig. 2B, data not shown, n = 20). Analysis of limb skeletons confirmed these findings (n = 4). The forelimb autopods lacked all digits and were instead characterized by a single cartilage element. A single zeugopod element replaced the radius and ulna structures. All forelimb bone elements (the scapula, humerus, zeugopod, and autopods) were significantly shorter than those of wt. Surprisingly, they were also slightly shorter than those of Shh mutants. These phenotypes may potentially arise from an additional loss of Indian Hedgehog (Ihh) function (Karp et al., 2000). Although the length of the forelimb skeletal elements varied slightly depending on each individual, the pattern was invariable (Fig. 3I). Interestingly, the Gli3Δ701/Δ701 forelimb skeletal phenotypes resembled those of Shh mutant forelimbs (Fig. 3, compare I to K). The hindlimb phenotypes were more variable than those of the forelimb. This was most likely due to low levels of Cre in the hindlimbs, as previously reported (Logan et al., 2002). Most hindlimb autopods examined exhibited three identifiable first digits (Fig. 2B). Similarly, most Gli3Δ701/Δ701 hindlimb zeugopods and femurs were composed of very short tibia and fibula (Fig. 3J). Although these hindlimb phenotypes were not the same as those of Shh mutants due to the nature of Prx1-Cre, they did share a somewhat similar patterning (Fig. 3, compare J to L). In contrast, forelimb patterning of Gli3Δ699/Δ699mutants was largely normal, except for an additional fused digit and a lack of ossification. Hindlimb digit patterning was also normal, although the tibia was significantly shorter (Fig. 3M–N). Thus, Gli3Δ699/Δ699 limb phenotypes are significantly milder than those of Gli3Δ701/Δ701 mutants. Taken together, these results strongly indicate that Shh mutant limb phenotypes are the result of expression of Gli3 repressor in the mutant limbs, thus supporting the hypothesis that the balanced counteraction between Gli3 repressor and Shh activity controls A/P patterning.
The molecular basis of Gli3Δ701 mutant limb phenotypes
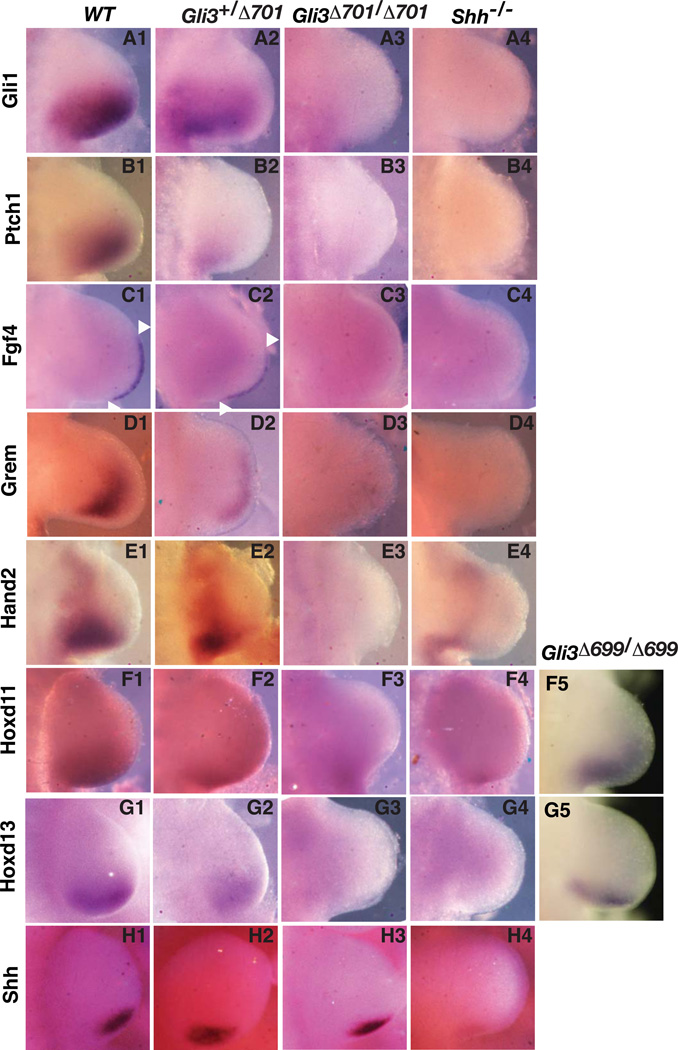
To understand the molecular basis of Gli3Δ701 limb phenotypes, we analyzed the expression of several genes related to limb patterning. Since Prx1-Cre expresses Cre protein more efficiently in the forelimbs (Logan et al., 2002), our study focused on only the forelimbs of E10.5 mouse embryos (n=3 for the following whole mount in situ hybridizations). Gli1 and Patched1 (Ptch1) are two direct Gli targets and are normally expressed in the posterior region of the developing limbs (Goodrich et al., 1996; Marigo et al., 1996). In situ hybridization analysis showed that both Gli1 and Ptch1 expression was reduced in Gli3+/Δ701 mouse limbs and not detected in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh mutant limbs. These results confirm that Gli3Δ701 is indeed a potent transcriptional repressor (Fig. 4As, Bs).
Figure 4. Expression of molecular markers in wt, Gli3Δ701, Gli3Δ699, and Shh mutant limb buds.
Whole mount in situ hybridization of E10.5 mouse embryos was performed with riboprobes corresponding to the indicated genes (left). The right limb buds are shown with the anterior at the top and posterior at the bottom. Compared to that in wt limb buds (A1–G1), the expression of the Gli1, Ptch1, Fgf4, Grem, Hand2, Hoxd11, and Hoxd13 genes is reduced in Gli3+/Δ701 limb buds (A2–G2) or not detected in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 (A3–G3) and Shh mutants (A4–G4). However, Shh remains expressed in both Gli3+/Δ701 and Gli3Δ701/Δ701 limbs (H2, H3). The reduced Hoxd11 and Hoxd13 expression is detected in Gli3Δ699/Δ699 limbs (F5, G5). Arrowheads indicate the edge of Fgf4 expression.
Proximodistal limb outgrowth requires fibroblast growth factor gene (Fgf) signals, and Fgf4 expression is restricted to the posterior two-thirds of the apical ridge (Martin, 1998). Shh maintains expression of Fgf4 by regulating that of the Gremlin (Grem) gene (Zuniga et al., 1999). In the Gli3+/Δ701 limb buds, Fgf4 expression in the apical ectodermal ridge (AER) was slightly weaker and more posteriorly restricted as compared to wt. Its expression in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh mutant limbs was undetectable (Fig. 4Cs). Similarly, Grem expression was significantly reduced in the Gli3+/Δ701 mutant limbs and undetected in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh mutant limbs (Fig. 4Ds). These results may explain why both Gli3Δ701 and Shh mutant limbs were significantly shorter than those of wt.
The Hand2 basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor is normally expressed in the posterior region of mouse limb buds, and its expression is restricted by Gli3R (te Welscher et al., 2002a). As predicted, the Hand2 expression domain in Gli3+/Δ701 limb buds was smaller than that in wt, while its expression in Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh mutant limb buds was inhibited (Fig. 4Es).
3’-Hoxd genes are essential for autopod patterning (Zakany and Duboule, 1999). The expression of both Hoxd11 and Hoxd13 is posteriorly restricted in wt mouse limb buds, as it is stimulated by Shh signaling but inhibited by Gli3R. Consistent with the patterning of Gli3Δ701 and Gli3Δ699 mutant limbs, the expression of both Hoxd11 and Hoxd13 was markedly reduced in Gli3+/Δ701 limb buds, slightly lower in Gli3Δ699/Δ699 limb buds, or undetectable in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh mutant limb buds (Fig. 4Fs, Gs). Taken together, these results indicate that Gli3Δ701 can effectively suppress expression of the patterning genes examined in the developing limbs and its repressing activity is greater than that of Gli3Δ699. The fact that expression of these genes is inhibited in both Gli3Δ701/Δ701 and Shh−/− limbs demonstrates that Gli3Δ701 repressing activity is likely to be similar to the net wt Gli3 transcriptional activity in the Shh mutant.
A previous study showed ectopic Shh expression in the anterior region of Gli3 null mutant limbs (Buscher et al., 1997), suggesting that Gli3 can inhibit Shh expression. This raises the possibility that expression of the above Shh-dependent genes in Gli3Δ701/Δ701 limbs was indirectly inhibited through the inhibition of Shh expression. To rule out this possibility, Shh expression in Gli3Δ701 mutant limbs was investigated. As in wt, Shh expression in both Gli3+/Δ701 and Gli3Δ701/Δ701 limbs was unaffected (Fig. 4Hs). Thus, the Gli3Δ701 repressor can inhibit expression of these limb patterning genes independently of Shh expression.
Two previous studies showed that Gli3 null mutant limb phenotypes resemble those of Gli3 and Shh double mutants (Litingtung et al., 2002; te Welscher et al., 2002b). This finding supports the hypothesis that Shh patterns limb by inhibiting the generation of the Gli3 repressor and that the balanced counteraction between Gli3 and Shh controls A/P limb patterning. Based on this hypothesis, mice expressing only the Gli3 repressor are expected to exhibit limb phenotypes resembling those of mice lacking Shh expression. Surprisingly, previous studies using the Gli3Δ699 mutant allele did not show that this was the case (Hill et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2007b). Because of the caveat of this allele, the hypothesis that Shh patterns A/P limb by inhibiting Gli3 repressor generation needs to be reevaluated. In the present study, we created a “cleaner” Gli3Δ701mutant allele that conditionally expresses the Gli3 repressor. We demonstrate that mouse limbs homozygous for Gli3Δ701 indeed exhibit phenotypes that resemble those of Shh mutant limbs (Figs. 2 and 3). Our observations that the expression of each Shh-dependent gene examined is also inhibited in Gli3Δ701 mouse limbs further support this finding. In addition, the effect of Gli3Δ701 repressor on limb patterning is independent of Shh expression, as Shh remains expressed in Gli3Δ701 mutant limbs (Fig. 4). Furthermore, a comparison of both limb digit patterning and Hoxd11 and Hoxd13 expression between Gli3Δ701 and Gli3Δ699 mutants indicates that Gli3Δ701 is more potent than Gli3Δ699. Therefore, our study strongly supports that A/P limb patterning is controlled by the antagonistic interaction between Shh and Gli3.
We previously showed that the ratio of Gli3A to Gli3R determines limb digit patterning and Shh signaling patterns A/P limbs by inhibiting Gli3 processing and creating the Gli3A/Gli3R ratio gradient (Wang et al., 2000; Wang et al., 2007b). In the Gli3+/Δ701 limbs, the mutant allele expresses only a repressor, while the wt allele produces normal Gli3 protein, which consists of both Gli3A and Gli3R. Since the Gli3Δ701 repressor is not regulated by Shh, the Gli3A/Gli3R ratio gradient must be disrupted in Gli3+/Δ701 mutant limbs. This is likely to be the mechanism underlying Gli3+/Δ701 mutant limb phenotypes.
It is worth noting that findings from this and previous studies do not rule out the potential involvement of Gli2 in limb patterning, although the Gli2 null mutant does not exhibit defects in limb patterning (Mo et al., 1997). It is conceivable that the role of Gli2R in limb patterning is masked by Gli3R or is too small to be significant, as Gli2FL is not efficiently processed into Gli2R (Pan et al., 2006). The role of Gli2A in posterior limb patterning has recently been reported (Bowers et al.). However, since the Gli3 plays a predominant role in limb patterning, the role of both Gli2A and Gli2R in limb patterning is likely to be masked by that of Gli3 and becomes noticeable only in the Gli3 mutant background. Therefore, it appears that the role of Gli2 in limb patterning is relatively small. This explains why expression of Gli3 repressor alone is sufficient to produce the defective limb phenotypes reminiscent of those of the Shh mutant. Thus, the results of this and previous studies further support the hypothesis that the balanced counteraction between Gli3 and Shh is sufficient to direct A/P limb patterning.
Highlights.
A Gli3 conditional mutant allele (Gli3Δ701C) expresses only the Gli3 repressor
Mouse limbs expressing Gli3Δ701 repressor resemble those of Shh mutants
Gli3Δ701 repressor inhibits the expression of genes necessary for limb patterning
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Licia Selleri, Philip Beachy, and Ulrich Ruther for the Actin-Flpe, Shh, and Gli3Δ699 mutant mice, respectively. T. C. and M. Y. were supported by the China Scholarship Council. This work was supported by an NIH grant (R01CA111673) to B.W.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- Auerbach W, Dunmore JH, Fairchild-Huntress V, Fang Q, Auerbach AB, Huszar D, Joyner AL. Establishment and chimera analysis of 129/SvEv- and C57BL/6-derived mouse embryonic stem cell lines. Biotechniques. 2000;29:1024–1028. 1030, 1032. doi: 10.2144/00295st04. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesecker LG. Strike three for GLI3. Nat Genet. 1997;17:259–260. doi: 10.1038/ng1197-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose J, Grotewold L, Ruther U. Pallister-Hall syndrome phenotype in mice mutant for Gli3. Hum Mol Genet. 2002;11:1129–1135. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.9.1129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers M, Eng L, Lao Z, Turnbull RK, Bao X, Riedel E, Mackem S, Joyner AL. Limb anterior-posterior polarity integrates activator and repressor functions of GLI2 as well as GLI3. Dev Biol. 370:110–124. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buscher D, Bosse B, Heymer J, Ruther U. Evidence for genetic control of Sonic hedgehog by Gli3 in mouse limb development. Mech Dev. 1997;62:175–182. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(97)00656-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Harris MP, Simandl BK, Li Y, Beachy PA, Fallon JF. Manifestation of the limb prepattern: limb development in the absence of sonic hedgehog function. Dev Biol. 2001;236:421–435. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C, Litingtung Y, Lee E, Young KE, Corden JL, Westphal H, Beachy PA. Cyclopia and defective axial patterning in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog gene function. Nature. 1996;383:407–413. doi: 10.1038/383407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding Q, Motoyama J, Gasca S, Mo R, Sasaki H, Rossant J, Hui CC. Diminished Sonic hedgehog signaling and lack of floor plate differentiation in Gli2 mutant mice. Development. 1998;125:2533–2543. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.14.2533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich LV, Johnson RL, Milenkovic L, McMahon JA, Scott MP. Conservation of the hedgehog/patched signaling pathway from flies to mice: induction of a mouse patched gene by Hedgehog. Genes Dev. 1996;10:301–312. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill P, Gotz K, Ruther U. A SHH-independent regulation of Gli3 is a significant determinant of anteroposterior patterning of the limb bud. Dev Biol. 2009;328:506–516. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.02.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui CC, Joyner AL. A mouse model of greig cephalopolysyndactyly syndrome: the extra-toesJ mutation contains an intragenic deletion of the Gli3 gene. Nat Genet. 1993;3:241–246. doi: 10.1038/ng0393-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp SJ, Schipani E, St-Jacques B, Hunzelman J, Kronenberg H, McMahon AP. Indian hedgehog coordinates endochondral bone growth and morphogenesis via parathyroid hormone related-protein-dependent and -independent pathways. Development. 2000;127:543–548. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.3.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmita M, Tarchini B, Zakany J, Logan M, Tabin CJ, Duboule D. Early developmental arrest of mammalian limbs lacking HoxA/HoxD gene function. Nature. 2005;435:1113–1116. doi: 10.1038/nature03648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus P, Fraidenraich D, Loomis CA. Some distal limb structures develop in mice lacking Sonic hedgehog signaling. Mech Dev. 2001;100:45–58. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(00)00492-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litingtung Y, Dahn RD, Li Y, Fallon JF, Chiang C. Shh and Gli3 are dispensable for limb skeleton formation but regulate digit number and identity. Nature. 2002;418:979–983. doi: 10.1038/nature01033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan M, Martin JF, Nagy A, Lobe C, Olson EN, Tabin CJ. Expression of Cre Recombinase in the developing mouse limb bud driven by a Prxl enhancer. Genesis. 2002;33:77–80. doi: 10.1002/gene.10092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Martinez A, Chang DT, Chiang C, Porter JA, Ros MA, Simandl BK, Beachy PA, Fallon JF. Limb-patterning activity and restricted posterior localization of the amino-terminal product of Sonic hedgehog cleavage. Curr Biol. 1995;5:791–796. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marigo V, Johnson RL, Vortkamp A, Tabin CJ. Sonic hedgehog differentially regulates expression of GLI and GLI3 during limb development. Dev Biol. 1996;180:273–283. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1996.0300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin GR. The roles of FGFs in the early development of vertebrate limbs. Genes Dev. 1998;12:1571–1586. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.11.1571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matise MP, Epstein DJ, Park HL, Platt KA, Joyner AL. Gli2 is required for induction of floor plate and adjacent cells, but not most ventral neurons in the mouse central nervous system. Development. 1998;125:2759–2770. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.15.2759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mo R, Freer AM, Zinyk DL, Crackower MA, Michaud J, Heng HH, Chik KW, Shi XM, Tsui LC, Cheng SH, Joyner AL, Hui C. Specific and redundant functions of Gli2 and Gli3 zinc finger genes in skeletal patterning and development. Development. 1997;124:113–123. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy A, Gertsenstein M, Vintersten K, Behringer R. Manipulating the mouse embryo: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor, NY: CSHL Press; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pan Y, Bai CB, Joyner AL, Wang B. Sonic hedgehog signaling regulates Gli2 transcriptional activity by suppressing its processing and degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:3365–3377. doi: 10.1128/MCB.26.9.3365-3377.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park HL, Bai C, Platt KA, Matise MP, Beeghly A, Hui CC, Nakashima M, Joyner AL. Mouse Gli1 mutants are viable but have defects in SHH signaling in combination with a Gli2 mutation. Development. 2000;127:1593–1605. doi: 10.1242/dev.127.8.1593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle RD, Johnson RL, Laufer E, Tabin C. Sonic hedgehog mediates the polarizing activity of the ZPA. Cell. 1993;75:1401–1416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90626-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P. The PDGF alpha receptor is required for neural crest cell development and for normal patterning of the somites. Development. 1997;124:2691–2700. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.14.2691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Welscher P, Fernandez-Teran M, Ros MA, Zeller R. Mutual genetic antagonism involving GLI3 and dHAND prepatterns the vertebrate limb bud mesenchyme prior to SHH signaling. Genes Dev. 2002a;16:421–426. doi: 10.1101/gad.219202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- te Welscher P, Zuniga A, Kuijper S, Drenth T, Goedemans HJ, Meijlink F, Zeller R. Progression of vertebrate limb development through SHH-mediated counteraction of GLI3. Science. 2002b;298:827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1075620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempe D, Casas M, Karaz S, Blanchet-Tournier MF, Concordet JP. Multisite Protein Kinase A and Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3{beta} Phosphorylation Leads to Gli3 Ubiquitination by SCF{beta}TrCP. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:4316–4326. doi: 10.1128/MCB.02183-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vortkamp A, Gessler M, Grzeschik KH. GLI3 zinc-finger gene interrupted by translocations in Greig syndrome families. Nature. 1991;352:539–540. doi: 10.1038/352539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Fallon JF, Beachy PA. Hedgehog-regulated processing of Gli3 produces an anterior/posterior repressor gradient in the developing vertebrate limb. Cell. 2000;100:423–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80678-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B, Li Y. Evidence for the direct involvement of {beta}TrCP in Gli3 protein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:33–38. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0509927103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Pan Y, Wang B. A hypermorphic mouse Gli3 allele results in a polydactylous limb phenotype. Dev Dyn. 2007a;236:769–776. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C, Ruther U, Wang B. The Shh-independent activator function of the full-length Gli3 protein and its role in vertebrate limb digit patterning. Dev Biol. 2007b;305:460–469. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.02.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. Whole mount in situ hybridization of vertebrate embryos. In: Wilkinson D, editor. In situ hybridization: A Practical Approach. Oxford: IRL Press; 1992. pp. 75–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y, Drossopoulou G, Chuang PT, Duprez D, Marti E, Bumcrot D, Vargesson N, Clarke J, Niswander L, McMahon A, Tickle C. Relationship between dose, distance and time in Sonic Hedgehog-mediated regulation of anteroposterior polarity in the chick limb. Development. 1997;124:4393–4404. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.21.4393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakany J, Duboule D. Hox genes in digit development and evolution. Cell Tissue Res. 1999;296:19–25. doi: 10.1007/s004410051262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuniga A, Haramis AP, McMahon AP, Zeller R. Signal relay by BMP antagonism controls the SHH/FGF4 feedback loop in vertebrate limb buds. Nature. 1999;401:598–602. doi: 10.1038/44157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]